-
Články
- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
- Kongresy
- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
and Exhibit Metabolic Symbioses
Unlike the traditional view that most diseases are caused by infection with a single bacterial species, some chronic diseases including periodontitis result from the perturbation of the natural microbiota and the proliferation of a number of opportunistic pathogens. Both Porphyromonas gingivalis and Treponema denticola have been associated with the progression and severity of chronic periodontitis and have been shown to display synergistic virulence in animal models. However, the underlying mechanisms to these observations are unclear. Here we demonstrate that these two bacteria grow synergistically in continuous co-culture and modify their gene expression. The expression of T. denticola genes encoding known virulence factors and enzymes involved in the uptake and metabolism of the amino acid glycine was up-regulated in co-culture. T. denticola stimulated the proteolytic P. gingivalis to produce free glycine, which T. denticola used as a major carbon source. Our study shows P. gingivalis and T. denticola co-operate metabolically and this helps to explain their synergistic virulence in animal models and their intimate association in vivo.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Pathog 10(3): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1003955
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1003955Summary
Unlike the traditional view that most diseases are caused by infection with a single bacterial species, some chronic diseases including periodontitis result from the perturbation of the natural microbiota and the proliferation of a number of opportunistic pathogens. Both Porphyromonas gingivalis and Treponema denticola have been associated with the progression and severity of chronic periodontitis and have been shown to display synergistic virulence in animal models. However, the underlying mechanisms to these observations are unclear. Here we demonstrate that these two bacteria grow synergistically in continuous co-culture and modify their gene expression. The expression of T. denticola genes encoding known virulence factors and enzymes involved in the uptake and metabolism of the amino acid glycine was up-regulated in co-culture. T. denticola stimulated the proteolytic P. gingivalis to produce free glycine, which T. denticola used as a major carbon source. Our study shows P. gingivalis and T. denticola co-operate metabolically and this helps to explain their synergistic virulence in animal models and their intimate association in vivo.
Introduction
Chronic periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of the supporting tissues of the teeth with a polymicrobial aetiology. However, whilst the concepts of the roles of particular oral bacterial species in disease have changed over the past two decades there is wide consensus that anaerobic, proteolytic, amino acid fermenting species including Porphyromonas gingivalis, Treponema denticola and Tannerella forsythia play a crucial role in initiation and/or progression of disease [1]–[5]. P. gingivalis has recently been proposed to be a “keystone pathogen” that through synergistic interactions aids the proliferation of other oral bacterial species resulting in the formation of a pathogenic polymicrobial plaque [3].
We have previously demonstrated in a longitudinal human study that the imminent progression of chronic periodontitis in patients on a maintenance program could be predicted by increases in the relative proportions of P. gingivalis and/or T. denticola in subgingival plaque above threshold levels [6]. This is consistent with other clinical studies demonstrating that P. gingivalis levels in subgingival plaque are predictive of human disease progression [7], [8]. P. gingivalis and T. denticola are frequently found to co-exist in deep periodontal pockets and have been co-localized to the superfical layers of subgingival plaque as microcolonies adjacent to the pocket epithelium [1], [9]–[13], suggesting possible interbacterial interactions that might contribute towards disease [14], [15]. When co-inoculated intra-orally in animal models of periodontitis P. gingivalis and T. denticola exhibit a synergistic pathogenesis [16]–[18]. These two bacteria display a symbiotic relationship in nutrient utilization and growth promotion in vitro [14], [19] and bimodal coaggregation between P. gingivalis and T. denticola has been demonstrated [15], [20]–[23], which might explain their co-localization and aid synergistic biofilm production [24]–[26]. P. gingivalis and T. denticola responded to each other's presence in a polymicrobial biofilm by modulating the abundance of a range of proteins [26]. Together these data suggest there is an intimate relationship between these two species that has evolved to enhance their survival and virulence. However, the physiochemical interactions that result in the observed symbiotic and synergistic effects during P. gingivalis and T. denticola co-culture remain largely unknown.
In this study we used continuous co-culture to demonstrate that P. gingivalis and T. denticola symbiotically co-exist and that each bacterium adapts to the presence of the other by modulating gene expression, particularly those genes involved in metabolism and virulence. We show that the presence of P. gingivalis caused an up-regulation of T. denticola glycine catabolism and that this amino acid supported the growth of T. denticola. T. denticola conditioned medium induced free glycine production by P. gingivalis implying intimate metabolic co-operativity between these species. The up-regulation of T. denticola virulence factors in co-culture helps explain the synergistic virulence of P. gingivalis and T. denticola in animal models of disease.
Materials and Methods
Bacterial strains and culture conditions
P. gingivalis strain W50 and T. denticola ATCC 35405 were obtained from the culture collection of the Oral Health Cooperative Research Centre, The University of Melbourne, and grown in oral bacterial growth medium (OBGM), that meets the growth requirements of both P. gingivalis and T. denticola [18], [26], [27]. Batch culture was in pre-reduced OBGM at 37°C in a MK3 anaerobic workstation (Don Whitley Scientific, Adelaide, Australia) with a gas composition of 5% CO2, 5% H2 and 90% N2 (BOC Gases, Wetherill Park, Australia). Bacterial cell density was monitored by measuring the absorbance at 650 nm (A650 nm).
To initiate the mono-species continuous culture, 300 mL of batch-grown inoculum in exponential growth phase (A650 nm of ∼0.6 for P. gingivalis or A650 nm of ∼0.2 for T. denticola) was mixed with 600 mL of fresh OBGM and transferred to a Bioflo 110 Modulator Benchtop Fermentor (New Brunswick Scientific, NJ, USA). The culture was maintained at 37°C, continuously agitated at 50 rpm and gassed with a constant stream of anaerobic gas (10% CO2 in N2) (BOC Gases). After 24 h, medium flow was commenced with OBGM pumped into the fermentor maintaining a working volume of 900 mL, with a flow rate of 39 mL h−1, giving a mean generation time of 15.75 h. Samples were collected after the A650 nm of the culture remained stable for a period of ten generations (158 h).
To establish co-culture P. gingivalis was inoculated into established T. denticola mono-species continuous cultures. After the T. denticola samples were harvested from a mono-culture chemostat, co-culture was established by replacing 300 mL of T. denticola culture with batch-grown exponential phase P. gingivalis (A650 nm∼0.6). The medium flow to the fermentor was stopped for 12 h to enable establishment of co-culture, after which medium flow was resumed at 39 mL h−1. Three independent biological replicates each of P. gingivalis and T. denticola mono - and co-cultures were grown.
Bacterial enumeration
Mono-culture bacterial cell density was determined by correlating A650 nm to a standard curve [28] whilst P. gingivalis and T. denticola cells numbers in co-culture were determined by quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) as described previously [6], [26], [28].
DNA microarray slides
The 60-mer oligonucleotide probes representing predicted open reading frames (ORFs) of the P. gingivalis and T. denticola genomes to be used for microarray slide preparation were designed using OligoArray 2.l [29] and using the bioinformatic services of Illumina Inc. (CA, USA). The difference in GC content of P. gingivalis (48%) and T. denticola (38%) genomes was exploited in probe design. BLAST analysis demonstrated that probes from one organism had less than 80% similarity to that from the other organism to minimize the chances of cross-species hybridization. The custom made T. denticola ATCC 35405 microarray contained 2518 probes representing 89% of the predicted ORFs in the T. denticola genome as described previously in Mitchell et al. [30]. The P. gingivalis probe set design was based upon the P. gingivalis W83 genome sequence [31] and ORF predictions available through The J. Craig Venter Institute (www.jcvi.org), with additional P. gingivalis ORFs predicted by the Los Alamos National Laboratory Oralgen project (www.oralgen.lanl.gov). The final set of 1977 probes corresponded to 96% of the predicted P. gingivalis ORFs. The full complement of probes for both genomes were printed twice each onto Corning UltraGAPs coated slides using a Virtek Microarray spotter by the Australian Genome Research Facility (Melbourne, Australia). Microarray Sample Pool (MSP) control probes were also included to aid intensity-dependent normalisation [32].
Total RNA extraction and purification
RNA was isolated using the GenElute Total RNA Purification Kit (Sigma Aldrich, Castle Hill, Australia) and treated with DNase using the Turbo DNA-free kit (Ambion, TX, USA). The amount, integrity and purity of the RNAs were assessed using the Experion Automated Electrophoresis System (Bio-Rad, CA, USA). The absence of genomic DNA contamination from P. gingivalis and T. denticola in the RNA sample was determined by performing PCR on RNA samples using TDE0762 (forward: GGCTCCGAATCAAAACGATA, reverse: CTATCGACTCCCCGTTTTCA) and PG0719 (forward: GCATTGCAGCATAGCGAATA, reverse: GCCGATGGAAAAAGTGTGTT) primer pairs respectively while the respective genomic DNAs were used as positive controls.
Microarray analysis
Aliquots of P. gingivalis and T. denticola (100 mL) were harvested from 3 mono-cultures and from 3 co-cultures, with technical replicates harvested 2 days apart. qPCR showed that there were six times as many P. gingivalis as T. denticola in co-culture (vide infra) therefore 6∶1 equivalents of P. gingivalis:T. denticola mono-culture RNAs were mixed prior to cDNA synthesis (vide infra) for use in comparison with the co-culture cDNA. Labeled cDNA hybridization targets were produced using either 5 µg of genomic DNA or 6 µg of purified total RNA template, 5 µg of random hexamers (Life Technologies, MD, USA) and aminoallyl dUTP nucleotides incorporated during cDNA synthesis. The genomic cDNA was produced using Platinum Taq DNA polymerase (Life Technologies) whilst RNA was reverse transcribed using Superscript III Reverse Transcriptase (Life Technologies). cDNA were purified using QlAquick columns (Qiagen, CA, USA) and labeled with monoreactive Cy3 or Cy5 dye (40 nmol) (GE Healthcare Lifesciences, Quebec, Canada). Equal numbers of samples from mono - and co-culture cDNAs were labeled with Cy3 and Cy5 respectively and in reverse combination in order to accommodate for different Cy3 and Cy5 labeling efficiencies. To ensure the specificity of the probes, the dual-genome array was probed with P. gingivalis or T. denticola labeled cDNA. Five T. denticola probes (TDE0780, TDE1033, TDE1804, TDE2113 and TDE2213) were found to cross-hybridize to P. gingivalis DNA and six P. gingivalis probes (PG1340, PG1473, PG1525, PG1666, PG1731 and PG2175) were found to cross-hybridize to T. denticola DNA. The expression of these genes was excluded from the subsequent transcriptomic analysis. The microarray hybridization and scanning were conducted essentially as described previously [30], [33] but with 49% formamide in the hybridization buffer and use of 46°C as the hybridization temperature.
Data analysis
Microarray background subtraction and data analysis were conducted in R statistical environment using GenePix Pro 6.0 and LIMMA as described previously [30], [34]. The Benjamini-Hochberg method was used to control the false discovery rate to correct for multiple testing [35]. Genes with a fold change equal to or above 1.4 and an adjusted p≤0.05 were considered to be significantly differentially regulated. Annotation and putative protein functions were based on the National Center for Biotechnology Information Refseq database and Clusters of Orthologous Groups of protein (COG) database [36]. Operon predictions, COG assignments and COG functional categories were obtained from the Microbes Online database [37]. Microarray data are available in the ArrayExpress database (www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress) under accession number E-MTAB-2214 (P. gingivalis) and E-MTAB-2257 (T. denticola).
Validation of microarray results using quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR)
Differential expression of selected genes was validated by qRT-PCR of cDNAs using SYBR Green-based detection on a Rotor Gene 3000 system (Corbett Research, Sydney, Australia) as reported previously [30]. To normalize the amount of mRNA in each reaction, a pool of six reference genes TDE2535, TDE0872, TDE1208, TDE1999, TDE1226 and TDE0002 [30] was assessed for expression stability using the geNorm program [38]. Analysis indicated that the geometric mean of the three most stable genes TDE2535, TDE1208 and TDE0872 with average pair-wise variations of 0.146 was sufficient to calculate a normalization factor for each sample. Primers for the validation gene set TDE1624, TDE1625, TDE1626, TDE1627, TDE1259, TDE2119, TDE2120, TDE0405, TDE0762, TDE1669, TDE0387, TDE0627 and TDE0832 were designed using Primer3 [39] (Table S1).
Scanning electron microscopy
Co-cultures from continuous culture were collected then processed and imaged using a Philips XL30 field-emission scanning electron microscope at a voltage of 2 kV as described previously [30].
Analysis of glycine concentration
Batch cultures of P. gingivalis (50 mL) with a starting cell density of 1×107 cells were grown using a) OBGM, b) OBGM supplemented 1∶1 with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (OBGM/PBS) and c) OBGM supplemented 1∶1 with cell-free T. denticola conditioned growth medium (OBGM/T. denticola conditioned medium). T. denticola conditioned medium was prepared by filtering (0.1 µm) a 7-day culture of T. denticola grown in OBGM. Aliquots of the culture medium (30 µL) were collected and immediately diluted with 70 µL of deionized water, 300 µL of CHCl3 and 100 µL of CH3OH. The extracted medium was snap-frozen on liquid nitrogen and stored at −80°C for later gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis [40] (Protocol S1). A glycine standard curve was obtained by the addition of various amounts of glycine to T. denticola conditioned medium (which had no detectable free glycine) in preference to use of pure glycine standards to account for matrix effects from the medium. The difference in free glycine levels relative to that at t = 0 h for each replicate was expressed as a function of P. gingivalis cell numbers in different media. A regression line was fitted using a linear mixed modelling approach, which allowed the regression lines to be fitted with random slopes by considering the fixed effects for the different growth medium and time interaction (SPSS version 20, IBM, IL, USA). For the determination of the total glycine content of cell-free media samples were freeze-dried and hydrolyzed at 150°C for 2 h in the presence of 6 M HCl containing phenol (1% v/v).
Isotope-labeled glycine studies
[U-13C]glycine (Cambridge Isotope Laboratories, MA, USA) was added to a final concentration of 5 mM to a 24 h T. denticola culture in OBGM. Bacterial culture (1.5 mL) was collected every 24 h for 8 days and passed through a 0.22 µM filter to obtain a cell-free fraction. Samples were kept at −80°C until further analysis. Sample preparation for 13C-nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and spectra analyses were conducted by Metabolomics Australia (Melbourne, Australia) as previously published [40].
Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) production by P. gingivalis
Escherichia coli JRG902 [41] and E. coli JW3957-1, a TPP auxotrophic strain (ΔthiE764::kan), were obtained from the Keio collection [42]. E. coli strains were grown in M9 medium [43] with different combinations of TPP (5.88 nM) and/or cell-free P. gingivalis conditioned medium that was obtained by growing P. gingivalis in OMIZ-M/TD [44] without TPP and filtering (0.2 µM) the culture. Growth was measured by A650 nm.
Results
P. gingivalis and T. denticola continuous culture
Mono - and co-cultures of P. gingivalis and T. denticola were established in continuous culture using OBGM. Three independent continuous mono-cultures of P. gingivalis entered steady state 3 days after establishment with an average absorbance (A650 nm) of 1.86±0.14 equating to 3.9±0.3×109 cells mL−1. The three T. denticola mono-cultures also reached steady state approximately 8 days after inoculation with an average A650 nm of 0.23±0.02 equating to 7.7±0.7×108 cells mL−1 (Figure 1). Co-cultures of P. gingivalis and T. denticola entered steady-state after 4 days with an average A650 nm of 1.73±0.09 (Figure 1). There were 6.0±0.7×109 P. gingivalis cells mL−1 and 1.0±0.1×109 T. denticola cells mL−1 under steady state conditions for the three biological replicates as determined by qPCR. Thus cell densities of both P. gingivalis and T. denticola increased significantly, by 54% and 30% (p<0.01) respectively, in co-culture compared with mono-culture. Interestingly, the 50% increase in total bacterial cell number during co-culture was not reflected by a concomitant increase in absorbance. SEM analysis of a co-culture showed that there was considerable coaggregation between the species with P. gingivalis adhering along the entire length of T. denticola cells, which would explain the lower culture A650 nm than would be expected for this density of discrete cells (Figure 2).
Fig. 1. Continuous culture of P. gingivalis and T. denticola mono- and co-cultures. 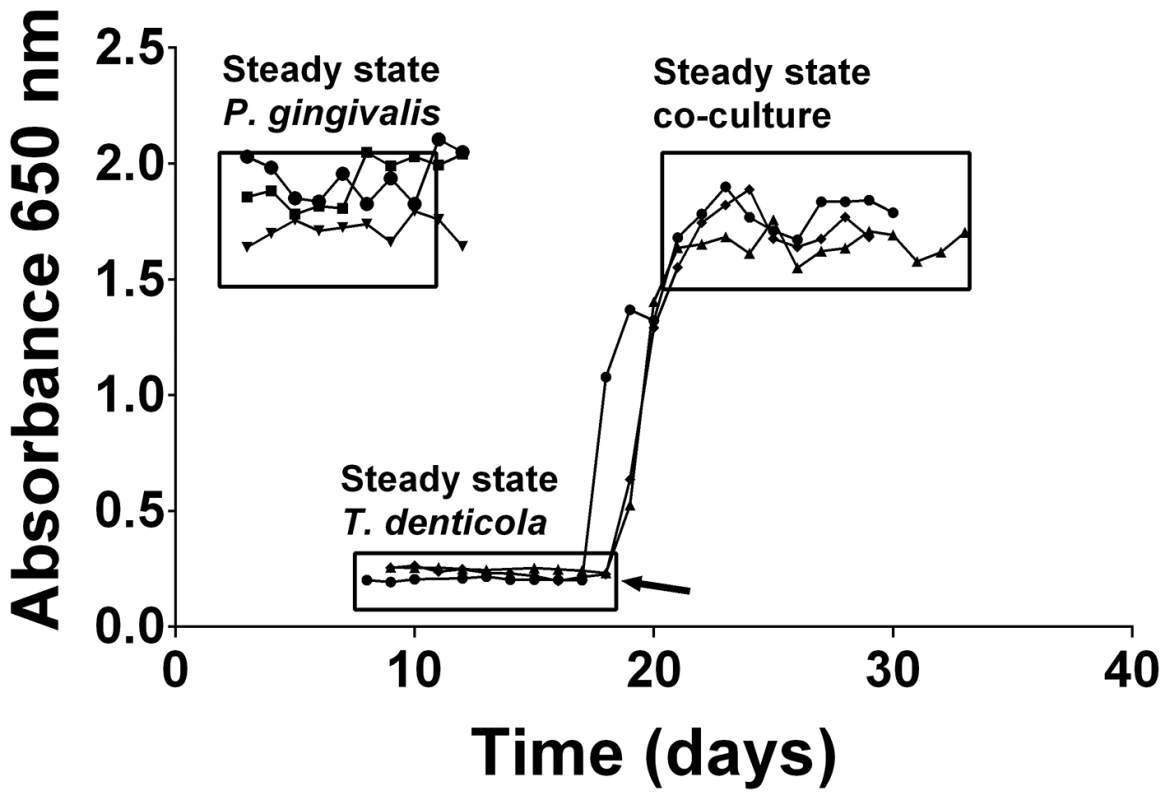
Cell density of P. gingivalis and T. denticola mono- and co-cultures from three independent continuous cultures in OBGM with the dilution rate of 0.044 h−1 and mean generation time of 15.8 h as determined by measuring A650 nm. The arrow shows the addition of P. gingivalis to a steady state T. denticola culture. Fig. 2. Scanning electron micrograph of P. gingivalis and T. denticola grown in continuous culture. 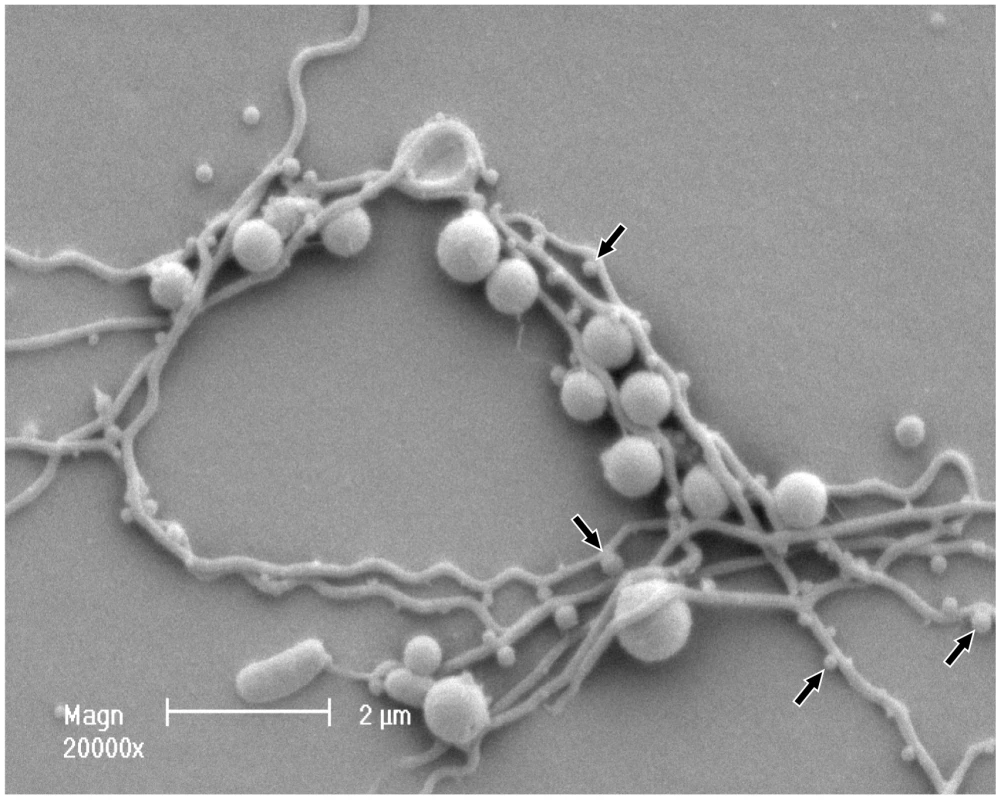
Co-culture was collected, fixed on a coverslip, dehydrated, covered with colloidal silver, gold-coated and imaged using a Philips XL30 field-emission scanning electron microscope. Electron micrographs showed that P. gingivalis and T. denticola coaggregated. T. denticola is a long helical shaped spirochete with an average length of 5 to 20 µm. P. gingivalis is a coccobacillus with an average diameter of 1 µm. Putative T. denticola outer sheath vesicles and/or P. gingivalis outer membrane vesicles are indicated by arrows along the length of T. denticola. Differential gene expression in co-culture
The expression of 184 T. denticola genes (6.6% of the genome) and 134 P. gingivalis genes (7.4% of the genome) was differentially regulated (adjusted p≤0.05 and fold change of ≥1.4) in co-culture in comparison with mono-culture. Many of these genes were predicted to be polycistronic, with 33 predicted T. denticola and 16 predicted P. gingivalis operons containing two or more differentially co-regulated genes. The direction of change of expression was consistent within the predicted operons, with no single operon containing both up-regulated and down-regulated genes (Table S2; Table S3). Differentially expressed genes were sorted into functional categories on the basis of clusters of orthologous groups (COG) [45]. The majority of T. denticola (103/184) and P. gingivalis (80/134) differentially expressed genes encoded proteins that belong to category R (general function prediction), category S (function unknown) or the not assigned category (Table 1).
Tab. 1. T. denticola and P. gingivalis genes differentially expressed during continuous co-culture relative to mono-culture, grouped by COG category. 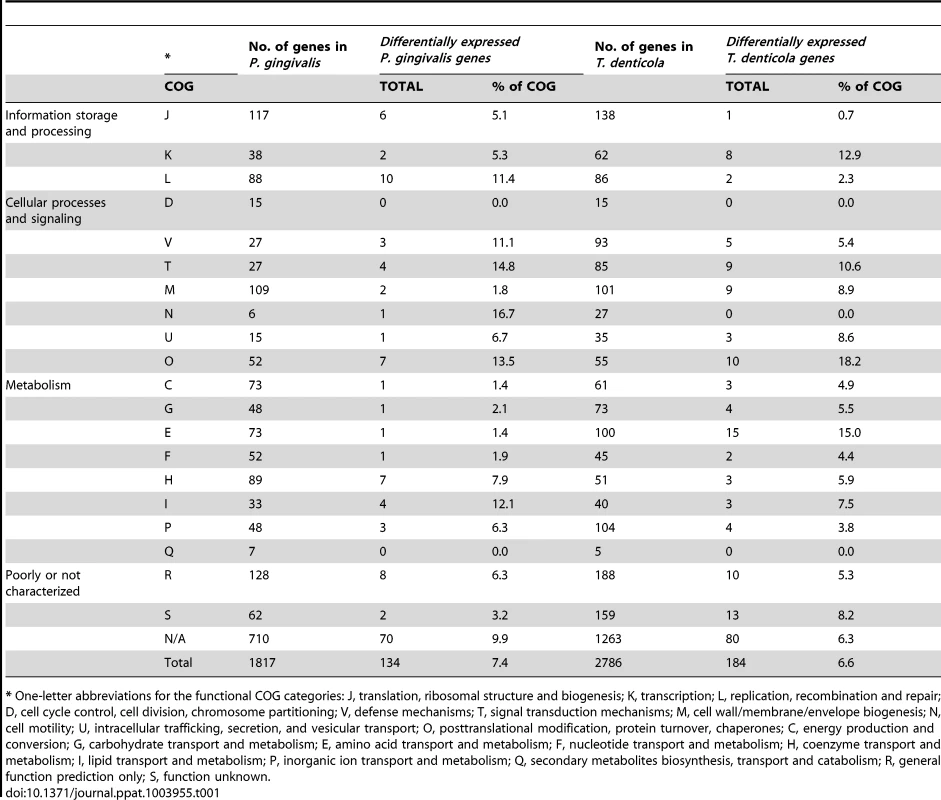
* One-letter abbreviations for the functional COG categories: J, translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis; K, transcription; L, replication, recombination and repair; D, cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning; V, defense mechanisms; T, signal transduction mechanisms; M, cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis; N, cell motility; U, intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport; O, posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones; C, energy production and conversion; G, carbohydrate transport and metabolism; E, amino acid transport and metabolism; F, nucleotide transport and metabolism; H, coenzyme transport and metabolism; I, lipid transport and metabolism; P, inorganic ion transport and metabolism; Q, secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism; R, general function prediction only; S, function unknown. T. denticola differentially expressed genes
Thirty-four differentially expressed T. denticola genes were assigned to COGs related to metabolism, with 15 of these clustering in category E (amino acid transport and metabolism), representing 15% of the total genes assigned to this COG (Table 1). TDE0392 and TDE0389 which encode the putative Fe-S-dependent β subunits (HgdCA, HgdB) of (R)-2-hydroxyglutaryl-CoA dehydratase, an iron-sulfur cluster (4Fe-4S)-dependent enzyme involved in the fermentation of glutamate, as well as TDE0387 which encodes its 4Fe-4S-dependent activator HgdC, were down-regulated during co-culture. In addition, the gene encoding carbamate kinase (TDE2476) was down-regulated suggesting reduced glutamate catabolism by T. denticola when co-cultured with P. gingivalis. In contrast genes encoding enzymes involved in the glycine cleavage system (GcvP1, GcvP2 and GcvH), the glycine reductase system (Protein B2) and oligopeptide/dipeptide/amino acid transporters (OppA, TDE1067, TDE0985) were up-regulated suggesting an increased glycine catabolism by T. denticola.
The increased expression of genes encoding components of the glycine cleavage and glycine reductase systems was confirmed by qRT-PCR using TDE2535, TDE0872 and TDE1208 as stable reference genes. There was a significant correlation between the expression ratios determined by both microarray and qRT-PCR (R2 = 0.9839) (Figure S1). This comparison revealed a slight compression of the gene expression data from the DNA microarray analysis and gave a higher up-regulation of components of the glycine cleavage and glycine reductase systems with a >1.4 fold up-regulation of TDE1627, the T-protein of the glycine cleavage system and TDE2120, the GrdE2 of the glycine reductase system (Table 2).
Tab. 2. Expression of T. denticola genes encoding enzymes involved in glycine or glycine-related metabolism during co-culture with P. gingivalis. 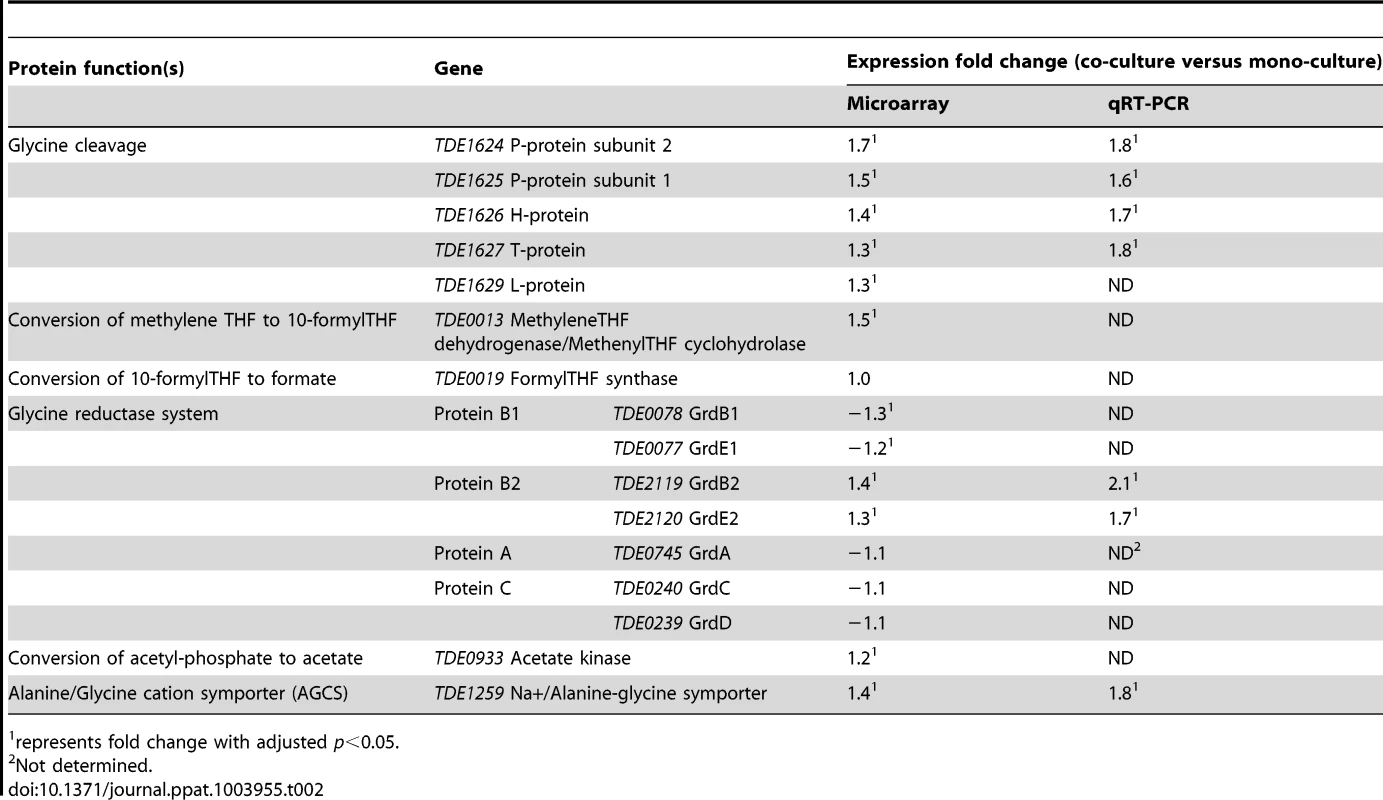
represents fold change with adjusted p<0.05. The COG category with the most differentially expressed genes was O (posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones), where 10 genes (18.2%) had altered expression, nine of which were down-regulated (Table 1). Notably, genes encoding virulence factors were amongst the most up-regulated during co-culture, including those encoding the major sheath protein (TDE0405), the dentilisin protease complex (TDE0761 and TDE0762) and cystalysin (TDE1669). Altered chemotactic responses were also evident with reduction in expression of five receptors, the methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins TDE0338, TDE0484, TDE1009, TDE2270 and TDE2496. Also down-regulated were genes that encode a FeS assembly ATPase (SufC), FeS assembly protein (SufB) and peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerases (TDE1925, TDE2287, TDE2391).
P. gingivalis differentially expressed genes
Co-culture with T. denticola had no effect on the transcription of P. gingivalis genes belonging to categories Q (secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism) and D (cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning) (Table 1). Furthermore, little effect on the transcription of genes in categories M (cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis), C (energy production and conversion), G (carbohydrate transport and metabolism), E (amino acid transport and metabolism) and F (nucleotide transport and metabolism) was observed. Six differentially expressed genes in category H (coenzyme transport and metabolism) were up-regulated, four of which (thiH, thiG, thiE/D, thiS) occur in a predicted five gene operon (PG2107-11) suggesting increased thiamine biosynthesis during co-culture. In addition PG2010 (thiC) was also significantly up-regulated (adjusted p = 0.01) but did not meet the 1.4-fold cut-off criterion. The putative thiamine transporter, PnuT (PG1898) was significantly up-regulated 1.5 fold (Table S3). Three genes involved in the initial stages of fatty acid biosynthesis fabG, fabF, acpP were down-regulated (Table S3).
Free glycine use by T. denticola
The increased transcription of genes encoding enzymes in glycine metabolism in T. denticola when co-cultured with P. gingivalis prompted us to investigate T. denticola glycine metabolism further. Suspension of T. denticola in OBGM containing a starting concentration of 1.46 mM glycine, resulted in the rapid depletion of this amino acid over 72 h, coinciding with entry into stationary growth (Figure 3a). Further supplementation of the OBGM to 10 mM glycine enhanced T. denticola growth, resulting in a 1.75-fold increase in final cell density. Addition of glycine to a stationary T. denticola culture caused the resumption of bacterial growth (Figure 3b). These data show that T. denticola consumed free glycine and that glycine availability had a significant impact on T. denticola growth.
Fig. 3. T. denticola growth and glycine. 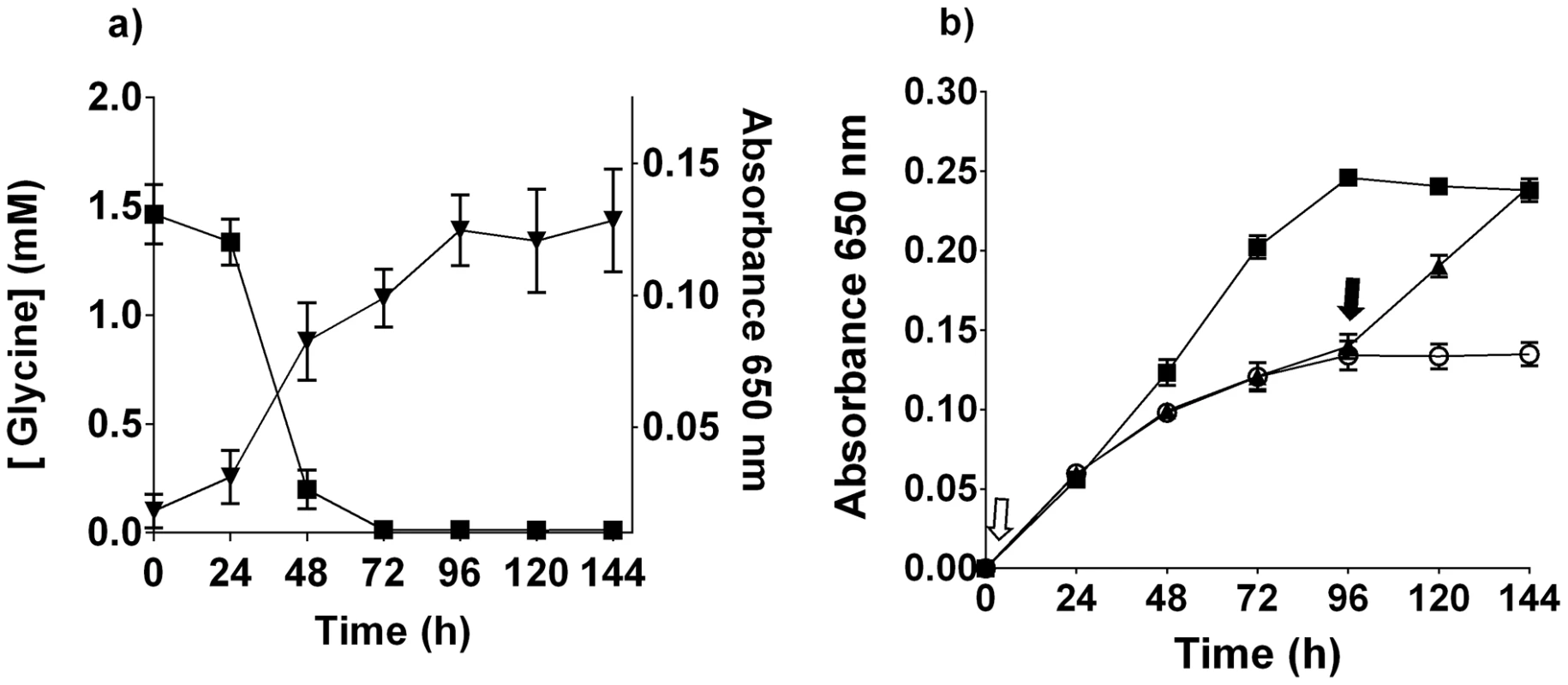
(a) The concentration of free glycine in T. denticola culture (black square; left axis). T. denticola growth curve in the same medium (black inverted triangle; right axis). Data points are the mean and standard deviation of three biological replicates. (b) Glycine (10 mM) was added to OBGM either before inoculation with T. denticola (black square, open arrow) or at 96 h after inoculation (black triangle, filled arrow) and bacterial growth was determined by A650 nm measurement. T. denticola culture with no added glycine (white circle). Results are expressed as mean ± standard deviation obtained from eight replicates. Metabolic fate of free glycine
Direct evidence for glycine catabolism in T. denticola was provided by metabolic labeling with 5 mM [U-13C]glycine. [U-13C]glycine was added to a 24 h batch-grown T. denticola culture and consumption of 13C-glycine and production of 13C-labeled end-products determined by 13C-NMR analysis of the culture medium (Figure S2). [U-13C]glycine was completely consumed by 144 h, with production of 13C-acetate (3.67 mM) and 13C-lactate (1 mM) (Figure 4). The major isotopomers of acetate and lactate were uniformly labeled, although low levels of [1-13C]acetate and/or [2-13C]acetate, were also detected (data not shown).
Fig. 4. The extracellular products of T. denticola [U-13C]glycine fermentation. ![The extracellular products of <i>T. denticola</i> [U-<sup>13</sup>C]glycine fermentation.](https://www.prolekare.cz/media/cache/resolve/media_object_image_small/media/image/68cdfe8296c4990b1a4882e3463260a2.png)
[U-13C]glycine (5.00 mM) was added to a 24 h T. denticola culture and aliquots were collected every 24 h, filtered and the identity and the quantity of the 13C-labeled compounds was determined using NMR spectroscopy. black cross, [U-13C]glycine; black circle, [U-13C]acetate; black inverted triangle, dual or uniformly-labeled lactate; black triangle, [U-13C]bicarbonate; white circle, dual or uniformly-labeled alanine. Catabolism of 13C-glycine was also associated with the production of H13CO3. The yields of H13CO3 (0.17 mM) are likely to be an underestimate due to equilibration with the CO2 enriched atmosphere above the medium. A small amount of 13C-labeled alanine was also produced with ∼0.14 mM being detected at the 168 h time point.
T. denticola conditioned medium stimulates free glycine production by P. gingivalis
Increased expression of T. denticola genes encoding glycine catabolic pathways during co-culture suggested that there may be increased glycine availability. We therefore determined if P. gingivalis growth could provide this additional glycine and if T. denticola could stimulate P. gingivalis glycine production. When P. gingivalis was grown in OBGM there was a small increase in free glycine (Figure 5) while no increase in free glycine was evident in uninoculated OBGM over the same time period (data not shown). When P. gingivalis was grown in OBGM/T. denticola conditioned medium free glycine increased from 0.75±0.04 mM at time 0 h to 2.26±0.66 mM after 46 h, a significant difference of 1.51 mM (p<0.01) whereas the free glycine in the OBGM/PBS control culture increased only 0.26±0.04 mM (p<0.01) (Figure 5) after 46 h. In contrast free glycine content was unchanged in the uninoculated OBGM/T. denticola conditioned medium control (Figure 5). To account for the differing number of P. gingivalis cells in the different media over time and the influence of this on free glycine generation, the change in glycine concentration was expressed as a function of P. gingivalis cell number. A regression line was fitted using a linear mixed modelling approach with the slope representing glycine production per 109 P. gingivalis cells (Figure 6). Glycine production by P. gingivalis grown in OBGM/PBS was 0.171±0.012 µmole glycine/109 cells which was not statistically different from that determined in OBGM at 0.164±0.020 µmole glycine/109 cells (p>0.10) (Figure 6). However, free glycine production by P. gingivalis in OBGM/T. denticola conditioned medium was 0.549±0.090 µmole/109 cells, which was more than three times that observed in OBGM or OBGM/PBS (p<0.01).
Fig. 5. P. gingivalis cell numbers and free glycine content in different cultures. 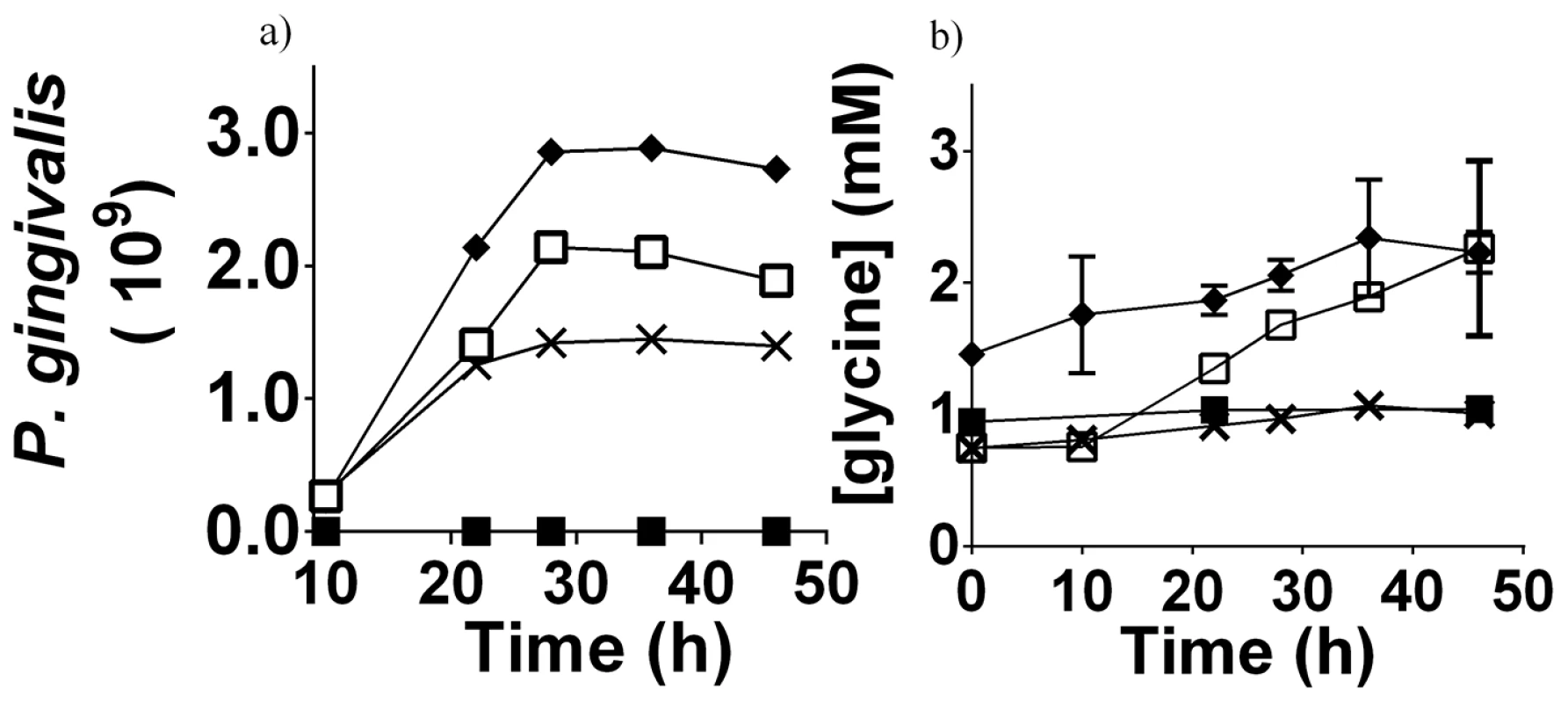
a) The cell numbers of P. gingivalis in different media as determined by absorbance at 650 nm. b) The concentration of free glycine in different P. gingivalis cultures over time, as determined by GC-MS. Data shown are the average of three biological replicates. P. gingivalis grown in:- OBGM – black diamond; OBGM/PBS – black cross; OBGM/T. denticola conditioned medium – white square. Uninoculated OBGM/T. denticola conditioned medium – black square. Fig. 6. Free glycine production during P. gingivalis growth. 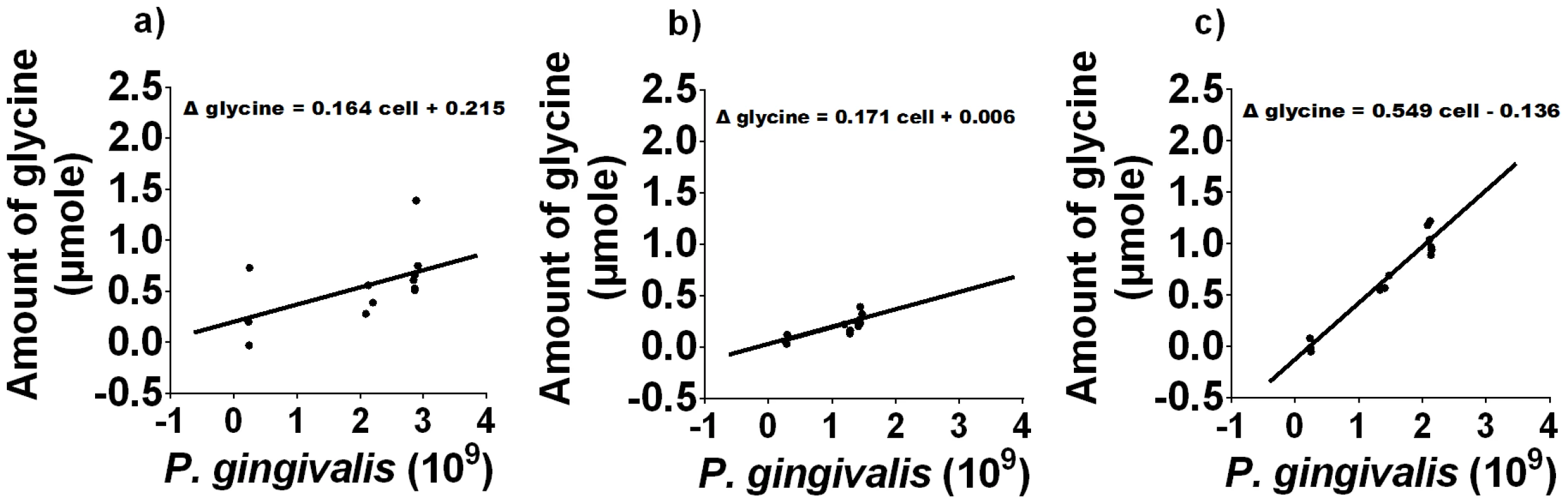
The difference in the amount of free glycine relative to that at t = 0 h as a function of P. gingivalis cell numbers in a) OBGM/PBS, b) OBGM and c) OBGM/T. denticola conditioned medium. A regression line was fitted using a linear mixed modelling approach. The slope represents the amount of glycine produced/109 P. gingivalis cells. To determine the source of this increased free glycine the free and total glycine concentrations were determined prior to and 48 h after P. gingivalis inoculation in OBGM/T. denticola conditioned and OBGM/PBS media. Peptide-bound glycine (total - free) decreased by 1.264±0.143 µmole/109 cells in the OBGM/T. denticola conditioned medium, significantly (p<0.01) more than the 0.733±0.056 µmole/109 cells decrease in OBGM/PBS. These data indicate a higher rate of peptide hydrolysis and release of free glycine by P. gingivalis in the OBGM/T. denticola conditioned medium. Total glycine decreased by 0.765±0.090 µmole/109 cells in the OBGM/T. denticola conditioned medium, compared with the 0.583±0.030 µmole/109 cells decrease in OBGM/PBS, indicating a slightly higher rate of uptake by P. gingivalis in the OBGM/T. denticola conditioned medium.
P. gingivalis TPP production
The increased transcription of P. gingivalis genes during co-culture that encoded thiamine biosynthesis and transport-related proteins prompted us to examine whether P. gingivalis produces excess thiamine that could be used by T. denticola, a thiamine auxotroph. Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) is a micronutrient that is required in extremely low concentrations for bacterial growth that are difficult to detect biochemically. We therefore used an E. coli auxotrophic strain, JW3957-1 to determine excess thiamine production and release by P. gingivalis. E. coli JW3957-1 was unable to grow in M9 minimal medium supplemented with uninoculated P. gingivalis growth medium unless it was supplemented with 5.88 nM TPP. In contrast the E. coli parent strain JRG902 was able to grow to a similar cell density with or without 5.88 nM TPP (Figure 7a). The addition of P. gingivalis cell-free spent medium caused inhibition of E. coli JRG902 growth by an undefined mechanism that was independent of TPP addition (Figure 7b). However the addition of P. gingivalis cell-free spent medium did enable limited growth of E. coli JW3957-1, indicating that there was some available TPP in the medium that had been produced and released by P. gingivalis (Figure 7b). Addition of 5.88 nM TPP resulted in a similar final cell density of both E. coli JW3957-1 and JRG902.
Fig. 7. Excess thiamine pyrophosphate production by P. gingivalis. 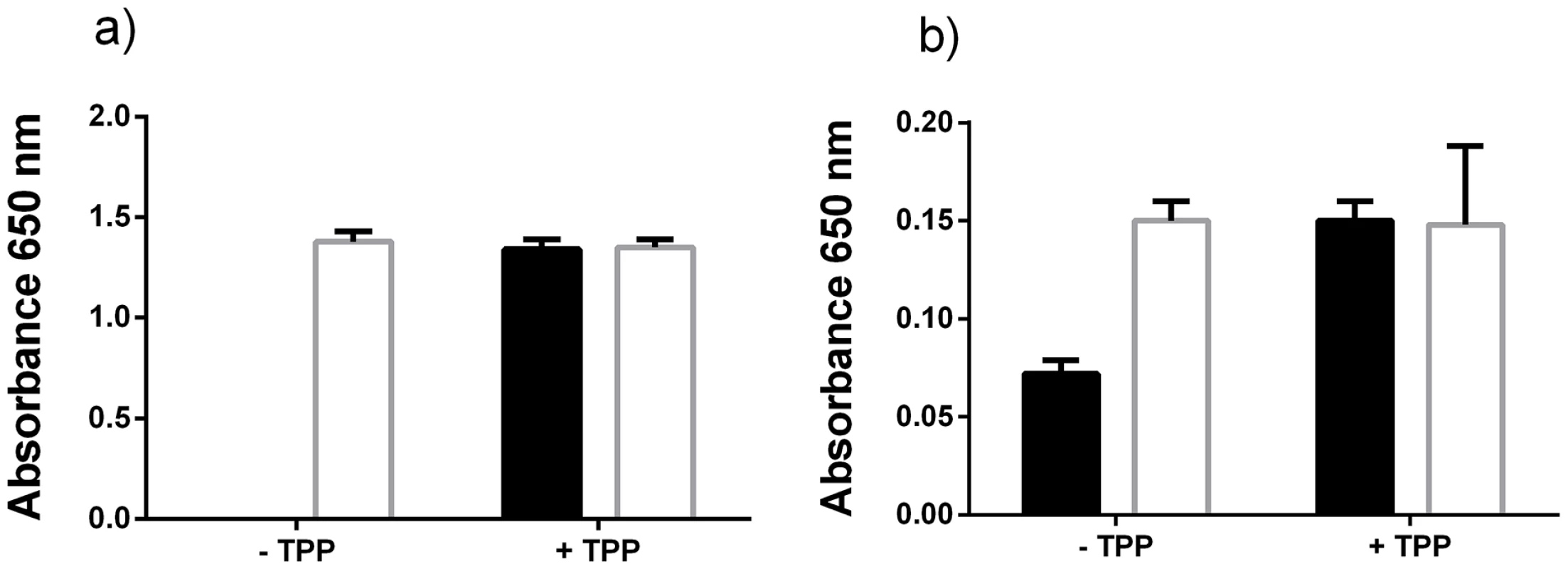
The E. coli TPP auxotrophic strain JW3957-1 (black shading) and the parent strain JRG902 (white shading) were cultured in M9 growth medium (that lacks thiamine) supplemented with either (a) uninoculated P. gingivalis medium (that lacks thiamine) or (b) cell-free P. gingivalis spent medium. The bacterium was cultured with or without TPP addition (5.88 nM). Discussion
P. gingivalis and T. denticola are frequently found together in subgingival plaque samples taken from diseased periodontal sites [1], [6], [10] as spatially co-localized micro-colonies on the surface of the plaque adjacent to the host pocket epithelium [12], [13]. This implies a strong ecological relationship and potential interactions that may contribute to the progression of chronic periodontitis. In this study, we showed that the sum of the interactions (including competition and cooperation) between P. gingivalis and T. denticola resulted in sustained interspecies growth symbiosis in continuous culture over an extended time frame. In addition, the two species reached a reproducible steady state with a cell density significantly higher than in mono-culture that strongly suggests metabolic synergy.
A dual species transcriptome analysis determined that T. denticola and P. gingivalis responded to each other in co-culture by altering the expression of a substantial proportion of genes, notably those involved in T. denticola metabolism and virulence. The shift in metabolism was evidenced by altered expression in genes encoding proteins involved in iron acquisition, utilization and storage by each species, altered glutamate and glycine catabolism by T. denticola and changes in P. gingivalis fatty acid and thiamine pyrophosphate synthesis. This suggests that there may be metabolites produced by each species that enables the other to bypass or alter specific metabolic processes. The up-regulation of the expression of P. gingivalis genes encoding thiamine pyrophosphate biosynthesis indicated an increased production of TPP by P. gingivalis. This may be a result of competition with T. denticola, which is auxotrophic for TPP, or may indicate that that there is some cross-feeding of TPP from P. gingivalis to T. denticola. Due to the difficulties of biochemically measuring nanomolar concentrations of TPP we used an E. coli TPP auxotrophic strain to demonstrate that P. gingivalis produces free TPP that can be utilized by other bacterial species. This indicates that there is a likelihood that T. denticola benefits from P. gingivalis TPP biosynthesis and release in co-culture.
Genes encoding proteins involved in iron storage, heme acquisition and thioredoxin were down-regulated in P. gingivalis co-cultured with T. denticola indicating that P. gingivalis experienced a metabolic shift as a result of co-culture. P. gingivalis is auxotrophic for porphyrin, therefore also for heme and cobalamins as it lacks key enzymes in the early steps of porphyrin biosynthesis [31]. The P. gingivalis gene hmuY (PG1551) that encodes an outer-membrane hemin binding protein important in heme acquisition was the most down-regulated P. gingivalis gene during co-culture with T. denticola, supporting our recent finding of a significant decrease in HmuY abundance in a polymicrobial biofilm containing P. gingivalis and T. denticola [26]. Succinate produced by T. denticola has been reported to alleviate the P. gingivalis requirement for heme during growth in heme-limited medium [14], [46].
In addition fatty acid cross-feeding has previously been demonstrated between P. gingivalis and T. denticola [15] which is consistent with the down-regulation of genes encoding enzymes participating in the initial stage of fatty acid synthesis found in our study. Hence, these results suggest that the presence of T. denticola helps P. gingivalis reduce energy consuming processes which may explain the increase in cell biomass of P. gingivalis grown in the presence of T. denticola.
The coaggregation of T. denticola with P. gingivalis in co-culture as shown by SEM would assist T. denticola in uptake of nutrients produced by P. gingivalis, and vice versa. In the polymicrobial biota of subgingival dental plaque, which is subject to the flow of gingival crevicular fluid, the ability of T. denticola to adhere to other bacteria and to stimulate production of metabolites such as glycine by other species to provide energy and to compensate for it auxotrophies [44], [47] would be of significant benefit to survival and thus virulence. The motility of T. denticola and chemotactic responses would also be significant to its survival. Decreased expression of genes encoding MCP chemotaxis receptors by T. denticola in co-culture with P. gingivalis relative to mono-culture indicates that several substrates, possibly glycine and TPP are in greater abundance in the co-culture such that chemotaxis to a more prefered environment is of lesser importance.
Genes involved in T. denticola glutamate metabolism were down-regulated in co-culture. This potential shift in catabolism may be related to reduced FeS-cofactor biosynthesis and competition as P. gingivalis has a preference for glutamate and aspartate [48], [49]. Significant up-regulation in the expression of T. denticola genes encoding peptidases and enzymes involved in glycine catabolism in co-culture relative to mono-culture was also observed. T. denticola is predicted to have an alanine/glycine cation symporter (TDE1259), a complete glycine cleavage system and the glycine reductase system [47]. Glycine is utilized as an important energy and carbon source in many proteolytic clostridia and Gram-positive bacteria mainly via the activity of the glycine reductase system [50]. We have previously identified, using mass spectrometry, some enzymes of these pathways in T. denticola which were abundant suggesting glycine catabolism may be a major energy source for this spirochete [27]. The importance of the glycine reductase system is also suggested by the recent report demonstrating inhibition of T. denticola growth through the impairment of selenoprotein production such as Protein A and B of the glycine reductase system by stannous salts and auranofin [51]. In support of the contention that glycine catabolism is important in T. denticola free glycine was rapidly depleted from T. denticola growth medium and the addition of glycine significantly increased T. denticola final cell density. Glycine was catabolized by T. denticola with approximately 73% of labeled [U-13C]glycine carbon being incorporated into acetate and the majority of the remainder being incorporated into lactate, suggesting that the majority of the glycine was reduced by the glycine reductase system, where ATP is generated via substrate level phosphorylation [52], [53]. The mechanism by which glycine is catabolized to lactate is less well defined but could involve conversion to serine and pyruvate, with production of NAD (Figure 8). Hence, the preferential use of exogenously acquired glycine for catabolism rather than protein biosynthesis is consistent with glycine catabolism having a major role in energy production in T. denticola.
Fig. 8. Proposed T. denticola glycine catabolic pathways. 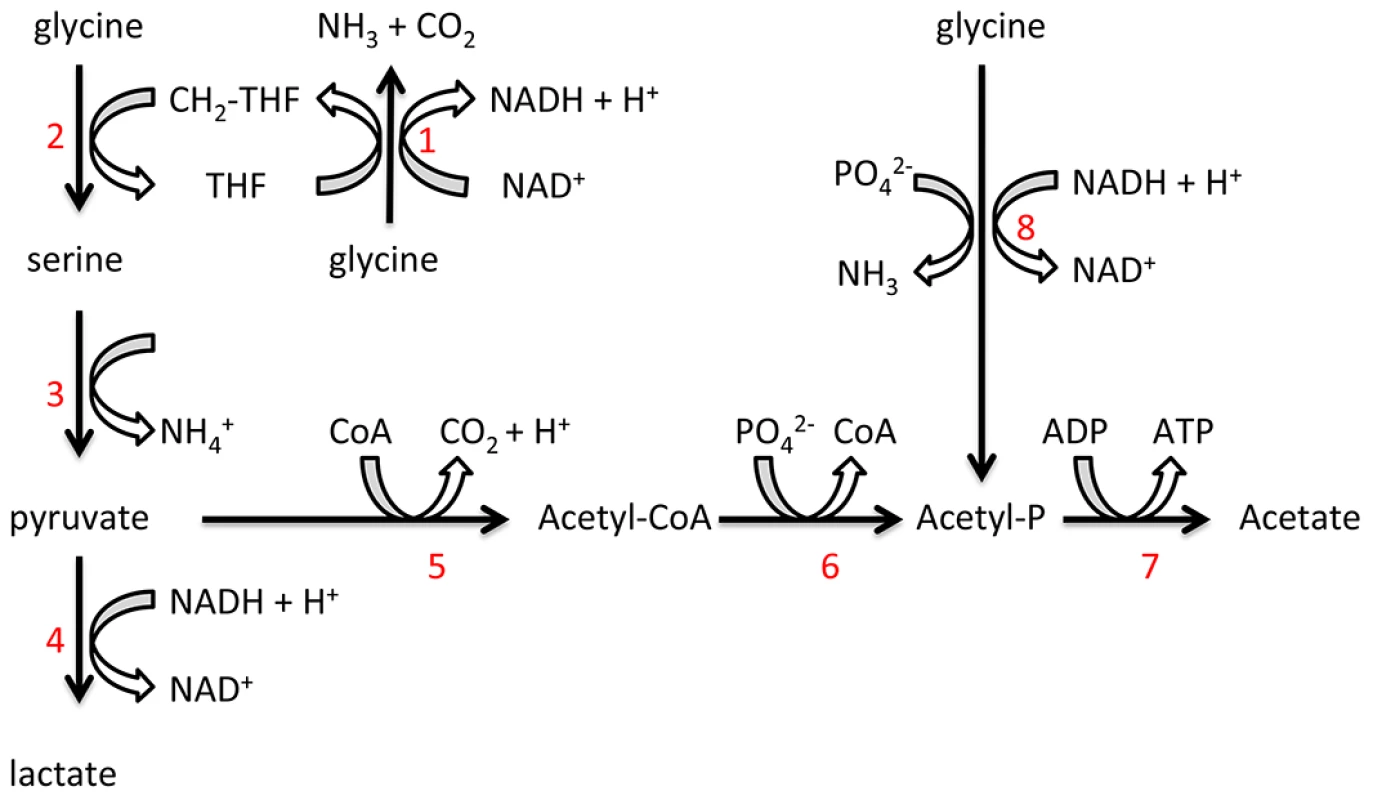
Glycine can be oxidized by the glycine cleavage system (1), producing NH3, CO2 and CH2-THF. Glycine and CH2-THF can be condensed to form serine by serine hydroxymethyltransferase (2). Serine is deaminated to produce pyruvate by serine dehydratase (3). Lactate dehydrogenase (4) catalyzes the interconversion of pyruvate and lactate with concomitant interconversion of NADH and NAD+. Pyruvate can also be metabolized to acetate by pyruvate-ferredoxin oxidoreductase (5), phosphate acetyltransferase (6) and acetate kinase (7). Glycine can also be reduced to acetyl-P by the glycine reductase system (8). P. gingivalis relies mainly on the uptake of peptides as a source of amino acids for energy production and it transports few free amino acids [48], [49]. In mono-culture, P. gingivalis did not utilize free glycine and the concentration of free glycine in the culture supernatant increased slightly over time. The addition of cell-free T. denticola conditioned medium to a P. gingivalis culture significantly increased the concentration of free glycine in the culture medium. This stimulation of free glycine production is consistent with the increased expression of T. denticola genes encoding glycine catabolic pathways and might partially explain the increase in T. denticola cell numbers during co-culture. The increase in free glycine was dependent on the presence of P. gingivalis and a result of an increase in the hydrolysis of glycine-containing peptides in the medium not de novo synthesis of glycine by P. gingivalis. The transcriptomic data of this current study indicated that two P. gingivalis genes (PG0753 and PG0383) encoding putative proteases were significantly up-regulated during co-culture with T. denticola. It is possible that these up-regulated enzymes acting in concert are involved in the observed increase in free glycine. Whatever the precise mechanism this result represents the first demonstration of the stimulation of peptide hydrolysis by P. gingivalis to release free glycine in response to the presence of T. denticola conditioned culture fluid. During infection of a host, P. gingivalis glycine production would be beneficial for establishment and growth of T. denticola, especially as the bacterium is motile and may respond chemotactically to the amino acid.
Transcriptome analysis of T. denticola gene expression as a result of co-culture with P. gingivalis identified the up-regulation of genes encoding several known T. denticola virulence factors including dentilisin protease complex, major sheath protein and cystalysin, which may in part explain the observed synergistic pathogenicity of T. denticola and P. gingivalis co-infections in animal models [16], [18], [19], [54]–[58]. As some of these proteins have also been shown to be involved in coaggregation of T. denticola with P. gingivalis [59]–[62] the up-regulation of these genes might enhance the coaggregation we observed in co-culture and aid site colonisation and synergistic biofilm formation by these species.
Collectively the results of this study indicate that P. gingivalis and T. denticola sense and respond to each other's presence and exhibit metabolic symbioses during co-culture which may contribute towards their establishment and persistence in the periodontal pocket. The co-aggregation, metabolite cross-feeding and up-regulation of T. denticola genes encoding virulence factors help explain the temporal and spatial co-localization of the two species as surface microcolonies in subgingival plaque closely associated with chronic periodontitis [6], [12] and the synergistic virulence of these bacteria in animal models of disease [18].
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. SocranskySS, HaffajeeAD, CuginiMA, SmithC, KentRL (1998) Microbial complexes in subgingival plaque. J Clin Periodontol 25 : 134–144.
2. DarveauRP (2010) Periodontitis: a polymicrobial disruption of host homeostasis. Nat Rev Microbiol 8 : 481–490.
3. HajishengallisG, LiangS, PayneMA, HashimA, JotwaniR, et al. (2011) Low-abundance biofilm species orchestrates inflammatory periodontal disease through the commensal microbiota and complement. Cell Host Microbe 10 : 497–506.
4. HajishengallisG, LamontRJ (2012) Beyond the red complex and into more complexity: the polymicrobial synergy and dysbiosis (PSD) model of periodontal disease etiology. Mol Oral Microbiol 27 : 409–419.
5. MarshPD (2003) Are dental diseases examples of ecological catastrophes? Microbiology 149 : 279–294.
6. ByrneSJ, DashperSG, DarbyIB, AdamsGG, HoffmannB, et al. (2009) Progression of chronic periodontitis can be predicted by the levels of Porphyromonas gingivalis and Treponema denticola in subgingival plaque. Oral Microbiol Immunol 24 : 469–477.
7. BrownLF, BeckJD, RozierRG (1994) Incidence of attachment loss in community-dwelling older adults. J Periodontol 65 : 316–323.
8. HaffajeeAD, SocranskySS, LindheJ, KentRL, OkamotoH, et al. (1991) Clinical risk indicators for periodontal attachment loss. J Clin Periodontol 18 : 117–125.
9. SimonsonLG, McMahonKT, ChildersDW, MortonHE (1992) Bacterial synergy of Treponema denticola and Porphyromonas gingivalis in a multinational population. Oral Microbiol Immunol 7 : 111–112.
10. KigureT, SaitoA, SeidaK, YamadaS, IshiharaK, et al. (1995) Distribution of Porphyromonas gingivalis and Treponema denticola in human subgingival plaque at different periodontal pocket depths examined by immunohistochemical methods. J Periodontal Res 30 : 332–341.
11. RiviereGR, SmithKS, CarranzaNJr, TzagaroulakiE, KaySL, et al. (1996) Associations between Porphyromonas gingivalis and oral treponemes in subgingival plaque. Oral Microbiol Immunol 11 : 150–155.
12. ZijngeV, van LeeuwenMB, DegenerJE, AbbasF, ThurnheerT, et al. (2010) Oral biofilm architecture on natural teeth. PLoS One 5: e9321.
13. WoodSR, KirkhamJ, MarshPD, ShoreRC, NattressB, et al. (2000) Architecture of intact natural human plaque biofilms studied by confocal laser scanning microscopy. J Dent Res 79 : 21–27.
14. GrenierD (1992) Nutritional interactions between two suspected periodontopathogens, Treponema denticola and Porphyromonas gingivalis. Infect Immun 60 : 5298–5301.
15. GrenierD (1992) Demonstration of a bimodal coaggregation reaction between Porphyromonas gingivalis and Treponema denticola. Oral Microbiol Immunol 7 : 280–284.
16. KesavaluL, HoltSC, EbersoleJL (1998) Virulence of a polymicrobic complex, Treponema denticola and Porphyromonas gingivalis, in a murine model. Oral Microbiol Immunol 13 : 373–377.
17. KesavaluL, SathishkumarS, BakthavatchaluV, MatthewsC, DawsonD, et al. (2007) Rat model of polymicrobial infection, immunity, and alveolar bone resorption in periodontal disease. Infect Immun 75 : 1704–1712.
18. OrthRK, O'Brien-SimpsonNM, DashperSG, ReynoldsEC (2011) Synergistic virulence of Porphyromonas gingivalis and Treponema denticola in a murine periodontitis model. Mol Oral Microbiol 26 : 229–240.
19. NiliusAM, SpencerSC, SimonsonLG (1993) Stimulation of in vitro growth of Treponema denticola by extracellular growth factors produced by Porphyromonas gingivalis. J Dent Res 72 : 1027–1031.
20. OnagawaM, IshiharaK, OkudaK (1994) Coaggregation between Porphyromonas gingivalis and Treponema denticola. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll 35 : 171–181.
21. YaoES, LamontRJ, LeuSP, WeinbergA (1996) Interbacterial binding among strains of pathogenic and commensal oral bacterial species. Oral Microbiol Immunol 11 : 35–41.
22. KolenbranderPE (2000) Oral microbial communities: biofilms, interactions, and genetic systems. Annu Rev Microbiol 54 : 413–437.
23. ItoR, IshiharaK, ShojiM, NakayamaK, OkudaK (2010) Hemagglutinin/Adhesin domains of Porphyromonas gingivalis play key roles in coaggregation with Treponema denticola. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 60 : 251–260.
24. KuramitsuHK, ChenW, IkegamiA (2005) Biofilm formation by the periodontopathic bacteria Treponema denticola and Porphyromonas gingivalis. J Periodontol 76 : 2047–2051.
25. YamadaM, IkegamiA, KuramitsuHK (2005) Synergistic biofilm formation by Treponema denticola and Porphyromonas gingivalis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 250 : 271–277.
26. Zainal-AbidinZ, VeithPD, DashperSG, ZhuY, CatmullDV, et al. (2012) Differential proteomic analysis of a polymicrobial biofilm. J Proteome Res 11 : 4449–4464.
27. VeithPD, DashperSG, O'Brien-SimpsonNM, PaoliniRA, OrthR, et al. (2009) Major proteins and antigens of Treponema denticola. Biochim Biophys Acta 1794 : 1421–1432.
28. OrthR, O'Brien-SimpsonN, DashperS, WalshK, ReynoldsE (2010) An efficient method for enumerating oral spirochetes using flow cytometry. J Microbiol Methods 80 : 123–128.
29. RouillardJM, ZukerM, GulariE (2003) OligoArray 2.0: design of oligonucleotide probes for DNA microarrays using a thermodynamic approach. Nucleic Acids Res 31 : 3057–3062.
30. MitchellHL, DashperSG, CatmullDV, PaoliniRA, ClealSM, et al. (2010) Treponema denticola biofilm-induced expression of a bacteriophage, toxin-antitoxin systems and transposases. Microbiology 156 : 774–788.
31. NelsonKE, FleischmannRD, DeBoyRT, PaulsenIT, FoutsDE, et al. (2003) Complete genome sequence of the oral pathogenic bacterium Porphyromonas gingivalis strain W83. J Bacteriol 185 : 5591–5601.
32. YangYH, DudoitS, LuuP, LinDM, PengV, et al. (2002) Normalization for cDNA microarray data: a robust composite method addressing single and multiple slide systematic variation. Nucleic Acids Res 30: e15.
33. LoAW, SeersCA, BoyceJD, DashperSG, SlakeskiN, et al. (2009) Comparative transcriptomic analysis of Porphyromonas gingivalis biofilm and planktonic cells. BMC Microbiol 9 : 18.
34. DashperSG, AngCS, VeithPD, MitchellHL, LoAW, et al. (2009) Response of Porphyromonas gingivalis to heme limitation in continuous culture. J Bacteriol 191 : 1044–1055.
35. BenjaminiY, HochbergY (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Statist Soc B 57 : 289–300.
36. TatusovRL, FedorovaND, JacksonJD, JacobsAR, KiryutinB, et al. (2003) The COG database: an updated version includes eukaryotes. BMC Bioinformatics 4 : 41.
37. AlmEJ, HuangKH, PriceMN, KocheRP, KellerK, et al. (2005) The MicrobesOnline Web site for comparative genomics. Genome Res 15 : 1015–1022.
38. VandesompeleJ, De PreterK, PattynF, PoppeB, Van RoyN, et al. (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3: research0034.0031–research0034.0011.
39. RozenS, SkaletskyH (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol Biol 132 : 365–386.
40. SaundersEC, NgWW, ChambersJM, NgM, NadererT, et al. (2011) Isotopomer profiling of Leishmania mexicana promastigotes reveals important roles for succinate fermentation and aspartate uptake in tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) anaplerosis, glutamate synthesis, and growth. J Biol Chem 286 : 27706–27717.
41. GuestJR (1977) Menaquinone biosynthesis: mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 requiring 2-succinylbenzoate. J Bacteriol 130 : 1038–1046.
42. BabaT, AraT, HasegawaM, TakaiY, OkumuraY, et al. (2006) Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 in-frame, single-gene knockout mutants: the Keio collection. Mol Syst Biol 2 : 2006 0008.
43. Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning : a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.
44. WyssC (2007) Fatty acids synthesized by oral treponemes in chemically defined media. FEMS Microbiol Lett 269 : 70–76.
45. TatusovRL, KooninEV, LipmanDJ (1997) A genomic perspective on protein families. Science 278 : 631–637.
46. MayrandD, McBrideBC (1980) Ecological relationships of bacteria involved in a simple, mixed anaerobic infection. Infect Immun 27 : 44–50.
47. SeshadriR, MyersGS, TettelinH, EisenJA, HeidelbergJF, et al. (2004) Comparison of the genome of the oral pathogen Treponema denticola with other spirochete genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101 : 5646–5651.
48. DashperSG, BrownfieldL, SlakeskiN, ZilmPS, RogersAH, et al. (2001) Sodium ion-driven serine/threonine transport in Porphyromonas gingivalis. J Bacteriol 183 : 4142–4148.
49. TakahashiN, SatoT, YamadaT (2000) Metabolic pathways for cytotoxic end product formation from glutamate - and aspartate-containing peptides by Porphyromonas gingivalis. J Bacteriol 182 : 4704–4710.
50. ConeJE, Del RioRM, DavisJN, StadtmanTC (1976) Chemical characterization of the selenoprotein component of clostridial glycine reductase: identification of selenocysteine as the organoselenium moiety. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 73 : 2659–2663.
51. Jackson-RosarioS, SelfWT (2009) Inhibition of selenium metabolism in the oral pathogen Treponema denticola. J Bacteriol 191 : 4035–4040.
52. AndreesenJR (1994) Glycine metabolism in anaerobes. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 66 : 223–237.
53. AndreesenJR (2004) Glycine reductase mechanism. Curr Opin Chem Biol 8 : 454–461.
54. EbersoleJL, KesavaluL, SchneiderSL, MachenRL, HoltSC (1995) Comparative virulence of periodontopathogens in a mouse abscess model. Oral Dis 1 : 115–128.
55. KimizukaR, KatoT, IshiharaK, OkudaK (2003) Mixed infections with Porphyromonas gingivalis and Treponema denticola cause excessive inflammatory responses in a mouse pneumonia model compared with monoinfections. Microbes Infect 5 : 1357–1362.
56. KesavaluL, WalkerSG, HoltSC, CrawleyRR, EbersoleJL (1997) Virulence characteristics of oral treponemes in a murine model. Infect Immun 65 : 5096–5102.
57. GemmellE, BirdPS, CarterCL, DrysdaleKE, SeymourGJ (2002) Effect of Fusobacterium nucleatum on the T and B cell responses to Porphyromonas gingivalis in a mouse model. Clin Exp Immunol 128 : 238–244.
58. WashizuM, IshiharaK, HonmaK, OkudaK (2003) Effects of a mixed infection with Porphyromonas gingivalis and Treponema denticola on abscess formation and immune responses in mice. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll 44 : 141–147.
59. CogoniV, Morgan-SmithA, FennoJC, JenkinsonHF, DymockD (2012) Treponema denticola chymotrypsin-like proteinase (CTLP) integrates spirochaetes within oral microbial communities. Microbiology 158 : 759–770.
60. HashimotoM, OgawaS, AsaiY, TakaiY, OgawaT (2003) Binding of Porphyromonas gingivalis fimbriae to Treponema denticola dentilisin. FEMS Microbiol Lett 226 : 267–271.
61. VeseyPM, KuramitsuHK (2004) Genetic analysis of Treponema denticola ATCC 35405 biofilm formation. Microbiology 150 : 2401–2407.
62. RosenG, GenzlerT, SelaMN (2008) Coaggregation of Treponema denticola with Porphyromonas gingivalis and Fusobacterium nucleatum is mediated by the major outer sheath protein of Treponema denticola. FEMS Microbiol Lett 289 : 59–66.
Štítky
Hygiena a epidemiologie Infekční lékařství Laboratoř
Článek DHX36 Enhances RIG-I Signaling by Facilitating PKR-Mediated Antiviral Stress Granule FormationČlánek Oral Bacteria and CancerČlánek A Non-Coding RNA Promotes Bacterial Persistence and Decreases Virulence by Regulating a Regulator in
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Pathogens
Nejčtenější tento týden
2014 Číslo 3- Stillova choroba: vzácné a závažné systémové onemocnění
- Diagnostika virových hepatitid v kostce – zorientujte se (nejen) v sérologii
- Perorální antivirotika jako vysoce efektivní nástroj prevence hospitalizací kvůli COVID-19 − otázky a odpovědi pro praxi
- Choroby jater v ordinaci praktického lékaře – význam jaterních testů
- Diagnostický algoritmus při podezření na syndrom periodické horečky
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- Conflicting Interests in the Pathogen–Host Tug of War: Fungal Micronutrient Scavenging Versus Mammalian Nutritional Immunity
- Putting Fungi to Work: Harvesting a Cornucopia of Drugs, Toxins, and Antibiotics
- Mycobacteriophages: Windows into Tuberculosis
- Human African Trypanosomiasis and Immunological Memory: Effect on Phenotypic Lymphocyte Profiles and Humoral Immunity
- Five Things to Know about Genetically Modified (GM) Insects for Vector Control
- A Missing Dimension in Measures of Vaccination Impacts
- Eosinophils Are Important for Protection, Immunoregulation and Pathology during Infection with Nematode Microfilariae
- Clonality of HTLV-2 in Natural Infection
- Production, Fate and Pathogenicity of Plasma Microparticles in Murine Cerebral Malaria
- Group B Streptococcal Infection of the Choriodecidua Induces Dysfunction of the Cytokeratin Network in Amniotic Epithelium: A Pathway to Membrane Weakening
- New Insights into How Adapts to Its Mammalian Host during Bubonic Plague
- Foodborne Transmission of Nipah Virus in Syrian Hamsters
- A Polysaccharide Virulence Factor from Elicits Anti-inflammatory Effects through Induction of Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist
- Structural and Functional Characterization of a Complex between the Acidic Transactivation Domain of EBNA2 and the Tfb1/p62 Subunit of TFIIH
- Adaptive Gene Amplification As an Intermediate Step in the Expansion of Virus Host Range
- DHX36 Enhances RIG-I Signaling by Facilitating PKR-Mediated Antiviral Stress Granule Formation
- Hepatitis B Virus Infection and Immunopathogenesis in a Humanized Mouse Model: Induction of Human-Specific Liver Fibrosis and M2-Like Macrophages
- Crk Adaptors Negatively Regulate Actin Polymerization in Pedestals Formed by Enteropathogenic (EPEC) by Binding to Tir Effector
- Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Contributes Significantly to Establishment of a Bioenergetically Favorable Environment for Vaccinia Virus Infection
- A Cytosolic Chaperone Complexes with Dynamic Membrane J-Proteins and Mobilizes a Nonenveloped Virus out of the Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Intracellular Promote Invasive Cell Motility through Kinase Regulation of the Host Actin Cytoskeleton
- MAVS-MKK7-JNK2 Defines a Novel Apoptotic Signaling Pathway during Viral Infection
- RON5 Is Critical for Organization and Function of the Moving Junction Complex
- Immune Suppression by Neutrophils in HIV-1 Infection: Role of PD-L1/PD-1 Pathway
- and Exhibit Metabolic Symbioses
- The Herpes Virus Fc Receptor gE-gI Mediates Antibody Bipolar Bridging to Clear Viral Antigens from the Cell Surface
- Target Cell Availability, Rather than Breast Milk Factors, Dictates Mother-to-Infant Transmission of SIV in Sooty Mangabeys and Rhesus Macaques
- Evolution of the Retroviral Restriction Gene : Inhibition of Non-MLV Retroviruses
- Infection of Adult Thymus with Murine Retrovirus Induces Virus-Specific Central Tolerance That Prevents Functional Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation
- Fha Interaction with Phosphothreonine of TssL Activates Type VI Secretion in
- In Vivo Administration of a JAK3 Inhibitor during Acute SIV Infection Leads to Significant Increases in Viral Load during Chronic Infection
- Lack of Detectable HIV-1 Molecular Evolution during Suppressive Antiretroviral Therapy
- Activation of HIV-1 from Latent Infection via Synergy of RUNX1 Inhibitor Ro5-3335 and SAHA
- A Compact, Multifunctional Fusion Module Directs Cholesterol-Dependent Homomultimerization and Syncytiogenic Efficiency of Reovirus p10 FAST Proteins
- The Role of Host and Microbial Factors in the Pathogenesis of Pneumococcal Bacteraemia Arising from a Single Bacterial Cell Bottleneck
- Genetic Dissection of Gut Epithelial Responses to
- Two-Component System Cross-Regulation Integrates Response to Heme and Cell Envelope Stress
- Oral Mycobiome Analysis of HIV-Infected Patients: Identification of as an Antagonist of Opportunistic Fungi
- A Model System for Studying the Transcriptomic and Physiological Changes Associated with Mammalian Host-Adaptation by Serovar Copenhageni
- Inflammasome Sensor NLRP1 Controls Rat Macrophage Susceptibility to
- ChIP-Seq and RNA-Seq Reveal an AmrZ-Mediated Mechanism for Cyclic di-GMP Synthesis and Biofilm Development by
- The Hypervariable Amino-Terminus of P1 Protease Modulates Potyviral Replication and Host Defense Responses
- Caspase-1-Dependent and -Independent Cell Death Pathways in Infection of Macrophages
- The Effect of Cell Growth Phase on the Regulatory Cross-Talk between Flagellar and Spi1 Virulence Gene Expression
- Different Mutagenic Potential of HIV-1 Restriction Factors APOBEC3G and APOBEC3F Is Determined by Distinct Single-Stranded DNA Scanning Mechanisms
- Oral Bacteria and Cancer
- Identification of OmpA, a Protein Involved in Host Cell Invasion, by Multi-Phenotypic High-Content Screening
- Transovarial Transmission of a Plant Virus Is Mediated by Vitellogenin of Its Insect Vector
- VE-Cadherin Cleavage by LasB Protease from Facilitates Type III Secretion System Toxicity in Endothelial Cells
- Dimerization of VirD2 Binding Protein Is Essential for Induced Tumor Formation in Plants
- Crystal Structure of the Vaccinia Virus DNA Polymerase Holoenzyme Subunit D4 in Complex with the A20 N-Terminal Domain
- Post-Translational Regulation via Clp Protease Is Critical for Survival of
- Modulation of Phagosomal pH by Promotes Hyphal Morphogenesis and Requires Stp2p, a Regulator of Amino Acid Transport
- Rotavirus Activates Lymphocytes from Non-Obese Diabetic Mice by Triggering Toll-Like Receptor 7 Signaling and Interferon Production in Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells
- Cytomegalovirus m154 Hinders CD48 Cell-Surface Expression and Promotes Viral Escape from Host Natural Killer Cell Control
- Interferon Regulatory Factor-1 Protects from Fatal Neurotropic Infection with Vesicular Stomatitis Virus by Specific Inhibition of Viral Replication in Neurons
- HMGB1-Promoted and TLR2/4-Dependent NK Cell Maturation and Activation Take Part in Rotavirus-Induced Murine Biliary Atresia
- An Immunomics Approach to Schistosome Antigen Discovery: Antibody Signatures of Naturally Resistant and Chronically Infected Individuals from Endemic Areas
- PPARγ Agonists Improve Survival and Neurocognitive Outcomes in Experimental Cerebral Malaria and Induce Neuroprotective Pathways in Human Malaria
- A Non-Coding RNA Promotes Bacterial Persistence and Decreases Virulence by Regulating a Regulator in
- Viral OTU Deubiquitinases: A Structural and Functional Comparison
- Heterogeneity and Breadth of Host Antibody Response to KSHV Infection Demonstrated by Systematic Analysis of the KSHV Proteome
- Influenza A Virus Assembly Intermediates Fuse in the Cytoplasm
- Broadly Reactive Human CD8 T Cells that Recognize an Epitope Conserved between VZV, HSV and EBV
- Oncogenic Human Papillomaviruses Activate the Tumor-Associated Lens Epithelial-Derived Growth Factor (LEDGF) Gene
- Erythrocyte Invasion: Combining Function with Immune Evasion
- IL-1α and Complement Cooperate in Triggering Local Neutrophilic Inflammation in Response to Adenovirus and Eliminating Virus-Containing Cells
- Chronic Exposure to Type-I IFN under Lymphopenic Conditions Alters CD4 T Cell Homeostasis
- PLOS Pathogens
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Cytomegalovirus m154 Hinders CD48 Cell-Surface Expression and Promotes Viral Escape from Host Natural Killer Cell Control
- Human African Trypanosomiasis and Immunological Memory: Effect on Phenotypic Lymphocyte Profiles and Humoral Immunity
- DHX36 Enhances RIG-I Signaling by Facilitating PKR-Mediated Antiviral Stress Granule Formation
- Conflicting Interests in the Pathogen–Host Tug of War: Fungal Micronutrient Scavenging Versus Mammalian Nutritional Immunity
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Vladimír Palička, CSc., Dr.h.c., doc. MUDr. Václav Vyskočil, Ph.D., MUDr. Petr Kasalický, CSc., MUDr. Jan Rosa, Ing. Pavel Havlík, Ing. Jan Adam, Hana Hejnová, DiS., Jana Křenková
Autoři: MUDr. Irena Krčmová, CSc.
Autoři: MDDr. Eleonóra Ivančová, PhD., MHA
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Eva Kubala Havrdová, DrSc.
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



