-
Články
Top novinky
Reklama- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
Top novinky
Reklama- Kongresy
- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Top novinky
ReklamaExamination of Prokaryotic Multipartite Genome Evolution through Experimental Genome Reduction
Rhizobia are free-living bacteria of agricultural and environmental importance that form root-nodules on leguminous plants and provide these plants with fixed nitrogen. Many of the rhizobia have a multipartite genome, as do several plant and animal pathogens. All isolates of the alfalfa symbiont, Sinorhizobium meliloti, carry three large replicons, the chromosome (∼3.7 Mb), pSymA megaplasmid (∼1.4 Mb), and pSymB chromid (∼1.7 Mb). To gain insight into the role and evolutionary history of these replicons, we have ‘reversed evolution’ by constructing a S. meliloti strain consisting solely of the chromosome and lacking the pSymB chromid and pSymA megaplasmid. As the resulting strain was viable, we could perform a detailed phenotypic analysis and these data provided significant insight into the biology and metabolism of S. meliloti. The data lend direct experimental evidence in understanding the evolution and role of the multipartite genome. Specifically the large secondary replicons increase the organism's niche range, and this advantage offsets the metabolic burden of these replicons on the cell. Additionally, the single-chromosome strain offers a useful platform to facilitate future forward genetic approaches to understanding and manipulating the symbiosis and plant-microbe interactions.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Genet 10(10): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004742
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004742Summary
Rhizobia are free-living bacteria of agricultural and environmental importance that form root-nodules on leguminous plants and provide these plants with fixed nitrogen. Many of the rhizobia have a multipartite genome, as do several plant and animal pathogens. All isolates of the alfalfa symbiont, Sinorhizobium meliloti, carry three large replicons, the chromosome (∼3.7 Mb), pSymA megaplasmid (∼1.4 Mb), and pSymB chromid (∼1.7 Mb). To gain insight into the role and evolutionary history of these replicons, we have ‘reversed evolution’ by constructing a S. meliloti strain consisting solely of the chromosome and lacking the pSymB chromid and pSymA megaplasmid. As the resulting strain was viable, we could perform a detailed phenotypic analysis and these data provided significant insight into the biology and metabolism of S. meliloti. The data lend direct experimental evidence in understanding the evolution and role of the multipartite genome. Specifically the large secondary replicons increase the organism's niche range, and this advantage offsets the metabolic burden of these replicons on the cell. Additionally, the single-chromosome strain offers a useful platform to facilitate future forward genetic approaches to understanding and manipulating the symbiosis and plant-microbe interactions.
Introduction
While most bacterial genomes have only a single chromosome, many are more complex and consist of two or more large replicons. Depending on their characteristics, these replicons are classified as a chromosome (largest replicon containing most of the core genes), megaplasmid (laterally acquired with a plasmid origin of replication and lacking core genes), or a chromid (displays characteristics of both chromosomes and megaplasmids) [1]. While this genome organization is most commonly found in the proteobacteria, it is by no means limited to this class [2]. Interestingly, multipartite genomes are prevalent among plant symbionts (eg. Sinorhizobium and Rhizobium species) and plant and animal pathogens (eg. Agrobacterium, Vibrio, Burkholderia, and Brucella) [1], [2]. As such, understanding the general role and evolution of these accessory replicons may provide vital insight into the biology of these organisms and possible strategies to promote or suppress these interactions.
The potential advantages of multipartite genomes imply that this genome architecture is not simply an evolutionary peculiarity. For example, the division of a genome may decrease the time required for genome replication, potentially allowing more rapid growth. Indeed, multipartite genomes are larger on average [1] and some of the fastest replicating species have divided genomes [3]. However, each replicon within a divided genome is not of equal size [3] and there is no correlation between genome size and maximal growth rate [4]. Alternatively, multipartite genomes may provide a method of controlling gene dosage and thus expression, as in Vibrio species [3], [5]. This can consequently result in weaker purifying selection and greater rates of evolution on the smaller replicon, as observed in Vibrio and Burkholderia [6], [7]. However, this does not hold true for slow-replicating species with a divided genome [5]. A third hypothesis is that multipartite genomes allow for additional genome expansion once the chromosome reaches its maximal size [8]. Yet, some species with multipartite genomes have primary chromosomes smaller than 2.5 Mb, while some species with a single chromosome have genomes greater than 9 Mb [9], [10]. Moreover, Brucella species generally have two chromosome-like replicons, except for Brucella suis biovar 3, which has a single chromosome equivalent in size to the total of both replicons in related strains due to integration of one replicon into the other [11], [12]. While all three of the ideas discussed above may help promote the maintenance of a divided genome architecture once established, the observations inconsistent with each suggest they are unlikely to be general driving forces for multipartite genome evolution.
An alternative hypothesis is that multipartite genomes allow for the functional division of genes onto separate replicons [13]. Several lines of evidence are consistent with this idea: uneven COG distribution between each replicon such as in Burkholderia xenovorans [7] and Rhizobium etli [14], replicon-dependent evolution in Sinorhizobium meliloti [15], and replicon-dependent gene regulation in Vibrio cholerae [16] and S. meliloti [17]. Furthermore, an association exists between the presence of a divided genome and an interaction with a host organism [18]. This hypothesis implies that secondary replicons are over-represented in cellular processes specific to host interaction, which, if true, should focus the genetic analyses of these processes; however, the acceptance of this idea is limited due to a paucity of experimental support [1].
S. meliloti is a N2-fixing endosymbiont of legumes, and inhabits diverse environments including bulk soil, the rhizosphere, and the legume root nodule. It is an interesting organism to study the evolution of multipartite genomes as the large 6.7 megabase (Mb) genome of the model strain Rm1021 (and the highly related strain, Rm2011) is divided into a chromosome (∼3.7 Mb), an evolutionarily old and conserved chromid (pSymB; ∼1.7 Mb), and an evolutionarily recent and variable megaplasmid (pSymA; ∼1.4 Mb) [19]–[21]. Each of these is present in all wild-type isolates [20], [21], and there is no evidence that pSymA or pSymB are naturally lost by S. meliloti. This indicates that each replicon is a stable and indispensible part of the genome in the natural environment. Both pSymA and pSymB encode major pathways of interaction with the plant symbiont and the environment: exopolysaccharide biosynthesis and many ABC transporters are encoded by pSymB [22], and the nodulation and nitrogen fixation genes are present on pSymA [23]. The complete removal of pSymA has been described [24], and we now report the removal of pSymB and the construction of a strain lacking both pSymA and pSymB. This reduced genome provides a novel platform to facilitate forward genetic studies of rhizobium and bacterium-plant interactions, and we employed it here to experimentally test hypotheses surrounding the evolution and role of multipartite genomes.
Results/Discussion
S. meliloti forms N2-fixing root nodules on alfalfa and all wild-type S. meliloti isolates examined thus far carry replicons equivalent to pSymA and pSymB [20], [21]. Despite intensive investigation of S. meliloti over the past 40 years, there have been no reports of the successful removal of the pSymB chromid, with the earliest documented attempts published 25 years ago [25], [26]. The removal of pSymB as reported here was made possible through the application of several findings. First, the two essential genes (engA and tRNAarg) that are located on pSymB were integrated into the chromosome [27]. Second, an active toxin-antitoxin locus (smb21127/smb21128) on pSymB was removed through the introduction of a 234 kilobase deletion (ΔB180) [28]. And third, cells that failed to inherit the remaining 1.45 Mb of pSymB were recovered by selecting for the gain of a small plasmid carrying the incα incompatibility gene from the pSymB replication and partitioning repABC locus, rendering it incompatible with pSymB [29]. The latter transconjugants were obtained at a frequency of ∼10−4/recipient on LBmc medium containing excess cobalt, as the major S. meliloti cobalt uptake system (cbtJKL) is located on pSymB [30]. Additionally, using a similar procedure, pSymB was removed from a previously isolated strain lacking pSymA [24], resulting in cells with a genome consisting solely of the chromosome. For simplicity we refer to strains lacking pSymA, pSymB, or both, as ΔpSymA, ΔpSymB, or ΔpSymAB, respectively. The genomes of the parent and three cured strains were sequenced using an Illumina MiSeq and reads were aligned to the previously reported Rm1021 and Rm2011 genome sequences [19], [31] to confirm the absence of pSymA and/or pSymB sequences, as appropriate. The removal of pSymB is described in greater detail in the materials and methods.
Several other prokaryotic genome reduction studies have been reported in the past (e.g. Escherichia coli [32], Bacillus subtilis [33], and Rhizobium leguminosarum [34], [35], with the largest being a 38.9% (1.8 Mb) reduction of the E. coli genome [36]. The ΔpSymAB strain reported here lacks 3.04 megabases, 2866 genes, and 45.4% of the S. meliloti genome, and thus represents the largest genome reduction reported to date and includes the first complete removal of an essential chromid from a genome. The ΔpSymAB strain will facilitate new studies within a wide range of fields including refining the minimal symbiotic genome, general plant-microbe interactions, functional and evolutionary genomics, and biotechnology. Here, we detail phenotypic analyses of the S. meliloti strains lacking one or two replicons, and relate these observations to a generalized model for multipartite genome evolution.
Nutritional requirements
Optimal growth of the ΔpSymAB strain on complex LB or TY media required cobalt [30] and calcium supplementation, while growth on minimal M9 medium is best with thiamine [37] and iron [38] addition. The affect of calcium could possibly be related to the loss of exopolysaccharide loci on pSymB. No additional nutritional requirements were identified, which was unexpected as the genome sequence indicated the asparagine biosynthesis genes to be located on pSymB [19]. Below we describe the growth of S. meliloti in sterile bulk soil, and interestingly, we observed that growth of the ΔpSymB and ΔpSymAB strains in this soil did not require thiamine supplementation. This indicates that thiamine biosynthesis, the sole nutrient whose biosynthesis is pSymB-dependent, is not required for growth in S. meliloti's natural environment, although thiamine concentrations may limit growth in the rhizosphere [39]. Thus, very few fundamental genes are located on these replicons.
Effects on growth
Growth profiles of each strain were examined in complex and minimal media (Figures 1A, 1B, S1) by monitoring the change in OD600. The light scattering properties of all strains were the same as in soil mesocosm experiments described below, a 10−4 dilution of cell suspensions with an OD600 value of 1 repeatedly resulted in viable counts of 4×103 CFU gm−1 of soil for each strain, indicating that the CFU/OD600 in the inoculum was 2×109 for all strains (Figure 1C, 2A, 3B). Removal of both replicons led to a surprisingly small growth deficit in minimal medium, with the ΔpSymAB strain showing only a 1.37-fold slower growth rate than that of the wild type. However, a striking pattern emerged when the effect of the removal of pSymA and pSymB was examined independently: loss of the evolutionarily older pSymB resulted in a 1.6-fold slower growth rate, while loss of the evolutionarily younger pSymA led to a 1.18-fold increase in growth rate. Qualitatively similar exponential phase dynamics are observed in complex media, although a large decrease in stationary phase density is observed when the cells lack pSymB.
Fig. 1. The effect of the removal of pSymA and/or pSymB on the growth of S. meliloti. 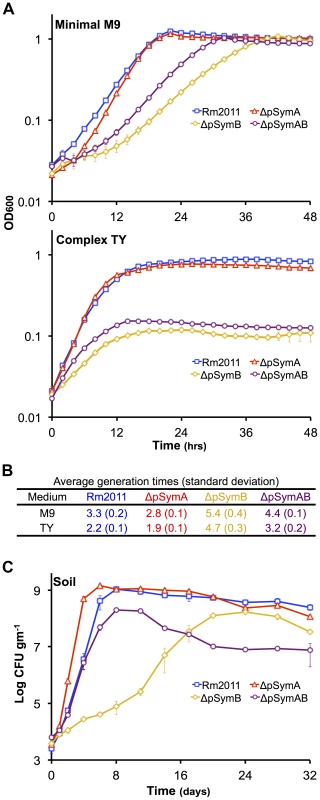
The growth of S. meliloti was examined in M9 minimal medium (A – top panel), TY complex medium (A – bottom panel), or sterile bulk soil mesocosms (C). Data points represent averages from triplicate (A) or duplicate (C) samples. Error bars represent +/− one standard deviation from triplicate samples (A) or the range from duplicate samples (C). (B) Average generation times and standard deviations for each strain grown in M9 or TY media, calculated from a total of six replicates from two independent experiments. Blue – wild type; red – ΔpSymA; yellow –ΔpSymB; purple – ΔpSymAB. Fig. 2. The decreased stationary phase density of strains lacking pSymB in bulk soil is due to carbon limitation and can be traced to two loci. 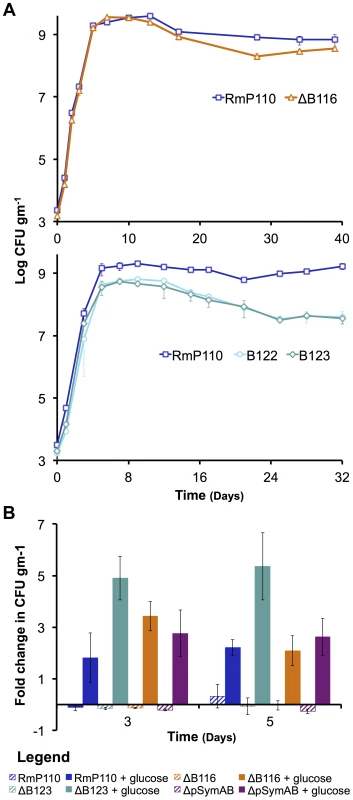
(A – top panel) The strain with a deletion of B116 (orange) shows a slight, but repeatable, decrease in stationary phase density relative to the wild type (dark blue). (A – bottom panel) The strains with deletions of B123 (dark teal) and B122 (light teal), a sub-region of B123, show a large decrease in stationary phase density relative to the wild type (dark blue). (B) Stationary phase soil populations were supplemented with either 15 mM glucose (solid bars) or 5 mM NH4Cl, 2 mM KH2PO4, and 1 mM MgSO4 (striped bars). Only the addition of a carbon source (glucose) stimulated further growth for the wild type (dark blue), the ΔpSymAB strain (purple), and strains with deletions of B123 (dark teal), which includes that entire B122 region, and B116 (orange). (A and B) Data points represent the average from duplicate experiments, while error bars represent the range from duplicate samples. Fig. 3. Environment specific growth inhibition by a pSymA-encoded siderophore. 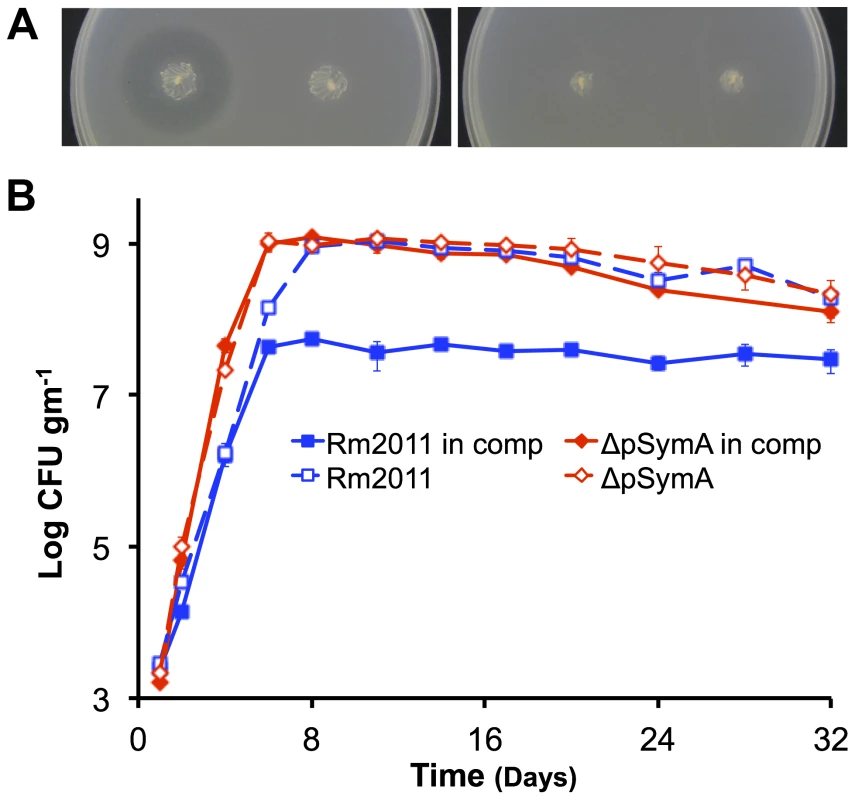
Growth of the ΔpSymAB strain is inhibited by a siderophore produced by the wild type (left stab) when grown in TY medium (A – left panel), but not if the overlay is supplemented with 150 µM FeCl3 (A – right panel). This inhibition fails to occur when the siderophore biosynthesis genes are knocked out in the wild type, as is the case in S. meliloti RmFL2950 (58) (right stab). (B) When co-inoculated in the same soil mesocosm, the ΔpSymA strain easily outcompetes the wild type, and the wild type fails to inhibit growth of the ΔpSymA strain. Data points represent averages of duplicate samples, while error bars represent the range from duplicate samples. Solid lines indicate growth pattern during co-inoculation, while dotted lines indicate growth pattern when individually inoculated. Blue – wild type; red –ΔpSymA. Others have observed a fitness improvement following the loss of large replicons, such as a megaplasmid from Agrobacterium tumefaciens [40] or large virulence plasmids from pathogenic Escherichia coli [41]. Thus, it appears a general characteristic for large replicons is to be metabolically expensive, and that their maintenance indicates they must provide a fitness advantage to the cell not necessarily evident during laboratory growth; the symbiotic nodulation and N2-fixation loci on pSymA would provide such a fitness benefit. While we also expect pSymB to impose a metabolic burden on growing cells, we postulate the loss of pSymB resulted in a decreased growth rate because of the acquisition of core genes (by core genes, we mean genes that encode products that are either essential for survival or are involved in central bacterial processes) on pSymB from the chromosome (eg. bacA, minCDE, bdhA). It has been shown that gene transfer occurs from the primary chromosome to secondary chromosomes and chromids [8], [27]; indeed, 25–30% of genes located on pSymB that are also present in the related species A. tumefaciens are located on the A. tumefaciens circular (primary) chromosome [42]. This suggests that since their divergence, there has been significant gene transfer between the primary chromosome and secondary replicons in S. meliloti and A. tumefaciens. Furthermore, a bioinformatics approach indicated that in Rhizobium etli there is a correlation between the evolutionary age of a replicon and the level of functional integration with the chromosome [14]. Thus, while gene transfer from the chromosome to pSymA presumably occurs as well, the young evolutionary age of pSymA has so far precluded a significant accumulation of core genes.
Metabolic capacity
The decreased stationary phase density of strains lacking pSymB (Figure 1B) prompted an examination of the metabolic capacity of these cells. Accordingly, wild-type S. meliloti and the cured derivatives were examined for the ability to grow (increase in OD600) with various sources of carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur. Wild-type S. meliloti grew on 73 carbon, 55 nitrogen, 53 phosphorus, and 20 sulfur sources (Table 1), and the removal of pSymA and particularly pSymB greatly decreased this potential (Table 1, Data sets S1, S2, S3, S4). This was most evident in carbon metabolism, as 50 of 73 carbon sources required pSymB and/or pSymA (Table 2) to be effectively utilized. As pSymA and pSymB account for 45% of the genome (20% and 25%, respectively), if the carbon transport and metabolic genes were randomly distributed throughout the genome, only 45% of the carbon sources metabolized by the wild type (equivalent 33 of the 73) should be dependent on these replicon. Thus, the data show that carbon utilization loci are over-represented on the non-chromosomal replicons (50 vs 33). Moreover, pSymB is essential for the metabolism of twice the expected number of carbon sources (36 vs 18), which is consistent with the prevalence of predicted solute ABC transporters on pSymB [22], [26], [27], [43]–[61]. Additionally, nitrogen and sulfur transport/metabolism is significantly enhanced by the presence of pSymB, although to a lesser extent than that of carbon metabolism, while phosphorus transport/metabolism is largely dependent on the chromosome (Table 1, Data sets S2, S3, S4).
Tab. 1. Nutrient sources supporting growth of S. meliloti. 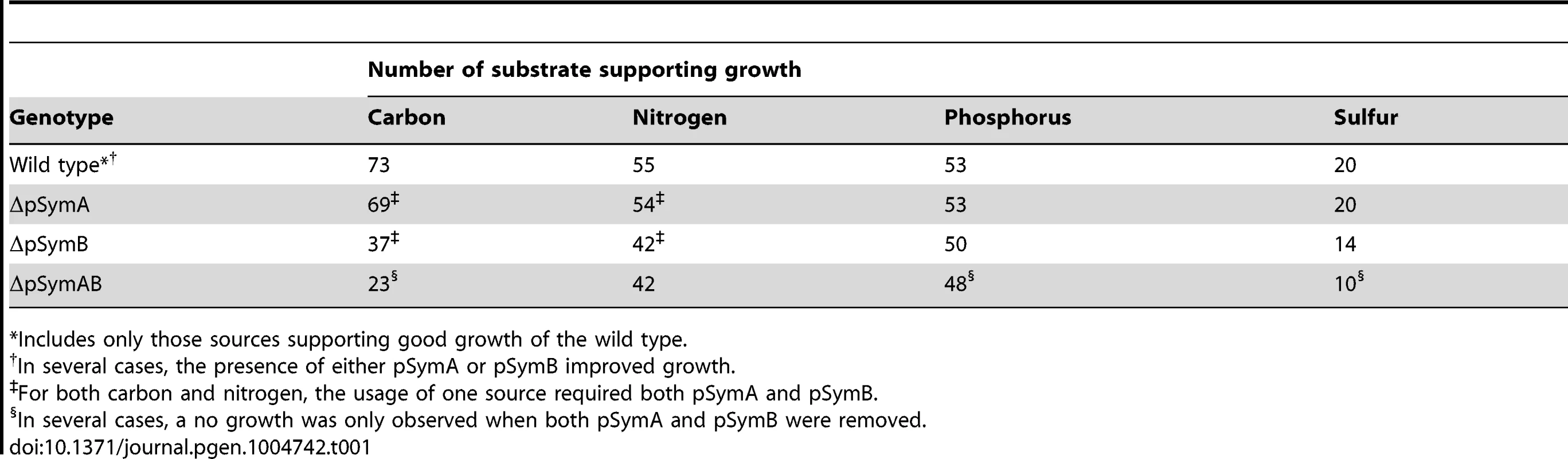
*Includes only those sources supporting good growth of the wild type. Tab. 2. Carbon sources supporting growth of S. meliloti.* 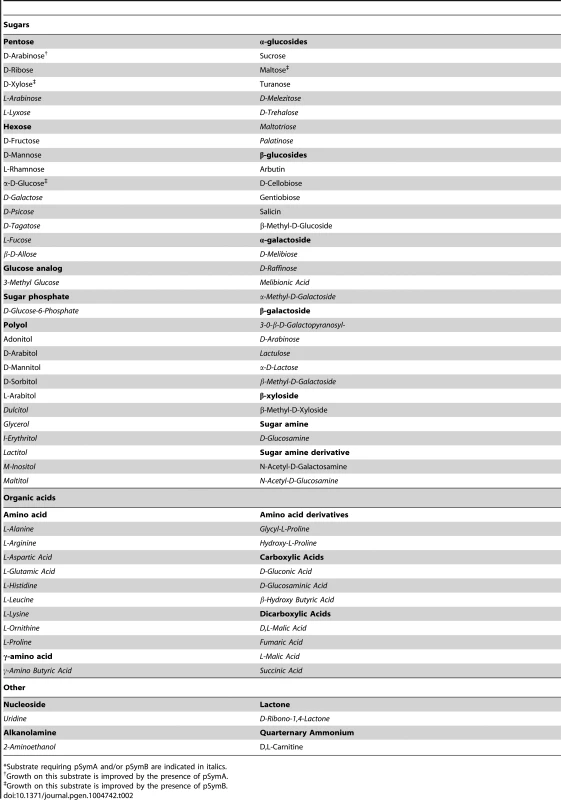
*Substrate requiring pSymA and/or pSymB are indicated in italics. Saprophytic competence
To investigate the environmental significance of pSymA and pSymB, we developed a sterile soil mesocosm system to study the growth of wild-type S. meliloti and the cured derivatives (Figure 1C) (see materials and methods). In this system, the exponential growth dynamics of each strain were qualitatively similar to that in minimal medium; the loss of pSymA resulted in faster growth, the loss of pSymB impaired growth, and the removal of both resulted in an intermediate phenotype. Additionally, strains lacking pSymB showed a decreased stationary phase cell density similar to that observed in complex medium and consistent with their decreased metabolic capacity.
To identify the region(s) responsible for the growth defect associated with the removal of pSymB, a library of 14 strains in which defined regions of pSymB were deleted (representing >90% of pSymB) [28] was screened for growth in soil. None of the pSymB deletion strains showed a significant change in exponential growth dynamics, and only the loss of the two regions identified as B116 (pSymB nucleotide (nt) position 1,256,503 to 1,307,752) and B122 (nt 1,529,711–1,572,422) showed a significant and reproducible reduction in the stationary phase density in soil (Figure 2A). To investigate whether carbon availability was a growth-limiting factor in the soil, 15 mM glucose was added to stationary phase soil cultures of the wild type, ΔpSymAB strain, and strains with deletions of either the B116 or B122 regions. Viable cell counts following 3 and 5 days of incubation showed that glucose stimulated growth of all four strains, whereas no growth stimulation was observed following supplementation with nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur (Figure 2B). Thus, the availability of a usable carbon source appears to be a major factor limiting stationary phase growth for all strains in the soil mesocosms.
The deletion of B116 results in a 2 fold decrease in viable cell density in bulk soil, and the removal of B122 results in a 5–25 fold reduction (Figure 2A). While we have not confirmed which genes within these regions are responsible for the observed phenotype, we note that the B122 region includes genes (bhbA-D) involved in metabolism of the carbon storage compound poly-3-hydroxybutyrate [62], while half of the B116 region spans a DNA fragment known to have translocated to pSymB from the chromosome in a S. meliloti ancestor [27]. As the stationary phase defect associated with the loss of both B116 and B122 is related to decreased carbon metabolic abilities (Figure 2B), it is reasonable to assume a multiplicative effect if both B116 and B122 are removed simultaneously, which would be a 10–50 fold decrease in stationary phase density. In fact, this is highly consistent with the observed stationary phase reduction of the ΔpSymB and ΔpSymAB strains (Figure 1C). Thus, we propose that the stationary phase defect associated with the removal of pSymB may be attributed predominately, if not entirely, to the loss of genes within these two regions.
In summary, the growth rate of S. meliloti in soil appears to be positively impacted by the removal of pSymA, but negatively impacted by the removal of pSymB, likely for the reasons discussed previously (see ‘effects on growth’). On the other hand, the evidence shows that few pSymA - or pSymB-encoded metabolic capabilities are biologically necessary during growth of S. meliloti in sterile bulk soil. Thus, we wondered what evolutionary pressures maintain these metabolic capabilities. Slater et al. [8] presented strong bioinformatics evidence suggesting the common ancestor of the Rhizobiales order contained a single chromosome, and that this species captured a repABC plasmid (which they referred to as the ITR) that has evolved into secondary chromosomes or chromids in many modern day Rhizobiales (eg. pSymB in S. meliloti, and the second chromosome of Agrobacterium species). The presence of exopolysaccharide biosynthetic genes, which facilitates a strong plant-microbe interaction [18], on pSymB [22] and the second chromosome of Agrobacterium species [8] suggest that these genes may have originated on the ITR. Furthermore, phylogenetic studies have concluded that the evolution of an association with plants was associated with a large increase in solute, and particularly sugar, transporters [63], [64]. Indeed, S. meliloti is capable of using a broad range of carbon sources for growth, and these functions are significantly over-represented on pSymB. Consequently, we suspect that an early plasmid derived from the ITR allowed improved colonization of the rhizosphere, leading to a selection for new genes specific to growth in this novel niche. Unlike plasmids, large rearrangements of bacterial chromosomes are generally selected against [8], [65], thus the subsequent genome expansion occurred primarily with the ITR-derived plasmid, resulting in a replicon specialized for growth in the rhizosphere. While the fitness advantage provided by pSymB in the rhizosphere was not directly assessed here, we note that many of the carbon sources unable to support growth of the ΔpSymAB strain are indeed present in the rhizosphere (e.g. organic acids, galactosides, and several polyols and sugars [66]–[68] (Table 2).
Competitive phenotype
In natural environments, microorganisms are found as mixed populations and compete with each other for available resources. We therefore wished to examine whether pSymA and pSymB influences the competitive fitness of S. meliloti. Interestingly, in an agar plate assay, growth of the wild-type S. meliloti was found to inhibit the growth of strains lacking pSymA (Figures 3A, S2), but not the ΔpSymB strain (Figure S2). While such inhibition was observed previously [69], the nature of the inhibition was not identified. To identify loci responsible for this phenotype, we analyzed a library of strains, in which defined regions of pSymA were deleted [28], for inhibition by the wild type. This screen identified a 64 kilobase region (A133) whose loss confers sensitivity to the inhibition by the wild type. This region encodes siderophore biosynthetic (rhbA-F) and uptake (rhtA, rhtX) genes [70], [71], and subsequent mutant analysis revealed that simply disrupting the siderophore uptake genes conferred sensitivity to inhibition by the wild type (Figure S2), while disrupting the biosynthetic genes in the wild-type background precluded inhibition of the ΔpSymAB strain (Figure 3A). Furthermore, no inhibition was observed in the presence of excess iron (Figure 3A). Taken together, these analyses revealed that inhibition was mediated through the siderophore sequestering environmental iron from the ΔpSymA or ΔpSymAB strains (Figures 3A, S2).
The effect of this siderophore during soil growth was examined through co-inoculation of the wild type and the ΔpSymA strain in the same soil mesocosm (Figure 3B). Consistent with carbon being the growth-limiting nutrient and available iron being in excess, the presence of the wild type did not impact the growth of the ΔpSymA strain, and the ΔpSymA strain easily outcompeted the wild type. In line with this result, Loper and Henkels [72] previously reported that the Pseudomonas fluorescens siderophore was not expressed during growth in bulk soil. However, the synthesis/uptake of a siderophore may impact fitness in the rhizosphere [72] and possibly affect symbiosis [70].
In addition to intra-species competition, inter-species competition is a major fitness determinant. We assessed the growth of the ΔpSymAB strain in the presence of three competing species: Pseudomonas syringae, Streptomyces ceolicolor, and a soil-isolated Aspergillus species (Figure 4). The early exponential growth of the S. meliloti strain was not adversely impacted by any of the competing species, and the ΔpSymAB strain was able to establish a stable population in the presence of these species over the course of the 26-day assay. However, we observed that the maximum cell density attained by the ΔpSymAB strain was decreased ∼10–20 fold when co-inoculated with a competitor, which may be attributed to inter-species competition for common nutrients and energy sources. As a whole, our data nonetheless suggest that neither pSymA nor pSymB are required for S. meliloti to effectively establish a long-term population or compete for resources with other species, and their loss does not render S. meliloti susceptible to killing by these species.
Fig. 4. Effect of competing species on the growth of the S. meliloti ΔpSymAB strain in bulk soil mesocosms. 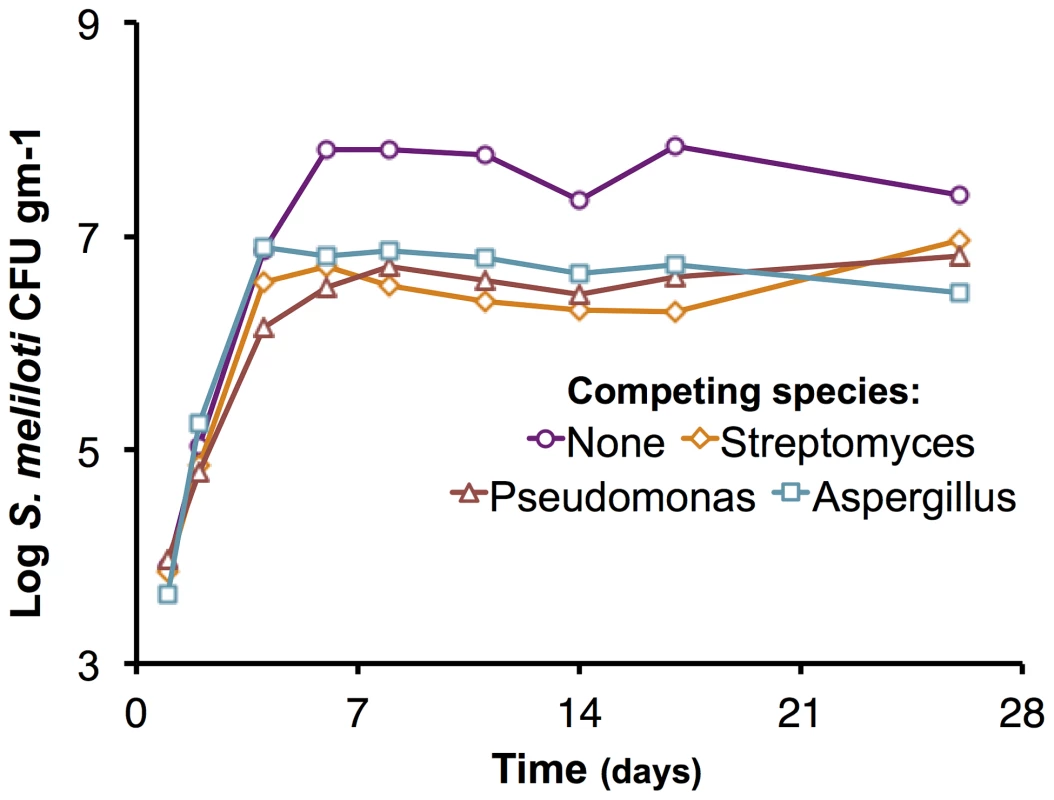
The S. meliloti ΔpSymAB strain was grown in bulk soil mesocosms in the presence of either an Aspergillus species, Pseudomonas syringae, or Streptomyces ceolicolor and the growth of the ΔpSymAB strain was examined. The decreased stationary phase density during competition is presumably reflective of competition for nutrients and the reduced availability of nutrients due to usage by the competitor. On the other hand, there is a relative lack of effect on the early exponential growth of the ΔpSymAB strain, and it is able to establish a stable stationary phase population in the presence of the competing species. See materials and methods for details on experimental set-up. Purple – ΔpSymAB alone; teal – ΔpSymAB with a soil-isolated Aspergillus species; brown – ΔpSymAB with P. syringae; orange – ΔpSymAB with S. ceolicolor. Data points represent single values. Model of multipartite genome evolution
There are two general scenarios for the evolution of multipartite genome evolution. The schism hypothesis suggests that second chromosomes or chromids result from the split of an ancestral chromosome into two [18]. This has been suggested to have occurred in Rhodobacter sphaeroides [73]. Alternatively, the plasmid hypothesis suggests chromids result from the capture of a megaplasmid that subsequently acquires core genes from the chromosome [18]. The often-observed bias for essential genes to be located on one chromosome suggests that the plasmid hypothesis is more generally applicable [18], and evidence suggests that the plasmid hypothesis is true in the case of Vibrio, Agrobacterium, Rhizobium, and Sinorhizobium, among others [2], [8], [13], [18], [21].
Several hypotheses exist about the function of multipartite genomes, and the evolution of multipartite genomes through the plasmid hypothesis; however, little experimental evidence has previously been reported to support these ideas. The presence of two replicons with distinct evolutionary histories (ie. pSymA was a much more recent addition to the genome than pSymB) and characteristics (ie. megaplasmid vs chromid), and the presence of strains lacking one or both of these replicons makes S. meliloti an ideal system in which to experimentally develop a model describing the evolution of multipartite genomes. In the proposed model (Figure 5), as a first step a host cell captures a plasmid that encodes genetic determinants allowing the cell to occupy a novel niche. Inhabiting this new environment puts an evolutionary pressure on the cell to obtain additional genetic material that provides a fitness benefit unique to this location. As genetic rearrangements of bacterial chromosomes are generally associated with a fitness cost [65], this new genetic material is disproportionately acquired by the plasmid, resulting in a plasmid specialized for a specific niche. As plasmids are mobile elements, this enrichment of niche-specific traits is advantageous as it would promote plasmid retention following transfer to a new unichromosomal organism. From the host's view, while this plasmid is valuable in the new niche, its specialized nature means it provides little advantage in the original environment and is in fact a fitness burden due to its metabolic load. In S. meliloti, pSymA represents an example of a plasmid that encodes functions essential to a specialized niche (forming N2-fixing root nodules with legumes) and yet imposes a fitness cost to cells growing in the species original environment (bulk soil). Thus, strains lacking pSymA grow more rapidly and outcompete wild-type S. meliloti in bulk soil (Figures 1, 3B), although ΔpSymA strains are unable to form root nodules [23], [38] and growth of the ΔpSymA strains may be inhibited by the wild type in specific environments (Figure 3A).
Fig. 5. Schematic illustrating the described model of multipartite genome evolution and chromid formation. 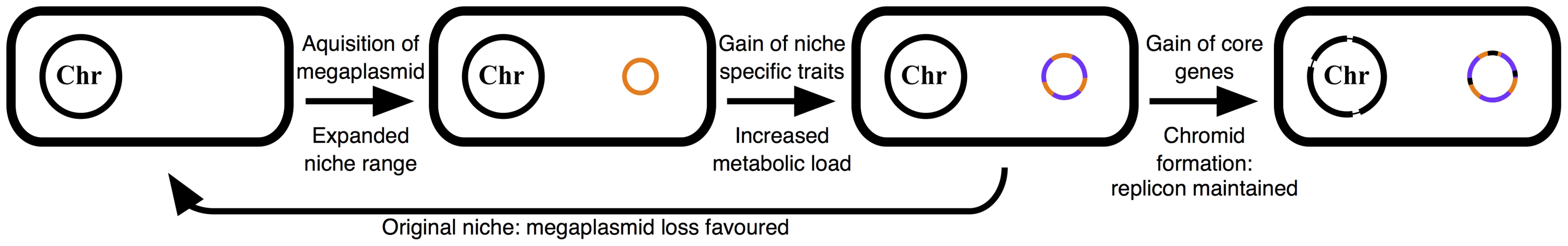
The acquisition of a megaplasmid (orange) expands the niche range of the cell. Subsequently, this replicon accumulates horizontally acquired genes that provide a fitness advantage in this novel environment (purple). This results in a large metabolic load being associated with the megaplasmid, and its loss is favoured in the cell's original niche. However, gene transfer from the chromosome (black) renders the megaplasmid (now a chromid) indespensible in all environments. See the text ‘model of multipartite genome evolution’ for additional details. Over time, random translocations from the chromosome to a resident plasmid would result in the formation of a chromid, leading to an evolutionary pressure to maintain the chromid in all environments, including the species original niche where the loss of the replicon would otherwise be favored. pSymB has had a long association with the S. meliloti lineage and during this time has acquired core elements from the chromosome [8], [27], [42]. Loss of this replicon adversely affects the growth of S. meliloti in bulk soil (Figure 1C) despite the reduced metabolic demand of no longer maintaining the chromid. However, the many metabolic functions dependent on pSymB largely appear to not be necessary for growth in bulk soil, and may be more relevant during growth in the rhizosphere, consistent with a niche-specialized role of this replicon. Overall, the phenotypic data reported here support a model where environmental specialization is a general driving force for multipartite genome evolution, with secondary replicons being enriched for functions unique to the new environment. Indeed, previous comparative genomics analysis [1], [8], [15] presented evidence consistent with many of the core postulates of this model that were derived through experimental examination.
While this model addresses the evolution and primary role of secondary replicons, it is still unclear as to why this genome architecture persists, and why secondary replicons do not integrate into the chromosome. Integration has been postulated to have occurred in Mesorhizobium and Bradyrhizobium [8], which carry a single large chromosome, despite having similar lifestyles to Sinorhizobium and Rhizobium, which have divided genomes. While it is possible that the presence of a divided genome is an evolutionarily transient event, this seems unlikely. As discussed in the introduction, several advantages have been ascribed to the presence of a multipartite genome that may promote its maintenance. Indeed, S. meliloti strains that carry all three replicons recombined into one show a growth defect [74], illustrating how genome structure and not just gene content affects the cell's phenotype. There may also be constraints on the ability of a chromid or megaplasmid to recombine into the chromosome. The origin and terminus of replication separate bacterial chromosomes into subdivisions that tend to be equal in size. Large insertions, such as the integration of a secondary replicon into the primary chromosome, would disrupt this balance and thus be unfavourable [75]. Additionally, it has been suggested that there is an upper size limit of bacterial chromosomes, which could potentially preclude the integration of a large replicon into the chromosome [8]. Finally, plasmids, being mobile elements, can move into naïve cells, leading to further propagation of their DNA. As such, the fitness of the plasmid would be reduced following recombination into the main chromosome.
Materials and Methods
Except for the strains and plasmids contructed in this study, all other strains and plasmids have been previously described [27]–[29], [37], [76]–[78] and are listed in Table S1.
Growth conditions
Complex media included LB (10 gm/L tryptone, 5 gm/L yeast extract, 5 gm/L sodium chloride), LBmc (LB with 2.5 mM MgSO4 2.5 mM CaCl2), and TY (5 gm/L tryptone, 2.5 gm/L yeast extract, 10 mM CaCl2). For growth of S. meliloti, complex media was supplemented with 2 µM CoCl2. Minimal media included M9 (41 mM Na2HPO4, 22 mM KH2PO4, 8.6 mM NaCl, 18.7 mM NH4Cl, 4.1 µM biotin, 42 nM CoCl2, 1 mM MgSO4, 0.25 mM CaCl2, 38 µM FeCl3, 5 µM thiamine-HCl, 10 mM sucrose) and a 4-morpholinepropanesulfonic acid (MOPS) buffered medium (M9 with the phosphate buffer replaced with 40 mM MOPS and 20 mM KOH, with 2 mM KH2PO4). For the phenotype macroarray analysis, cultures were grown in M9 medium for the carbon and sulfur analyses, while strains where grown in MOPS medium for the nitrogen and phosphorus analyses. Additionally, the concentration of biotin was reduced to 40 nM for the analysis of sulfur metabolism. Unless stated otherwise, antibiotics were added to the following concentrations (µg/mL) for S. meliloti (E. coli), when appropriate: streptomycin 200 (N/A), spectinomycin 100 (100), tetracycline 5 (5), gentamicin 60 (20), neomycin 200 (N/A), kanamycin N/A (25), and chloramphenicol N/A (5). Antibiotic concentrations were halved for liquid media. S. meliloti was grown at 30°C and E. coli was grown at 37°C.
Genetic techniques
Common genetic techniques and manipulations were performed as previously described [76], [79], [80].
Growth curves
Overnight cultures were washed, resuspended, and diluted in fresh media. 150 µL of diluted cultures (OD600∼0.05, measured with a 1 cm wavelength) were inoculated into 96-well plates, with each strain done in triplicate. The edges of the 96-well plates were taped to prevent moisture loss and the 96-well plates were incubated in a Tecan Safire for 48 hours at 30°C (+/−1°C) with shaking. OD600 measurements were taken every 15 minutes. A Perl script was written to calculate averages, standard deviations, and generation times.
Phenotype macroarray
Phenotype macroarrays were performed in Biolog plates (PM1, PM2A, PM3B, PM4A). Overnight cultures were washed, resuspended, and starved overnight in media free of the appropriate nutrient. Starved cultures were washed, resuspended, and diluted in fresh media, then 100 µL was inoculated into each well of the Biolog plates. Plates were incubated at 30°C for 5–7 days in a SteadyShake 757 Benchtop Incubator Shaker (Amerex Instruments, Inc.), with OD600 readings taken every 12–24 hours.
Soil preparation
In 2007, a 40 kg soil sample was obtained from an alfalfa field within a dairy farm near Guelph, Ontario, Canada, which does not apply pesticides, fertilizers, or herbicides. Large materials were manually removed, and following 9 days of drying, the soil was passed through a sieve to remove fragments larger than 2 mm. The soil was heat sealed in polyethylene freezer bags (FoodSaver; Jarden Corporation) as 100–300 gm samples. Soil samples were subjected to γ-irradiation (using 6°Co as a source) at the McMaster University Nuclear Reactor with a final dosage of 25.0 kGy (over a period of 54.3 hrs). As subsequent testing revealed the soil was not sterile, a second round of γ–irradiation at a final dosage of 42.3 kGy was performed, and stored at −20°C until use. However, as a Dienococcus species still remained viable, soil samples were autoclaved once (123°C; 17 psig; 20 minutes) within a few days of beginning each growth assay. A chemical analysis of the soil was performed by the University of Guelph Laboratory Services Agricultural and Food Laboratory (Guelph, Ontario, Canada), and the results are presented in Table S2.
Soil growth protocol
47.62 gm (40 gm dry weight) of γ–irradiated soil was added to 500 mL screw-capped glass bottles (Gibco), autoclaved, and allowed to cool. Within a few days, S. meliloti strains were grown in LBmc or TY and cells were washed once with 0.85% NaCl and three times with de-ionized, autoclaved water (ddH2O). Cells were resupended in ddH2O, adjusted to an OD600 of 1 and serial diluted to 10−4, which equals approximately 2×105 CFU/mL. 1 mL of this dilution, together with an additional 1.38 mL ddH2O, was added to each mesocosm. The resulting mesocosm contained 50 gm soil (40 gm dry weight a 20% moisture (wt/vol)), and ∼4×103 CFU gm−1. Soil mesocosms were incubated at room temperature (22°C+/−2°C) in the dark, and soil moisture content was maintained by the addition of ddH2O every one to two weeks (at the rate of 48 µL per day).
To determine cell density, 0.62 gm samples were removed from each mesocosm into a 2 mL Eppendorf tube in a sterile environment. 1 mL of 0.85% NaCl was added to each tube and cells were re-suspended with vigorous vortexing. Soil particles were pelleted by vortexing for 1 minute at 60 g. The supernatant was serial diluted and plated on LB or LBmc to determine CFU gm−1.
Throughout co-inoculation experiments, when plating for CFU gm−1, dilutions were plated on non-selective and selective media. When wild-type S. meliloti and the ΔpSymA strain were co-inoculated, each strain was inoculated to ∼2×103 CFU gm−1, and strains were differentiated based on growth with 10 mM trigonelline as the sole carbon source as only the wild type will grow. For co-inoculation of S. meliloti with P. syringae, S. meliloti was inoculated to ∼2×103 CFU gm−1 while P. syringae was inoculated to ∼8×102 CFU gm−1, and CFU gm−1 was determined by plating on LB with streptomycin (S. meliloti) or LB with 20 µg/mL rifampicin (P. syringae). When co-inoculated with S. ceolicolor, S. meliloti was inoculated to ∼2×103 CFU gm−1 while S. ceolicolor was inoculated with 2×103 spores gm−1, and S. meliloti was selected for with streptomycin. Co-inoculation with Aspergillus was initiated with ∼4×103 CFU gm−1 of S. meliloti and ∼8×102 spores gm−1 of Aspergillus, and CFU gm−1 of S. meliloti was determined on LB with 100 µg/mL cycloheximide.
Isolation of a soil Aspergillus species
A 0.45 gm sample of non-sterilized soil used for the soil growth assays was vigorously vortexed in 1 mL 0.85% saline, and dilutions were plated on YPD medium (10 gm/L yeast extract, 20 gm/L peptone, 20 gm/L dextrose, 15 gm/L) with 50 µg/mL chloramphenicol. Based on morphology, an Aspergillus species was identified and streak purified on YPD. The Aspergillus was sporulated on LCA medium [81] for eight days at 30°C, and spores were re-suspended in PBS (0.8% NaCl, 0.02% KCl, 0.144% Na2HPO4, 0.024% KH2PO4) with 100 µg/mL streptomycin. Spores/mL were determined by counting spores with a hemacytometer.
Bacteriocin assay
This assay was performed essentially as described previously [69], [82]. Strains being tested for bacteriocin production were stabbed into TY agar plates and incubated at 30°C overnight. The next day, surface growth of the producer was largely removed using a sterile toothpick. Overnight cultures of strains being tested for bacteriocin sensitivity were diluted to an OD600∼0.01 in TY, and 1 mL was mixed with 5 mL of TY with 240 µg/mL streptomycin or spectinomycin and 0.6% agar (giving a final concentration of Sm200 or Sp200 and 0.5% agar), and all 6 mL were poured onto the plates with the stabbed producers. The inclusion of streptomycin or spectinomycin was to prevent the producer from growing into the soft agar overlay. Plates were incubated at 30°C for two nights, following which zones of clearance were identified. When applicable, 150 µM FeCl3 was added to the soft agar overlay.
Removal of pSymB
Previous work has indicated that there are only two single copy essential genes outside of the chromosome (engA and tRNAarg), both located on pSymB [27], [28]. Previously, these two essential genes were integrated into the chromosome [27]. However, this integration included a neomycin resistance marker, and we wished to use neomycin as a selective marker during the process of removing pSymB. Thus, it was necessary to begin by constructing a neomycin sensitive integration of the essential genes into the chromosome.
Based on how the integration was performed, there are two possible orientations of the genes following integration (Figures S3A, S3B), and using PCR we determined that the construct integrated as seen in Figure S3B (RmP2686). Using the same procedure as previously followed [27], we isolated a second strain with the orientation illustrated in Figure S3A (RmP2711). The insertion in RmP2711 was transduced into a metH::Tn5-B20 strain selecting for spectinomycin resistance; metH is located ∼5 kilobases upstream of the engA/tRNA insertion site (Figure S3C). The resulting strain was the recipient in a transduction with a phage lysate prepared from RmP2686 (Figure S3D). Colonies were selected for based on a MetH+ phenotype on minimal medium and screened for Nm resistance. Following the isolation of a neomycin sensitive colony, PCR was used to confirm that the genetic organization of the insertion was as expected (Figure S3E). The insertion in this final strain, RmP2719, is stable and is neomycin sensitive.
The two-gene operon, smb21127/smb21128 (pSymB nt: 766,498–767,430), functions as an active toxin-antitoxin locus, although it is possible to delete this system with a low frequency [28]. Therefore, the deletion ΔB180 (pSymB nt: 635,940 nt–869,645) was transduced into S. meliloti strain Rm2011, selecting for neomycin resistance. Subsequently, the chromosomal integration of engA and tRNAarg was transduced into this strain, selecting for spectinomycin resistance. The resulting strain, RmP3005 carries the essential pSymB genes on the chromosome as well as a 234 kilobase deletion that removed the only known active toxin-antitoxin system on this replicon.
The replication and segregation machinery of pSymB is encoded by the repABC operon [29]. An incompatibility factor, incA, is encoded within the repB and repC intergenic region; thus, pSymB cannot be stably co-inherited with another replicon carrying an exact copy of incA [29]. Thus, pTH1414 (pOT1 carrying the pSymB incA region) [29] was introduced into S. meliloti RmP3005, and streptomycin/gentamicin resistant colonies were selected for on LB supplemented with 2 µM cobalt chloride to compensate for the loss of the major S. meliloti cobalt uptake ABC transporter (CbtJKL), which is pSymB-encoded [30]. Recovered colonies were streak purified, and initially the inability to amplify six pSymB fragments using PCR was evidence that pSymB was indeed lost. One colony was inoculated in LBmc broth, serial diluted and plated on LB, and colonies were screened for loss of pTH1414 by patching for gentamicin sensitivity. A gentamicin sensitive colony was purified and stored as S. meliloti RmP3009.
In order to construct the strain lacking both pSymA and pSymB, the same procedure was followed as above, with two modifications. The starting strain lacked pSymA [24]. Additionally, the chromosomal integration of engA and tRNAarg from S. meliloti RmP2719 was transduced into this strain prior to the transduction of ΔB180. Following the removal of pSymB using incompatibility, and the subsequent loss of pTH1414, the resulting strain was frozen as S. meliloti RmP2917, which lacks both pSymA and pSymB.
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. HarrisonPW, LowerRP, KimNK, YoungJP (2010) Introducing the bacterial ‘chromid’: Not a chromosome, not a plasmid. Trends Microbiol 18 : 141–148 doi:10.1016/j.tim.2009.12.010
2. LandetaC, DávalosA, CevallosMA, GeigerO, BromS, et al. (2011) Plasmids with a chromosome-like role in rhizobia. J Bacteriol 193 : 1317–1326 doi:10.1128/JB.01184-10
3. CouturierE, RochaEP (2006) Replication-associated gene dosage effects shape the genomes of fast-growing bacteria but only for transcription and translation genes. Mol Microbiol 59 : 1506–1518 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05046.x
4. Vieira-SilvaS, TouchonM, RochaEP (2010) No evidence for elemental-based streamlining of prokaryotic genomes. Trends Ecol Evol 25 : 319–20 author reply 320–1. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2010.03.001
5. DryseliusR, IzutsuK, HondaT, IidaT (2008) Differential replication dynamics for large and small Vibrio chromosomes affect gene dosage, expression and location. BMC Genomics 9 : 559 doi:10.1186/1471-2164-9-559
6. CooperVS, VohrSH, WrocklageSC, HatcherPJ (2010) Why genes evolve faster on secondary chromosomes in bacteria. PLoS Comput Biol 6: e1000732 doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000732
7. ChainPS, DenefVJ, KonstantinidisKT, VergezLM, AgullóL, et al. (2006) Burkholderia xenovorans LB400 harbors a multi-replicon, 9.73-mbp genome shaped for versatility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103 : 15280–15287 doi:10.1073/pnas.0606924103
8. SlaterSC, GoldmanBS, GoodnerB, SetubalJC, FerrandSK, et al. (2009) Genome sequences of three Agrobacterium biovars help elucidate the evolution of multichromosome genomes in bacteria. J Bacteriol 191 : 2501–2511 doi:10.1128/JB.01779-08
9. MichauxS, PaillissonJ, Carles-NuritMJ, BourgG, Allardet-ServentA, et al. (1993) Presence of two independent chromosomes in the Brucella melitensis 16 M genome. J Bacteriol 175 : 701–705.
10. KanekoT, NakamuraY, SatoS, MinamisawaK, UchiumiT, et al. (2002) Complete genomic sequence of nitrogen fixing symbiotic bacterium Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110. DNA Res 9 : 189–197 doi:10.1093/dnares/9.6.189
11. Jumas-BilakE, Michaux-CharachonS, BourgG, O'CallaghanD, RamuzM (1998) Differences in chromosome number and genome rearrangements in the genus Brucella. Mol Microbiol 27 : 99–106 doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00661.x
12. MorenoE (1998) Genome evolution within the alpha proteobacteria: why do some bacteria not possess plasmids and others exhibit more than one different chromosome? FEMS Micriobiol Rev 22 : 255–275 doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.1998.tb00370.x
13. HeidelbergJF, EisenJA, NelsonWC, ClaytonRA, GwinnML, et al. (2000) DNA sequence of both chromosomes of the cholera pathogen Vibrio cholerae. Nature 406 : 477–483 doi:10.1038/35020000
14. GonzálezV, SantamaríaRI, BustosP, Hernández-GonzálezI, Medrano-SotoA, et al. (2006) The partitioned Rhizobium etli genome: Genetic and metabolic redundancy in seven interacting replicons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103 : 3834–3839 doi:10.1073/pnas.0508502103
15. GalardiniM, PiniF, BazzicalupoM, BiondiEG, MengoniA (2013) Replicon-dependent bacterial genome evolution: The case of Sinorhizobium meliloti. Genome Biol Evol 5 : 542–558 doi:10.1093/gbe/evt027
16. XuQ, DziejmanM, MekalanosJJ (2003) Determination of the transcriptome of Vibrio cholerae during intraintestinal growth and midexponential phase in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100 : 1286–1291 doi:10.1073/pnas.0337479100
17. BeckerA, BergèsH, KrolE, BruandC, RübergS, et al. (2004) Global changes in gene expression in Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 under microoxic and symbiotic conditions. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 17 : 292–303 doi:10.1094/MPMI.2004.17.3.292
18. EganES, FogelMA, WaldorMK (2005) Divided genomes: Negotiating the cell cycle in prokaryotes with multiple chromosomes. Mol Microbiol 56 : 1129–1138 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04622.x
19. GalibertF, FinanTM, LongSR, PühlerA, AbolaP, et al. (2001) The composite genome of the legume symbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti. Science 293 : 668–672 doi:10.1126/science.1060966
20. EpsteinB, BrancaA, MudgeJ, BhartiAK, BriskineR, et al. (2012) Population genomics of the facultatively mutualistic bacteria Sinorhizobium meliloti and S. medicae. PLoS Genet 8: e1002868 doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002868
21. GuoHJ, WangET, ZhangXX, LiQQ, ZhangYM, et al. (2014) Replicon-dependent differentiation of symbiosis-related genes in Sinorhizobium strains nodulating Glycine max. Appl Environ Microbiol 80 : 1245–1255 doi:10.1128/AEM.03037-13
22. FinanTM, WeidnerS, WongK, BuhrmesterJ, ChainP, et al. (2001) The complete sequence of the 1,683-kb pSymB megaplasmid from the N2-fixing endosymbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98 : 9889–9894 doi:10.1073/pnas.161294698
23. BarnettMJ, FisherRF, JonesT, KompC, AbolaAP, et al. (2001) Nucleotide sequence and predicted functions of the entire Sinorhizobium meliloti pSymA megaplasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98 : 9883–9888 doi:10.1073/pnas.161294798
24. OresnikIJ, LiuSL, YostCK, HynesMF (2000) Megaplasmid pRme2011a of Sinorhizobium meliloti is not required for viability. J Bacteriol 182 : 3582–3586 doi:10.1128/JB.182.12.3582-3586.2000
25. HynesMF, QuandtJ, O'ConnellMP, PühlerA (1989) Direct selection for curing and deletion of Rhizobium plasmids using transposons carrying the Bacillus subtilis sacB gene. Gene 78 : 111–120.
26. CharlesTC, FinanTM (1991) Analysis of a 1600-kilobase Rhizobium meliloti megaplasmid using defined deletions generated in vivo. Genetics 127 : 5–20.
27. diCenzoG, MilunovicB, ChengJ, FinanTM (2013) The tRNAarg gene and engA are essential genes on the 1.7-mb pSymB megaplasmid of Sinorhizobium meliloti and were translocated together from the chromosome in an ancestral strain. J Bacteriol 195 : 202–212 doi:10.1128/JB.01758-12
28. MilunovicB, diCenzoGC, MortonRA, FinanTM (2014) Cell growth inhibition upon deletion of four toxin-antitoxin loci from the megaplasmids of Sinorhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol 196 : 811–824 doi:10.1128/JB.01104-13
29. MacLellanSR, SmallboneLA, SibleyCD, FinanTM (2005) The expression of a novel antisense gene mediates incompatibility within the large repABC family of alpha-proteobacterial plasmids. Mol Microbiol 55 : 611–623 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04412.x
30. ChengJ, PoduskaB, MortonRA, FinanTM (2011) An ABC-type cobalt transport system is essential for growth of Sinorhizobium meliloti at trace metal concentrations. J Bacteriol 193 : 4405–4416 doi:10.1128/JB.05045-11
31. SalletE, RouxB, Sauviac, JardinaudMF, CarrèreS, et al. (2013) Next-generation annotation of prokaryotic genomes with EuGene-P: application to Sinorhizobium meliloti 2011. DNA Res 20 : 339–354 doi:10.1093/dnares/dst014
32. PósfaiG, PlunkettG3rd, FehérT, FrischD, KeilGM, et al. (2006) Emergent properties of reduced-genome Escherichia coli. Science 312 : 1044–1046 doi:10.1126/science.1126439
33. AraK, OzakiK, NakamuraK, YamaneK, SekiguchiJ, et al. (2007) Bacillus minimum genome factory: Effective utilization of microbial genome information. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 46 : 169–178 doi:10.1042/BA20060111
34. HynesMF, McGregorNF (1990) Two plasmids other than the nodulation plasmid are necessary for formation of nitrogen-fixing nodules by Rhizobium leguminosarum. Mol Microbiol 4 : 67–574 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00625.x
35. Moënne-LoccozY, BaldaniJI, WeaverRW (1995) Sequential heat-curing of Tn5-Mob-sac labeled plasmids from Rhizobium to obtain derivatives with various combinations of plasmids and no plasmid. Lett Appl Microbiol 20 : 175–179 doi:10.1111/j.1472-765X.1995.tb00420.x
36. IwadateY, HondaH, SatoH, HashimotoM, KatoJ (2011) Oxidative stress sensitivity of engineered Escherichia coli cells with a reduced genome. FEMS Microbiol Lett 322 : 25–33 doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2011.02331.x
37. FinanTM, KunkelB, De VosGF, SignerER (1986) Second symbiotic megaplasmid in Rhizobium meliloti carrying exopolysaccharide and thiamine synthesis genes. J Bacteriol 167 : 66–72.
38. YurgelSN, MortimerMW, RiceJT, HumannJL, KahnML (2013) Directed construction and analysis of a Sinorhizobium meliloti pSymA deletion mutant library. Appl Environ Microbiol 79 : 2081–2087 doi:10.1128/AEM.02974-12
39. StreitWR, JosephCM, PhillipsDA (1996) Biotin and other water-soluble vitamins are key growth factors for alfalfa root colonization by Rhizobium meliloti 1021. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 9 : 330–338.
40. MortonER, MerrittPM, BeverJD, FuquaC (2013) Large deletions in the pAtC58 megaplasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens can confer reduced carriage cost and increased expression of virulence genes. Genome Biol Evol 5 : 1353–1364 doi:10.1093/gbe/evt095
41. MellataM, AmeissK, MoH, CurtissR3rd (2010) Characterization of the contribution to virulence of three large plasmids of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli chi7122 (O78:K80:H9). Infect Immun 78 : 1528–1541 doi:10.1128/IAI.00981-09
42. WongK, GoldingGB (2003) A phylogenetic analysis of the pSymB replicon from the Sinorhizobium meliloti genome reveals a complex evolutionary history. Can J Microbiol 49 : 269–280 doi:10.1139/w03-037
43. MauchlineTH, FowlerJE, EastAK, SartorAL, ZaheerR, et al. (2006) Mapping the Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 solute-binding protein-dependent transportome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103 : 17933–17938 doi:10.1073/pnas.0606673103
44. PoystiNJ, LoewenED, WangZ, OresnikIJ (2007) Sinorhizobium meliloti pSymB carries genes necessary for arabinose transport and catabolism. Microbiology 153 : 727–736 doi:10.1099/mic.0.29148-0
45. FinanTM, OresnikI, BottacinA (1988) Mutants of Rhizobium meliloti defective in succinate metabolism. J Bacteriol 170 : 3396–3403.
46. GeddesBA, OresnikIJ (2012) Inability to catabolize galactose leads to increased ability to compete for nodule occupancy in Sinorhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol 194 : 5044–5053 doi:10.1128/JB.00982-12
47. WillisLB, WalkerGC (1999) A novel Sinorhizobium meliloti operon encodes an alpha-glucosidase and a periplasmic-binding-protein-dependent transport system for alpha-glucosides. J Bacteriol 181 : 4176–4184.
48. JensenJB, PetersNK, BhuvaneswariTV (2002) Redundancy in periplasmic binding protein-dependent transport systems for trehalose, sucrose, and maltose in Sinorhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol 184 : 2978–2986 doi:10.1128/JB.184.11.2978-2986.2002
49. DingH, YipCB, GeddesBA, OresnikIJ, HynesMF (2012) Glycerol utilization by Rhizobium leguminosarum requires an ABC transporter and affects competition for nodulation. Microbiology 158 : 1369–1378 doi:10.1099/mic.0.057281-0
50. SteeleTT, FowlerCW, GriffittsJS (2009) Control of gluconate utilization in Sinorhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol 191 : 1355–1358 doi:10.1128/JB.01317-08
51. BiondiEG, TattiE, CompariniD, GiuntiniE, MocaliS, et al. (2009) Metabolic capacity of Sinorhizobium (Ensifer) meliloti strains as determined by phenotype MicroArray analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 75 : 5396–5404 doi:10.1128/AEM.00196-09
52. RichardsonJS, HynesMF, OresnikIJ (2004) A genetic locus necessary for rhamnose uptake and catabolism in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii. J Bacteriol 186 : 8433–8442 doi:10.1128/JB.186.24.8433-8442.2004
53. LambertA, ØsteråsM, MandonK, PoggiMC, Le RudulierD (2001) Fructose uptake in Sinorhizobium meliloti is mediated by a high-affinity ATP-binding cassette transport system. J Bacteriol 183 : 4709–4717 doi:10.1128/JB.183.16.4709-4717.2001
54. GageDJ, LongSR (1998) Alpha-galactoside uptake in Rhizobium meliloti: Isolation and characterization of agpA, a gene encoding a periplasmic binding protein required for melibiose and raffinose utilization. J Bacteriol 180 : 5739–5748.
55. GeddesBA, OresnikIJ (2012) Genetic characterization of a complex locus necessary for the transport and catabolism of erythritol, adonitol and L-arabitol in Sinorhizobium meliloti. Microbiology 158 : 2180–2191 doi:10.1099/mic.0.057877-0
56. KohlerPR, ZhengJY, SchoffersE, RossbachS (2010) Inositol catabolism, a key pathway in Sinorhizobium meliloti for competitive host nodulation. Appl Environ Microbiol 76 : 7972–7980 doi:10.1128/AEM.01972-10
57. Kibitkin K (2011) Transport and metabolism of β-glycosidic sugars in Sinorhizobium meliloti. MSc thesis, McMaster University. Available at: http://hdl.handle.net/11375/9897. Accessed 10 July 2014.
58. GeddesBA, PickeringBS, PoystiNJ, CollinsH, YudistiraH, et al. (2010) A locus necessary for the transport and catabolism of erythritol in Sinorhizobium meliloti. Microbiology 156 : 2970–2981 doi:10.1099/mic.0.041905-0
59. AmpomahOY, AvetisyanA, HansenE, SvensonJ, HuserT, et al. (2013) The thuEFGKAB operon of rhizobia and Agrobacterium tumefaciens codes for transport of trehalose, maltitol, and isomers of sucrose and their assimilation through the formation of their 3-keto derivatives. J Bacteriol 195 : 3797–3807 doi:10.1128/JB.00478-13
60. MacleanAM, WhiteCE, FowlerJE, FinanTM (2009) Identification of a hydroxyproline transport system in the legume endosymbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 22 (9) 1116–1127 doi:10.1094/MPMI-22-9-1116
61. WhiteCE, GavinaJM, MortonR, Britz-McKibbinP, FinanTM (2012) Control of hydroxyproline catabolism in Sinorhizobium meliloti. Mol Microbiol 85 : 1133–1147 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2012.08164.x
62. CharlesTC, AnejaP (1999) Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase encoding gene of sinorhizobium meliloti. Gene 226 : 121–127 doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(98)00555-1
63. BoussauB, KarlbergEO, FrankAC, LegaultBA, AnderssonSG (2004) Computational inference of scenarios for alpha-proteobacterial genome evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101 : 9722–9727 doi:10.1073/pnas.0400975101
64. PiniF, GalardiniM, BazzicalupoM, MengoniA (2011) Plant-bacteria association and symbiosis: are there common genomic trains in alphaproteobacteria? Genes 2 : 1017–1032 doi:10.3390/genes2041017
65. RochaEPC (2006) Inference and analysis of the relative stability of bacterial chromosomes. Mol Biol Evol 23 : 513–522 doi:10.1093/molbev/msj052
66. BringhurstRM, CardonZG, GageDJ (2001) Galactosides in the rhizosphere: Utilization by Sinorhizobium meliloti and development of a biosensor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98 : 4540–4545 doi:10.1073/pnas.071375898
67. KneeEM, GongFC, GaoM, TeplitskiM, JonesAR, et al. (2001) Root mucilage from pea and its utilization by rhizosphere bacteria as a sole carbon source. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 14 : 775–784 doi:10.1094/MPMI.2001.14.6.775
68. RamachandranVK, EastAK, KarunakaranR, DownieJA, PoolePS (2011) Adaptation of Rhizobium leguminosarum to pea, alfalfa and sugar beet rhizospheres investigated by comparative transcriptomics. Genome Biol 12: R106–2011-12-10-r106 doi:10.1186/gb-2011-12-10-r106
69. Perrine-WalkerFM, HynesMF, RolfeBG (2009) HocartCH (2009) Strain competition and agar affect the interaction of rhizobia with rice. Can J Microbiol 55 : 1217–1223 doi:10.1139/w09-077
70. LynchD, O'BrienJ, WelchT, ClarkeP, Ó CuívP, et al. (2001) Genetic organization of the region encoding regulation, biosynthesis, and transport of rhizobactin 1021, a siderophore produced by Sinorhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol 183 : 2576–2585 doi:10.1128/JB.183.8.2576-2585.2001
71. Ó CuívP, ClarkeP, LynchD, O'ConnellM (2004) Identification of rhtX and fptX, novel genes encoding proteins that show homology and function in the utilization of the siderophores rhizobactin 1021 by Sinorhizobium meliloti and pyochelin by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, respectively. J Bacteriol 186 : 2996–3005 doi:10.1128/JB.186.10.2996-3005.2004
72. LoperJE, HenkelsMD (1997) Availability of iron to Pseudomonas fluorescens in rhizosphere and bulk soil evaluated with an ice nucleation reporter gene. Appl Environ Microbiol 63 : 99–105.
73. ChoudharyM, MackenzieC, NerengK, SodergrenE, WeinstockGM, et al. (1997) Low resolution sequencing of Rhodobacter sphaeroides 2.4.1T: chromosome II is a true chromosome. Microbiology 143 : 3085–3099 doi:10.1099/00221287-143-10-3085
74. GuoX, FloresM, MavinguiP, FuentesSI, HernándezG, et al. (2003) Natural genomic design in Sinorhizobium meliloti: novel genomic architectures. Genome Res 13 : 1810–1817 doi:10.1101/gr.1260903
75. SongJ, WareA, LiuS-L (2003) Wavelet to predict bacterial ori and ter: a tendency towards a physical balance. BMC Genomics 4 : 17 doi:10.1186/1471-2164-4-17
76. CowieA, ChengJ, SibleyCD, FongY, ZaheerR, et al. (2006) An integrated approach to functional genomics: Construction of a novel reporter gene fusion library for Sinorhizobium meliloti. Appl Environ Microbiol 72 : 7156–7167 doi:10.1128/AEM.01397-06
77. MeadeHM, LongSR, RuykunGB, BrownSE, AusubelFM (1982) Physical and genetic characterization of symbiotic and auxotrophic mutants of Rhizobium meliloti induced by transposon Tn5 mutagenesis. J Bacteriol 149 : 114–122.
78. YuanZC, ZaheerR, FinanTM (2006) Regulation and properties of PstSCAB, a high-affinity, high-velocity phosphate transport system of Sinorhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol 188 : 1089–1102 doi:10.1128/JB.188.3.1089-1102.2006
79. Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T. (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
80. FinanTM, HartweigE, LeMieuxK, BergmanK, WalkerGC, et al. (1984) General transduction in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol 159 : 120–124.
81. MiuraK, KudoMY (1970) An agar-medium for aquatic hyphomycetes. Trans Mycol Soc Jpn 11 : 116–118.
82. HirschPR (1979) Plasmid-determined bacteriocin production by Rhizobium leguminosarum. H Gen Microbiol 113 : 219–228.
Štítky
Genetika Reprodukční medicína
Článek Oligoasthenoteratozoospermia and Infertility in Mice Deficient for miR-34b/c and miR-449 LociČlánek The Kinesin AtPSS1 Promotes Synapsis and is Required for Proper Crossover Distribution in MeiosisČlánek Payoffs, Not Tradeoffs, in the Adaptation of a Virus to Ostensibly Conflicting Selective PressuresČlánek BMP-FGF Signaling Axis Mediates Wnt-Induced Epidermal Stratification in Developing Mammalian SkinČlánek Role of STN1 and DNA Polymerase α in Telomere Stability and Genome-Wide Replication in ArabidopsisČlánek RNA-Processing Protein TDP-43 Regulates FOXO-Dependent Protein Quality Control in Stress ResponseČlánek Integrating Functional Data to Prioritize Causal Variants in Statistical Fine-Mapping StudiesČlánek Salt-Induced Stabilization of EIN3/EIL1 Confers Salinity Tolerance by Deterring ROS Accumulation inČlánek Ethylene-Induced Inhibition of Root Growth Requires Abscisic Acid Function in Rice ( L.) SeedlingsČlánek Metabolic Respiration Induces AMPK- and Ire1p-Dependent Activation of the p38-Type HOG MAPK PathwayČlánek Signature Gene Expression Reveals Novel Clues to the Molecular Mechanisms of Dimorphic Transition inČlánek A Mouse Model Uncovers LKB1 as an UVB-Induced DNA Damage Sensor Mediating CDKN1A (p21) DegradationČlánek Dominant Sequences of Human Major Histocompatibility Complex Conserved Extended Haplotypes from to
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Genetics
Nejčtenější tento týden
2014 Číslo 10- Akutní intermitentní porfyrie
- Farmakogenetické testování pomáhá předcházet nežádoucím efektům léčiv
- Růst a vývoj dětí narozených pomocí IVF
- IVF a rakovina prsu – zvyšují hormony riziko vzniku rakoviny?
- Pilotní studie: stres a úzkost v průběhu IVF cyklu
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- An Deletion Is Highly Associated with a Juvenile-Onset Inherited Polyneuropathy in Leonberger and Saint Bernard Dogs
- Licensing of Yeast Centrosome Duplication Requires Phosphoregulation of Sfi1
- Oligoasthenoteratozoospermia and Infertility in Mice Deficient for miR-34b/c and miR-449 Loci
- Basement Membrane and Cell Integrity of Self-Tissues in Maintaining Immunological Tolerance
- The Kinesin AtPSS1 Promotes Synapsis and is Required for Proper Crossover Distribution in Meiosis
- Germline Mutations in Are Associated with Familial Gastric Cancer
- POT1a and Components of CST Engage Telomerase and Regulate Its Activity in
- Controlling Meiotic Recombinational Repair – Specifying the Roles of ZMMs, Sgs1 and Mus81/Mms4 in Crossover Formation
- Payoffs, Not Tradeoffs, in the Adaptation of a Virus to Ostensibly Conflicting Selective Pressures
- FHIT Suppresses Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and Metastasis in Lung Cancer through Modulation of MicroRNAs
- Genome-Wide Mapping of Yeast RNA Polymerase II Termination
- Examination of Prokaryotic Multipartite Genome Evolution through Experimental Genome Reduction
- White Cells Facilitate Opposite- and Same-Sex Mating of Opaque Cells in
- BMP-FGF Signaling Axis Mediates Wnt-Induced Epidermal Stratification in Developing Mammalian Skin
- Genome-Wide Association Study of CSF Levels of 59 Alzheimer's Disease Candidate Proteins: Significant Associations with Proteins Involved in Amyloid Processing and Inflammation
- COE Loss-of-Function Analysis Reveals a Genetic Program Underlying Maintenance and Regeneration of the Nervous System in Planarians
- Fat-Dachsous Signaling Coordinates Cartilage Differentiation and Polarity during Craniofacial Development
- Identification of Genes Important for Cutaneous Function Revealed by a Large Scale Reverse Genetic Screen in the Mouse
- Sensors at Centrosomes Reveal Determinants of Local Separase Activity
- Genes Integrate and Hedgehog Pathways in the Second Heart Field for Cardiac Septation
- Systematic Dissection of Coding Exons at Single Nucleotide Resolution Supports an Additional Role in Cell-Specific Transcriptional Regulation
- Recovery from an Acute Infection in Requires the GATA Transcription Factor ELT-2
- HIPPO Pathway Members Restrict SOX2 to the Inner Cell Mass Where It Promotes ICM Fates in the Mouse Blastocyst
- Role of and in Development of Abdominal Epithelia Breaks Posterior Prevalence Rule
- The Formation of Endoderm-Derived Taste Sensory Organs Requires a -Dependent Expansion of Embryonic Taste Bud Progenitor Cells
- Role of STN1 and DNA Polymerase α in Telomere Stability and Genome-Wide Replication in Arabidopsis
- Keratin 76 Is Required for Tight Junction Function and Maintenance of the Skin Barrier
- Encodes the Catalytic Subunit of N Alpha-Acetyltransferase that Regulates Development, Metabolism and Adult Lifespan
- Disruption of SUMO-Specific Protease 2 Induces Mitochondria Mediated Neurodegeneration
- Caudal Regulates the Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Pair-Rule Waves in
- It's All in Your Mind: Determining Germ Cell Fate by Neuronal IRE-1 in
- A Conserved Role for Homologs in Protecting Dopaminergic Neurons from Oxidative Stress
- The Master Activator of IncA/C Conjugative Plasmids Stimulates Genomic Islands and Multidrug Resistance Dissemination
- An AGEF-1/Arf GTPase/AP-1 Ensemble Antagonizes LET-23 EGFR Basolateral Localization and Signaling during Vulva Induction
- The Proteomic Landscape of the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus Clock Reveals Large-Scale Coordination of Key Biological Processes
- RNA-Processing Protein TDP-43 Regulates FOXO-Dependent Protein Quality Control in Stress Response
- A Complex Genetic Switch Involving Overlapping Divergent Promoters and DNA Looping Regulates Expression of Conjugation Genes of a Gram-positive Plasmid
- ZTF-8 Interacts with the 9-1-1 Complex and Is Required for DNA Damage Response and Double-Strand Break Repair in the Germline
- Integrating Functional Data to Prioritize Causal Variants in Statistical Fine-Mapping Studies
- Tpz1-Ccq1 and Tpz1-Poz1 Interactions within Fission Yeast Shelterin Modulate Ccq1 Thr93 Phosphorylation and Telomerase Recruitment
- Salt-Induced Stabilization of EIN3/EIL1 Confers Salinity Tolerance by Deterring ROS Accumulation in
- Telomeric (s) in spp. Encode Mediator Subunits That Regulate Distinct Virulence Traits
- Ethylene-Induced Inhibition of Root Growth Requires Abscisic Acid Function in Rice ( L.) Seedlings
- Ancient Expansion of the Hox Cluster in Lepidoptera Generated Four Homeobox Genes Implicated in Extra-Embryonic Tissue Formation
- Mechanism of Suppression of Chromosomal Instability by DNA Polymerase POLQ
- A Mutation in the Mouse Gene Leads to Impaired Hedgehog Signaling
- Keeping mtDNA in Shape between Generations
- Targeted Exon Capture and Sequencing in Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- TIF-IA-Dependent Regulation of Ribosome Synthesis in Muscle Is Required to Maintain Systemic Insulin Signaling and Larval Growth
- At Short Telomeres Tel1 Directs Early Replication and Phosphorylates Rif1
- Evidence of a Bacterial Receptor for Lysozyme: Binding of Lysozyme to the Anti-σ Factor RsiV Controls Activation of the ECF σ Factor σ
- Hsp40s Specify Functions of Hsp104 and Hsp90 Protein Chaperone Machines
- Feeding State, Insulin and NPR-1 Modulate Chemoreceptor Gene Expression via Integration of Sensory and Circuit Inputs
- Functional Interaction between Ribosomal Protein L6 and RbgA during Ribosome Assembly
- Multiple Regulatory Systems Coordinate DNA Replication with Cell Growth in
- Fast Evolution from Precast Bricks: Genomics of Young Freshwater Populations of Threespine Stickleback
- Mmp1 Processing of the PDF Neuropeptide Regulates Circadian Structural Plasticity of Pacemaker Neurons
- The Nuclear Immune Receptor Is Required for -Dependent Constitutive Defense Activation in
- Genetic Modifiers of Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Associated Café-au-Lait Macule Count Identified Using Multi-platform Analysis
- Juvenile Hormone-Receptor Complex Acts on and to Promote Polyploidy and Vitellogenesis in the Migratory Locust
- Uncovering Enhancer Functions Using the α-Globin Locus
- The Analysis of Mutant Alleles of Different Strength Reveals Multiple Functions of Topoisomerase 2 in Regulation of Chromosome Structure
- Metabolic Respiration Induces AMPK- and Ire1p-Dependent Activation of the p38-Type HOG MAPK Pathway
- The Specification and Global Reprogramming of Histone Epigenetic Marks during Gamete Formation and Early Embryo Development in
- The DAF-16 FOXO Transcription Factor Regulates to Modulate Stress Resistance in , Linking Insulin/IGF-1 Signaling to Protein N-Terminal Acetylation
- Genetic Influences on Translation in Yeast
- Analysis of Mutants Defective in the Cdk8 Module of Mediator Reveal Links between Metabolism and Biofilm Formation
- Ribosomal Readthrough at a Short UGA Stop Codon Context Triggers Dual Localization of Metabolic Enzymes in Fungi and Animals
- Gene Duplication Restores the Viability of Δ and Δ Mutants
- Selection on a Variant Associated with Improved Viral Clearance Drives Local, Adaptive Pseudogenization of Interferon Lambda 4 ()
- Break-Induced Replication Requires DNA Damage-Induced Phosphorylation of Pif1 and Leads to Telomere Lengthening
- Dynamic Partnership between TFIIH, PGC-1α and SIRT1 Is Impaired in Trichothiodystrophy
- Signature Gene Expression Reveals Novel Clues to the Molecular Mechanisms of Dimorphic Transition in
- Mutations in Moderate or Severe Intellectual Disability
- Multifaceted Genome Control by Set1 Dependent and Independent of H3K4 Methylation and the Set1C/COMPASS Complex
- A Role for Taiman in Insect Metamorphosis
- The Small RNA Rli27 Regulates a Cell Wall Protein inside Eukaryotic Cells by Targeting a Long 5′-UTR Variant
- MMS Exposure Promotes Increased MtDNA Mutagenesis in the Presence of Replication-Defective Disease-Associated DNA Polymerase γ Variants
- Coexistence and Within-Host Evolution of Diversified Lineages of Hypermutable in Long-term Cystic Fibrosis Infections
- Comprehensive Mapping of the Flagellar Regulatory Network
- Topoisomerase II Is Required for the Proper Separation of Heterochromatic Regions during Female Meiosis
- A Splice Mutation in the Gene Causes High Glycogen Content and Low Meat Quality in Pig Skeletal Muscle
- KDM5 Interacts with Foxo to Modulate Cellular Levels of Oxidative Stress
- H2B Mono-ubiquitylation Facilitates Fork Stalling and Recovery during Replication Stress by Coordinating Rad53 Activation and Chromatin Assembly
- Copy Number Variation in the Horse Genome
- Unifying Genetic Canalization, Genetic Constraint, and Genotype-by-Environment Interaction: QTL by Genomic Background by Environment Interaction of Flowering Time in
- Spinster Homolog 2 () Deficiency Causes Early Onset Progressive Hearing Loss
- Genome-Wide Discovery of Drug-Dependent Human Liver Regulatory Elements
- Developmentally-Regulated Excision of the SPβ Prophage Reconstitutes a Gene Required for Spore Envelope Maturation in
- Protein Phosphatase 4 Promotes Chromosome Pairing and Synapsis, and Contributes to Maintaining Crossover Competence with Increasing Age
- The bHLH-PAS Transcription Factor Dysfusion Regulates Tarsal Joint Formation in Response to Notch Activity during Leg Development
- A Mouse Model Uncovers LKB1 as an UVB-Induced DNA Damage Sensor Mediating CDKN1A (p21) Degradation
- Notch3 Interactome Analysis Identified WWP2 as a Negative Regulator of Notch3 Signaling in Ovarian Cancer
- An Integrated Cell Purification and Genomics Strategy Reveals Multiple Regulators of Pancreas Development
- Dominant Sequences of Human Major Histocompatibility Complex Conserved Extended Haplotypes from to
- The Vesicle Protein SAM-4 Regulates the Processivity of Synaptic Vesicle Transport
- A Gain-of-Function Mutation in Impeded Bone Development through Increasing Expression in DA2B Mice
- Nephronophthisis-Associated Regulates Cell Cycle Progression, Apoptosis and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition
- Beclin 1 Is Required for Neuron Viability and Regulates Endosome Pathways via the UVRAG-VPS34 Complex
- The Not5 Subunit of the Ccr4-Not Complex Connects Transcription and Translation
- Abnormal Dosage of Ultraconserved Elements Is Highly Disfavored in Healthy Cells but Not Cancer Cells
- Genome-Wide Distribution of RNA-DNA Hybrids Identifies RNase H Targets in tRNA Genes, Retrotransposons and Mitochondria
- The Chromosomal Association of the Smc5/6 Complex Depends on Cohesion and Predicts the Level of Sister Chromatid Entanglement
- Cell-Autonomous Progeroid Changes in Conditional Mouse Models for Repair Endonuclease XPG Deficiency
- PLOS Genetics
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- The Master Activator of IncA/C Conjugative Plasmids Stimulates Genomic Islands and Multidrug Resistance Dissemination
- A Splice Mutation in the Gene Causes High Glycogen Content and Low Meat Quality in Pig Skeletal Muscle
- Keratin 76 Is Required for Tight Junction Function and Maintenance of the Skin Barrier
- A Role for Taiman in Insect Metamorphosis
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Vladimír Palička, CSc., Dr.h.c., doc. MUDr. Václav Vyskočil, Ph.D., MUDr. Petr Kasalický, CSc., MUDr. Jan Rosa, Ing. Pavel Havlík, Ing. Jan Adam, Hana Hejnová, DiS., Jana Křenková
Autoři: MUDr. Irena Krčmová, CSc.
Autoři: MDDr. Eleonóra Ivančová, PhD., MHA
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Eva Kubala Havrdová, DrSc.
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



