-
Články
- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
- Kongresy
- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
P47 Mice Are Compromised in Expansion and Activation of CD8 T Cells and Susceptible to Infection
Macrophage activation of NADPH oxidase NOX2) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) is suggested to mediate control of Trypanosoma cruzi infection that is the causative agent of Chagas disease. However, how NOX2/ROS deficiency affects parasite persistence and chronic disease is not known. In this study, we present the first evidence that NOX2 and ROS shape the T cell-mediated adaptive immunity, and its deficiency result in compromised splenic activation of type 1 cytotoxic CD8+ T cell response to T. cruzi infection. Subsequently, p47phox−/ − mice that lack NOX2 activity were more unable to control parasite replication and dissemination and succumbed to susceptible to T. cruzi infection. Our study highlights how redox state of innate immune cells alters the adaptive immunity to intracellular pathogens; and suggests that understanding the molecular and cellular mechanisms affected by redox state of immune cells at basal level could be exploited in designing future therapeutic and vaccination strategies against T. cruzi infection and Chagas disease.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Pathog 10(12): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004516
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1004516Summary
Macrophage activation of NADPH oxidase NOX2) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) is suggested to mediate control of Trypanosoma cruzi infection that is the causative agent of Chagas disease. However, how NOX2/ROS deficiency affects parasite persistence and chronic disease is not known. In this study, we present the first evidence that NOX2 and ROS shape the T cell-mediated adaptive immunity, and its deficiency result in compromised splenic activation of type 1 cytotoxic CD8+ T cell response to T. cruzi infection. Subsequently, p47phox−/ − mice that lack NOX2 activity were more unable to control parasite replication and dissemination and succumbed to susceptible to T. cruzi infection. Our study highlights how redox state of innate immune cells alters the adaptive immunity to intracellular pathogens; and suggests that understanding the molecular and cellular mechanisms affected by redox state of immune cells at basal level could be exploited in designing future therapeutic and vaccination strategies against T. cruzi infection and Chagas disease.
Introduction
Chagas disease is caused by the protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi [1], [2]. During acute phase of infection, parasites can be found in the circulating blood, and host may develop fever or swelling around the site of inoculation, and rarely, severe inflammation in heart muscle or brain. Several years after exposure to T. cruzi, ∼30% of the infected individuals develop clinical symptoms of chronic cardiomyopathy associated with progressive cardiomegaly, arrhythmia, thromboembolic events, and heart failure [3], [4].
Both innate and acquired immune responses are required for control of T. cruzi and critical for host survival (reviewed in [5], [6]). Upon infection, macrophages serve as first responders by activation of phagocytic NADPH oxidase, referred as NOX2. NADPH oxidase is a multi-subunit complex and utilizes NADPH as an electron donor to reduce O2 to superoxide (O2·−), that is then dismutated into other oxidants (e.g. H2O2) [7]. The plasma membrane-associated proteins gp91phox and p22phox compose the flavocytochrome-b558 complex that is the major component responsible for enzyme stability and activity. Phosphorylation of cytosolic factors (p47phox, p67phox, and p40phox), and small Rho GTPases in response to exogenous or endogenous stimuli initiates their translocation to the cell membrane, and NADPH oxidase activation [7]–[9]. Activated phagocytes exert cytotoxic effects via NOX2-dependent reactive oxygen species (ROS) production that mediates pathogen killing by oxidative damage of DNA, proteins and lipids, and suggested to play an important role in control of T. cruzi [10]–[14].
Besides innate immune mechanisms, a body of literature demonstrates that adaptive immune responses are required for parasite control. CD4+T cells assist in the control of T. cruzi through secretion of Th1 cytokines, amplification of the phagocytic activity of macrophages, stimulation of B cell proliferation and antibody production, and enhancement of the CD8+T cells response (reviewed in [6], [15]. CD8+T cells recognize processed parasite antigens presented in association with MHC class I molecules on the surface of infected host cells and contribute to the control of T. cruzi, either by cytolysis of parasite-infected cells or by the secretion of cytokines that may induce trypanocidal activity (reviewed in [6], [16]). Current literature suggests that NADPH oxidase activity may modulate adaptive immune responses via ROS signaling of cytokine gene expression and regulation of the efficient antigen presentation for T cell activation and proliferation [17], [18], though the cell type involved in NADPH oxidase-mediated regulation of adaptive immunity are not fully detailed.
In this study, we have assessed the host response to T. cruzi infection in the event of phagocytic NADPH oxidase deficiency. We first monitored the susceptibility of wild-type (WT) versus p47phox−/− mice to T. cruzi infection, and then proceeded with a step-wise approach to identify the immune mechanisms that may be altered and contributed to susceptibility of p47phox−/− mice to T. cruzi. Our data show that p47phox−/− macrophages were not compromised in phagocytic activity, and mounted enhanced levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), nitric oxide (NO), and cytokines in response to T. cruzi infection. In vivo activation of CD4+T cell subset and inflammatory cytokine response was also similar to or more pronounced in p47phox−/− mice when compared to that observed in WT controls in response to T. cruzi infection. However, in the event of NOX2 deficiency, generation and activation of CD8+T cell response was severely compromised leading to increased parasite burden, tissue pathogenesis and mortality. We discuss the involvement of distinct innate receptor signaling pathways governing the activation and proliferation of T cell subsets and the various mechanisms contributing to increased susceptibility of p47phox−/− mice to T. cruzi infection.
Results
Susceptibility of p47phox−/− mice to T. cruzi infection
We used well-established experimental models [19], [20] to assess the role of NAD(P)H oxidase (NOX2) in immunity to T. cruzi infection. C57BL/6 (WT and p47phox−/−) mice were assessed at day 7 post-infection (pi) for the expression level of p47phox as an indicator of NOX2 activation in innate immune cells. The low level of baseline expression of p47phox was increased by 2-fold in splenic (Fig. 1A) and bone-marrow monocytes/macrophages of WT mice. The splenic and BM monocytes of p47phox−/− mice exhibited no expression of p47 before or after T. cruzi infection. These data confirmed that p47phox−/− mice lacked the ability to induce NOX2 activity in phagocytes in response to T. cruzi infection.
Fig. 1. p47phox−/− mice are susceptible to T. cruzi infection and exhibit increased mortality and parasite burden. 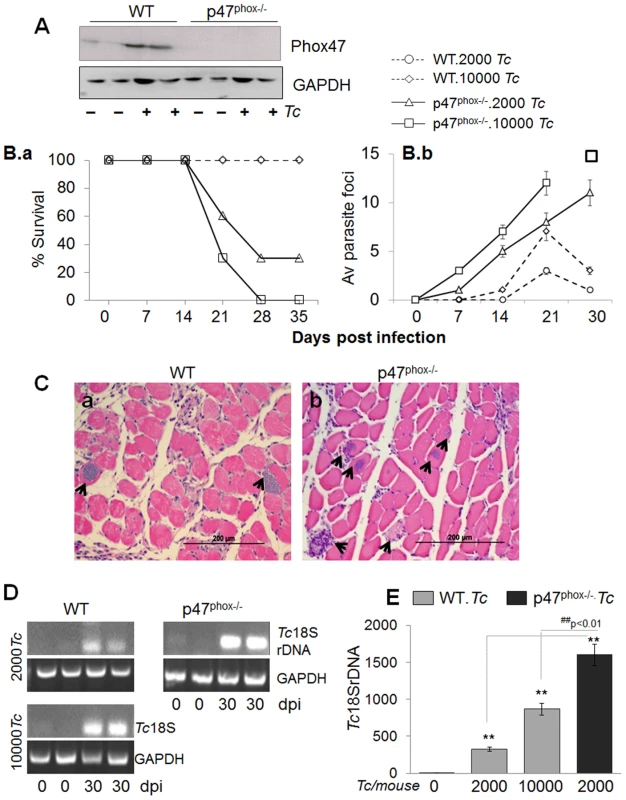
(A) Western blotting of splenic macrophages and heart tissue, probed with anti-p47phox antibody. The data presented are from mice infected with 10,000 parasites and harvested at day 7 pi. (B–E) C57BL/6 (WT and p47phox−/−) mice were infected with T. cruzi (2,000 or 10,000 parasites/mouse). (B.a) Percent survival from infection was monitored daily. (B.b) Tissue parasite foci in skeletal muscle tissue sections of infected mice were monitored by light microscopy at weekly intervals. (C) Histologic examination of heart tissue-sections for parasite foci (data shown is at day 30 post-infection, original magnification: 200×; arrows mark the parasite nests). (D&E) Semi-quantitative PCR (D) and real time quantitative PCR (E) analysis of parasite burden in the heart tissue of infected mice at day 30 pi. Data in all figures are presented as mean ± SD and significance presented as *normal-versus-infected, #WT/infected-versus-p47phox−/−/infected (*, #p<0.05, **,##p<0.01, n = 8/group). Challenge infection with 10,000 T. cruzi per mouse proved to be lethal for p47phox−/− mice as all mice succumbed within 28 days pi (Fig. 1B.a). When inoculum was reduced to 2000 parasites, 70% of p47phox−/− mice still succumbed by 30 days pi. In comparison, 100% of WT mice challenged with 2000 or 10000 parasites survived (Fig. 1B.a).
The increased mortality of p47phox−/− mice was associated with increased tissue parasites (Fig. 1B.b, Fig. 1.C–E). Histological analysis of skeletal muscle and heart tissue sections (three sections/tissue >10-microscopic fields (mf) per slide, n = 8 mice/group) was conducted to obtain a score of parasite foci in tissues (Table 1). An average of skeletal tissue parasite foci in WT and p47phox−/− mice infected with 2000 or 10000 parasites is presented in Fig. 1B.b. The p47phox−/− mice infected with 2000 or 10000 parasites exhibited an early increase in tissue parasitemia by day 7 pi that further increased in a linear manner at days 14 and 21 pi (Fig. 1B.b). In comparison, WT mice exhibited a delayed, 2–5-fold lower level of parasite foci in skeletal muscle tissue during 7–21 days pi (Fig. 1B.b). At 30 days pi, parasite foci in WT mice infected with 2000 or 10000 parasites were controlled, while p47phox−/− continued to exhibit an increase in tissue parasite foci (Fig. 1B.b). A similar pattern of increase in parasite foci was observed in heart tissue of p47phox−/− mice during the 7–30 days pi (Table 1). We noted >5 parasite foci/mf in heart tissue sections of p47phox−/− mice infected with 2000 or 10000 parasites and harvested at day 30 pi (Fig. 1C.b). In comparison, contained (0–2 pseudocysts/mf) were noted in heart tissue of WT mice infected with 2000 or 10000 parasites (Fig. 1C.a, Table 1) A semi-quantitative PCR showed the Tc18SrDNA signal was significantly higher in the myocardium of infected/p47phox−/− mice at day 30 pi than was observed in the myocardium of WT mice infected with the same dose or 5-fold higher dose of parasites (Fig. 1D). Quantitative real-time PCR validated the findings of semi-quantitative PCR and showed 2–5-fold increase in myocardial (Fig. 1E, ##p<0.01), and skeletal muscle and circulatory parasite burden in infected/p47phox−/− mice as compared to that detected in infected/WT mice. These data suggested the p47phox−/− mice failed to control tissue parasites and succumbed to T. cruzi infection.
Tab. 1. Tissue burden of parasite foci and inflammation in wild type and p47phox−/− mice infected by T. cruzi. 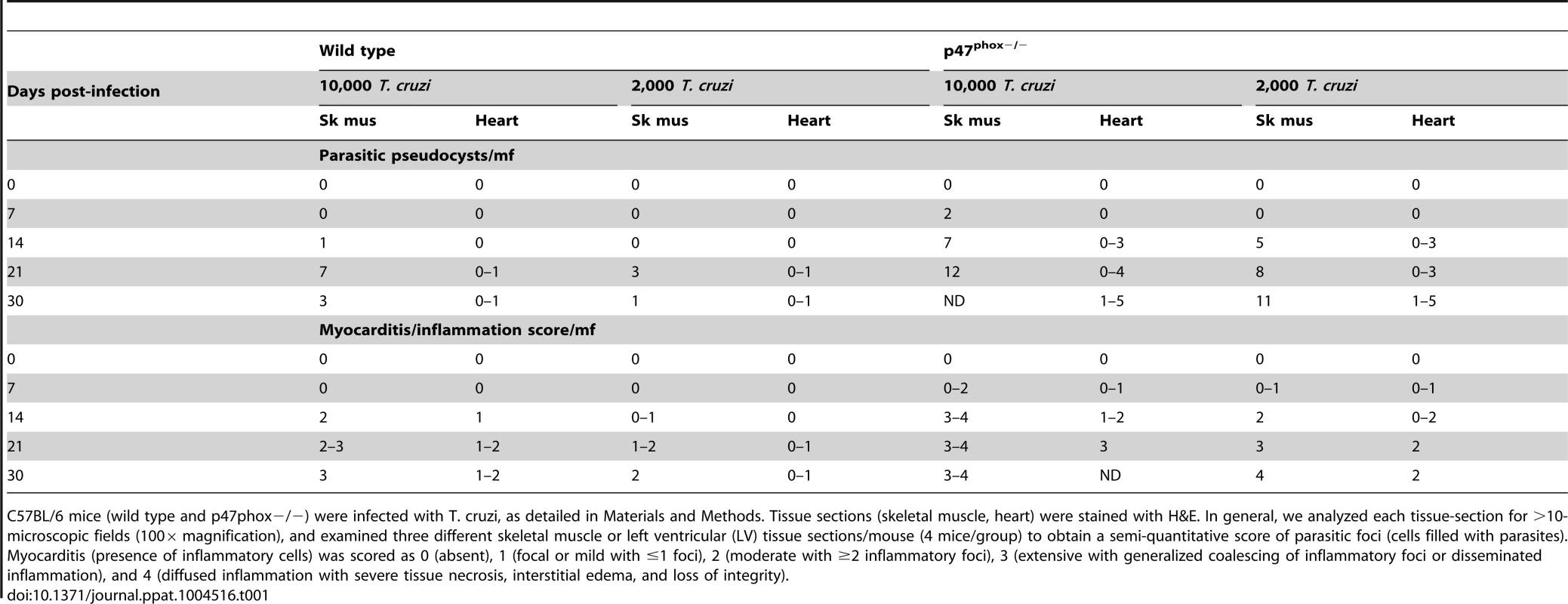
C57BL/6 mice (wild type and p47phox−/−) were infected with T. cruzi, as detailed in Materials and Methods. Tissue sections (skeletal muscle, heart) were stained with H&E. In general, we analyzed each tissue-section for >10-microscopic fields (100× magnification), and examined three different skeletal muscle or left ventricular (LV) tissue sections/mouse (4 mice/group) to obtain a semi-quantitative score of parasitic foci (cells filled with parasites). Myocarditis (presence of inflammatory cells) was scored as 0 (absent), 1 (focal or mild with ≤1 foci), 2 (moderate with ≥2 inflammatory foci), 3 (extensive with generalized coalescing of inflammatory foci or disseminated inflammation), and 4 (diffused inflammation with severe tissue necrosis, interstitial edema, and loss of integrity). Phagocytic activity of P47phox−/− macrophages is not compromised
One plausible explanation for increased susceptibility of p47phox−/− mice to T. cruzi could be that p47phox−/− macrophages were compromised in phagocytic activity, and, therefore, failed to control parasites' dissemination. To test this, we isolated BM and splenic monocytes from WT and p47phox−/− mice, in vitro differentiated to macrophages with interferon gamma (IFN-γ), and incubated in presence of T. cruzi for 0, 6, 12, 24 h. The data presented in Fig. S1 are from splenic monocytes and representative of the results from triplicate experiments with splenic and BM monocytes. Giemsa staining showed the monocytes of p47phox−/− mice had a similar or better capacity than the WT monocytes to differentiate to macrophages by 6 h pi (Fig. S1.b&g). Likewise, p47phox−/− phagocytes' capacity to uptake parasites (i.e. phagocytic efficiency) was not significantly compromised. Counting of >200 cells/slide showed that by 6 h, 25% and 15% of WT and p47phox−/− macrophages were infected (average 6–15 parasites/cell), and at 12 h, >50% of WT and p47phox−/− macrophages were full of replicative, amastigote form of parasites (Fig. S1.c,d,h,i). At 24 h pi, some of the WT macrophages were ruptured releasing parasites while p47phox−/− macrophages continued to exhibit parasites contained within phagosome (Fig. S1.e&j, p<0.01).
To obtain a quantitative measure of parasite uptake, primary BM and splenic cells were incubated for 24 h with CFSE-labeled T. cruzi, and then labeled with fluorescence-conjugated antibodies to examine the frequency of CFSE+ macrophages (APC-CD11b+) and neutrophils (PE-Ly6B+) by flow cytometry. Representative flow cytometry data from BM-macrophages and BM-neutrophils incubated with CFSE-labeled parasites are presented in Fig. 2A, and percentage of CFSE+CD11b+ and CFSE+Ly6B+ macrophages and neutrophils, respectively, from BM and splenic cells are presented in Fig. 2B. We noted a higher extent of infection of BM cells derived from p47phox−/− mice as compared to that noted in BM cells from WT mice (CD11b+ macrophages: 71% versus 36%; Ly6+ neutrophils: 23.5% versus 13.5%; p47phox−/− versus WT, respectively, Fig. 2A & Fig. 2B.a). The splenic cells from p47−/− and WT mice exhibited comparable rate of infection efficiency at 24 h post-incubation that were not statistically different (CD11b+ macrophages: 10.65% versus 16.8%; Ly6+ neutrophils: 3.28% versus 9.45%, p47phox−/− versus WT, respectively, Fig. 2B.b). The hemacytometer counting of parasites in supernatants showed comparable number of parasites were released from p47phox−/− and WT macrophages at 24 h and 48 h pi (Fig. 2C). Together, the data presented in Fig. S1 and Fig. 2 suggested that BM and splenic monocytes from WT and p47phox−/− mice were equally competent in differentiating to macrophages and parasite uptake, and NOX2 deficiency did not result in increased parasite release from infected macrophages.
Fig. 2. T. cruzi uptake, intracellular replication and release by p47phox−/− phagocytes. 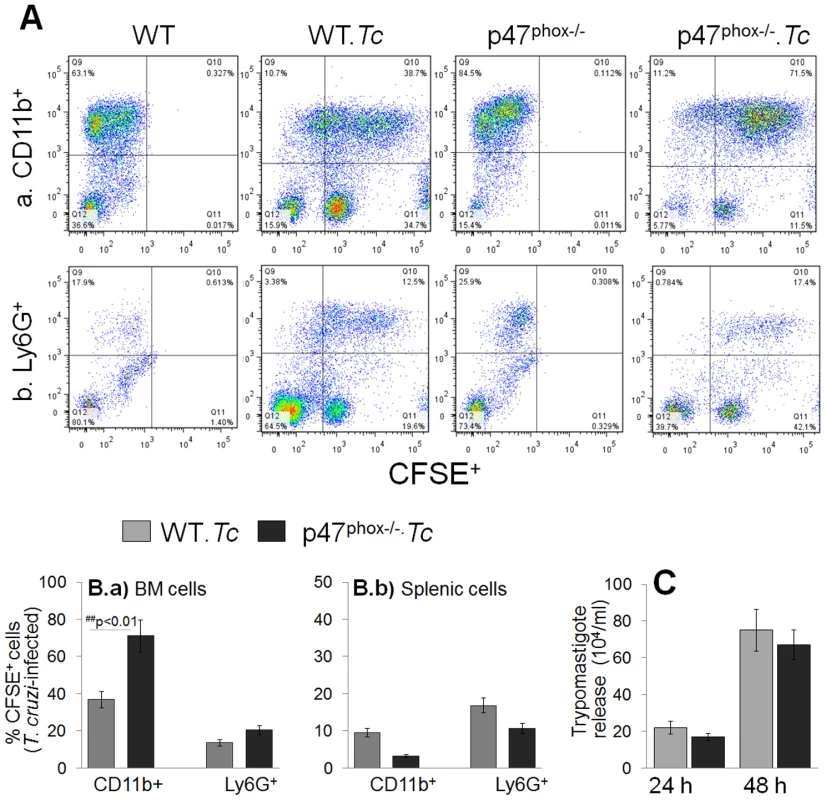
(A) Bone marrow (BM) and splenic cells were isolated from WT and p47phox−/− mice and in vitro incubated for 24 h with CFSE-labeled T. cruzi followed by 30 min with fluorescence conjugated anti-CD11b (macrophage marker) and anti-Ly6G (neutrophil marker) antibodies. The antibody-labeled cells were fixed, and analyzed by flow cytometry. Representative flow cytometry analyses of BM cells infected with CFSE-labeled T. cruzi are shown. (B) Bar graphs of the percentage of BM (Ba) and splenic (Bb) cell populations (CFSE+CD11b+: infected macrophages, CFSE+Ly6+: infected neutrophils). Data are derived from 3 independent experiments. (C) Supernatants of infected splenic monocytes were monitored for parasite release at 24 h and 48 h post-incubation by light microscopy. Data are presented as mean ± SD and significance presented as *normal-versus-infected, #WT/infected-versus-p47phox−/−/infected (*, #p<0.05, **,##p<0.01. In vitro functional activation of p47phox−/− macrophages in response to T. cruzi
Macrophages control the invading pathogen through production of ROS, NO, and inflammatory cytokines. Isolated BM and splenic monocytes from WT and p47phox−/− mice were incubated for 0, 6, 12 and 24 h with T. cruzi (± recombinant IFN-γ). We measured ROS levels using H2DCFDA that is cell permeable and when oxidized by ROS, releases fluorescent DCF. A gradual increase in DCF fluorescence beginning at 6 h that reached the maximal level at 24 h pi was observed in WT macrophages. Macrophages from WT mice responded to T. cruzi infection (± rIFN-γ) by 5-fold increase in DCF fluorescence (Fig. 3A.a). The p47phox−/− splenic macrophages (±rIFN-γ) exhibited 2.5-fold lesser DCF fluorescence in response to T. cruzi when compared to that noted in infected/WT cells (Fig. 3A.a, ##p<0.01). Likewise, the p47phox−/− BM macrophages (± rIFN-γ) exhibited a 2-fold decline in ROS levels as compared to that noted in WT BM macrophages upon T. cruzi infection. The superoxide-dependent formation of formazan blue crystals was noted to be significantly increased in WT and slightly increased in p47phox−/− splenic macrophages incubated for 24 h with T. cruzi (Fig. 3A.b). T. cruzi-induced increase in DCF fluorescence and nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) reduction was quenched by >90% when cells were incubated in presence of 0.5 mM apocynin (inhibits NADPH oxidase activity) or 10 µM N-acetyl cysteine (ROS scavenger), suggesting the observed increase in ROS is primarily due to NOX-dependent ROS from infected macrophages. The iNOS mRNA level, determined by qRT-PCR, was increased by 4-fold in p47phox−/− splenocytes as compared to that noted in WT controls, infected in vitro for 24 h (Fig. 3B). The release of cytokines in supernatants of primary BM and splenic cells incubated with T. cruzi for 24 h was measured by an ELISA. The p47phox−/− BM and splenic cells responded to T. cruzi by >10-fold increase in IFN-γ and TNF-α release that was significantly higher than that observed in infected/WT cells (Fig. 3C). Together the data presented in Fig. 3 suggested that p47phox−/− macrophages lacked the ability to mount a strong NOX2-dependent ROS; however, exhibited a higher extent of iNOS and proinflammatory cytokine expression in response to T. cruzi infection. The p47phox−/− monocytes/macrophages also responded to heat-inactivated T. cruzi with a strong proinflammatory cytokines production.
Fig. 3. In vitro functional activation of p47phox−/− macrophages in response to T. cruzi infection. 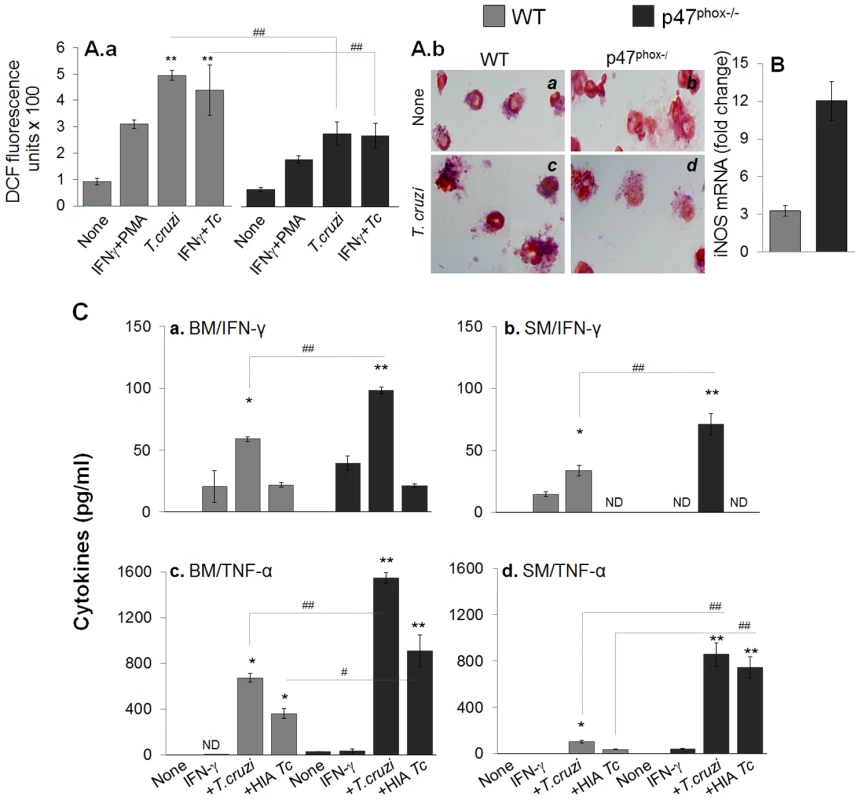
(A&B) Isolated splenocytes from WT and p47phox−/− mice were in vitro infected with live or heat-inactivated (HIA) T. cruzi for 24 h (± IFNγ). Cells incubated with phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) were used as positive controls. (A.a) H2DCFDA oxidation by intracellular ROS was monitored by fluorimetry. (A.b) Nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) reduction to formazan blue crystals by cellular superoxide was visualized by light microscopy. (B) RT-PCR quantitation of iNOS mRNA level. (C) BM (panels a&c) and splenic (panels c&d) cells were stimulated with IFN-γ, washed, and then exposed to T. cruzi (live or heat-inactivated) for 24 h. The release of IFN-γ (panels a&b) and TNF-α (panels c&d) in supernatants was monitored by an ELISA. ND: not detectable. Tissue inflammatory infiltrate in p47phox−/− mice infected by T. cruzi
To further gain an indication of the effects of phagocytes' NOX2 deficiency on host immunity to T. cruzi; we looked at the tissue infiltration of immune cells in T. cruzi infected WT and p47phox−/− mice by histological studies (Fig. 4, Fig. S2, and Table 1). The p47phox−/− mice injected with 2000 parasites exhibited infiltration of inflammatory infiltrate in skeletal muscle and heart tissue as early as day 7 post-infection (pi, Fig. 4.e, Table 1). The inflammatory foci were observed in all tissue sections by 14 days pi (score: 2), and extensive inflammation with large inflammatory foci or diffused inflammation throughout the tissue section (score: 2–4) was observed at 21–30 days pi in skeletal muscle (Fig. 4.f–h) and heart tissue (Fig. S1.m–o) of p47phox−/− mice. In WT mice, infection with 2000 parasites resulted in minimal inflammation of the skeletal muscle (Fig. 4.a&b) and heart tissue (Table 1) at 7–14 days pi; and inflammatory infiltrate was moderately increased (score: 1–2) at 21–30 days pi (Fig. 4.c&d, Table 1). These data suggested that p47phox−/− mice responded to T. cruzi infection (2000 parasites/mouse) with an increase in tissue infiltration of inflammatory infiltrate that was higher than that observed in WT mice given the same dose of parasites. Infection with a 5-fold higher dose of parasites was required to elicit the extent of increase in inflammatory infiltrate in skeletal muscle (score: 2–4, Fig. S1.d&e) and heart tissue (score: 1–2, Fig. S1.i&j) of WT mice as was noted in skeletal muscle and heart tissue of p47phox−/− mice infected with 2,000 parasites.
Fig. 4. Histological analysis of inflammatory infiltrate in T. cruzi-infected p47phox−/− mice. 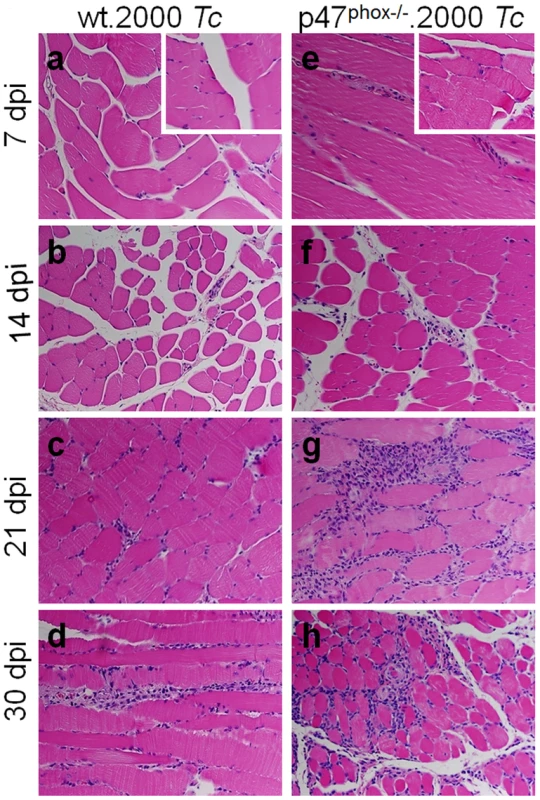
Shown are representative images of H&E staining (blue: nuclear, pink: muscle/cytoplasm/keratin) of skeletal muscle sections from WT (panels a–d) and p47phox−/− (panels e–h) mice infected with T. cruzi (2000 parasites/mouse), and harvested at day 7 (a&e), 14 (b&f), 21 (c&g), and 30 (d&h) post-infection. H&E stained images from normal mice are shown as insets in panels a and e (magnification: 40×). Functional response of splenocytes and BM cells in p47phox−/− mice infected with T. cruzi
To examine the quality of inflammatory response in vivo, WT and p47phox−/− mice were harvested at day 7, 14, 21, and 30 post-infection. BM and splenic cells from infected mice were either directly analyzed or in vitro stimulated in presence of T. cruzi trypomastigote lysate (TcL) and utilized for functional assessment. Shown in Fig. 5A are intracellular ROS levels in splenic cells of infected mice at day 30 pi, determined by dihydroethidium (DHE) fluorescence. DHE is cell permeable, and when oxidized to ethidium, accumulates in nuclei and fluoresces bright red. We noted a significant increase in ethidium fluorescence in splenocytes of infected/WT, but not of infected/p47phox−/− mice, at all time-points pi (Fig. 5A.a&b). Likewise, BM cells isolated at day 7, 14, 21, and 30 from infected/WT mice, but not from infected/p47phox−/− mice, exhibited a significant increase in DHE fluorescence. DHE fluorescence was quenched when cells were incubated in presence of 0.5 mM apocynin (NOX2 inhibitor). Note that 4′-6-diamidino-2-phenylindole-dihydrochloride (DAPI, binds nuclear DNA) staining of the splenocytes (Fig. 5A.c&d) of infected/WT and infected/p47phox−/− mice was comparable.
Fig. 5. In vivo ROS, nitric oxide, and cytokine profile in p47phox−/− mice infected with T. cruzi. 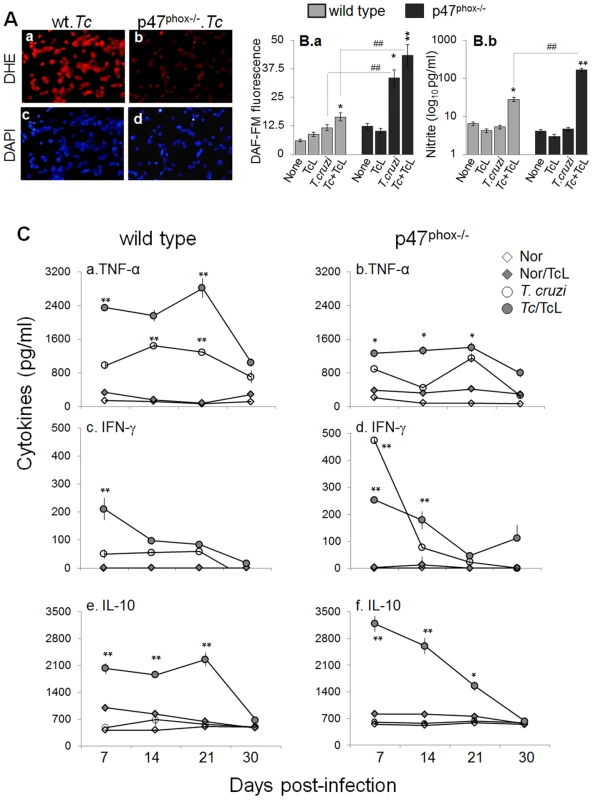
Mice (WT and p47phox−/−) were infected with T. cruzi as described in Materials and Methods. (A) Splenic single cell population from infected mice (30 dpi) were cyto-spinned on glass slides. Shown is fluorescence staining for dihydroethidium (measures intracellular ROS, binds DNA). Cells stained with DAPI (binds nuclei, blue) are shown as controls. (B) Splenocytes were harvested from T. cruzi-infected mice at day 30 pi, and in vitro incubated for 24 h (± TcL). Shown is intracellular nitric oxide (panel a) and nitrite levels in the supernatant (panel b), determined by using DAF-FM staining/fluorimetry and Griess reagent assay, respectively. (C) Splenocytes were harvested from infected mice at day 7, 14, 21, and 30 post-infection, and incubated in vitro (± TcL) for 48 h. Shown are the TNF-α (a&b), IFN-γ (c&d) and IL-10 (e&f) levels in cell-free supernatants, determined by an ELISA. ND: not detectable. The intracellular nitric oxide levels in BM and splenic cells harvested at day 7, 14, 21 and 30 pi was first determined by DAF-FM-based fluorimetry. DAF-FM is cell permeable, and forms fluorescent benzotriazole upon reaction with nitric oxide. Shown in Fig. 5B.a are arbitrary units of DAF-FM fluorescence in splenic cells of infected mice harvested at day 30 pi. Our data showed a 4-fold increase in DAF-FM fluorescence in splenocytes of infected/p47phox−/ − mice that was further increased upon in vitro stimulation with TcL. In comparison, splenic cells of infected/WT mice exhibited a significant increase in intracellular nitric oxide (DAF-FM fluorescence) only after secondary in vitro stimulation with TcL, and this response was ∼3-fold lesser than that observed with splenocytes of infected/p47phox−/ − mice (Fig. 5B.a). Because DAF-FM may exhibit non-specific signal by reacting with N compounds others than nitric oxide, we also performed a Griess reagent assay to evaluate the nitric oxide production rate, reflected by nitrite release. Splenocytes of infected/p47phox−/− mice, in vitro stimulated with TcL, exhibited a robust increase in nitrite release that was >5.8-fold higher than that noted with splenic cells from infected/WT mice (Fig. 5B.b). Likewise, BM monocytes of infected/p47phox−/− mice responded to in vitro antigenic stimulus (TcL) by a robust 7-fold and 8-fold increase in DAF-FM fluorescence and nitrite release, respectively. The extent of TcL-stimulated nitrite release was 4-fold (32.8±4.7 versus 8.07±0.6 pg nitrite/ml) higher in BM cells of infected/p47phox−/− mice than that noted in BM cells of infected/WT mice (##p<0.001). In all experiments, incubation of splenic or BM monocytes from infected mice with 5 µmol/ml L-NAME (inhibits iNOS activity/nitric oxide) abolished the DAF-FM fluorescence and nitrite release.
To examine the in vivo cytokine profile in response to infection, BM and splenic cells from WT and p47phox−/− mice were harvested at 7, 14, 21, and 30 days pi, in vitro incubated with or without second antigenic stimulus for 48 h, and supernatants were submitted to an ELISA. Overall, splenocytes of WT and p47phox−/− mice (± T. cruzi lysate) were activated early upon infection, as is evidenced by a significant increase in TNF-α, IFN-γ and IL-10 levels at day 7 pi (Fig. 5C). No IL-4 release was observed. The splenocytes of infected/WT mice exhibited a predominance of TNF-α (TNF-α>IL-10>IFN-γ) release throughout the course of infection (Fig. 5C.a,c,e). In comparison, splenocytes of infected/p47phox−/− mice (± TcL) exhibited a mixed response with a predominance of IL-10 (IL-10>TNF-α>IFN-γ) at 7, 14, 21 and 30 days post-infection (Fig. 5C.b,d,f). The BM cells of WT and p47phox−/− mice infected with T. cruzi (±TcL) exhibited a similar pattern of cytokine response as was noted in splenocytes. Together, the data presented in Fig. 5 suggested that compromised ROS production capacity due to NOX2 deficiency was compensated by an increased iNOS and nitric oxide levels in p47phox−/− mice infected with T. cruzi. However, p47phox−/− mice exhibited a subdued proinflammatory cytokine response (IL-10>TNF-α) during T. cruzi infection.
Characterization of T cell response in p47phox−/− mice infected by T. cruzi
CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are important constituents of the adaptive immunity against T. cruzi. To gain an appreciation for the role of NOX2 in determining T cell functional profile, we evaluated the in vivo quality and potency of the cellular immune responses elicited in WT versus p47phox−/− mice. Splenocytes, harvested at 30 days post-infection, were incubated in presence and absence of TcL antigenic stimulus, and T cell proliferation determined by an MTT assay (Fig. 6A). The CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were examined for proliferative capacity (Ki67+), intracellular cytokine profile (IFN-γ, TNF-α) and marker of lytic capacity (CD107a) by flow cytometry. The mean fluorescence intensity (±SD) indicative of T cell profile (Fig. 6B, n = 6/group) were derived from representative quadrant images of flow cytometry results presented in Fig. 6C. Splenic lymphocytes of WT mice exhibited 3.6–4.2-fold increase in proliferation in response to T. cruzi infection (± in vitro stimulation with TcL, Fig. 6A). In comparison, p47phox−/− mice exhibited a ∼40% lower rate of splenic lymphocyte proliferation in response to T. cruzi infection, and no effect of in vitro stimulation with TcL was noted (Fig. 6A, ##p<0.01).
Fig. 6. The p47phox−/− mice lacked the ability to develop CD8+T cell response to T. cruzi infection. 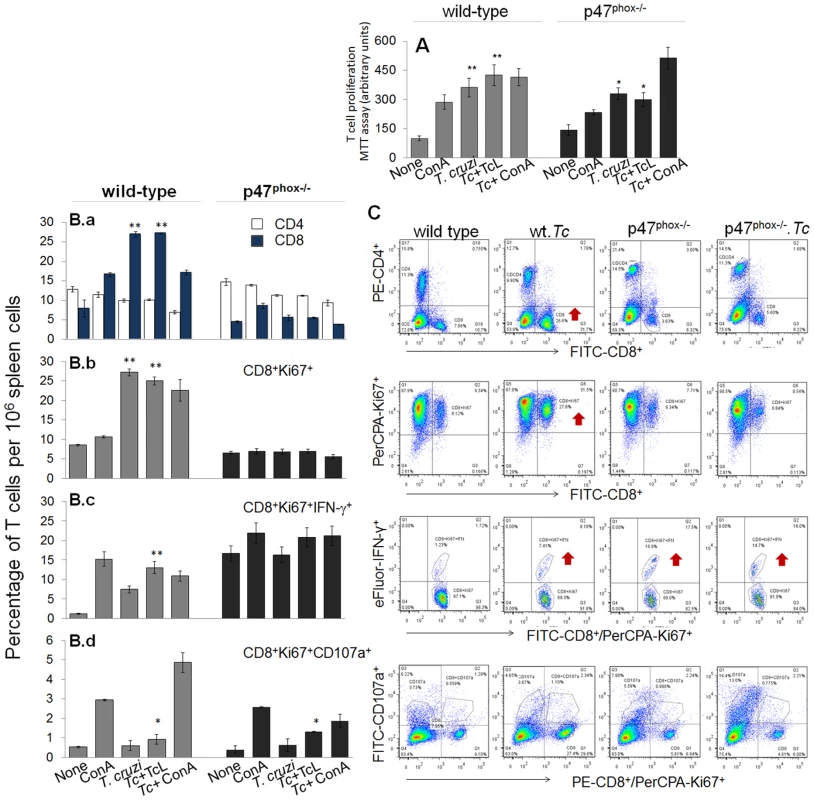
Mice were infected with T. cruzi, and harvested at day 30 pi. Splenocytes were in vitro incubated for 48 h in presence or absence of TcL as 2nd antigenic stimulus (controls: concanavalin A). (A) Cell proliferation determined by an MTT assay. (B&C) After in vitro stimulation (±TcL), splenocytes from infected mice were labeled for 30-min with fluorescent- conjugated specific antibodies as described in Materials and Methods, and analyzed by flow cytometry. Splenic frequency of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (B.a) are shown. Shown are also the mean percentage of CD8+ T cells that were Ki67+ (PerCPCy 5.5, B.b), IFN-γ+ (e-Fluor, B.c), and CD107a+ (PerCPA, B.d). Representative quandrant images of flow cytometry analysis of T cell subsets are shown in (C). When we performed the specific T cell population analysis, we found that in vivo population of CD4+T cells was comparable in naïve WT and p47phox−/− mice (range: 12–14%, Fig. 6B.a), and exhibited no significant change in proliferation (Ki67+) or IFN-γ+ phenotype in response to T. cruzi infection or subsequent incubation with TcL antigenic lysate. Instead, in vivo percentage of CD8+T cells in p47phox−/− naïve mice (4.5%) was ∼2-fold lower than that noted in WT normal controls (7.9%) (Fig. 6B.a). In response to T. cruzi infection, CD8+T cells expanded by 3.4-fold in WT mice (27% of total) while these cells expanded at a very low frequency in p47phox−/− mice (Fig. 6B.a). Functional characterization of CD8+T cells showed that a majority of the CD8+T cells were proliferative (Ki67+) in infected/WT mice (Fig. 6B.b) and a significant proportion of the CD8+Ki67+ cells (up to 13%) produced IFN-γ in an antigen-specific manner (Fig. 6B.c). In p47phox−/− mice, CD8+T cells exhibited no significant proliferating phenotype in response to T. cruzi infection (Fig. 6B.b). Further, up to 16% of the CD8+T cells exhibited IFN-γ+ phenotype in naïve p47phox−/− mice and these didn't increase in response to T. cruzi infection or second antigenic stimulation with TcL (Fig. 6B.b).
Transport of CD107a and CD107b to the plasma membrane of effector T cells is required for a) the cytolytic activity mediated by perforin and granzymes and b) the release of IFN-γ which exerts pleiotropic effects to suppress intracellular pathogens. Our data showed T. cruzi infection induced CD107a+CD8+T cells (2–4%) in infected/p47phox−/− mice (Fig. 6B.d), and a majority of these exhibited dual-positive (CD107a+IFN-γ+) cytolytic phenotype, comparable to that noted in infected/WT mice. Together, the data presented in Fig. 6 suggested that splenic CD8+T cells in p47phox−/− mice were low in number and failed to expand in response to T. cruzi infection, resulting in a substantial decline in proliferating, IFN-γ-producing cytolytic CD8+T cell response. In comparison, an expansive CD8+T cells proliferation that were predominantly IFN-γ+ with cytolytic capacity, and, thus, had a potential to act as effector T cells was induced in WT mice infected by T. cruzi.
Discussion
The present study shows that in the absence of NOX2 activity, a defective activation of CD8+T cell occurs, and contributes to the inability of mice to successfully control T. cruzi infection. Our data suggested that the NOX2 deficiency was compensated by enhanced levels of iNOS, nitric oxide, and inflammatory cytokines in macrophages; however, p47phox−/− mice were highly susceptible to T. cruzi because of the inability to activate a type 1 CD8+T cell response that is known to be essential for intracellular parasite control. Our study highlights how redox state of innate immune cells alters the adaptive immunity to intracellular pathogens, and understanding the molecular and cellular mechanisms affected by redox state of immune cells at basal level could be exploited in designing future vaccination strategies against T. cruzi infection and Chagas disease.
Current literature demonstrates that macrophage-derived free radicals (O2•−, nitric oxide) generated by the NOX2 complex and iNOS participate in cytotoxic mechanisms against microorganisms (reviewed in [21][22]). In the context of T. cruzi, it is suggested that nitric oxide plays a central role through its action on macrophage-derived peroxynitrite formation, a strong cytotoxic oxidant that is formed by the reaction of nitric oxide with O2•− [14], [23], [24]. Our in vitro studies showed that p47phox−/− monocytes were better than (or equal to) the WT controls in their ability to differentiate into macrophages and phagocytize parasites (Fig. S1). Though it appeared that a higher number of intracellular parasites were present in infected p47phox−/− macrophages at 24 h pi (Fig. S1 & Fig. 2); however, the extent of parasite release from p47phox−/− cells at 24 and 48 h pi was comparable to that noted in WT controls (Fig. 2C), thus suggesting that NOX2 deficiency did not result in increased parasite survival in infected macrophages. Our observations are supported by others demonstrating the enhanced replication of bacteria (e.g. Coxiella burnetii) in p47phox−/− macrophages, that was followed by a slightly delayed control of infection at a rate similar to the WT macrophages [25]. We propose that p47phox−/− macrophages, despite a lack of NOX2/ROS, were equipped to phagocytize and control the parasites through compensatory mechanisms. One, a low but detectable level of O2•− production in p47phox−/− macrophages (Fig. 3A&B) was sufficient to support the nitric oxide mediated cytotoxic peroxynitrite formation for parasite killing. Indeed, O2•− and nitric oxide can rapidly diffuse (diffusion control rates: ∼1010 m−1 s−1) and react to form peroxynitrite that is significantly more potent cytotoxin against trypomastigotes than H2O2 only [13], [14]. Secondly, a significant up regulation of the iNOS, nitric oxide and inflammatory cytokines (IFN-γ/TNF-α) in p47phox−/− macrophages in response to T. cruzi infection (Fig. 3) could have controlled the infectious pathogen. Others have also demonstrated increased iNOS and nitric oxide levels in gp91phox−/− mice infected by T. cruzi [26]. We surmise that in the event of defects in mounting NOX2/ROS, macrophages are capable of using alternative, compensatory mechanisms for pathogen control. Further studies will be required to conclusively establish if the peroxynitrite formation rate is indeed enhanced and identify the signaling mechanisms that were up regulated resulting in enhanced iNOS and inflammatory cytokines' expression in p47phox−/− macrophages in response to T. cruzi infection.
The production of cytokines (IL-12, TNF-α) by innate immune cells (macrophages, dendritic cells (DCs) shapes the adaptive immunity via activation of T cells. CD4+ and CD8+ T cells producing type 1 cytokines and CD8+T cell mediated cytolytic activity are required for control of T. cruzi infection (reviewed in [6], [16], [27]. Our observation of increased release of IFN-γ/TNF-α by p47phox−/− macrophages in vitro infected with T. cruzi (Fig. 3) suggest that NOX2/ROS might control the cytokinopathy via regulating the cytokine gene expression; however, NOX2 deficiency did not inhibit the phagocytes ability to provide inflammatory cytokine milieu for the recruitment and activation of T cells. Indeed flow cytometry analysis showed the CD4+T cells in p47phox−/− mice responded to T. cruzi infection and/or in vitro antigenic stimulus by activation and proliferation to a similar extent as was noted in WT mice (Fig. 6). Others have shown that IFN-γ/LPS-treated p47phox−/− mice secrete more IL-12 from DCs than similarly treated WT mice, and IFNγ/LPS matured p47phox−/− DCs biased more ovalbumin-specific CD4+T cells toward a Th1 phenotype than the WT controls in a ROS-dependent manner [28]. It is also suggested that CD4+ T cells from p47phox deficient mice exhibit augmented IFN-γ and diminished IL-4 production and an increased ratio of expression of T-bet (Th1-specific transcription factor) versus GATA-3 (Th2-specfic transcription factor), consistent with a Th1 skewing of naïve T cells [29]. Selective inhibition of TCR-induced STAT5 phosphorylation was identified as a potential mechanism for skewed helper CD4+T cell differentiation in p47phox−/− mice [29]. We surmise that p47phox-dependent NOX2 deficiency enhanced the macrophage maturation and inflammatory cytokine response; and provided help for CD4+ T cell activation in the context to T. cruzi infection in p47phox−/− mice. Yet, early splenic response to T. cruzi infection (7 days pi) in p47phox−/− mice was dominated by type 2 cytokines evidenced by a >2-fold decline in splenic TNF-α production and ∼2-fold increase in IL-10 release when compared to that noted in infected/WT controls, and likely responsible for susceptibility to T. cruzi infection (Fig. 5).
The phenotypic and functional characterization of CD8+T cells in p47phox−/− mice provides clues to the cellular mechanisms contributing to increased susceptibility to T. cruzi infection. It was intriguing to find that splenocytes from p47phox−/− mice, as compared to WT controls, contained ∼40% lower number of naïve CD8+ T cells. Further, CD8+T cells in p47phox−/− mice exhibited no proliferation and activation evidenced by none-to-minimal increase in cell frequency overall or the frequency of IFNγ+, CD107+ or IFNγ+CD107+ CD8+T cells in response to T. cruzi infection and secondary in vitro stimulation with antigenic lysate (Fig. 6). Others have shown that T∶ B cell ratio is lower in p47phox−/− mice as compared to the WT mice [30] and the CD8+T cells from p47phox−/− mice express higher levels of pro-apoptotic Bim and Puma proteins that promoted their removal by apoptosis [31]. Since FOXO3 dephosphorylation (activation) by protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) is known to contribute to transcriptional control of various apoptosis factors including pro-apoptotic Bim, blocking the PP2A activity attenuated the FOXO3 activation and Bim transcription and prolonged the survival of CD8+T lymphocytes in p47phox−/− mice [31]. These studies suggest that p47phox deficiency adversely affects the development and survival of naive CD8+T cells. Additionally, treatment with apocynin that suppresses ROS production by NOX2 directly inhibited the production of proinflammatory cytokines (e.g. TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-2) in anti-CD3/anti-CD28-stimulated CD8+T cells. It is proposed that apocynin effects were mediated via attenuation of anti-CD3/anti-CD28-induced NF-κB activation in CD8+T cells [32]. The compromised CD8+T cell activation was not likely due to inefficient antigen presentation as p47phox−/− dendritic cells are shown to be highly efficient in presentation of antigen to B cells in the context of antibody response to Streptococcus and Listeria infection [33]. Others have shown p47phox−/− DCs elicit enhanced ovalbumin-specific CD4+ T lymphocytes [28]. Further studies will be required to delineate the complex role of p47phox in antigen presentation by DCs, CD8+T lymphocytes survival and ROS-dependent mechanisms involved in NF-κB activation in cell-dependent manner. However, the literature discussed above and our findings allow us to surmise that compromised development of splenic CD8+T cells and their inability to respond to antigenic stimulus by generation of IFN-γ and cytolytic activity contributed to high tissue parasite burden in p47phox−/− mice.
It is important to note that the components of NADPH oxidase have diverse effects in heart failure. For example, the survival rate of p47phox−/− mice 4-weeks after myocardial infarction (MI) was significantly higher than that of WT mice (72% versus 48%) and the survival benefits were associated with a decline in LV dilatation and dysfunction, cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, apoptosis, and interstitial fibrosis in p47phox−/− mice [34]. Others have suggested the loss of p47phox enhanced the susceptibility to heart failure. Patel et al [35] showed that the expression of N-cadherin and β-catenin was up regulated in p47phox−/− mice subjected to biomechanical stress; however, actin filament cytoskeleton was disrupted because these mice lacked the ability to induce p47phox dependent cortactin-N-cadherin interaction required for adaptive cytoskeletal remodeling. In comparison, gp91phox−/− mice exhibited no increase in susceptibility to pressure overload and were equally capable of adaptive cytoskeletal modeling as was noted in controls. In the context of T. cruzi infection, Santiago et al [26] showed that gp91phox−/− mice develop increased circulatory collapse and succumbed to infection. Authors proposed that while a lack of superoxide from phagocytes was not detrimental in hosts' ability to control parasites, superoxide regulates nitric oxide concentrations, and enhanced nitric oxide levels in these mice resulted in a critical drop in blood pressure. These studies suggest that targeting NADPH oxidase system as a potential novel therapeutic target to prevent cardiac failure should be considered with caution.
In summary, we present the first evidence that NOX2/ROS of macrophage origin shapes the T cell-mediated adaptive immunity, and its deficiency results in compromised CD8+T cell response to T. cruzi infection. Our data show that macrophages from p47phox−/− mice were not compromised in the phagocytic activity and showed an enhanced iNOS/nitric oxide and pro-inflammatory cytokine levels in response to T. cruzi infection. However, in the event of NOX2 deficiency, generation and activation of CD8+T cell response was compromised, leading to increased parasite burden, tissue pathogenesis and mortality. We propose that future studies focused on understanding how NOX2/ROS induced innate receptor signaling pathways govern the activation and proliferation of T cell subsets will have the potential to identify specific targets for modulating the adaptive immunity and prevent T. cruzi infection and persistence in Chagas disease.
Materials and Methods
Ethics statement
All animal experiments were conducted following NIH guidelines for housing and care of laboratory animals and in accordance with The University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston in accordance with protocols approved by the institution's Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (protocol number 08-05-029).
Parasites and mice
T. cruzi trypomastigotes (SylvioX10/4 strain) were maintained and propagated by continuous in vitro passage in C2C12 cells. C57BL/6 mice (WT and p47phox−/−) were purchased from Jackson Laboratory (Sacramento, CA). Mice (8-weeks-old) were infected with T. cruzi (2,000 or 10,000 trypomastigotes/mouse, intra-peritoneal). Survival from infection was monitored daily. Mice were sacrificed at day 7, 14, 21, and 30 post-infection (pi), and sera/plasma and tissue samples were stored at 4°C and −80°C, respectively.
Western blotting
Bone marrow (BM) and splenic monocytes/macrophages, and heart and skeletal tissue were washed with ice-cold Tris-buffered saline (TBS), and homogenized in lysis buffer (tissue∶ buffer ratio, 1∶10, w/v). Homogenates (30-µg protein) were resolved on denaturing 10% acrylamide gels. Proteins were transferred to PVDF membranes, and probed with anti-p47phox primary antibody (1∶1000, Santa Cruz, Dallas TX) for 24 h at 4°C. Membranes were washed with TBS containing 0.1% Tween-20 and TBS, incubated with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibody, and signal was developed by using a chemiluminiscence detection system (GE-Healthcare, Piscataway, NJ) [36].
Tissue parasite burden
Skeletal muscle and heart tissues (50 mg) were subjected to Proteinase K lysis, and total DNA purified by phenol/chloroform extraction and ethanol precipitation method. Total DNA (100 ng) was used as a template in a PCR reaction for 28 cycles with oligonucleotides specific for T. cruzi 18S rDNA sequence (Forward: 5′-TAGTCATATGCTTGTTTC-3′, Reverse: 5′-GCAACAGCATTAATATACGC-3′) [19]. Quantitative estimate of parasite burden was obtained by real-time PCR on an iCycler thermal cycler with SYBR Green Supermix and Tc18S-sepecific oligonucleotides. Fold change was calculated as 2−ΔCt, where ΔCt represents the Ct (infected sample) - Ct (control) [20]. All data were normalized with host-specific GAPDH.
RT-PCR
Total RNA was isolated by using the RNeasy plus Kit (Qiagen), and analyzed for quality and quantity on a SpectraMax UV microplate reader. After reverse transcription of 2 µg RNA with poly(dT)18, first-strand cDNA was used as a template in a real-time PCR on an iCycler Thermal Cycler with SYBR-Green Supermix (Bio-Rad) and specific oligonucleotides for iNOS (5′-GTTTCTGGCAGCAGCGGCTC-3′ and 5′-GCTCCfTCGCTCAAGTTCAGC-3′) and GAPDH (5′-TGG CAA AGT GGA GAT TGT TG-3′ and 5′-TTC AGC TCT GGG ATG ACC TT-3′). The PCR Base Line Subtracted Curve Fit mode was applied for Threshold Cycle (Ct) and mRNA level measured by iCycler iQ Real-Time Detection Software (Bio-Rad). The threshold cycle (Ct) values for target mRNA were normalized to GAPDH mRNA, and the relative expression level of iNOS was calculated with the formula n-fold change = 2−ΔCt, where ΔCt represents Ct (iNOS) – Ct (GAPDH) [37].
Histology
Tissue sections were fixed in 10% buffered formalin for 24 h, dehydrated in absolute ethanol, cleared in xylene, and embedded in paraffin. Five-micron tissue-sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin, and evaluated by light microscopy using an Olympus BX-15 microscope equipped with a digital camera. In general, we analyzed each tissue-section for >10-microscopic fields (100× magnification), and examined three different tissue sections/mouse (4 mice/group) to obtain a semi-quantitative score of parasitic pseudocysts (foci). Myocarditis (presence of inflammatory cells) was scored as 0 (absent), 1 (focal or mild with ≤1 foci), 2 (moderate with ≥2 inflammatory foci), 3 (extensive with generalized coalescing of inflammatory foci or disseminated inflammation), and 4 (diffused inflammation with severe tissue necrosis, interstitial edema, and loss of integrity) [38]. Inflammatory infiltrates was characterized as diffused or focal depending upon how closely the inflammatory cells were associated [39].
Parasite uptake, intracellular replication, and release by macrophages
Splenic and BM monocytes from WT and p47phox−/− mice were isolated as described [39]. Monocytes were distributed in 24-well plates (105/well) incubated with T. cruzi trypomastigotes (live or heat-inactivated; cell: parasite ratio, 1∶3) for 0, 6, 12, and 24 h at 37°C, 5% CO2. In some experiments, monocytes were incubated with 5-µg/ml IFN-γ for 4 h before exposure to T. cruzi. Cells were submitted to Giemsa staining (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO), and parasite uptake and intracellular replication monitored in 200 randomly selected cells by light microscopy.
T. cruzi trypomastigotes were labeled with 5-µM carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE) fluorescent dye for 10 min, washed, and then incubated with splenocytes or BM monocytes (106 cells/well; cell: parasite ratio, 1∶3) for 4 h. Cells were labeled with AP-anti-CD11b (macrophage marker) or R-PE-anti-Ly6G (neutrophil marker) antibodies (0.5-µg/100-µl, e-Biosciences, San Diego, CA), fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde, and re-suspended in 100-µl PBS/1% BSA, and analyzed by flow cytometry.
Trypomastigotes release in supernatants of T. cruzi-infected macrophages after 24 h and 48 h incubation was counted under a light microscope by using a hemacytometer.
ROS production
Isolated primary monocytes from WT and p47phox−/− mice were in vitro exposed to T. cruzi for 0–24 h as above. Cells were incubated for 30 min with 5-µM CM-H2DCF-DA (detects intracellular ROS, Ex498 nm/Em598 nm) in Hank's Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS), and signal was monitored on a SpectraMax M5 microplate reader (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA). In some experiments, isolated primary monocytes from WT and p47phox−/− mice were in vitro exposed to T. cruzi for 24 h, and then incubated for 30 min with 0.1% nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT). NBT is a yellow water-soluble nitro-substituted aromatic tetrazolium compound that reacts with cellular superoxide ions to form water insoluble blue formazan crystals. Cells were counter-stained with safranin, and the percentage of NBT+ cells monitored by monitoring >200 randomly selected cells by light microscopy.
Mice (WT and p47phox−/−) were harvested at day 7–30 pi, and single cell suspension of splenic and BM cells were depleted of red blood cells by hypotonic lysis. Cells were cyto-spinned on glass slides (104 cells/slide), equilibrated in Kreb's buffer, and incubated with 5-µM dihydroethidium (DHE, detects intracellular ROS, Ex518 nm/Em605 nm) and images captured by fluorescence microscopy [40]. Cells stained with DAPI (stains all nuclei, blue) were used as controls. Splenocytes (106-cells/well/50 µl) were also incubated with APC-conjugated anti-CD11b antibody (e-Biosciences) and DHE, and macrophage-specific ROS production monitored by flow cytometry. All assays for monitoring the DCF or DHE fluorescence, NBT-based formazan crystal formation were performed in the presence and absence of 0.5 mM apocynin (NADPH oxidase inhibitor) to confirm the source of ROS.
Nitric oxide levels
Splenocytes of T. cruzi-infected mice (106-cells/well/100 µl) were incubated in presence or absence of T. cruzi antigenic lysate (TcL, 25-µg protein/well) for 24 h. TcL was prepared by subjecting parasites (1×109/ml PBS) to 5–6 freeze-thaw cycles followed by sonication on ice for 30-min. Cells were stained with 5-µM DAF-FM (detects intracellular nitric oxide), and florescence (Ex495 nm/Em515 nm) was monitored on a SpectraMax M5 microplate reader [41].
Nitrite level in supernatants of splenocytes, in vitro stimulated in presence or absence of TcL, was measured by Griess reagent assay. Briefly, supernatants were reduced with 0.01 unit/100 ml of nitrate reductase, and incubated for 10 min with 100 ml of 1% sulfanilamide made in 5% phosphoric acid/0.1% N-(1-napthyl) ethylenediamine dihydrochloride (1∶1,v/v). Formation of diazonium salt was monitored at 545 nm (standard curve: 2–50 mM sodium nitrite). DAF-FM fluorescence and Griess reagent assays were performed in presence and absence of 5 µmol/ml N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) that is an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase [42].
Cytokine release
Isolated primary splenocytes or BM monocytes were in vitro incubated with T. cruzi (live or heat-inactivated) for 48 h. The release of cytokines (IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-4, IL-10) in cell free supernatants was determined by using optEIA™ ELISA kits, according to the manufacturer's specifications (BD Biosciences (San Jose, CA).
For estimating splenic production of cytokines, infected mice were harvested at day 7, 14, 21 and 30 pi, and single cell suspension of splenocytes (106-cells/well/100 µl) incubated with media for 48 h (±TcL). Cytokine release was measured by an ELISA, as above.
Lymphocytes' proliferation, intracellular cytokine response and cytotoxicity
Single-cell splenocytes from WT and p47phox−/− mice harvested at day 30 pi were suspended in RPMI-5% FBS and distributed in 24-well plates (106 cells/well/200 µl). Cells were incubated in presence of Con A (5 µg/ml), or T cruzi trypomastigote lysate (TcL, 25-µg/ml) at 37°C, 5% CO2 for 48 h. The cell suspensions were utilized to measure the T cell proliferation by MTT assay [43].
To identify the T cell subsets in infected mice, splenocytes were incubated with or without (TcL), and then labeled for 30 min on ice with PE-Cy7-anti-CD3 (binds all T cells), FITC-anti-CD8 and PE-anti-CD4 antibodies (0.5–1 µg/100 µl, e-Biosciences). Following incubation, cells were fixed, washed and re-suspended in 100 µl PBS/2% BSA, and analyzed by flow cytometry [44].
To monitor the intracellular cytokine response, splenocytes were in vitro stimulated as above except that brefeldin A (10-µg/ml; Sigma) was added in the final 6 h to prevent protein secretion. Cells were labeled with PE-anti-CD4 and FITC-anti-CD8 antibodies, fixed, suspended in 100-µl permeabilization buffer (0.1% saponin/1% FBS in PBS) and then utilized for intracellular staining with e-Fluor-anti-IFN-γ, Cy5-anti-TNF-α and PerCP-PA-anti-Ki67 antibodies (0.5–2-µg/100-µl, e-Biosciences). Splenocytes were also incubated with Alexa-Fluor488-anti-CD107 antibody to determine the cytolytic activity of the activated/proliferating T cell subpopulations. Cells stained with isotype-matched IgGs were used as controls. Samples were visualized on a LSRII Fortessa Cell Analyzer by six-color flow cytometry, acquiring 30–50,000 events in a live lymphocyte gate, and further analysis performed using FlowJo software (ver.10.0.6, Tree-Star, San Carlo, CA) [44].
Data analysis
Data (mean ± SD) were derived from at least triplicate observations per sample (n≥8 animals/group). Normally distributed data (confirmed by Histogram and Q-Q plots) were analyzed by student's t-test (comparison of 2-groups) and 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey's post-hoc test (comparison of multiple groups). The level of significance is presented by * (normal-versus-infected) and # (WT-versus-p47phox−/−) (*, #p<0.05, **,##p<0.01).
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. HiguchiMD, BenvenutiLA, Martins ReisM, MetzgerM (2003) Pathophysiology of the heart in Chagas' disease: current status and new developments. Cardiovasc Res 60 : 96–107.
2. NagajyothiF, MachadoFS, BurleighBA, JelicksLA, SchererPE, et al. (2012) Mechanisms of Trypanosoma cruzi persistence in Chagas disease. Cell Microbiol 14 : 634–643.
3. TanowitzHB, WeissLM, MontgomerySP (2011) Chagas disease has now gone global. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 5: e1136.
4. TanowitzHB, MachadoFS, JelicksLA, ShiraniJ, de CarvalhoAC, et al. (2009) Perspectives on Trypanosoma cruzi-induced heart disease (Chagas disease). Prog Cardiovasc Dis 51 : 524–539.
5. MachadoFS, TylerKM, BrantF, EsperL, TeixeiraMM, et al. (2012) Pathogenesis of Chagas disease: time to move on. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 4 : 1743–1758.
6. MachadoFS, DutraWO, EsperL, GollobKJ, TeixeiraMM, et al. (2012) Current understanding of immunity to Trypanosoma cruzi infection and pathogenesis of Chagas disease. Seminars in Immunopathology 34 : 753–770.
7. PandayA, SahooMK, OsorioD, BatraS (2014) NADPH oxidases: an overview from structure to innate immunity-associated pathologies. Cell Mol Immunol doi:10.1038/cmi.2014.89 (Epub ahead of print)
8. BedardK, KrauseKH (2007) The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 87 : 245–313.
9. BatallerR, SchwabeRF, ChoiYH, YangL, PaikYH, et al. (2003) NADPH oxidase signal transduces angiotensin II in hepatic stellate cells and is critical in hepatic fibrosis. J Clin Invest 112 : 1383–1394.
10. CardoniRL, AntunezMI, MoralesC, NantesIR (1997) Release of reactive oxygen species by phagocytic cells in response to live parasites in mice infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. Am J Trop Med Hyg 56 : 329–334.
11. CardoniRL, RottenbergME, SeguraEL (1990) Increased production of reactive oxygen species by cells from mice acutely infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. Cell Immunol 128 : 11–21.
12. PiacenzaL, AlvarezMN, PeluffoG, RadiR (2009) Fighting the oxidative assault: the Trypanosoma cruzi journey to infection. Curr Opin Microbiol 12 : 415–421.
13. PineyroMD, ArcariT, RobelloC, RadiR, TrujilloM (2011) Tryparedoxin peroxidases from Trypanosoma cruzi: high efficiency in the catalytic elimination of hydrogen peroxide and peroxynitrite. Arch Biochem Biophys 507 : 287–295.
14. AlvarezMN, PeluffoG, PiacenzaL, RadiR (2011) Intraphagosomal peroxynitrite as a macrophage-derived cytotoxin against internalized Trypanosoma cruzi: consequences for oxidative killing and role of microbial peroxiredoxins in infectivity. J Biol Chem 286 : 6627–6640.
15. Vázquez-ChagoyánJC, GuptaS, GargNJ (2011) Vaccine development against Trypanosoma cruzi and Chagas disease. Advanced parasitol 75 : 121–146.
16. PadillaAM, BustamanteJM, TarletonRL (2009) CD8+ T cells in Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Curr Opin Immunol 21 : 385–390.
17. KotsiasF, HoffmannE, AmigorenaS, SavinaA (2013) Reactive oxygen species production in the phagosome: impact on antigen presentation in dendritic cells. Antioxid Redox Signal 18 : 714–729.
18. LamGY, HuangJ, BrumellJH (2010) The many roles of NOX2 NADPH oxidase-derived ROS in immunity. Semin Immunopathol 32 : 415–430.
19. GargNJ, PopovVL, PapaconstantinouJ (2003) Profiling gene transcription reveals a deficiency of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in Trypanosoma cruzi-infected murine hearts: implications in chagasic myocarditis development. Biochim Biophys Acta 1638 : 106–120.
20. GargNJ, BhatiaV, GerstnerA, deFordJ, PapaconstantinouJ (2004) Gene expression analysis in mitochondria from chagasic mice: Alterations in specific metabolic pathways. Biochemical J 381 : 743–752.
21. GutierrezFR, MineoTW, PavanelliWR, GuedesPM, SilvaJS (2009) The effects of nitric oxide on the immune system during Trypanosoma cruzi infection. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 104 Suppl 1 : 236–245.
22. Dupre-CrochetS, ErardM, NubetaeO (2013) ROS production in phagocytes: why, when, and where? J Leukoc Biol 94 : 657–670.
23. AlvarezMN, PiacenzaL, IrigoinF, PeluffoG, RadiR (2004) Macrophage-derived peroxynitrite diffusion and toxicity to Trypanosoma cruzi. Arch Biochem Biophys 432 : 222–232.
24. NaviliatM, GualcoG, CayotaA, RadiR (2005) Protein 3-nitrotyrosine formation during Trypanosoma cruzi infection in mice. Braz J Med Biol Res 38 : 1825–1834.
25. ParraM, PickettT, DeloguG, DheenadhayalanV, DebrieAS, et al. (2004) The mycobacterial heparin-binding hemagglutinin is a protective antigen in the mouse aerosol challenge model of tuberculosis. Infect Immun 72 : 6799–6805.
26. SantiagoHC, Gonzalez LombanaCZ, MacedoJP, UtschL, TafuriWL, et al. (2012) NADPH phagocyte oxidase knockout mice control Trypanosoma cruzi proliferation, but develop circulatory collapse and succumb to infection. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 6: e1492.
27. TarletonRL (2007) Immune system recognition of Trypanosoma cruzi. Curr Opin Immunol 19 : 430–434.
28. JendrysikMA, VasilevskyS, YiL, WoodA, ZhuN, et al. (2011) NADPH oxidase-2 derived ROS dictates murine DC cytokine-mediated cell fate decisions during CD4 T helper-cell commitment. PLoS One 6: e28198.
29. ShatynskiKE, ChenH, KwonJ, WilliamsMS (2012) Decreased STAT5 phosphorylation and GATA-3 expression in NOX2-deficient T cells: role in T helper development. Eur J Immunol 42 : 3202–3211.
30. DonaldsonM, AntignaniA, MilnerJ, ZhuN, WoodA, et al. (2009) p47phox-deficient immune microenvironment signals dysregulate naive T-cell apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 16 : 125–138.
31. LiuQ, YiL, Sadiq-AliS, KoontzSM, WoodA, et al. (2012) PP2A-dependent control of transcriptionally active FOXO3a in CD8(+) central memory lymphocyte survival requires p47(phox). Cell Death Dis 3: e375.
32. NamSJ, OhIS, YoonYH, KwonBI, KangW, et al. (2013) Apocynin regulates cytokine production of CD8 T cells. Clin Exp Med 14(3): 261–268.
33. VasilevskyS, LiuQ, KoontzSM, KastenmayerR, SheaK, et al. (2011) Role of p47phox in antigen-presenting cell-mediated regulation of humoral immunity in mice. Am J Pathol 178 : 2774–2782.
34. DoerriesC, GroteK, Hilfiker-KleinerD, LuchtefeldM, SchaeferA, et al. (2007) Critical role of the NAD(P)H oxidase subunit p47phox for left ventricular remodeling/dysfunction and survival after myocardial infarction. Circ Res 100 : 894–903.
35. PatelVB, WangZ, FanD, ZhabyeyevP, BasuR, et al. (2013) Loss of p47phox subunit enhances susceptibility to biomechanical stress and heart failure because of dysregulation of cortactin and actin filaments. Circ Res 112 : 1542–1556.
36. DhimanM, NakayasuES, MadaiahYH, ReynoldsBK, WenJJ, et al. (2008) Enhanced nitrosative stress during Trypanosoma cruzi infection causes nitrotyrosine modification of host proteins: implications in Chagas' disease. Am J Pathol 173 : 728–740.
37. WenJ-J, GuptaS, GuanZ, DhimanM, CondonD, et al. (2010) Phenyl-alpha-tert-butyl-nitrone and benzonidazole treatment controlled the mitochondrial oxidative stress and evolution of cardiomyopathy in chronic chagasic rats. J Am Coll Cardiol 55 : 2499–2508.
38. BartlettEJ, LenzoJC, SivamoorthyS, MansfieldJP, CullVS, et al. (2004) Type I IFN-beta gene therapy suppresses cardiac CD8+ T-cell infiltration during autoimmune myocarditis. Immunol Cell Biol 82 : 119–126.
39. DhimanM, GargNJ (2011) NADPH oxidase inhibition ameliorates Trypanosoma cruzi-induced myocarditis during Chagas disease. J Pathol 225 : 583–596.
40. WanX-X, GuptaS, ZagoMP, DavidsonMM, DoussetP, et al. (2012) Defects of mtDNA replication impaired the mitochondrial biogenesis during Trypanosoma cruzi infection in human cardiomyocytes and chagasic patients: The role of Nrf1/2 and antioxidant response. J Am Heart Assoc 1: e003855.
41. GuptaS, SilvaTS, OsizugboJE, TuckerL, SprattHM, GargNJ (2014) Serum mediated activation of macrophages reflects Tcvac2 vaccine efficacy against Chagas disease. Infect Immun 82(4): 1382–1389.
42. DhimanM, CoronadoYA, VallejoCK, PetersenJR, EjilemeleA, et al. (2013) Innate immune responses and antioxidant/oxidant imbalance are major determinants of human chagas disease. Plos NTD 7: e2364.
43. MosmannT (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65 : 55–63.
44. GuptaS, GargNJ (2013) TcVac3 induced control of Trypanosoma cruzi infection and chronic myocarditis in mice. Plos One 8: e59434.
Štítky
Hygiena a epidemiologie Infekční lékařství Laboratoř
Článek Selective Susceptibility of Human Skin Antigen Presenting Cells to Productive Dengue Virus InfectionČlánek Molecular Evolution of Broadly Neutralizing Llama Antibodies to the CD4-Binding Site of HIV-1
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Pathogens
Nejčtenější tento týden
2014 Číslo 12- Stillova choroba: vzácné a závažné systémové onemocnění
- Diagnostika virových hepatitid v kostce – zorientujte se (nejen) v sérologii
- Perorální antivirotika jako vysoce efektivní nástroj prevence hospitalizací kvůli COVID-19 − otázky a odpovědi pro praxi
- Jak souvisí postcovidový syndrom s poškozením mozku?
- Infekční komplikace virových respiračních infekcí – sekundární bakteriální a aspergilové pneumonie
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- Microbial Programming of Systemic Innate Immunity and Resistance to Infection
- Unique Features of HIV-1 Spread through T Cell Virological Synapses
- Measles Immune Suppression: Functional Impairment or Numbers Game?
- Cellular Mechanisms of Alpha Herpesvirus Egress: Live Cell Fluorescence Microscopy of Pseudorabies Virus Exocytosis
- Rubella Virus: First Calcium-Requiring Viral Fusion Protein
- Plasma Membrane-Located Purine Nucleotide Transport Proteins Are Key Components for Host Exploitation by Microsporidian Intracellular Parasites
- Selective Susceptibility of Human Skin Antigen Presenting Cells to Productive Dengue Virus Infection
- Loss of Dynamin-Related Protein 2B Reveals Separation of Innate Immune Signaling Pathways
- Intraspecies Competition for Niches in the Distal Gut Dictate Transmission during Persistent Infection
- Unveiling the Intracellular Survival Gene Kit of Trypanosomatid Parasites
- Extreme Divergence of Tropism for the Stem-Cell-Niche in the Testis
- HTLV-1 Tax-Mediated Inhibition of FOXO3a Activity Is Critical for the Persistence of Terminally Differentiated CD4 T Cells
- P47 Mice Are Compromised in Expansion and Activation of CD8 T Cells and Susceptible to Infection
- Hypercytotoxicity and Rapid Loss of NKp44 Innate Lymphoid Cells during Acute SIV Infection
- Molecular Evolution of Broadly Neutralizing Llama Antibodies to the CD4-Binding Site of HIV-1
- Crystal Structure of Calcium Binding Protein-5 from and Its Involvement in Initiation of Phagocytosis of Human Erythrocytes
- Chronic Parasitic Infection Maintains High Frequencies of Short-Lived Ly6CCD4 Effector T Cells That Are Required for Protection against Re-infection
- Specific Dysregulation of IFNγ Production by Natural Killer Cells Confers Susceptibility to Viral Infection
- HSV-2-Driven Increase in the Expression of αβ Correlates with Increased Susceptibility to Vaginal SHIV Infection
- Murine Anti-vaccinia Virus D8 Antibodies Target Different Epitopes and Differ in Their Ability to Block D8 Binding to CS-E
- Brothers in Arms: Th17 and Treg Responses in Immunity
- Granulocytes Impose a Tight Bottleneck upon the Gut Luminal Pathogen Population during Typhimurium Colitis
- A Negative Feedback Modulator of Antigen Processing Evolved from a Frameshift in the Cowpox Virus Genome
- Discovery of Replicating Circular RNAs by RNA-Seq and Computational Algorithms
- The Non-receptor Tyrosine Kinase Tec Controls Assembly and Activity of the Noncanonical Caspase-8 Inflammasome
- Targeted Changes of the Cell Wall Proteome Influence Ability to Form Single- and Multi-strain Biofilms
- Apoplastic Venom Allergen-like Proteins of Cyst Nematodes Modulate the Activation of Basal Plant Innate Immunity by Cell Surface Receptors
- The Toll-Dorsal Pathway Is Required for Resistance to Viral Oral Infection in
- Anti-α4 Antibody Treatment Blocks Virus Traffic to the Brain and Gut Early, and Stabilizes CNS Injury Late in Infection
- Initiation of ART during Early Acute HIV Infection Preserves Mucosal Th17 Function and Reverses HIV-Related Immune Activation
- Microbial Urease in Health and Disease
- Emergence of MERS-CoV in the Middle East: Origins, Transmission, Treatment, and Perspectives
- Blocking Junctional Adhesion Molecule C Enhances Dendritic Cell Migration and Boosts the Immune Responses against
- IL-28B is a Key Regulator of B- and T-Cell Vaccine Responses against Influenza
- A Natural Genetic Variant of Granzyme B Confers Lethality to a Common Viral Infection
- Neutral Sphingomyelinase in Physiological and Measles Virus Induced T Cell Suppression
- Differential PfEMP1 Expression Is Associated with Cerebral Malaria Pathology
- The Role of the NADPH Oxidase NOX2 in Prion Pathogenesis
- Rapid Evolution of Virus Sequences in Intrinsically Disordered Protein Regions
- The Central Role of cAMP in Regulating Merozoite Invasion of Human Erythrocytes
- Expression of Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1 (SOCS1) Impairs Viral Clearance and Exacerbates Lung Injury during Influenza Infection
- Cellular Oxidative Stress Response Controls the Antiviral and Apoptotic Programs in Dengue Virus-Infected Dendritic Cells
- SUMOylation by the E3 Ligase TbSIZ1/PIAS1 Positively Regulates VSG Expression in
- Monocyte Recruitment to the Dermis and Differentiation to Dendritic Cells Increases the Targets for Dengue Virus Replication
- Oral Streptococci Utilize a Siglec-Like Domain of Serine-Rich Repeat Adhesins to Preferentially Target Platelet Sialoglycans in Human Blood
- SV40 Utilizes ATM Kinase Activity to Prevent Non-homologous End Joining of Broken Viral DNA Replication Products
- Amphipathic α-Helices in Apolipoproteins Are Crucial to the Formation of Infectious Hepatitis C Virus Particles
- Proteomic Analysis of the Acidocalcisome, an Organelle Conserved from Bacteria to Human Cells
- Experimental Cerebral Malaria Pathogenesis—Hemodynamics at the Blood Brain Barrier
- PLOS Pathogens
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Plasma Membrane-Located Purine Nucleotide Transport Proteins Are Key Components for Host Exploitation by Microsporidian Intracellular Parasites
- Rubella Virus: First Calcium-Requiring Viral Fusion Protein
- Emergence of MERS-CoV in the Middle East: Origins, Transmission, Treatment, and Perspectives
- Unique Features of HIV-1 Spread through T Cell Virological Synapses
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Vladimír Palička, CSc., Dr.h.c., doc. MUDr. Václav Vyskočil, Ph.D., MUDr. Petr Kasalický, CSc., MUDr. Jan Rosa, Ing. Pavel Havlík, Ing. Jan Adam, Hana Hejnová, DiS., Jana Křenková
Autoři: MUDr. Irena Krčmová, CSc.
Autoři: MDDr. Eleonóra Ivančová, PhD., MHA
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Eva Kubala Havrdová, DrSc.
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



