-
Články
- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
- Kongresy
- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Lateral and End-On Kinetochore Attachments Are Coordinated to Achieve Bi-orientation in Oocytes
In acentrosomal oocytes, spindle assembly depends on the chromosomes. The nature of the chromosome-microtubule interactions in oocytes that organize spindle bipolarity and orientation of the homologs has been unclear. We have found that several types of functional chromosome-microtubule interactions exist in oocytes, and that each type participates in unique aspects of chromosome orientation and spindle assembly. We present here a model for chromosome-based spindle assembly and chromosome movements in oocytes that highlights the multiple and unappreciated roles played by the kinetochores and has implications for how homologous chromosomes bi-orient during meiosis.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Genet 11(10): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1005605
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005605Summary
In acentrosomal oocytes, spindle assembly depends on the chromosomes. The nature of the chromosome-microtubule interactions in oocytes that organize spindle bipolarity and orientation of the homologs has been unclear. We have found that several types of functional chromosome-microtubule interactions exist in oocytes, and that each type participates in unique aspects of chromosome orientation and spindle assembly. We present here a model for chromosome-based spindle assembly and chromosome movements in oocytes that highlights the multiple and unappreciated roles played by the kinetochores and has implications for how homologous chromosomes bi-orient during meiosis.
Introduction
It is well established that oocyte spindle assembly in many organisms occurs in the absence of centrosomes [1–3]. Instead, chromatin-based mechanisms play an important role in spindle assembly. The interactions between chromosomes and microtubules are paramount in oocytes, necessary for both the assembly of the spindle and the forces required for chromosome segregation. Less well understood, however, is the nature of the functional connections between chromosomes and microtubules in these cells. The role of the kinetochores, the primary site of interaction between chromosomes and microtubules, is poorly understood in acentrosomal systems. For example, spindles will assemble and chromatin will move without kinetochores in both Caenorhabditis elegans and mouse oocytes [4, 5]. In addition, both C. elegans and mouse oocytes experience a prolonged period during which chromosomes have aligned but end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments have not formed [6–8]. We have previously shown that the central spindle, composed of antiparallel microtubules that assemble adjacent to the chromosomes, is important for spindle bipolarity and homolog bi-orientation [9, 10]. These studies suggest that lateral interactions between the chromosomes and microtubules drive homolog bi-orientation, but whether these interactions are kinetochore-based is not clear.
There have been few studies directly analyzing kinetochore function in oocyte spindle assembly and chromosome segregation [5, 11, 12]. Assembling a functional spindle requires the initiation of microtubule accumulation around the chromatin, the organization of microtubules into a bipolar structure, and the maturation of the spindle from promoting chromosome alignment to promoting segregation. Whether the kinetochores are required for spindle assembly or the series of regulated and directed movements chromosomes undergo to ensure their proper partitioning into daughter cells is not known. In Drosophila, the chromosomes begin the process within a single compact structure called the karyosome [13]. Within the karyosome, centromeres are clustered prior to nuclear envelope breakdown (NEB) [14]. This arrangement, which is established early in prophase and maintained throughout diplotene/diakinesis, is also found in many other cell types [15]. It is possible that the function of centromere clustering is to influence the orientation of the centromeres on the spindle independent of chiasmata [16, 17]. Following NEB, the centromeres separate. In Drosophila oocytes, centromere separation depends on the chromosomal passenger complex (CPC) [10]. Whether this movement depends on interactions between chromosomes and microtubules remains to be established [10].
Following centromere separation, homologous centromeres move towards opposite spindle poles. During this time in Drosophila oocytes, the karyosome elongates and achiasmate chromosomes may approach the poles, separating from the main chromosome mass [18]. As prometaphase progresses, the chromosomes once again contract into a round karyosome. These chromosome movements appear analogous to the congression of chromosomes to the metaphase plate that ultimately results in the stable bi-orientation of chromosomes. In mitotic cells, congression depends on lateral interactions between kinetochores and microtubules [19, 20], and bi-orientation depends on the formation of end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments [21, 22]. In oocytes, lateral chromosome-microtubule interactions have been suggested to be especially important, but how lateral and end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments are coordinated to generate homolog bi-orientation has not been studied [9, 23].
To investigate the roles of lateral and end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments in spindle assembly and prometaphase chromosome movements of acentrosomal oocytes, we characterized Drosophila oocytes lacking kinetochore components. The KNL1/Mis12/Ndc80 (KMN) complex is at the core of the kinetochore, providing a link between centromeric DNA and microtubules [24, 25]. Both KNL1 and NDC80 bind to microtubules in vitro [26], but NDC80 is required specifically for end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments [24]. Therefore, we examined oocytes lacking either NDC80 to eliminate end-on attachments or the Drosophila homolog of KNL1, SPC105R, to eliminate all kinetochore-microtubule interactions. We also examined Drosophila oocytes lacking the centromere-associated kinesin motor CENP-E because CENP-E promotes the movement of chromosomes along lateral kinetochore-microtubule attachments in a variety of cell types [19, 20].
Our work has identified three distinct functions of kinetochores that lead to the correct orientation of homologs at meiosis I. First, SPC105R is required for the co-orientation of sister centromeres at meiosis I. This is a unique process that fuses sister centromeres, ensuring they attach to microtubules from the same pole at meiosis I. Second, lateral kinetochore-microtubule attachments are sufficient for prometaphase chromosome movements, which may be required for each pair of homologous centromeres to establish connections with microtubules from opposite poles. Third, end-on attachments are dispensable for prometaphase movement but are essential to stabilize homologous chromosome bi-orientation. Surprisingly, we found that although Drosophila oocytes do not undergo traditional congression of chromosomes to the metaphase plate, CENP-E is required to prevent chromosomes from becoming un-aligned and to promote the correct bi-orientation of homologous chromosomes. We also show that the initiation of acentrosomal chromatin-based spindle assembly does not depend on kinetochores, suggesting the presence of important additional interaction sites between chromosomes and microtubules. The stability of the oocyte spindle, however, becomes progressively more dependent on kinetochores as the spindle transitions from prometaphase to metaphase. Overall, this work shows that oocytes integrate several chromosome-microtubule connections to promote spindle formation and the different types of chromosome movements that ensure the proper segregation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis.
Results
Loss of SPC105R disrupts kinetochore assembly in Drosophila oocytes
To study the role of kinetochores in oocyte spindle assembly and chromosome orientation, we sought to eliminate kinetochore function in Drosophila oocytes. Mutations in Drosophila kinetochore genes are lethal prior to the initiation of oogenesis [27–30], and germline clones of kinetochore mutants failed to complete oogenesis (S1 Table). Therefore, we used RNAi to deplete kinetochore proteins in Drosophila oocytes (see Materials and Methods). Mitotic cells lacking NDC80 have persistent lateral kinetochore-microtubule attachments [31], while loss of SPC105R (the Drosophila homolog of KNL1) results in destabilization of all kinetochore-microtubule attachments [32]. Therefore, we decided to use Ndc80 and Spc105R depletion to examine the roles of kinetochores and discriminate between the roles of lateral and end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments in oocytes. One Ndc80 (GL00625) and two Spc105R (GL00392 and HMS01548) RNAi constructs were obtained. In oocytes, expression of these constructs knocked down Ndc80 gene expression by 94% and Spc105R gene expression by 87% and 96%, respectively. No significant phenotypic differences were observed between the two Spc105R constructs; therefore, for simplicity all experiments shown used only the GL00392 hairpin except where noted.
We found that localization of NDC80 and SPC105R to kinetochores was absent in Ndc80 - or Spc105R-depleted oocytes, respectively (S2 Table and Fig 1A and 1B), showing that the RNAi knockdown was effective. In addition, NDC80 and NSL1 (a member of the Mis12 complex) failed to localize to kinetochores in Spc105R-depleted oocytes (S2 Table and Fig 1A and 1C), while both SPC105R and NSL1 localized to kinetochores in Ndc80-depleted oocytes (S2 Table and Fig 1B and 1C). These results are consistent with results from mitotic cells in Drosophila embryos and cell culture [28, 33]: localization of KMN complex proteins in Drosophila depends on SPC105R but not NDC80.
Fig. 1. Loss of SPC105R or the CPC disrupts kinetochore assembly in oocytes. 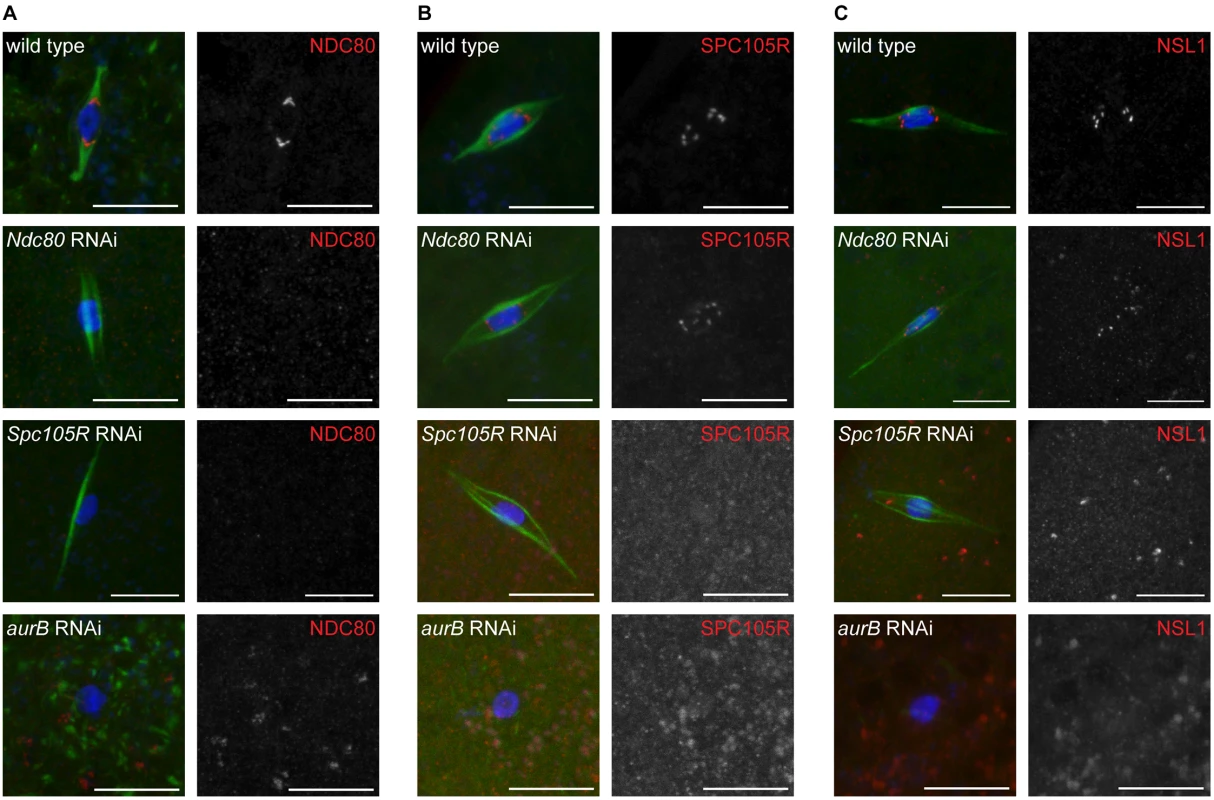
Confocal images of localization of (A) NDC80, (B) SPC105R, and (C) NSL1 (Mis12 complex) in wild-type oocytes and after knockdown of Ndc80, Spc105R, or aurB. DNA is shown in blue and tubulin is shown in green in merged images. Kinetochore components are shown in red in merged images and white in single channel images. Scale bars represent 10 μm. Loss of NDC80 or SPC105R disrupts kinetochore-microtubule attachments in oocytes
To determine if kinetochore-microtubule attachments are affected in oocytes depleted of kinetochore components, we examined microtubule localization relative to the centromere protein, CENP-C. The robust central spindle makes it difficult to directly observe kinetochore microtubules; therefore, we used conditions that depolymerize central spindle microtubules to directly observe kinetochore microtubules. Wild-type oocytes exposed to colchicine (see Materials and Methods for details) resulted in the loss of most spindle microtubules except for those that ended at the centromeres (Fig 2B, 17/18 oocytes). In contrast, in colchicine-treated oocytes lacking NDC80, the microtubules were weaker, and those remaining often appeared to be interacting laterally with the centromeres (Fig 2D, 7/12 oocytes). In colchicine-treated oocytes lacking SPC105R, no end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments were observed (0/12 oocytes), and we observed some oocytes in which all of the microtubules were eliminated (Fig 2F, 3/12 oocytes). These results suggest that NCD80 is required for end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments, while all kinetochore-microtubule interactions depend on SCP105R.
Fig. 2. Loss of NDC80 or SPC105R disrupts interactions between kinetochores and microtubules in oocytes. 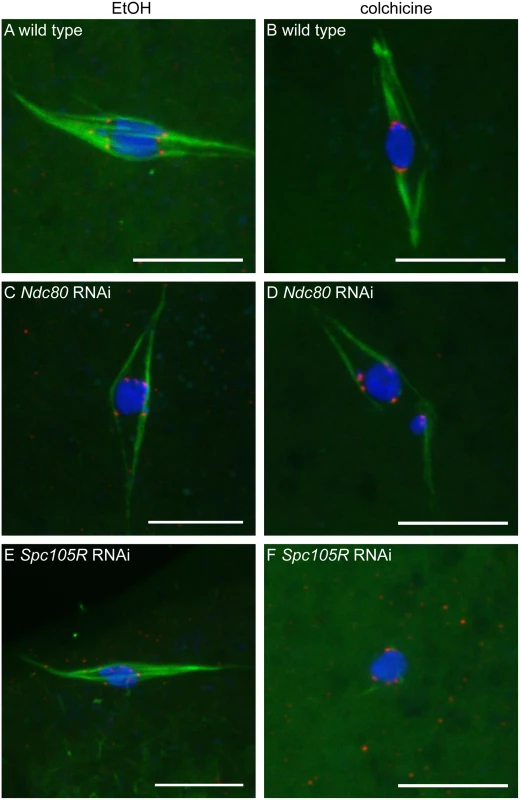
Confocal images of wild-type oocytes (A,B) and after knockdown of Ndc80 (C,D) or Spc105R (E,F). Oocytes were treated with either ethanol (EtOH) (A,C,E) or colchicine (B,D,F). DNA is shown in blue, tubulin is shown in green, and CENP-C is in red. Scale bars represent 10 μm To confirm that SPC105R, but not NDC80, is required for kinetochore-microtubule interactions, we measured the distance between each centromere and the nearest microtubules in oocytes not treated with colchicine. In wild type, the majority of centromeres were within 0.2 μm of the microtubules (Fig 3A and 3B). A similar frequency was found with loss of NDC80, suggesting these defective kinetochores still interacted with the microtubules (Fig 3A and 3B, P = 0.07). Oocytes lacking SPC105R, however, had significantly fewer centromeres within 0.2 μm of the microtubules (Fig 3A and 3B, P = <0.0001). Based on the results with colchicine, it is likely that centromeres lacking SPC105R move within 0.2 μm of a microtubule by chance. These results suggest SPC105R, but not NDC80, is required for the kinetochores to attach to the microtubules.
Fig. 3. Chromosome orientation depends on the kinetochore in oocytes. 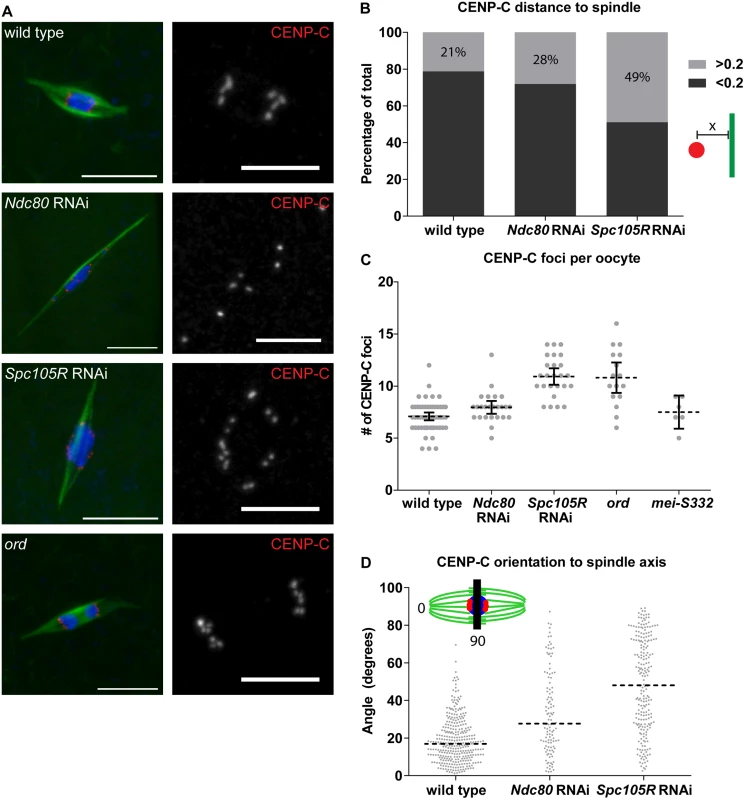
(A) Confocal images of the centromere protein CENP-C (red in merged images, white in single channel) in wild-type oocytes, after knockdown of Ndc80 or Spc105R, and in ord mutants. Single channel images are zoomed in relative to merged to highlight CENP-C foci. In ord mutants, due to defects in cohesion or crossing over, precocious anaphase is observed [80, 81]. DNA is in blue and tubulin is in green in merged images. Scale bars represent 10 μm in merged, 5 μm in CENP-C single channel images. (B) Bar graph showing the ratio of CENP-C foci closer to (dark gray) and further from (light gray) the spindle than 0.2 μM. Inset shows a centromere in red, a microtubule in green, and the distance measurement denoted by “x”. (C) Dot plot of the number of CENP-C foci per oocyte in wild type, after Ndc80 or Spc105R knockdown, in ord mutants, and in mei-S332 mutants (encoding the Drosophila homolog of Shugoshin). Horizontal dotted lines show the mean, error bars show 95% confidence intervals. (D) Dot plot of the angle of CENP-C foci with respect to the spindle axis in wild-type oocytes and after knockdown of Ndc80 or Spc105R. Horizontal dotted lines show the median. The red bar in the inset shows a line perpendicular to the spindle axis: centromeres located on this line would result in 90 degree angle measurements, while centromeres in line with the spindle axis measure 0 degrees. Differences in the width of the karyosome, in wild-type oocytes (3.13 μm), and after knockdown of Ndc80 (3.43 μm) or Spc105R (3.32 μm), are not great enough to explain the differences in angles of CENP-C foci. To examine microtubule interactions using a functional readout for end-on attachments, we examined the localization of ROD. ROD is part of the RZZ complex, which localizes to kinetochores until the formation of end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments when it leaves the kinetochore by streaming along the kinetochore microtubules [34]. In wild-type oocytes, ROD was present at kinetochores, and we observed streams of ROD along microtubules (S1 and S2 Figs), suggesting that end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments indeed form in Drosophila oocytes. In C. elegans, localization of the RZZ complex to the kinetochore depends on KNL-1, the homolog of Drosophila SPC105R [35]. Similarly, we did not observe localization of ROD to kinetochores in Spc105R-depleted oocytes (S1 Fig). In Ndc80-depleted oocytes, however, ROD was present at kinetochores, but in most oocytes we did not observe streaming along the microtubules (S1 Fig). Therefore, the lack of ROD streaming demonstrates that end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments do not form in the absence of NDC80.
Lateral kinetochore-microtubule attachments drive prometaphase chromosome movements
To determine the role of kinetochore-microtubule attachments in oocyte chromosome movement, we examined prometaphase karyosome configurations after knockdown of Ndc80 or Spc105R. During prometaphase I, chromosomes undergo movements to facilitate contact with the spindle, a process that may be required for chromosome alignment [18]. In Drosophila oocytes, chromosomes are compacted into a karyosome [13] so congression to the metaphase plate is unnecessary. Prometaphase chromosome movements still occur and are visible through the elongation of the karyosome and the separation of achiasmate chromosomes from the karyosome (S3 Fig). Collections of oocytes can be enriched for either prometaphase or metaphase depending on how the females are treated (see Materials and Methods) [18]. We found that prometaphase karyosome configurations in Ndc80-depleted oocytes were similar in frequency to wild type (28% vs. 26%; Table 1). In contrast, in Spc105R-depleted oocytes, elongation of the karyosome and separation of achiasmate chromosomes was rarely observed (6% of oocytes; Table 1). Therefore, prometaphase chromosome movements depend on SPC105R, but not NDC80, suggesting that lateral kinetochore-microtubule attachments are sufficient to drive prometaphase chromosome movements in oocytes.
Tab. 1. Prometaphase karyosome configurations in the absence of kinetochore components. 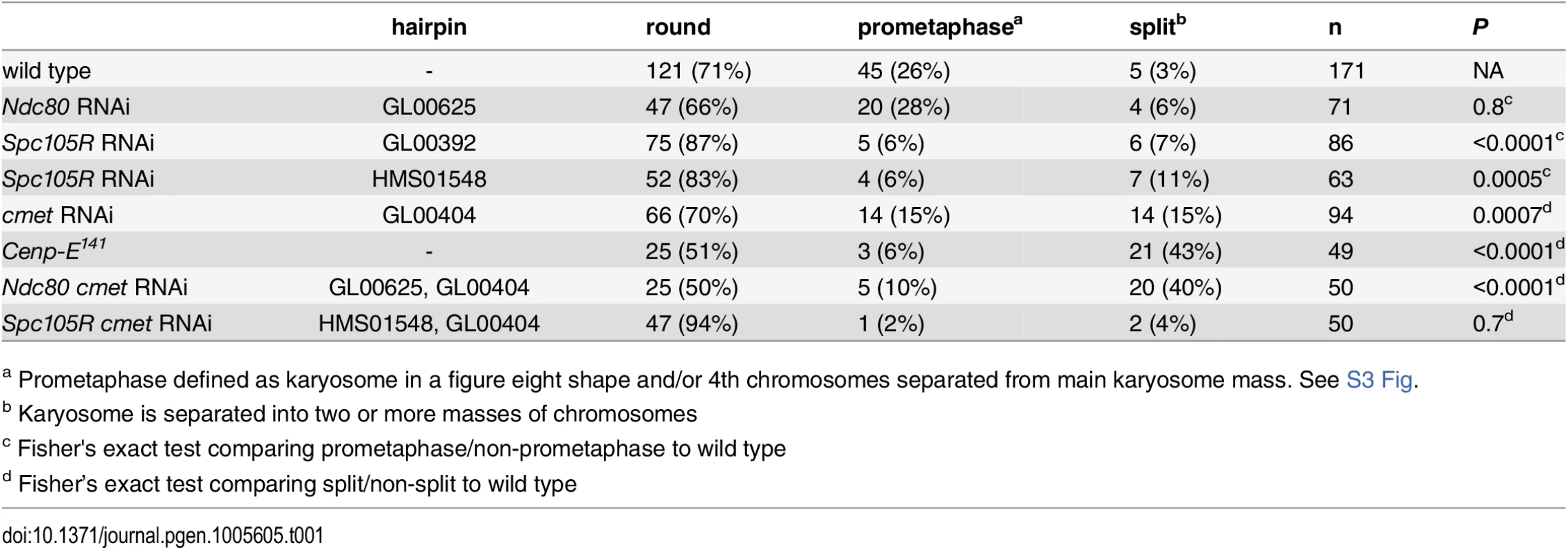
a Prometaphase defined as karyosome in a figure eight shape and/or 4th chromosomes separated from main karyosome mass. See S3 Fig. Chromosome co-orientation at meiosis I depends on SPC105R
Karyosome morphology does not reveal information about individual chromosomes. Therefore, to gain a more direct picture of chromosome behavior in the absence of kinetochore proteins, we examined the position of all centromeres using immunolocalization of CENP-C (Fig 3A). Drosophila have four pairs of homologous chromosomes. Because each homologous chromosome is formed from four chromatids, 16 centromeres are present at meiosis I. During meiosis I, however, sister centromeres are fused to promote their co-orientation toward one pole. In agreement with this, we found an average of 7.0 CENP-C foci were visible per wild-type oocyte (Fig 3C). The deviation from the expected value of eight is due to an inability to resolve centromeres of different chromosomes that are fortuitously close together. In Spc105R-depleted oocytes, the average CENP-C foci number was significantly elevated to 11.1 (P = <0.0001; Fig 3C), suggesting a loss of co-orientation. This difference is in contrast to Ndc80-depleted oocytes that had an average of 7.7 CENP-C foci, which does not differ significantly from wild type (P = 0.13; Fig 3C). One possibility is that kinetochore-microtubule attachments are required for co-orientation. An alternative, however, is that SPC105R is required for the kinetochore localization of proteins that do not depend on NDC80 [36]. In yeast, the monopolin complex promotes co-orientation [37], and MEIKIN provides this function in vertebrates [38]. Perhaps SPC105R is required for the kinetochore localization of the as-yet-unidentified invertebrate functional equivalent of monopolin/MEIKIN.
Although little is known about the molecular mechanism of co-orientation in metazoan oocytes, sister chromatid cohesion has been shown to be involved [22]. To determine whether loss of cohesion results in sister centromere separation in Drosophila oocytes, we examined ord mutants (Fig 3A and 3C). ORD is required for sister chromatid cohesion during meiosis [39]. In ord mutants, we observed an average of 10.8 CENP-C foci, which is not significantly different from Spc105R-depleted oocytes (P = 0.76; Fig 3C). We also examined sister centromere separation in mei-S332 mutants, which mutate the Drosophila homolog of Shugoshin [40]. With an average of 7.5 CENP-C foci, this is not significantly different than wild type (P = 0.47; Fig 3C), but is significantly different from both Spc105R depletion (P = 0.0005) and ord mutants (P = 0.01), consistent with the conclusion that MEI-S332 function is not required until anaphase I [22]. These results suggest that SPC105R is required for co-orientation in oocytes, perhaps through the protection of sister chromatid cohesion during meiosis I.
Lateral and end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments are required for orientation towards a spindle pole
While only Spc105R-depleted oocytes had a co-orientation defect, immunolocalization of CENP-C revealed a defect present in both Ndc80 - and Spc105R-depleted oocytes. In wild-type Drosophila oocytes, centromere foci are clustered into two groups at the edge of the karyosome closest to each spindle pole (Fig 3A). This represents when microtubule connections to the spindle poles pull homologous chromosomes in opposite directions. In Ndc80 - and Spc105R-depleted oocytes, the centromere foci were not clustered into two groups oriented toward each spindle pole, but rather were scattered around the karyosome (Fig 3A). This is a failure of the centromeres to orient towards a spindle pole.
To quantify this phenotype, we measured the angle of displacement of each CENP-C focus with respect to the axis of the half spindle, defined by the line between a point at the spindle pole and the center point of the karyosome (Fig 3D). Oriented centromeres have measurements as low as 0 degrees, while centromeres that fail to orient and are scattered around the karyosome result in angle measurements up to 90 degrees. In wild type, CENP-C foci angles had a median value of 17 degrees (Fig 3D). CENP-C angles in Ndc80 - or Spc105R-depleted oocytes were skewed significantly higher with median values of 28 degrees and 48 degrees, respectively (P = <0.0001 for each; Fig 3D), demonstrating that kinetochore-microtubule attachments are required for chromosomes to orient towards a spindle pole. However, there was also a significant difference in CENP-C foci angles between Ndc80 - and Spc105R-depleted oocytes (P = <0.0001). This is reflected in the data by the greater number of oocytes with angles close to 90 degrees in Spc105R-depleted oocytes. These data show that loss of NDC80 disturbs chromosome orientation, although not as dramatically as loss of SPC105R. To explain this difference, we suggest that lateral kinetochore-microtubule attachments are sufficient for some partial or unstable chromosome orientation, while end-on attachments cement orientation towards a spindle pole.
Bi-orientation of homologous centromeres depends on lateral kinetochore-microtubule attachments
Karyosome morphology and immunolocalization of CENP-C in Ndc80 - or Spc105R-depleted oocytes suggested kinetochore-microtubule attachments allowed chromosomes to orient towards a spindle pole. To test whether each chromosome associated randomly with a pole, or if homologs oriented towards opposite poles (“bi-orientation”), we used FISH to examine specific chromosomes. Chromosome bi-orientation at meiosis I depends on the establishment of connections between homologous chromosome pairs and opposite spindle poles. When this occurs, tension across the homologous chromosome pair generates an increase in the inter-homolog centromere distance. We used FISH probes to the repetitive sequences present at the centromeres of the second and third chromosomes to determine directly whether the separation of homologous centromeres away from each other depends on kinetochores and their end-on attachment to microtubules in oocytes (Fig 4A). In wild type, we observed an average distance between homologous centromeres of 3.0 μm (Fig 4B). In Ndc80-depleted oocytes, the average distance between homologous centromeres was not significantly reduced (2.7 μm, P = 0.4; Fig 4B), suggesting that end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments are not required for homologous centromeres to move away from each other. In contrast, in Spc105R-depleted oocytes, the average distance was significantly reduced to 1.8 μm (P = 0.0007; Fig 4B). These results suggest that lateral kinetochore-microtubule attachments are sufficient for homologous centromeres to orient towards a spindle pole and separate from each other in what may be the first step in the bi-orientation process.
Fig. 4. Homologous chromosome bi-orientation depends on kinetochores and CENP-E in oocytes. 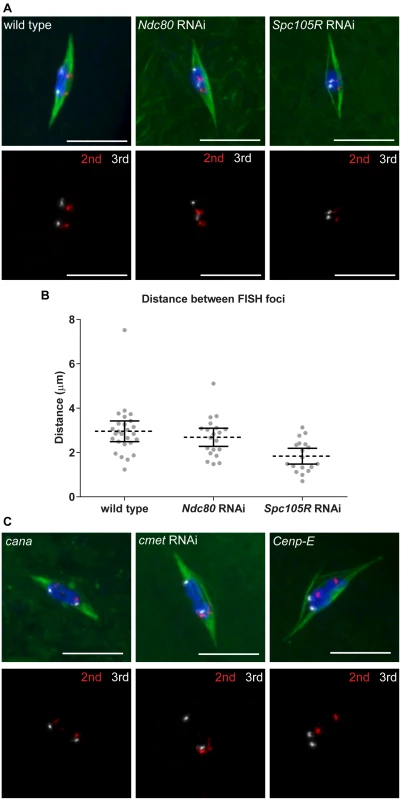
Confocal images of FISH probes marking the 2nd (red) and 3rd (white) chromosome centromeres. DNA is in blue and tubulin is in green in merged images. Only FISH probes are shown in the panel below each merged image. Scale bars represent 10 μm. (A) Oocytes from wild type and after knockdown of Ndc80 or Spc105R. (B) Dot plot of the distance between pairs of FISH foci in wild-type oocytes and after knockdown of Ndc80 or Spc105R. Horizontal dotted lines show the mean, error bars show 95% confidence intervals. (C) Oocytes from cana/Df, after knockdown of cmet, and Cenp-E germline clones. The data is summarized in Table 2. CENP-E is required for chromosome alignment and bi-orientation
Because CENP-E is a kinesin motor involved in the lateral movement of chromosomes along microtubules, we hypothesized that CENP-E could mediate some of the kinetochore-dependent movements that depend on SPC105R but not NDC80. Drosophila melanogaster is unusual because it has two Cenp-E genes, cana and cmet, arranged in inverse orientation on the chromosome (S4 Fig). The proteins encoded by cana and cmet show considerable sequence similarity throughout their motor and stalk domains (42% identical overall), and only 6 out of the 12 sequenced Drosophila species have two copies of Cenp-E, suggesting a recent duplication event.
It was previously shown that cmet mutants are inviable [41]. We generated cana mutants and cana cmet double mutants, which we refer to as Cenp-E mutants (see Materials and Methods for details). Like cmet mutants, Cenp-E mutants are inviable; however, cana mutants are viable and fertile. To determine the function of CENP-E in chromosome movement in oocytes, we focused on cana hemizygous mutants, depletion of cmet by RNAi (GL00404 from TRiP), and Cenp-E germline clones generated using the dominant female sterile technique [42]. In oocytes, expression of the GL00404 construct knocked down cmet gene expression by 75%.
In cana mutant, cmet-depleted, or Cenp-E mutant oocytes, bipolar spindles formed (Fig 5). However, in cmet-depleted or Cenp-E mutant oocytes, the karyosome frequently split into multiple masses (Fig 5 and Table 1 and S3 Table). This karyosome defect was more frequent in Cenp-E mutant oocytes than in cmet-depleted oocytes (43% vs 15%, P = 0.001), demonstrating that both CENP-E homologs are required for proper karyosome organization. CANA and CMET are partially redundant because CMET is necessary for karyosome organization even when there is a functional copy of CANA. These results are the first evidence that the second Drosophila CENP-E homolog CANA is functional. Additionally, these results suggest that, although traditional chromosome congression does not occur in Drosophila oocytes, CENP-E is required to prevent chromosomes from becoming un-aligned and separated from the main karyosome mass.
Fig. 5. Loss of CENP-E disrupts chromosome alignment in oocytes. 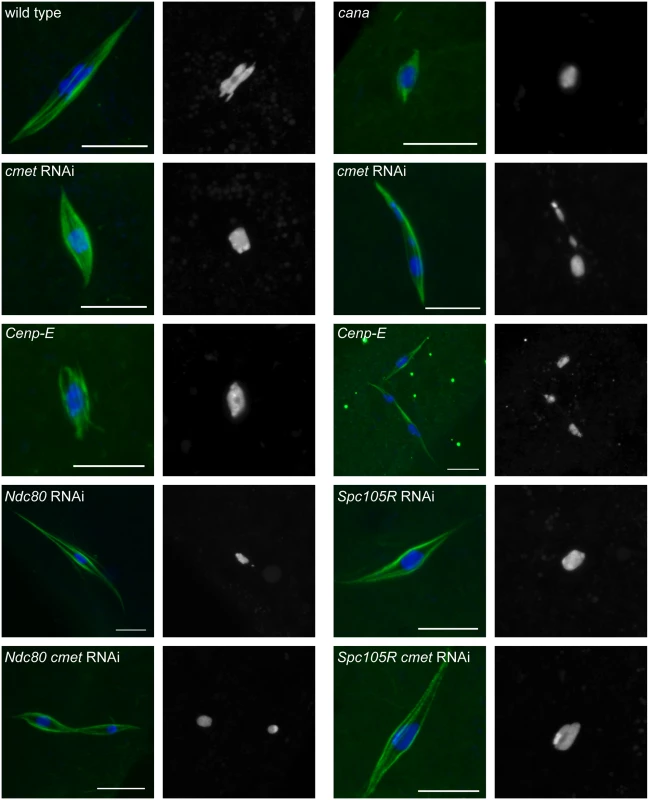
Confocal images of karyosome and spindle organization in oocytes from wild type, cana/Df, after knockdown of cmet, Cenp-E germline clones, and after knockdown of Ndc80, Spc105R (HMS01548), Ndc80 and cmet, or Spc105R (HMS01548) and cmet. DNA is in blue and tubulin is in green in merged images. Single channel images show DNA in white. Scale bars represent 10 μm. To further explore the role of CENP-E in chromosome movements in oocytes, we examined the orientation of centromeres using FISH. Because cana mutants are fertile and do not exhibit chromosome segregation errors, not surprisingly we found no defect in centromere orientation (Fig 4C and Table 2). In contrast, homologous centromeres were frequently mis-oriented in both cmet-depleted and Cenp-E mutant oocytes (Fig 4C and Table 2). The frequency of mis-orientation was similar between cmet-depleted and Cenp-E mutant oocytes (29% vs 24%, P = 0.7), suggesting that CMET is the primary CENP-E homolog functioning in bi-orientation. Importantly, the cmet mis-orientation phenotype is distinct from either Ndc80 or Spc105R depletion in that centromeres are not scattered around the karyosome: they orient, but often towards the wrong spindle pole (Fig 4C). This suggests that stable end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments are not eliminated in the absence of CENP-E, but that CENP-E is required for establishing the correct kinetochore-microtubule attachments to direct homologs toward opposite spindle poles.
Tab. 2. Centromere bi-orientation in the absence of CANA and CMET. 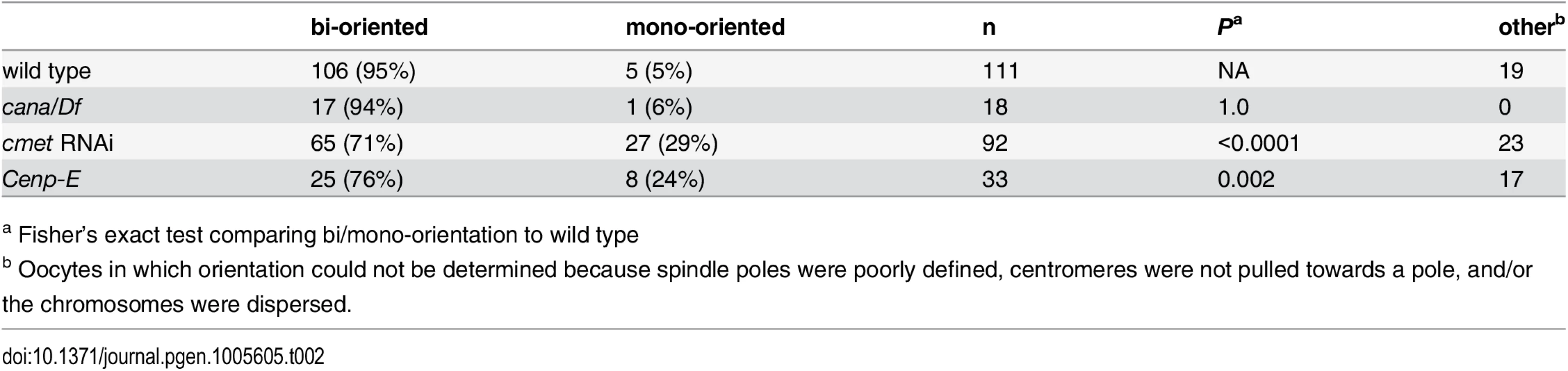
a Fisher’s exact test comparing bi/mono-orientation to wild type To determine more directly the nature of microtubule attachments in the absence of CENP-E, we examined the localization of ROD. ROD accumulates at kinetochores until the formation of end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments [34]. We found that ROD was present at kinetochores and streaming along microtubules in cmet-depleted oocytes, similar to wild type (S1 Fig). This demonstrates that CENP-E is not required to form end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments. However, one known role of CENP-E is in the regulation of end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachment stability [43, 44]. Consistent with this, upon closer investigation using live imaging, we observed an increased frequency of ROD at the kinetochores in cmet-depleted oocytes (S2 Fig). Kinetochores that are not streaming ROD should undergo re-orientation to achieve stable bi-orientation. This can be observed in live imaging of wild-type oocytes because kinetochores with accumulated ROD change position within the karyosome (S5 Fig). The kinetochores that accumulated ROD in the absence of CMET, however, often failed to change position within the karyosome (S5 Fig), suggesting that in the absence of CMET, the ability to re-orient following a failure to bi-orient is defective.
CENP-E prevents chromosome movement via lateral kinetochore-microtubule attachments
Because the karyosome is maintained in the absence of the kinetochore components NDC80 or SPC105R (Table 1), active congression via kinetochore-microtubule attachments may not be required for chromosome organization in Drosophila oocytes. On the other hand, the karyosome splits apart in the absence of CENP-E, resulting in the un-alignment of chromosomes (Table 1). Because CENP-E is typically thought to move chromosomes via lateral kinetochore-microtubule attachments, we wanted to test whether the splitting apart of the karyosome in the absence of CENP-E depends on kinetochore-microtubule attachments.
We examined karyosome configurations in two types of oocytes: those depleted of both cmet and Ndc80 or both cmet and Spc105R (Fig 5 and Table 1). We found that loss of CMET in the absence of SPC105R did not result in karyosome splitting (Table 1). This suggests that the movement of chromosomes that results in splitting of the karyosome depends on kinetochore-microtubule attachments. On the other hand, the karyosome split apart in Ndc80 cmet double-depleted oocytes (Table 1), suggesting that lateral kinetochore-microtubule attachments are sufficient for the splitting of the karyosome, and that CMET opposes this movement. Strikingly, the karyosome defect was enhanced in Ndc80 cmet double-depleted oocytes compared to cmet-depleted oocytes (40% vs. 15%, P = 0.004). In fact, Ndc80 cmet double-depleted oocytes are not significantly different from Cenp-E oocytes (40% vs. 43%, P = 0.8). One possibility is that NDC80 is required for CANA function such that loss of NDC80 and CMET together effectively recapitulates the complete loss of CENP-E. Alternatively, NDC80 (via end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments) and CMET (via lateral kinetochore-microtubule attachments) may work together to oppose the forces driving chromosome un-alignment. In any case, these results demonstrate that CENP-E prevents chromosome un-alignment via lateral-kinetochore microtubule attachments.
Oocyte spindle stability depends on kinetochores and the central spindle
Our results thus far show that kinetochores participate in chromosome alignment, bi-orientation, and co-orientation in Drosophila oocytes. Since chromatin-mediated pathways direct spindle assembly in oocytes [45], we investigated the contribution of the kinetochores to spindle assembly and stability at prometaphase I and metaphase I. Metaphase I-arrested spindles tend to be shorter than prometaphase spindles with less prominent central spindles (Fig 6A and 6B). In fact, we observed that spindles were weak, that is very small, faint, or lacking microtubules entirely (indicated below as “weak/absent”), more frequently in metaphase-enriched oocyte samples (33%, P = <0.0001) (see Materials and Methods for details of how metaphase - or prometaphase-enriched samples are collected) than in prometaphase-enriched oocyte samples (11%) (Fig 6D). This difference suggests that in Drosophila oocytes, spindle assembly proceeds via an elongation phase during which spindles are robust (prometaphase), followed by a contraction phase in which microtubule density decreases (metaphase).
Fig. 6. Prometaphase spindle stability depends on both kinetochore and central spindle components in oocytes. 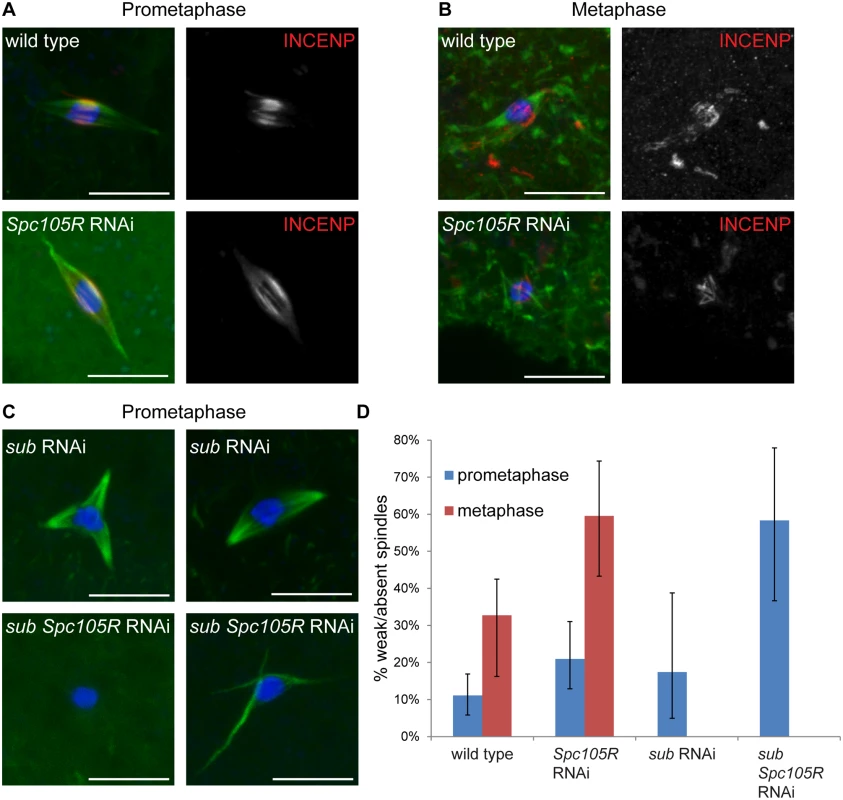
In all images, DNA is in blue, tubulin is in green, and the scale bars represent 10 μm. (A,B) Confocal images of wild-type oocytes and after Spc105R knockdown from prometaphase-enriched (A) and metaphase-enriched (B) collections. The CPC component INCENP is in red in merged images, white in single channel images. (C) Confocal images of sub-depleted and sub Spc105R double-depleted oocytes. For sub-depleted oocytes, a tripolar (left) and bipolar (right) spindle are shown. Monopolar spindles were also observed [9, 47]. In all sub-depleted oocytes, the prominent central spindle is missing. For sub Spc105R double-depleted oocytes, the absence of a spindle (left) and a spindle with thin and disorganized microtubules (right) are shown. (D) Graph showing the percentage of weak/absent spindles during prometaphase in wild-type oocytes (n = 171) and after Spc105R (n = 86), sub (n = 23), or sub Spc105R (n = 24) depletion, and metaphase in wild-type oocytes (n = 110) and after Spc105R depletion (n = 42). The frequency of weak/absent spindles at metaphase in sub- and sub Spc105R-depleted oocytes was not determined. Error bars show 95% confidence intervals. We found that Spc105R-depleted oocytes form bipolar spindles in prometaphase-enriched oocyte collections. In prometaphase-enriched collections, weak/absent spindles were increased in Spc105R-depleted oocytes compared to wild type (21%, P = 0.04; Fig 6D). This difference suggests that the prometaphase spindle is destabilized in the absence of kinetochore components. Weak/absent spindles were significantly increased compared to wild type in metaphase-enriched collections of Spc105R-depleted oocytes (60%, P = 0.003; Fig 6B and 6D). These results suggest that kinetochore microtubules contribute early to the organization of the prometaphase spindle, and then form the majority of microtubules in the metaphase-arrested spindle.
These results make predictions about the microtubules that assemble in Spc105R-depleted oocytes. First, although these spindles are bipolar, they should lack kinetochore microtubules. Indeed, Spc105R-depleted oocyte spindles appear hollow, as if they are missing the microtubules that, in wild type, end at the chromosomes (Figs 1, 3A, 4A, 5 and 6A). Ndc80-depleted oocytes also form hollow spindles (Figs 1, 3A, 4A and 5); therefore, the stable kinetochore microtubules are most likely only those that form end-on attachments. The microtubules in these hollow spindles could depend on the prominent central spindle that forms in Drosophila oocytes and is required for bipolarity and chromosome bi-orientation [10, 46]. To directly determine whether the central spindle forms properly in the absence of kinetochores, we examined localization of INCENP, a member of the CPC, in Spc105R-depleted oocytes. We found that INCENP localized normally in the hollow spindles from prometaphase-enriched collections (Fig 6A). Indeed, most spindles in Spc105R-depleted prometaphase oocytes are bipolar, suggesting the central spindle is sufficient to organize the spindle poles. However, the central spindle was disorganized in metaphase-enriched Spc105R-depleted oocytes (Fig 6B), indicating that kinetochores contribute to the stability of the central spindle at metaphase.
If all microtubules present in Spc105R-depleted oocytes are associated with the central spindle, then the meiotic spindle is likely composed of two types of microtubules: kinetochore-dependent and central spindle-dependent. To test this hypothesis, we knocked down both subito, which is required for the formation of the central spindle [46], and Spc105R in oocytes. We found that sub-depleted oocytes had polarity defects similar to sub null mutants [46, 47] (Fig 6C), but this depletion did not significantly increase weak/absent spindles in prometaphase-enriched collections (17%, P = 0.5; Fig 6D). In contrast, sub Spc105R double depletion resulted in a significant increase in weak/absent spindles in prometaphase-enriched collections (58%, P = <0.0001), comparable to the spindle destabilization observed in metaphase-enriched collections from Spc105R-depleted oocytes (Fig 6C and 6D). These results suggest that both the organization and the stability of the prometaphase oocyte spindle depend on kinetochores and the central spindle. The metaphase-arrested spindle, on the other hand, depends mostly on kinetochore microtubules.
Kinetochore assembly depends on the CPC
The CPC is required for the assembly of all microtubules around the karyosome in Drosophila oocytes (Fig 1) [10]. The CPC is also required for localization of central spindle components such as SUB [10]. Because we have shown that kinetochores and the central spindle coordinately contribute to spindle stability, we wanted to determine whether kinetochore assembly also depends on the CPC. We found that the KMN complex did not localize after depletion of aurB, which encodes the CPC component Aurora B kinase (Fig 1). Interestingly, loss of the CPC in Drosophila oocytes results in a complete loss of microtubules around the karyosome (Fig 1) [10]. This phenotype is more severe than the double knockdown of Spc105R and sub in which ~40% of oocytes showed significant spindle microtubules, albeit thin and disorganized (Fig 6C and 6D). These data demonstrate that while the CPC controls oocyte spindle stability through its regulation of kinetochore assembly and SUB localization, the CPC also regulates additional spindle assembly factors that promote the initiation of spindle assembly.
Discussion
In acentrosomal oocytes, spindle assembly depends on the chromosomes. How the chromosomes can organize a bipolar spindle that then feeds back and drives processes like bi-orientation of homologous centromeres has been unclear. Previously, we demonstrated that the central spindle is required for homolog bi-orientation [10]. Here, we have found that several types of functional chromosome-microtubule interactions exist in oocytes, and that each type participates in unique aspects of chromosome orientation and spindle assembly. We present a model for chromosome-based spindle assembly and chromosome movements in oocytes that highlights the multiple and unappreciated roles played by kinetochore proteins such as SPC105R and NDC80, with implications for how homologous chromosomes bi-orient during meiosis I (Fig 7).
Fig. 7. Model for acentrosomal spindle assembly and chromosome orientation. 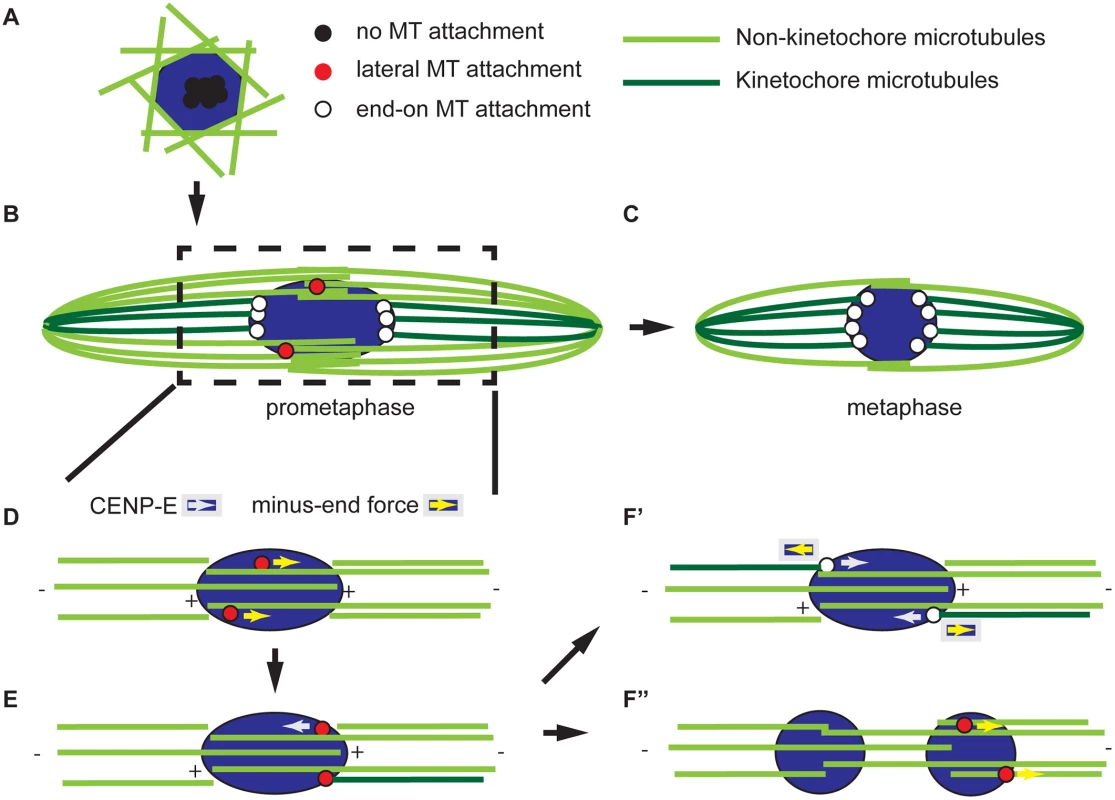
The spindle is composed of microtubules that make end-on attachments to kinetochores (dark green) and those that do not, such as those with plus ends that overlap in the central spindle (light green). (A) Meiotic spindle assembly begins with the accumulation of microtubules around the DNA and the centromeres clustered. These centromeres (shown in black) are not attached to microtubules. (B) Prometaphase is characterized by the presence of kinetochores (red) interacting laterally with microtubules. The process of building a bipolar spindle between panels A and B involves organizing a central spindle and pole-focusing and has been described in detail elsewhere [82, 83]. (C) At metaphase, all kinetochores have end-on attachments (white) and little interaction with the central spindle. Metaphase is also characterized by less reliance on the central spindle for stability. (D-F) A model for bi-orientation showing an enlargement of the spindle around the chromosomes. Kinetochores can move laterally along microtubules in a CENP-E-dependent plus-end direction or a minus-end direction by an unknown force. (D) In this example, two homologous centromeres are moving laterally in the minus-end direction along central spindle microtubules of the same polarity; therefore, they move towards the same pole. (E) This error is detected by an unknown mechanism, leading at least one of the kinetochores to fail to make an end-on attachment and move towards the other pole in a CENP-E dependent manner. (F’) If the kinetochore makes an end-on attachment following this movement, the homologs are bi-oriented. The kinetochores maintain their position by balancing the minus-end force with either the chiasmata or CENP-E. In the absence of CENP-E, errors cannot be corrected, leading to mono-orientation as in (E). (F”) Alternatively, the minus-end force can continue to move centromeres towards the poles, either through a lateral or end-on interaction, resulting in a splitting of the karyosome. Lateral and end-on microtubule attachments are required for centromere movement and bi-orientation
While the spindle is assembling and becoming organized, our evidence suggests that the chromosomes undergo a series of movements that ultimately result in the bi-orientation of homologous chromosomes. We found that the separation of clustered centromeres is CPC-dependent [10], but not kinetochore-dependent (Figs 3A and 7A). One possibility is that the CPC-dependent interaction of microtubules with non-kinetochore chromatin drives centromere separation. An alternative is that CPC activity may result in a release of the factors that hold centromeres together in a cluster prior to NEB. A candidate for this factor is condensin, a known target of the CPC, that has been shown to promote the “unpairing” of chromosomes in the Drosophila germline [48].
Following separation of clustered centromeres, each pair of homologous centromeres bi-orients by separating from each other towards opposite poles. How bi-orientation is established in acentrosomal oocytes is poorly understood. Previous studies in C. elegans and mouse oocytes have suggested a combination of kinetochore-dependent and kinetochore-independent (e.g. involving chromokinesins and chromosome arms) microtubule interactions drive chromosome alignment and segregation [23, 49]. We have found that kinetochores play multiple roles, and the process of chromosome bi-orientation can be broken down into a series of chromosome movements that depend mostly on the kinetochores. First, the centromeres make an attempt at bi-orientation (Fig 7D). In Drosophila oocytes, this results in the directed poleward movement of centromeres toward the edge of the karyosome and is accompanied by a stretching of the karyosome. Lateral kinetochore-microtubule attachments mediated by SPC105R are sufficient for this initial attempt at bi-orientation. End-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments via NDC80, however, are essential to maintain the bi-orientation of centromeres. Maintenance of centromere bi-orientation is associated with the stable positioning of the centromeres at the edges facing the poles (Fig 7F′).
The lateral-based chromosome movements required for chromosome orientation are probably mediated by the meiotic central spindle, which we previously showed was essential for chromosome segregation [9, 47]. In addition, recent reports in both mitotic and meiotic cells suggest that the initial orientation of chromosomes depends on the formation of a “prometaphase belt” that likely brings centromeres into the vicinity of the central spindle [7]. Therefore, we propose that the initial attempt at bi-orientation occurs during the period when both kinetochores and the central spindle are required for spindle stability (Fig 7B). Then, as the oocyte progresses toward metaphase, and the central spindle decreases in importance, this reflects a trend toward the formation of stable end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments that, in turn, stabilize the bipolar spindle (Fig 7C). This model is also corroborated by evidence from mouse oocytes that stable end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments form after a prolonged prometaphase [6].
CENP-E is required for bi-orientation and maintaining karyosome integrity
Our data demonstrate that some chromosome movements, critical for bi-orientation, are dependent on lateral kinetochore-microtubule attachments. The kinetochore-associated kinesin motor CENP-E is thought to be responsible for chromosome movement along lateral kinetochore-microtubule attachments, resulting in chromosome alignment on the metaphase plate [20]. However, because Drosophila meiotic chromosomes are compacted into a karyosome prior to NEB, they do not need to migrate in a plus-end-directed manner to achieve congression and alignment. Instead, centromeres must move toward the poles, perhaps in a minus-end directed manner, to achieve bi-orientation (Fig 7D). Interestingly, we found that CENP-E opposes this minus-end directed movement (Fig 7E) because in the absence of CENP-E, the karyosome split via lateral kinetochore-microtubule attachments (Figs 5 and 7F″). It is not yet clear what mediates the minus-end-directed movement, but the motors Dynein and NCD (the Drosophila kinesin-14 homolog) or microtubule flux [50, 51] are prime candidates.
We also observed that CMET is required for the correct bi-orientation of homologous chromosomes (Fig 4C and Table 2). The function proposed in opposing minus-end directed movement may be required for making the correct attachments. As the centromere moves to the edge of the karyosome, CENP-E may not only prevent its separation from the karyosome, but could also force it back towards the opposite pole in cases where the homologs are not bi-oriented (Fig 7E). A similar idea has been proposed for CENP-E in mouse oocytes [52]. Alternatively, CENP-E has a second function in tracking microtubule plus-ends and regulating kinetochore-microtubule attachments [43, 44, 53]. In fact, we found that end-on kinetochore-microtubule stability is affected in the absence of CENP-E (S2 and S5 Figs). Regulating the stability of microtubule plus-end attachments with kinetochores is critical for establishing correct bi-orientation of homologs [54]. Therefore, both functions of CENP-E could contribute to the correct bi-orientation of centromeres in Drosophila oocytes.
Co-orientation of sister centromeres
Loss of SPC105R has a more severe phenotype than loss of either NDC80 or CENP-E, consistent with a role as a scaffold [36]. It recruits additional microtubule interacting proteins like NDC80 and CENP-E and also recruits checkpoint proteins such as ROD [36]. In analyzing oocytes lacking SPC105R, we discovered another class of factors it may recruit: proteins required for co-orientation of sister centromeres during meiosis I. Co-orientation is a process that fuses the core centromeres and is important to ensure that two sister kinetochores attach to microtubules that are attached to the same spindle pole [22]. Co-orientation could involve a direct linkage between sister kinetochores, as may be the case with budding yeast Monopolin [55] or in maize, where a MIS12-NDC80 linkage may bridge sister kinetochores at meiosis I [56]. In contrast, in fission yeast meiosis I, cohesins are required for co-orientation. Cohesion is stably maintained at the core centromeres during meiosis I but not mitosis, and this depends on the meiosis-specific proteins Moa1 and Rec8 [57]. There is also evidence that Rec8 is required for co-orientation in Arabidopsis [58] and we found that loss of ORD, which is required for meiotic cohesion, also results in a loss of centromere co-orientation (Fig 3A and 3C). Further studies, however, are necessary to determine if cohesins are required for co-orientation in Drosophila. Indeed, the proteins and mechanism that mediate this process in animals has not been known. Recently, however, the vertebrate protein MEIKIN has been found to provide a similar function to Moa1 [38]. Interestingly, both Moa1 and MEIKIN depend on interaction with CENP-C, but do not show sequence homology. Thus, Drosophila may have a Moa1/MEIKIN ortholog that has not yet been identified. In the future, it will be important to identify the proteins recruited by SPC105R and their targets in maintaining centromere co-orientation and how these interact with proteins recruited by CENP-C. The mechanism may involve the known activity of SPC105R in recruiting PP1, because PP1 has been shown to have a role in maintaining cohesion in meiosis I of C. elegans [59].
Integrating homolog bi-orientation with spindle assembly and meiotic progression
Our model for spindle assembly and chromosome orientation raises several important questions for future consideration. The CPC is required for spindle assembly in Drosophila oocytes [10] and our results highlight the importance of two CPC targets in homolog bi-orientation. One target is central spindle proteins, possibly through the CPC-dependent recruitment of spindle organization factors such as SUB [10]. The CPC is also required for kinetochore assembly (Fig 1), similar to what has been shown in yeast, human cells, and Xenopus [60] and consistent with the finding in human cells that Aurora B promotes recruitment of the KMN complex to CENP-C [61, 62]. It will be important to identify targets of the CPC that drive the initiation of spindle assembly, centromere separation, and bi-orientation. In addition, while we have found that the CPC is required for kinetochore assembly, it is not known if the CPC promotes error correction by destabilizing kinetochore-microtubule attachments [63–65]. The CPC may not promote kinetochore-microtubule detachment during meiosis because of the different spatial arrangement of sister centromeres during meiosis I. Indeed, it is not known what is responsible for correcting incorrect attachments at meiosis I or how they are differentiated from correct attachments.
In prometaphase, the central spindle and kinetochores contribute to spindle stability. Our data suggests that the kinetochores increase in importance as the oocyte progresses to metaphase (Fig 7C), perhaps as a result of the stabilization of end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments as homologous chromosomes become bi-oriented. However, lateral kinetochore-microtubule interactions demonstrated some resistance to colchicine and allow bivalents to stretch in mouse oocytes [65]. Thus, further studies are necessary to determine if lateral kinetochore-microtubule interactions also confer some stability. Our model also proposes that the transition from prometaphase to metaphase involves a switch from dynamic lateral kinetochore-microtubule interactions to stable end-on kinetochore-microtubule attachments. This transition involves the loss of central spindle microtubules, which occurs regardless of microtubule attachment status. Further studies will be necessary to determine if the prometaphase-to-metaphase transition is developmentally regulated rather than being controlled by the spindle assembly checkpoint. As proposed in mouse oocytes [65, 66], this may contribute to the propensity for chromosome segregation errors in acentrosomal oocytes by closing the window of opportunity for error correction after key developmental milestones have been passed. Finally, one of the most poorly understood features of meiosis is co-orientation of sister centromeres at meiosis I [22, 55]. What SPC105R interacts with to mediate co-orientation will provide the first insights into the mechanism and regulation of this process in Drosophila.
Materials and Methods
Fly crosses and RNAi
Flies were crossed and maintained on standard media at 25°C. All loci not described in the text are described in FlyBase (flybase.org) [67]. Fly stocks from the Transgenic RNAi Project (TRiP, flyrnai.org) were obtained either directly or from the Bloomington Stock Center. The cmetΔ allele was a gift from Byron Williams and Michael Goldberg. The ord mutant was ord5/ord10 and the mei-S332 mutant was mei-S3321/Df(2R)BSC597. The GFP-tagged ROD transgenic line was a gift from Roger Karess. RNAi constructs generated by the Transgenic RNAi Project (TRiP) [68] were: aurB (previously known as ial, GL00202) [10], Ndc80 (GL00625), Spc105R (GL00392 and HMS01548), and cmet (GL00404). The sub RNAi construct (GL00583) was moved to a 2nd chromosome location through standard P element transposition crosses.
To deplete oocyte proteins by RNAi, the expression of a short hairpin RNA is under control of the UAS/GAL4 system [69]. To confine the expression to oocytes, we used matα4-GAL-VP16, which is expressed throughout oogenesis after the initiation of meiosis [10, 70]. The long duration of meiotic prophase allows knockdown of gene expression within one cell cycle, thereby eliminating the possibility of confounding effects from going through rounds of aberrant cell division with decreasing amounts of protein. Some cmet RNAi experiments used nanos-GAL4:VP16 [71]. When nanos-GAL4:VP16 was used to express short hairpins to aurB, Ndc80, or Spc105R, no oocytes were produced, probably due to the failure of the germline mitotic divisions. In all cases, the females expressing these short hairpins were sterile.
To quantify knockdown of gene expression, late-stage oocytes were collected from females carrying both driver and RNAi construct by mass disruption of abdomens in a blender filled with phospho-buffered saline (PBS). Oocytes were filtered through meshes to remove large body parts and allowed to settle quickly in solution to remove smaller egg chambers. For reverse transcriptase quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR), total RNA was extracted from late-stage oocytes using TRIzol Reagent (Life Technologies). RNA was converted to cDNA using the High Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit (Applied Biosystems). The qPCR was performed in a StepOnePlus (Life Technologies) real-time PCR system using TaqMan Gene Expression Assays (Life Technologies, Dm01843531_g1 for cmet, Dm01838612_g1 for Ndc80, Dm01792082_g1 for Spc105R, and Dm02134593_g1 for Rpll140 as control).
Generation of mutations in two Drosophila Cenp-E genes
Previous work has shown that cmetΔ mutations cause lethality [41], but no cana mutants have yet been reported. To generate mutations of either cana, cmet, or both genes, we screened for imprecise excision of a P element inserted between the cana and cmet genes (P{GawB}NP5235, S4 Fig). The insertion site is 217 bp away from cana and 832 bp away from cmet. Excisions were tested for viability by crossing to Df(2L)BSC236. DNA was prepared from adult flies for viable excisions [72] and screened for deletion by PCR and DNA sequencing. Lethal excisions were crossed to cmetΔ to check viability and to cana13 for PCR screening of cana deletion. For excisions that likely deleted both cana and cmet sequences, embryos homozygous for lethal excision chromosomes were selected over a GFP-tagged 2nd chromosome balancer [73] and DNA for PCR was prepared by the same method as adult flies.
Three cana mutants were isolated, but the results reported here focus on cana13 in which most of the motor domain was deleted (S4 Fig). Previous studies have shown that the motor domain of CENP-E is required for chromosome movement during mitosis [74], suggesting that cana13 is a null allele. Interestingly, however, there is an alternative transcript predicted for cana, encoding a protein that does not contain the motor domain (S4 Fig). Therefore, if there is a non-motor function for cana, this may not be affected by cana13. Hemizygous cana mutants (cana13/Df(2L)BSC236) are viable and fertile, and the percentage of X chromosome non-disjunction was similar to wild-type controls (0.1%, n = 2266). These results suggest that the motor domain of CANA does not play an essential role in mitosis or meiosis.
We also isolated three P element excisions that were lethal when heterozygous with cmetΔ, and PCR analysis also showed deletion of cana sequence, showing that both cana and cmet were deleted. For our studies, we focused on Df(2L)Cenp-E141, which will be referred to as Cenp-E141 (S4 Fig). This mutation deletes sequences encoding part of the CMET motor domain and the entire CANA motor domain, suggesting that it is null for CENP-E function. Although Cenp-E141 is lethal when heterozygous with either cmetΔ or Df(2L)BSC236, rare homozygotes can be found. These Cenp-E141 homozygotes, however, have developmental abnormalities, including no ovary development (in 100% of dissected the females, only rudimentary ovaries composed of predominantly somatic cells were present), consistent with the idea that CENP-E is important for cell division.
To generate oocytes lacking both Cenp-E genes, the Cenp-E141 allele was crossed onto a chromosome bearing an FLP recombination target (FRT) sequence inserted at 40A near the centromere on the left arm of chromosome 2. Females with this recombinant chromosome were crossed in vials to males with a matching FRT chromosome carrying the dominant female sterile mutation ovoD1 and a heat-shock-inducible FLP recombinase. After 3–4 days, the parents were transferred to new vials and progeny were heat shocked for one hour in a 37°C water bath. Female progeny carrying both FRT chromosomes and the FLPase were selected for examination as germline clones.
Immunofluorescence and microscopy
In a sample of late-stage Drosophila oocytes, three cell cycle stages are present: prophase, prometaphase, and metaphase. Oocytes in prophase are distinguished by the presence of the nuclear envelope. We skewed the proportion of prometaphase vs. metaphase oocytes in fixed samples by controlling the age of the females and speed of egg-laying [18]. Late-stage oocytes were collected either from two - to four-day-old females aged two days on yeast with males (“prometaphase”-enriched) or from three - to thirteen-day-old females aged three to five days on yeast without males (“metaphase”-enriched). Oocytes were prepared for immunofluorescence (5% formaldehyde/heptane fixation) and FISH (8% formaldehyde/100 mM cacodylate fixation) essentially as described [75]. For colchicine experiments, oocytes were incubated for 10 min in 0.12% ethanol (control) or 0.12% ethanol plus 150 μM colchicine prior to fixation.
Primary antibodies used for immunofluorescence were mouse anti-α-tubulin conjugated to FITC (1 : 50 dilution, clone DM1A, Sigma), rabbit anti-CENP-C (1 : 5000) [76], rat anti-INCENP (1 : 400) [77], chicken anti-NDC80 (1 : 500, Tom Maresca), rabbit anti-NSL1 (1 : 500) [29], rabbit anti-SPC105R (1 : 4000) [28], rabbit anti-GFP (1 : 400, Life Technologies), rat anti-α-tubulin (1 : 75, clone YOL 1/34, Millipore), and chicken anti-CID (1 : 250) [78]. Cy3-, Cy5-, AlexaFluor647 - (Jackson Immunoresearch), or AlexaFluor488 - (Molecular Probes) conjugated secondary antibodies were used. DNA was labeled with Hoechst 33342 (1 : 1000, Invitrogen) or TO-PRO-3 (1 : 1000, Invitrogen). FISH probes used were to the AACAC satellite (2nd chromosome) and dodeca satellite (3rd chromosome) as described [14, 75]. Samples were mounted in SlowFade Gold (Invitrogen). Images were collected on a Leica TCS SP5 or SP8 microscope with a 63x, 1.4 NA lens using LAS AF software. Images are shown as maximum projections.
Image analysis was performed with Imaris image analysis software (Bitplane). Spindles and CENP-C foci were identified and distances measured using the Distance Transformation Xtension. XYZ coordinates for CENP-C foci and spindle axes were determined using Imaris. This information was used to calculate angles with respect to the spindle axis using Microsoft Excel.
For live imaging, females were matured at 18°C for 4 to 7 days and oocytes from mature females were manually separated in halocarbon oil (Halocarbon). Oocyte stages 13 and 14 were determined by the morphology of the dorsal appendages [79]. pUASp-cmet shRNA (TRiP.GL00404)attP2/UASp-RCC1:mCherry nos-GAL4:VP16(MVD1) ROD:GFP and a wild-type chromosome over UASp-RCC1-mCherry nos-GAL4:VP16(MVD1) ROD:GFP were used for a cmet RNAi and a control. Imaging was carried out using an Axiovert (Zeiss) microscope attached to a spinning disc confocal head (Yokogawa) controlled by Volocity (PerkinElmer). Structures within oocytes were examined using the Plan Apochromat 63x, 1.4 NA lens (Zeiss). Immersol 518F oil (Zeiss) was applied. Z sections, separated by 0.5 μm, covering the entire fluorescent structure were taken every 1 min.
Statistical analysis
Statistical tests were performed using GraphPad Prism software. Prometaphase karyosome configurations and spindle stability were compared using Fisher’s exact test. Distances between CENP-C and the spindle, distances between homologous centromeres using FISH, and the number of CENP-C foci per oocyte were compared using a t test. CENP-C angles were compared using a Mann-Whitney test.
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. Szollosi D, Calarco P, Donahue RP. Absence of centrioles in the first and second meiotic spindles of mouse oocytes. J Cell Sci. 1972;11(2):521–41. 5076360
2. Theurkauf WE, Hawley RS. Meiotic spindle assembly in Drosophila females: behavior of nonexchange chromosomes and the effects of mutations in the nod kinesin-like protein. J Cell Biol. 1992;116(5):1167–80. 1740471
3. Albertson DG, Thomson JN. Segregation of holocentric chromosomes at meiosis in the nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans. Chromosome Res. 1993;1(1):15–26. 8143084
4. Deng M, Gao J, Suraneni P, Li R. Kinetochore-independent chromosome poleward movement during anaphase of meiosis II in mouse eggs. PLoS One. 2009;4(4):e5249. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005249 19365562
5. Dumont J, Oegema K, Desai A. A kinetochore-independent mechanism drives anaphase chromosome separation during acentrosomal meiosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12(9):894–901. doi: 10.1038/ncb2093 20729837
6. Brunet S, Maria AS, Guillaud P, Dujardin D, Kubiak JZ, Maro B. Kinetochore fibers are not involved in the formation of the first meiotic spindle in mouse oocytes, but control the exit from the first meiotic M phase. J Cell Biol. 1999;146(1):1–12. 10402455
7. Kitajima TS, Ohsugi M, Ellenberg J. Complete kinetochore tracking reveals error-prone homologous chromosome biorientation in mammalian oocytes. Cell. 2011;146(4):568–81. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.031 21854982
8. Wignall SM, Villeneuve AM. Lateral microtubule bundles promote chromosome alignment during acentrosomal oocyte meiosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(7):839–44. doi: 10.1038/ncb1891 19525937
9. Jang JK, Rahman T, McKim KS. The kinesinlike protein Subito contributes to central spindle assembly and organization of the meiotic spindle in Drosophila oocytes. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16(10):4684–94. 16055508
10. Radford SJ, Jang JK, McKim KS. The Chromosomal Passenger Complex is required for Meiotic Acentrosomal Spindle Assembly and Chromosome Bi-orientation. Genetics. 2012;192 : 417–29. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.143495 22865736
11. Sun SC, Zhang DX, Lee SE, Xu YN, Kim NH. Ndc80 regulates meiotic spindle organization, chromosome alignment, and cell cycle progression in mouse oocytes. Microsc Microanal. 2011;17(3):431–9. doi: 10.1017/S1431927611000274 21600073
12. Sun SC, Lee SE, Xu YN, Kim NH. Perturbation of Spc25 expression affects meiotic spindle organization, chromosome alignment and spindle assembly checkpoint in mouse oocytes. Cell Cycle. 2010;9(22):4552–9. 21084868
13. King RC. Ovarian Development in Drosophila melanogaster. New York: Academic Press Inc.; 1970.
14. Dernburg AF, Sedat JW, Hawley RS. Direct evidence of a role for heterochromatin in meiotic chromosome segregation. Cell. 1996;86(1):135–46. 8689681
15. Obeso D, Pezza RJ, Dawson D. Couples, pairs, and clusters: mechanisms and implications of centromere associations in meiosis. Chromosoma. 2014;123(1–2):43–55. doi: 10.1007/s00412-013-0439-4 24126501
16. Takeo S, Hawley RS. Rumors of its disassembly have been greatly exaggerated: the secret life of the synaptonemal complex at the centromeres. PLoS Genet. 2012;8(6):e1002807. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002807 22761598
17. Hughes SE, Gilliland WD, Cotitta JL, Takeo S, Collins KA, Hawley RS. Heterochromatic threads connect oscillating chromosomes during prometaphase I in Drosophila oocytes. PLoS Genet. 2009;5(1):e1000348. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000348 19165317
18. Gilliland WD, Hughes SF, Vietti DR, Hawley RS. Congression of achiasmate chromosomes to the metaphase plate in Drosophila melanogaster oocytes. Dev Biol. 2009;325(1):122–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.10.003 18977343
19. Cai S, O'Connell CB, Khodjakov A, Walczak CE. Chromosome congression in the absence of kinetochore fibres. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(7):832–8. 19525938. doi: 10.1038/ncb1890
20. Kapoor TM, Lampson MA, Hergert P, Cameron L, Cimini D, Salmon ED, et al. Chromosomes can congress to the metaphase plate before biorientation. Science. 2006;311(5759):388–91. 16424343
21. Bakhoum SF, Compton DA. Kinetochores and disease: keeping microtubule dynamics in check! Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012;24(1):64–70. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2011.11.012 22196931
22. Watanabe Y. Geometry and force behind kinetochore orientation: lessons from meiosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13(6):370–82. doi: 10.1038/nrm3349 22588367
23. Dumont J, Desai A. Acentrosomal spindle assembly and chromosome segregation during oocyte meiosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2012;22(5):241–9. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2012.02.007 22480579
24. Varma D, Salmon ED. The KMN protein network—chief conductors of the kinetochore orchestra. J Cell Sci. 2012;125(Pt 24):5927–36. doi: 10.1242/jcs.093724 23418356
25. DeLuca JG, Musacchio A. Structural organization of the kinetochore-microtubule interface. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012;24(1):48–56. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2011.11.003 22154944
26. Cheeseman IM, Chappie JS, Wilson-Kubalek EM, Desai A. The conserved KMN network constitutes the core microtubule-binding site of the kinetochore. Cell. 2006;127(5):983–97. 17129783
27. Schittenhelm RB, Heeger S, Althoff F, Walter A, Heidmann S, Mechtler K, et al. Spatial organization of a ubiquitous eukaryotic kinetochore protein network in Drosophila chromosomes. Chromosoma. 2007;116(4):385–402. 17333235
28. Schittenhelm RB, Chaleckis R, Lehner CF. Intrakinetochore localization and essential functional domains of Drosophila Spc105. Embo J. 2009;28(16):2374–86. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.188 19590494
29. Venkei Z, Przewloka MR, Glover DM. Drosophila Mis12 complex acts as a single functional unit essential for anaphase chromosome movement and a robust spindle assembly checkpoint. Genetics. 2011;187(1):131–40. doi: 10.1534/genetics.110.119628 20980244
30. Williams B, Leung G, Maiato H, Wong A, Li Z, Williams EV, et al. Mitch a rapidly evolving component of the Ndc80 kinetochore complex required for correct chromosome segregation in Drosophila. J Cell Sci. 2007;120(Pt 20):3522–33. 17895365
31. DeLuca JG, Dong Y, Hergert P, Strauss J, Hickey JM, Salmon ED, et al. Hec1 and nuf2 are core components of the kinetochore outer plate essential for organizing microtubule attachment sites. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16(2):519–31. 15548592
32. Feijão T, Afonso O, Maia AF, Sunkel CE. Stability of kinetochore-microtubule attachment and the role of different KMN network components in Drosophila. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2013;70(10):661–75.
33. Przewloka MR, Zhang W, Costa P, Archambault V, D'Avino PP, Lilley KS, et al. Molecular analysis of core kinetochore composition and assembly in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS One. 2007;2(5):e478. 17534428
34. Basto R, Scaerou F, Mische S, Wojcik E, Lefebvre C, Gomes R, et al. In vivo dynamics of the rough deal checkpoint protein during Drosophila mitosis. Curr Biol. 2004;14(1):56–61. 14711415
35. Gassmann R, Essex A, Hu JS, Maddox PS, Motegi F, Sugimoto A, et al. A new mechanism controlling kinetochore-microtubule interactions revealed by comparison of two dynein-targeting components: SPDL-1 and the Rod/Zwilch/Zw10 complex. Genes Dev. 2008;22(17):2385–99. doi: 10.1101/gad.1687508 18765790
36. Caldas GV, DeLuca JG. KNL1: bringing order to the kinetochore. Chromosoma. 2014;123(3):169–81. doi: 10.1007/s00412-013-0446-5 24310619
37. McCollum D. Monopolin. Curr Biol. 2012;22(22):R937–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.09.024 23174290
38. Kim J, Ishiguro K, Nambu A, Akiyoshi B, Yokobayashi S, Kagami A, et al. Meikin is a conserved regulator of meiosis-I-specific kinetochore function. Nature. 2015;517(7535):466–71. doi: 10.1038/nature14097 25533956
39. Bickel SE, Wyman DW, Miyazaki WY, Moore DP, Orr-Weaver TL. Identification of ORD, a Drosophila protein essential for sister chromatid cohesion. EMBO Journal. 1996;15 : 1451–9. 8635478
40. Kitajima TS, Kawashima SA, Watanabe Y. The conserved kinetochore protein shugoshin protects centromeric cohesion during meiosis. Nature. 2004;427(6974):510–7. 14730319
41. Yucel JK, Marszalek JD, McIntosh JR, Goldstein LS, Cleveland DW, Philp AV. CENP-meta, an essential kinetochore kinesin required for the maintenance of metaphase chromosome alignment in Drosophila. J Cell Biol. 2000;150(1):1–11. 10893249
42. Chou TB, Perrimon N. The autosomal FLP-DFS technique for generating germline mosaics in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1996;144(4):1673–9. 8978054
43. Gudimchuk N, Vitre B, Kim Y, Kiyatkin A, Cleveland DW, Ataullakhanov FI, et al. Kinetochore kinesin CENP-E is a processive bi-directional tracker of dynamic microtubule tips. Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15(9):1079–88. doi: 10.1038/ncb2831 23955301
44. Maffini S, Maia AR, Manning AL, Maliga Z, Pereira AL, Junqueira M, et al. Motor-independent targeting of CLASPs to kinetochores by CENP-E promotes microtubule turnover and poleward flux. Curr Biol. 2009;19(18):1566–72. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.07.059 19733075
45. Dumont J, Desai A. Acentrosomal spindle assembly and chromosome segregation during oocyte meiosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2012;22(5):241–9. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2012.02.007 22480579
46. Jang JK, Rahman T, McKim KS. The kinesin-like protein Subito contributes to central spindle assembly and organization of the meiotic spindle in Drosophila oocytes. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16(10):4684–94. 16055508
47. Giunta KL, Jang JK, Manheim EA, Subramanian G, McKim KS. subito encodes a kinesin-like protein required for meiotic spindle pole formation in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 2002;160(4):1489–501. 11973304
48. Hartl TA, Smith HF, Bosco G. Chromosome alignment and transvection are antagonized by condensin II. Science. 2008;322(5906):1384–7. doi: 10.1126/science.1164216 19039137
49. Muscat CC, Torre-Santiago KM, Tran MV, Powers JA, Wignall SM. Kinetochore-independent chromosome segregation driven by lateral microtubule bundles. Elife. 2015;4.
50. Sharp DJ, Mennella V, Buster DW. KLP10A and KLP59C: the dynamic duo of microtubule depolymerization. Cell Cycle. 2005;4(11):1482–5. 16205125
51. Rogers GC, Rogers SL, Schwimmer TA, Ems-McClung SC, Walczak CE, Vale RD, et al. Two mitotic kinesins cooperate to drive sister chromatid separation during anaphase. Nature. 2004;427(6972):364–70. 14681690
52. Gui L, Homer H. Spindle assembly checkpoint signalling is uncoupled from chromosomal position in mouse oocytes. Development. 2012;139(11):1941–6. doi: 10.1242/dev.078352 22513372
53. Maia AF, Lopes CS, Sunkel CE. BubR1 and CENP-E have antagonistic effects upon the stability of microtubule-kinetochore attachments in Drosophila S2 cell mitosis. Cell Cycle. 2007;6(11):1367–78. 17525528
54. Godek KM, Kabeche L, Compton DA. Regulation of kinetochore-microtubule attachments through homeostatic control during mitosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015;16(1):57–64.
55. Nasmyth K. A meiotic mystery: How sister kinetochores avoid being pulled in opposite directions during the first division. Bioessays. 2015;37(6):657–65. doi: 10.1002/bies.201500006 25874377
56. Li X, Dawe RK. Fused sister kinetochores initiate the reductional division in meiosis I. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(9):1103–8. doi: 10.1038/ncb1923 19684578.
57. Sakuno T, Tada K, Watanabe Y. Kinetochore geometry defined by cohesion within the centromere. Nature. 2009;458(7240):852–8. doi: 10.1038/nature07876 19370027
58. Chelysheva L, Diallo S, Vezon D, Gendrot G, Vrielynck N, Belcram K, et al. AtREC8 and AtSCC3 are essential to the monopolar orientation of the kinetochores during meiosis. J Cell Sci. 2005;118(Pt 20):4621–32. 16176934
59. Tzur YB, Egydio de Carvalho C, Nadarajan S, Van Bostelen I, Gu Y, Chu DS, et al. LAB-1 targets PP1 and restricts Aurora B kinase upon entrance into meiosis to promote sister chromatid cohesion. PLoS Biol. 2012;10(8):e1001378. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001378 22927794
60. Emanuele MJ, Lan W, Jwa M, Miller SA, Chan CS, Stukenberg PT. Aurora B kinase and protein phosphatase 1 have opposing roles in modulating kinetochore assembly. J Cell Biol. 2008;181(2):241–54. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200710019 18426974
61. Kim S, Yu H. Multiple assembly mechanisms anchor the KMN spindle checkpoint platform at human mitotic kinetochores. J Cell Biol. 2015;208(2):181–96. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201407074 25601404
62. Rago F, Gascoigne KE, Cheeseman IM. Distinct organization and regulation of the outer kinetochore KMN network downstream of CENP-C and CENP-T. Curr Biol. 2015;25(5):671–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.01.059 25660545
63. Funabiki H, Wynne DJ. Making an effective switch at the kinetochore by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Chromosoma. 2013;122(3):135–58. doi: 10.1007/s00412-013-0401-5 23512483
64. Sarangapani KK, Asbury CL. Catch and release: how do kinetochores hook the right microtubules during mitosis? Trends Genet. 2014;30(4):150–9. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2014.02.004 24631209
65. Yoshida S, Kaido M, Kitajima TS. Inherent Instability of Correct Kinetochore-Microtubule Attachments during Meiosis I in Oocytes. Dev Cell. 2015.
66. Kolano A, Brunet S, Silk AD, Cleveland DW, Verlhac MH. Error-prone mammalian female meiosis from silencing the spindle assembly checkpoint without normal interkinetochore tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(27):E1858–67. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1204686109 22552228
67. St Pierre SE, Ponting L, Stefancsik R, McQuilton P. FlyBase 102—advanced approaches to interrogating FlyBase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(Database issue):D780–8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1092 24234449
68. Ni JQ, Zhou R, Czech B, Liu LP, Holderbaum L, Yang-Zhou D, et al. A genome-scale shRNA resource for transgenic RNAi in Drosophila. Nat Methods. 2011;8(5):405–7. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1592 21460824
69. Brand AH, Perrimon N. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development. 1993;118 : 401–15. 8223268
70. Sugimura I, Lilly MA. Bruno inhibits the expression of mitotic cyclins during the prophase I meiotic arrest of Drosophila oocytes. Dev Cell. 2006;10(1):127–35. 16399084
71. Rorth P. Gal4 in the Drosophila female germline. Mech Dev. 1998;78(1–2):113–8. 9858703
72. Gloor GB, Preston CR, Johnson-Schlitz DM, Nassif NA, Phillis RW, Benz WK, et al. Type I repressors of P element mobility. Genetics. 1993;135(1):81–95. 8224830
73. Casso D, Ramirez-Weber F, Kornberg TB. GFP-tagged balancer chromosomes for Drosophila melanogaster. Mech Dev. 2000;91(1–2):451–4. 10704882
74. Schaar BT, Chan GK, Maddox P, Salmon ED, Yen TJ. CENP-E function at kinetochores is essential for chromosome alignment. J Cell Biol. 1997;139(6):1373–82. 9396744
75. Radford SJ, Harrison AM, McKim KS. Microtubule-depolymerizing Kinesin KLP10A Restricts the Length of the Acentrosomal Meiotic Spindle in Drosophila Females. Genetics. 2012;192 : 431–40. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.143503 22865737
76. Heeger S, Leismann O, Schittenhelm R, Schraidt O, Heidmann S, Lehner CF. Genetic interactions of separase regulatory subunits reveal the diverged Drosophila Cenp-C homolog. Genes Dev. 2005;19(17):2041–53. 16140985
77. Wu C, Singaram V, McKim KS. mei-38 is required for chromosome segregation during meiosis in Drosophila females. Genetics. 2008;180(1):61–72. doi: 10.1534/genetics.108.091140 18757915
78. Blower MD, Karpen GH. The role of Drosophila CID in kinetochore formation, cell-cycle progression and heterochromatin interactions. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3(8):730–9. 11483958
79. Matthies HJ, Clarkson M, Saint RB, Namba R, Hawley RS. Analysis of meiosis in fixed and live oocytes by light microscopy. In: Sullivan W, Ashburner M, Hawley RS, editors. Drosophila Protocols. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2000. p. 67–85.
80. McKim KS, Jang JK, Theurkauf WE, Hawley RS. Mechanical basis of meiotic metaphase arrest. Nature. 1993;362(6418):364–6. 8455723
81. Bickel SE, Orr-Weaver TL, Balicky EM. The sister-chromatid cohesion protein ORD is required for chiasma maintenance in Drosophila oocytes. Curr Biol. 2002;12(11):925–9. 12062057
82. Matthies HJ, McDonald HB, Goldstein LS, Theurkauf WE. Anastral meiotic spindle morphogenesis: role of the non-claret disjunctional kinesin-like protein. J Cell Biol. 1996;134(2):455–64. 8707829
83. Cullen CF, Ohkura H. Msps protein is localized to acentrosomal poles to ensure bipolarity of Drosophila meiotic spindles. Nature Cell Biol. 2001;3 : 637–42. 11433295
Štítky
Genetika Reprodukční medicína
Článek Evidence of Selection against Complex Mitotic-Origin Aneuploidy during Preimplantation DevelopmentČlánek A Novel Route Controlling Begomovirus Resistance by the Messenger RNA Surveillance Factor PelotaČlánek A Follicle Rupture Assay Reveals an Essential Role for Follicular Adrenergic Signaling in OvulationČlánek Canonical Poly(A) Polymerase Activity Promotes the Decay of a Wide Variety of Mammalian Nuclear RNAsČlánek FANCI Regulates Recruitment of the FA Core Complex at Sites of DNA Damage Independently of FANCD2Článek Hsp90-Associated Immunophilin Homolog Cpr7 Is Required for the Mitotic Stability of [URE3] Prion inČlánek The Dedicated Chaperone Acl4 Escorts Ribosomal Protein Rpl4 to Its Nuclear Pre-60S Assembly SiteČlánek Chromatin-Remodelling Complex NURF Is Essential for Differentiation of Adult Melanocyte Stem CellsČlánek A Systems Approach Identifies Essential FOXO3 Functions at Key Steps of Terminal ErythropoiesisČlánek Integration of Posttranscriptional Gene Networks into Metabolic Adaptation and Biofilm Maturation inČlánek MET18 Connects the Cytosolic Iron-Sulfur Cluster Assembly Pathway to Active DNA Demethylation in
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Genetics
Nejčtenější tento týden
2015 Číslo 10- Akutní intermitentní porfyrie
- Farmakogenetické testování pomáhá předcházet nežádoucím efektům léčiv
- Růst a vývoj dětí narozených pomocí IVF
- Pilotní studie: stres a úzkost v průběhu IVF cyklu
- Vliv melatoninu a cirkadiálního rytmu na ženskou reprodukci
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- Gene-Regulatory Logic to Induce and Maintain a Developmental Compartment
- A Decad(e) of Reasons to Contribute to a PLOS Community-Run Journal
- DNA Methylation Landscapes of Human Fetal Development
- Single Strand Annealing Plays a Major Role in RecA-Independent Recombination between Repeated Sequences in the Radioresistant Bacterium
- Evidence of Selection against Complex Mitotic-Origin Aneuploidy during Preimplantation Development
- Transcriptional Derepression Uncovers Cryptic Higher-Order Genetic Interactions
- Silencing of X-Linked MicroRNAs by Meiotic Sex Chromosome Inactivation
- Virus Satellites Drive Viral Evolution and Ecology
- A Novel Route Controlling Begomovirus Resistance by the Messenger RNA Surveillance Factor Pelota
- Sequence to Medical Phenotypes: A Framework for Interpretation of Human Whole Genome DNA Sequence Data
- Your Data to Explore: An Interview with Anne Wojcicki
- Modulation of Ambient Temperature-Dependent Flowering in by Natural Variation of
- The Ciliopathy Protein CC2D2A Associates with NINL and Functions in RAB8-MICAL3-Regulated Vesicle Trafficking
- PPP2R5C Couples Hepatic Glucose and Lipid Homeostasis
- DCA1 Acts as a Transcriptional Co-activator of DST and Contributes to Drought and Salt Tolerance in Rice
- Intermediate Levels of CodY Activity Are Required for Derepression of the Branched-Chain Amino Acid Permease, BraB
- "Missing" G x E Variation Controls Flowering Time in
- The Rise and Fall of an Evolutionary Innovation: Contrasting Strategies of Venom Evolution in Ancient and Young Animals
- Type IV Collagen Controls the Axogenesis of Cerebellar Granule Cells by Regulating Basement Membrane Integrity in Zebrafish
- Loss of a Conserved tRNA Anticodon Modification Perturbs Plant Immunity
- Genome-Wide Association Analysis of Adaptation Using Environmentally Predicted Traits
- Oriented Cell Division in the . Embryo Is Coordinated by G-Protein Signaling Dependent on the Adhesion GPCR LAT-1
- Disproportionate Contributions of Select Genomic Compartments and Cell Types to Genetic Risk for Coronary Artery Disease
- A Follicle Rupture Assay Reveals an Essential Role for Follicular Adrenergic Signaling in Ovulation
- The RNAPII-CTD Maintains Genome Integrity through Inhibition of Retrotransposon Gene Expression and Transposition
- Canonical Poly(A) Polymerase Activity Promotes the Decay of a Wide Variety of Mammalian Nuclear RNAs
- Allelic Variation of Cytochrome P450s Drives Resistance to Bednet Insecticides in a Major Malaria Vector
- SCARN a Novel Class of SCAR Protein That Is Required for Root-Hair Infection during Legume Nodulation
- IBR5 Modulates Temperature-Dependent, R Protein CHS3-Mediated Defense Responses in
- NINL and DZANK1 Co-function in Vesicle Transport and Are Essential for Photoreceptor Development in Zebrafish
- Decay-Initiating Endoribonucleolytic Cleavage by RNase Y Is Kept under Tight Control via Sequence Preference and Sub-cellular Localisation
- Large-Scale Analysis of Kinase Signaling in Yeast Pseudohyphal Development Identifies Regulation of Ribonucleoprotein Granules
- FANCI Regulates Recruitment of the FA Core Complex at Sites of DNA Damage Independently of FANCD2
- LINE-1 Mediated Insertion into (Protein of Centriole 1 A) Causes Growth Insufficiency and Male Infertility in Mice
- Hsp90-Associated Immunophilin Homolog Cpr7 Is Required for the Mitotic Stability of [URE3] Prion in
- Genome-Scale Mapping of σ Reveals Widespread, Conserved Intragenic Binding
- Uncovering Hidden Layers of Cell Cycle Regulation through Integrative Multi-omic Analysis
- Functional Diversification of Motor Neuron-specific Enhancers during Evolution
- The GTP- and Phospholipid-Binding Protein TTD14 Regulates Trafficking of the TRPL Ion Channel in Photoreceptor Cells
- The Gyc76C Receptor Guanylyl Cyclase and the Foraging cGMP-Dependent Kinase Regulate Extracellular Matrix Organization and BMP Signaling in the Developing Wing of
- The Ty1 Retrotransposon Restriction Factor p22 Targets Gag
- Functional Impact and Evolution of a Novel Human Polymorphic Inversion That Disrupts a Gene and Creates a Fusion Transcript
- The Dedicated Chaperone Acl4 Escorts Ribosomal Protein Rpl4 to Its Nuclear Pre-60S Assembly Site
- The Influence of Age and Sex on Genetic Associations with Adult Body Size and Shape: A Large-Scale Genome-Wide Interaction Study
- Parent-of-Origin Effects of the Gene on Adiposity in Young Adults
- Chromatin-Remodelling Complex NURF Is Essential for Differentiation of Adult Melanocyte Stem Cells
- Retinoic Acid Receptors Control Spermatogonia Cell-Fate and Induce Expression of the SALL4A Transcription Factor
- A Systems Approach Identifies Essential FOXO3 Functions at Key Steps of Terminal Erythropoiesis
- Protein O-Glucosyltransferase 1 (POGLUT1) Promotes Mouse Gastrulation through Modification of the Apical Polarity Protein CRUMBS2
- KIF7 Controls the Proliferation of Cells of the Respiratory Airway through Distinct Microtubule Dependent Mechanisms
- Integration of Posttranscriptional Gene Networks into Metabolic Adaptation and Biofilm Maturation in
- Lateral and End-On Kinetochore Attachments Are Coordinated to Achieve Bi-orientation in Oocytes
- Protein Homeostasis Imposes a Barrier on Functional Integration of Horizontally Transferred Genes in Bacteria
- A New Method for Detecting Associations with Rare Copy-Number Variants
- Histone H2AFX Links Meiotic Chromosome Asynapsis to Prophase I Oocyte Loss in Mammals
- The Genomic Aftermath of Hybridization in the Opportunistic Pathogen
- A Role for the Chaperone Complex BAG3-HSPB8 in Actin Dynamics, Spindle Orientation and Proper Chromosome Segregation during Mitosis
- Establishment of a Developmental Compartment Requires Interactions between Three Synergistic -regulatory Modules
- Regulation of Spore Formation by the SpoIIQ and SpoIIIA Proteins
- Association of the Long Non-coding RNA Steroid Receptor RNA Activator (SRA) with TrxG and PRC2 Complexes
- Alkaline Ceramidase 3 Deficiency Results in Purkinje Cell Degeneration and Cerebellar Ataxia Due to Dyshomeostasis of Sphingolipids in the Brain
- ACLY and ACC1 Regulate Hypoxia-Induced Apoptosis by Modulating ETV4 via α-ketoglutarate
- Quantitative Differences in Nuclear β-catenin and TCF Pattern Embryonic Cells in .
- HENMT1 and piRNA Stability Are Required for Adult Male Germ Cell Transposon Repression and to Define the Spermatogenic Program in the Mouse
- Axon Regeneration Is Regulated by Ets–C/EBP Transcription Complexes Generated by Activation of the cAMP/Ca Signaling Pathways
- A Phenomic Scan of the Norfolk Island Genetic Isolate Identifies a Major Pleiotropic Effect Locus Associated with Metabolic and Renal Disorder Markers
- The Roles of CDF2 in Transcriptional and Posttranscriptional Regulation of Primary MicroRNAs
- A Genetic Cascade of Modulates Nucleolar Size and rRNA Pool in
- Inter-population Differences in Retrogene Loss and Expression in Humans
- Cationic Peptides Facilitate Iron-induced Mutagenesis in Bacteria
- EP4 Receptor–Associated Protein in Macrophages Ameliorates Colitis and Colitis-Associated Tumorigenesis
- Fungal Infection Induces Sex-Specific Transcriptional Changes and Alters Sexual Dimorphism in the Dioecious Plant
- FLCN and AMPK Confer Resistance to Hyperosmotic Stress via Remodeling of Glycogen Stores
- MET18 Connects the Cytosolic Iron-Sulfur Cluster Assembly Pathway to Active DNA Demethylation in
- Sex Bias and Maternal Contribution to Gene Expression Divergence in Blastoderm Embryos
- Transcriptional and Linkage Analyses Identify Loci that Mediate the Differential Macrophage Response to Inflammatory Stimuli and Infection
- Mre11 and Blm-Dependent Formation of ALT-Like Telomeres in Ku-Deficient
- Genome Wide Identification of SARS-CoV Susceptibility Loci Using the Collaborative Cross
- Identification of a Single Strand Origin of Replication in the Integrative and Conjugative Element ICE of
- The Type VI Secretion TssEFGK-VgrG Phage-Like Baseplate Is Recruited to the TssJLM Membrane Complex via Multiple Contacts and Serves As Assembly Platform for Tail Tube/Sheath Polymerization
- The Dynamic Genome and Transcriptome of the Human Fungal Pathogen and Close Relative
- Secondary Structure across the Bacterial Transcriptome Reveals Versatile Roles in mRNA Regulation and Function
- ROS-Induced JNK and p38 Signaling Is Required for Unpaired Cytokine Activation during Regeneration
- Pelle Modulates dFoxO-Mediated Cell Death in
- PLOS Genetics
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Single Strand Annealing Plays a Major Role in RecA-Independent Recombination between Repeated Sequences in the Radioresistant Bacterium
- The Rise and Fall of an Evolutionary Innovation: Contrasting Strategies of Venom Evolution in Ancient and Young Animals
- Genome Wide Identification of SARS-CoV Susceptibility Loci Using the Collaborative Cross
- DCA1 Acts as a Transcriptional Co-activator of DST and Contributes to Drought and Salt Tolerance in Rice
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Vladimír Palička, CSc., Dr.h.c., doc. MUDr. Václav Vyskočil, Ph.D., MUDr. Petr Kasalický, CSc., MUDr. Jan Rosa, Ing. Pavel Havlík, Ing. Jan Adam, Hana Hejnová, DiS., Jana Křenková
Autoři: MUDr. Irena Krčmová, CSc.
Autoři: MDDr. Eleonóra Ivančová, PhD., MHA
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Eva Kubala Havrdová, DrSc.
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



