-
Články
Top novinky
Reklama- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
Top novinky
Reklama- Kongresy
- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Top novinky
ReklamaPPM1A Regulates Antiviral Signaling by Antagonizing TBK1-Mediated STING Phosphorylation and Aggregation
Innate antiviral immunity is essential for the host defense system that rapidly detects and eliminates invading viruses. STING, an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated protein, plays important roles in the activation of type I IFN in response to DNA virus infection. Whereas excessive activation of STING can potentially cause lethal inflammatory diseases, STING activity must thus be precisely controlled to ensure the proper antiviral signaling transduction. However, the mechanisms of how STING activation is regulated are not fully understood. In this study, we find that PPM1A physically interacts with STING and negatively regulates STING-mediated antiviral signaling. Mechanistically, we find that PPM1A functions as a phosphatase that targets both STING and TBK1 for their dephosphorylation. Moreover, our study demonstrates that while TBK1 enhances STING aggregation in a kinase activity-dependent manner, PPM1A suppresses STING aggregation by dephosphorylating both STING and TBK1. Collectively, our study not only reveals that STING and TBK1 reciprocally regulate each other’s activity to elicit antiviral signaling, but also shows that PPM1A antagonizes STING aggregation by targeting both STING and TBK1, thereby maintaining proper antiviral responses.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Pathog 11(3): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004783
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1004783Summary
Innate antiviral immunity is essential for the host defense system that rapidly detects and eliminates invading viruses. STING, an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated protein, plays important roles in the activation of type I IFN in response to DNA virus infection. Whereas excessive activation of STING can potentially cause lethal inflammatory diseases, STING activity must thus be precisely controlled to ensure the proper antiviral signaling transduction. However, the mechanisms of how STING activation is regulated are not fully understood. In this study, we find that PPM1A physically interacts with STING and negatively regulates STING-mediated antiviral signaling. Mechanistically, we find that PPM1A functions as a phosphatase that targets both STING and TBK1 for their dephosphorylation. Moreover, our study demonstrates that while TBK1 enhances STING aggregation in a kinase activity-dependent manner, PPM1A suppresses STING aggregation by dephosphorylating both STING and TBK1. Collectively, our study not only reveals that STING and TBK1 reciprocally regulate each other’s activity to elicit antiviral signaling, but also shows that PPM1A antagonizes STING aggregation by targeting both STING and TBK1, thereby maintaining proper antiviral responses.
Introduction
Innate immunity is the first line of the host defense system against invading microorganisms, including viruses. The detection of conserved microbial molecules, known as pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), by the host cells involves multiple pattern recognition receptors (PRRs). Nucleic acids derived from viruses act as PAMPs to trigger the innate immune response when they are recognized by PRRs, leading to the production of a variety of cytokines, including type I interferons (IFNs).
Host cells have evolved multiple sensing systems to recognize PAMPs during viral infection, in a manner that depends on the cellular location and ligand specificity. For example, Toll-like receptors (TLRs) such as TLR3, TLR7, and TLR8 can detect different species of RNA viruses in the endosomal compartment [1], whereas the RIG-I-like receptors, RIG-I and MDA5 function as cytoplasmic sensors of viral RNA [2,3]. In response to RNA viral infection, RIG-I and MDA5 form a complex in the cytosol with the adaptor protein MAVS [4] (also known as IPS-1 [5], VISA [6], and CARDIF [7]), efficiently inducing a conformational switch of MAVS that causes MAVS aggregation and activation [8]. Activated MAVS then recruits TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) and the IκB kinase (IKK) complex to activate transcription factors interferon regulatory factor 3/7 (IRF3/7) and NF-κB respectively, which coordinately induce the production of type I IFNs and elicit the innate immune response.
Nucleic acids from DNA viruses also induce potent innate immune responses. A number of cytoplasmic DNA sensors, including AIM2 [9–12], DAI [13], IFI16 [14], DDX41 [15], and cGAS [16], have recently been identified. STING (also called MITA [17], and ERIS [18]) is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated molecule that acts as an adaptor for the activation of type I IFN in response to cytosolic nucleic acid ligands. Upon activation, STING interacts with TBK1 and activates transcription factor IRF3 to induce the production of type I interferon genes. Although STING is critical for the protection of the host against the invasion of DNA pathogens, its excessive activation can potentially cause lethal inflammatory diseases [19,20]. Therefore, STING activity must be precisely controlled to ensure a proper innate immune homeostasis in infected host cells. Several factors, such as RNF5 [21], Atg9a [22], ULK1 [23], and NLRC3 [24], have recently been shown to suppress the activation of STING. A previous study [25] suggested that, whereas STING induces TBK1 activation, STING itself can be phosphorylated and polymerized that further contributes to IRF3 activation, and the phosphorylated and polymerized STING thus probably forms a scaffold platform to recruit TBK1 and IRF3. These findings indicate an intriguing feed-forward mechanism, via the regulation between STING and TBK1, which efficiently triggers innate immune antiviral signaling.
Previous studies have suggested two distinct models regarding phosphorylation of STING for regulating its function. Konno et al. found that ULK1 phosphorylated STING at S366 for its degradation, and thereby suppressing the downstream IRF3 signaling activity [23]. However, a most recent study reported that STING phosphorylation at S366 by TBK1 is required for direct IRF3 recruitment and activation, rather than for STING degradation [26]. Thus, the issue of how STING phosphorylation contributes to STING signaling activity has remained largely unclear.
In an effort to understand the molecular mechanism underlying the regulation of STING in detail, we performed yeast two-hybrid screening and identified protein phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+-dependent, 1A (PPM1A), a member of the PP2C family of serine/threonine (Ser/Thr) protein phosphatases, as a STING-interacting protein. We demonstrated that PPM1A negatively regulates antiviral signaling by targeting STING for dephosphorylation in a phosphatase activity-dependent manner. We also found that PPM1A directly dephosphorylates STING and TBK1 in in vitro assays. Importantly, we provide evidence that whereas TBK1 promotes STING aggregation in a phosphorylation-dependent manner, PPM1A antagonizes STING aggregation by dephosphorylating both STING and TBK1, emphasizing that phosphorylation is a crucial step for efficient STING activation. Together, our findings identify a novel regulatory circuit in which STING and TBK1 reciprocally regulate one another to elicit antiviral signaling, whereas PPM1A dephosphorylates STING and TBK1, thereby balancing antiviral signal transduction.
Results
Identification of PPM1A as a STING-interacting protein
To understand the molecular mechanisms underlying the regulation of STING in the antiviral innate immune signaling pathway, we performed a yeast two-hybrid screen to identify STING-interacting factors using the C-terminal fragment of STING (amino acids 153–379) as bait. From this screening, we found that one of the positive clones encoded the full-length PPM1A protein (S1A Fig). PPM1A is a member of the PP2C family of Ser/Thr protein phosphatases. PP2C family members are known as negative regulators of cellular stress-response pathways [27] and are involved in cell-cycle control by dephosphorylating cyclin-dependent kinases [28] and also play roles in NF-κB pathway by dephosphorylating IKKβ and P65 [29,30]. To confirm that PPM1A interacts directly with STING, we performed histidine (His)/glutathione S-transferase (GST) in vitro pull-down experiments using recombinant His–STING (amino acids 153–379) and GST–PPM1A purified from bacteria. As shown in Fig. 1A, GST–PPM1A, but not GST control protein, pulled down His–STING (amino acids 153–379). Consistently, His–STING (amino acids 153–379) pulled down GST–PPM1A, but not the GST control protein (S1B Fig). To further determine the interaction under physiological condition, we performed co-immunoprecipitation experiments to examine whether STING physically interacts with PPM1A in cultured mammalian cells. As shown in Fig. 1B and C, epitope-tagged PPM1A and STING reciprocally co-immunoprecipitated with each other in transfected HEK293 cells. Consistent with these results, we found that endogenous PPM1A protein was present in the STING complex in THP-1 cells (Fig. 1D). Of note, we found that the endogenous STING–PPM1A association was even reliably detectable under normal physiological condition. Interestingly, we found that viral infection could increase the association between PPM1A and STING, since an apparent elevation of PPM1A levels were detected in the STING immunoprecipitates at the 8-hour time point post-HSV-1-infection (Fig. 1D). Taken together, our findings suggest that PPM1A interacts directly with STING.
Fig. 1. Identification of PPM1A as a protein that interacts with STING. 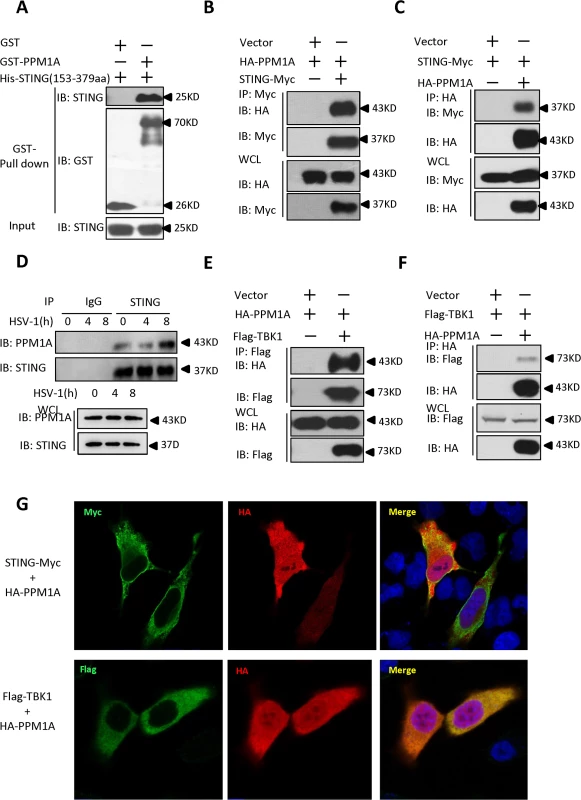
(A) Purified GST–PPM1A interacted with His–STING (amino acids 153–379) in an in vitro protein-binding assay. Purified His–STING (amino acids 153–379; 1 μg) was incubated with purified GST–PPM1A (1 μg) or GST (1 μg), and then pulled down with glutathione–Sepharose beads. Western blots were performed to analyze the presence of His-tagged STING and GST-tagged PPM1A proteins. (B, C) Epitope-tagged PPM1A and STING interacted with each other in HEK293 cells. HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated DNA plasmids. At 24 h post-transfection, the lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc beads (B) or anti-HA beads (C), followed by immunoblotting analysis with the indicated antibodies. WCL (bottom), expression of exogenous proteins in whole-cell lysates. (D) More PPM1A proteins were found to be present in the STING immunoprecipitates after HSV-1 virus infection. THP-1 cells were infected with or without HSV-1 at 5 MOI for the indicated times. The cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with rabbit anti-STING antibody or an IgG control antibody. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting with the anti-PPM1A and anti-STING antibodies. Expression levels of endogenous PPM1A and STING were detected with an immunoblotting analysis. (E, F) Epitope-tagged PPM1A and TBK1 interacted in HEK293 cells. Transfection and co-immunoprecipitation experiments were performed as in B and C, except that Flag-TBK1 expression vector was used instead of STING-Myc. (G) PPM1A is co-localized with both STING and TBK1 in transfected Hela cells. Hela cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids for 24 h, and then fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, stained with the indicated antibodies, and observed with confocal microscopy. Previous study has shown that PPM1B, another member of the PP2C family of Ser/Thr protein phosphatases, associates with TBK1 and negatively regulates antiviral signaling by antagonizing TBK1 activation through dephosphorylation [31]. Because PPM1A and PPM1B are highly similar at the amino acid level, we tested whether PPM1A also associates with TBK1 and regulates its function in HEK293 cells. To test this possibility, we performed co-immunoprecipitation experiments in HEK293 cells transfected with epitope-tagged PPM1A and TBK1. As shown in Fig. 1E and F, epitope-tagged PPM1A and TBK1 were co-immunoprecipitated in HEK293 cells. Consistent with this observation, our immunostaining assays showed that PPM1A co-localized with both STING and TBK1 in transfected Hela cells (Fig. 1G). On the basis of these observations, we reasoned that PPM1A might have a potential role in regulating STING-mediated antiviral innate immune pathway.
Overexpression of PPM1A inhibits STING-induced antiviral signaling
To determine whether PPM1A is involved in the regulation of STING activation, we first tested whether PPM1A contributes to the regulation of STING-induced type I IFN signaling using a cell-based luciferase reporter system. As shown in Fig. 2A and B, the expression of STING significantly activated the promoters of interferon-stimulated response element (ISRE) and IFNβ in HEK293 cells, whereas the co-expression of PPM1A with STING apparently reduced the STING-induced activation of these promoters, indicating a negative role for PPM1A in regulating STING activity. Because PPM1A acts as a Ser/Thr protein phosphatase, we next tested whether its catalytic activity is required for PPM1A to antagonize STING activation. As shown in luciferase reporter assays, the expression of PPM1A-R174G, a catalytically inactive form of PPM1A [32,33], had apparently lost its capacity to antagonize STING activation (Fig. 2A and B), suggesting that PPM1A suppresses STING function in its phosphatase activity-dependent manner.
Fig. 2. Overexpression of PPM1A inhibits STING-mediated antiviral signaling. 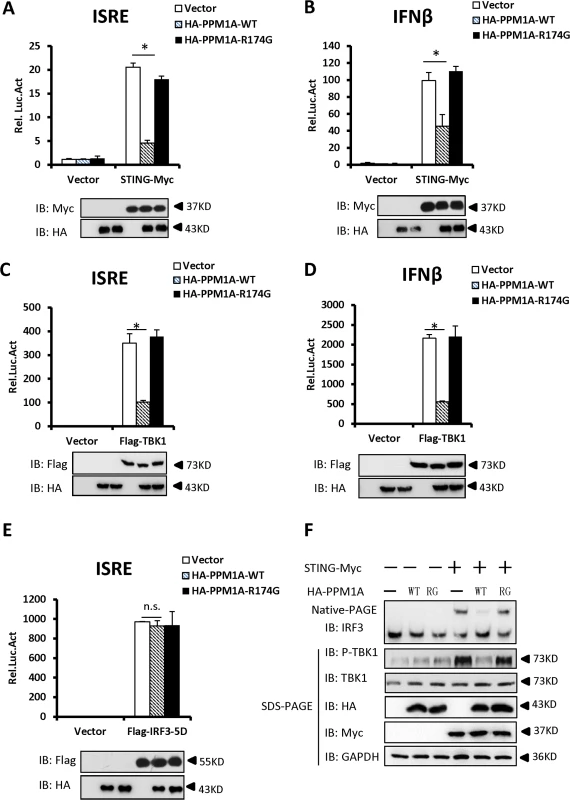
(A, B) Overexpression of PPM1A reduced STING-induced activation of the ISRE and IFN-β promoters, which was dependent on the phosphatase activity of PPM1A. HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated expression plasmids together with luciferase reporter constructs (50 ng) driven by the promoters of genes encoding ISRE (A) or IFN-β (B), and pRSV/LacZ (50 ng) as the internal control. Twenty-four hours after transfection, the cells were lysed for luciferase assays (upper panel) and immunoblotting assays (lower panel). Luciferase activity was measured and normalized to β-galactosidase activity. The results are presented relative to the luciferase activity in the control cells. (C, D) ISRE and IFN-β activation induced by TBK1 was also reduced by PPM1A-WT, but not by PPM1A-R174G. Twenty-four hours after transfection, the cells were lysed for luciferase assays (upper panel) and immunoblotting assays (lower panel). Transfections were performed as in A and B, except that the TBK1 expression vector was used instead of STING-Myc. (E). PPM1A did not affect the IRF3-5D-induced activation of the ISRE promoter. HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated expression plasmids together with ISRE-luc (50 ng), and pRSV/LacZ (50 ng) as the internal control. Twenty-four hours after transfection, the cells were lysed for luciferase assays (upper panel) and immunoblotting assays (lower panel). (F) PPM1A-WT, but not PPM1A-R174G, significantly reduced STING-induced IRF3 dimerization and TBK1 phosphorylation. HEK293 cells were transfected with expression plasmids as indicated. At 30 h after transfection, the cell lysates were resolved by native gel electrophoresis (upper panel) or SDS-PAGE (lower panels) and analyzed with the indicated antibodies. The data shown in A–E are from one representative experiment of at least three independent experiments (means ± SD of duplicate assays). The two-tailed Student’s t test was used to analyze statistical significance. * P < 0.05; n.s., No Significance, versus control groups. We next tested whether PPM1A affects the activation of TBK1 and IRF3. As shown in Fig. 2C and D, the activation of ISRE and IFN-β induced by TBK1, was also suppressed by the expression of wild-type PPM1A, but not by the mutant form, PPM1A-R174G, suggesting that PPM1A phosphatase activity is required for its function in regulating TBK1 activation. In contrast, the expression of PPM1A had no apparent effect on the activation of ISRE induced by IRF3-5D, a constitutively activated form of IRF3 (Fig. 2E), suggesting that PPM1A primarily regulates the signaling upstream of IRF3.
Because the dimerization of IRF3 and TBK1 phosphorylation (at the Ser 172 residue) are important events in the activation of the IFN-β signaling pathway, we tested whether PPM1A modulates STING-mediated IRF3 dimerization and TBK1 phosphorylation. As shown in Fig. 2F, the overexpression of STING led to the dimerization of IRF3 and increase of TBK1 phosphorylation, whereas the co-expression of the wild-type PPM1A, but not mutant PPM1A-R174G, significantly reduced the effects of STING overexpression on IRF3 dimerization and TBK1 phosphorylation. Collectively, our findings suggest that the overexpression of PPM1A antagonizes the STING - and TBK1-induced type I IFN signaling pathway.
Knockdown of PPM1A potentiates STING signaling
We next investigated whether endogenous PPM1A plays a role in regulating the antiviral response. We first synthesized two different pairs of small interfering RNA (siRNA) oligonucleotides targeting distinct coding regions of the PPM1A mRNA. As shown in Fig. 3A and B, both pairs of siRNA efficiently reduced the expression of endogenous PPM1A at both mRNA and protein levels in HEK293 cells. We selected siPPM1A-2 for the subsequent experiments because it more efficiently down-regulated the expression of PPM1A.
Fig. 3. Knockdown of PPM1A potentiates STING signaling. 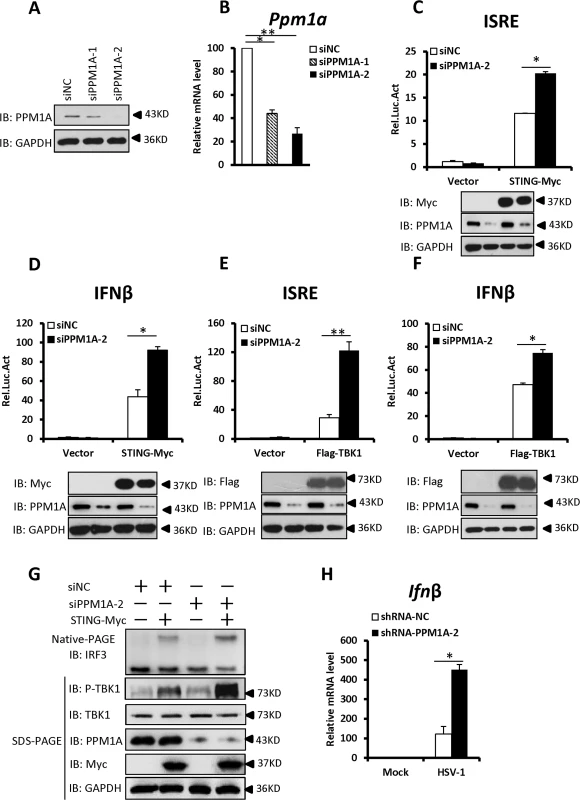
(A, B) Both pairs of PPM1A siRNAs efficiently reduced the levels of endogenous PPM1A at both the protein (A) and mRNA levels (B). HEK293 cells were transfected with siRNA (40 nM) targeting PPM1A or NC (non-targeting control). At 48 h after transfection, the cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting (A) or qRT-PCR (B). Data shown in B are the relative levels of Ppm1a mRNA in Ppm1a knockdown cells to the control cells; the Ppm1a mRNA abundance of the control group (siNC) was assigned a value of 100. (C, D) Knockdown of PPM1A potentiated STING-induced activation of the ISRE (C) and IFN-β (D) promoters. HEK293 cells were transfected with siNC (40 nM) or siPPM1A-2 (40 nM). At 48 h after transfection, the cells were transfected with empty vector or STING expression vector together with the reporter plasmids using Lipofectamine 2000 for 20 h. The cells were then lysed for luciferase assays (upper panel) and immunoblotting assays (lower panels). (E, F) Knockdown of PPM1A increased TBK-induced activation of the ISRE (E) and IFN-β (F) promoters. Transfection and luciferase assays were performed as in C and D, except that TBK1 expression vector was used instead of STING expression vector. (G) Knockdown of PPM1A significantly enhanced STING-induced IRF3 dimerization and TBK1 phosphorylation. HEK293 cells were transfected with siNC (40 nM) or siPPM1A-2 (40 nM) for 36 h, and then transfected with empty vector (400 ng) or STING-encoding vector (400 ng) for another 36 h using Lipofectamine 2000. The cell lysates were separated by native gel electrophoresis (upper panel) or SDS-PAGE (lower panel) and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (H) Knockdown of PPM1A clearly increased HSV-1-induced transcription of the Ifnβ gene. THP-1 cells were infected with a lentivirus targeting PPM1A for knockdown or NC for 72 h and then left uninfected or infected with HSV-1 at a MOI of 5 for 6 h. Cells were lysed and total RNA were isolated for qRT-PCR analysis. Data shown are the relative abundance of Ifnβ in the cells treated as indicated, the relative levels of Ifnβ in the control cells (siNC, mock) was assigned a value of 1. The data in B–F, and H are from one representative experiment of at least three independent experiments, (mean ± SD of duplicate in C–F or triplicate in B and H). A two-tailed Student’s t test was used to analyze statistical significance. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01 versus the control groups. We then determined the effects of PPM1A knockdown on the STING-mediated antiviral signaling. As shown in Fig. 3C–F, knockdown of PPM1A significantly enhanced the STING - or TBK1-mediated activation of the ISRE and IFNβ promoters in HEK293 cells. Consistent with this, the knockdown of PPM1A significantly enhanced STING-induced IRF3 dimerization and TBK1 phosphorylation at S172 (Fig. 3G), but did not apparently influence IRF3-5D-induced ISRE activation (S2A Fig). These data further support the notion that PPM1A negatively regulates STING signaling at the upstream of IRF3.
Given the critical role of STING in protecting the host from DNA pathogens, we next used the THP-1 cell line to test whether PPM1A affects the innate immune signaling induced by DNA virus Herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) by measuring the expression of endogenous Ifnβ. As shown in quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) assays, short hairpin RNA (shRNA)-mediated PPM1A knockdown clearly increased HSV-1-induced endogenous Ifnβ expression (Figs. 3H and S2B), providing further evidence showing the negative role of PPM1A in regulating STING signaling.
Enhanced STING signaling in Ppm1a-deficient cells
To better understand the biological importance of PPM1A in regulating antiviral signaling, we generated Ppm1a–/—mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and examined the effects of Ppm1a deletion on the activation of STING signaling. We used a double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) containing 45 nucleotides, known as “IFN stimulatory DNA” (ISD), as a stimulator to activate the IFN-β signaling cascade in MEFs. As shown in Fig. 4A–D, the ISD-induced transcription of antiviral genes, including Cxcl10, Ifnβ, Rantes, and Isg15, were strongly increased in Ppm1a–/—MEFs compared to those in Ppm1a+/+ MEFs. In support of this, the level of IFN-β protein induced by ISD was also increased in Ppm1a–/—MEFs when measured with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Fig. 4E). Furthermore, levels of IRF3 dimerization and phosphorylation of endogenous TBK1 induced by ISD were also markedly increased in Ppm1a–/—MEFs, when compared to Ppm1a+/+ MEFs under the same experimental conditions (Fig. 4F-G). Additionally, we observed that the levels of Ifnβ at both mRNA and protein induced by HSV-1 virus infection were increased in Ppm1a–/—bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM), compared to the Ppm1a+/+ control (S3A and S3B Fig). We next sought to perform a rescue experiment to better understand the biological roles and the specificity of PPM1A in antiviral signaling using the Ppm1a–/—MEF cells. As shown in Figs. 4H and S4, expression of wild-type PPM1A, but not mutant PPM1A-R174G, could reverse the enhancement of Ifnβ expression induced by ISD treatment or HSV-1 infection in Ppm1a–/—MEFs. Taken together, these data indicated PPM1A play a negative role in STING-mediated antiviral signaling.
Fig. 4. Enhanced STING signaling in Ppm1a-deficient cells. 
(A–D) PPM1A deficiency enhanced the transcriptional levels of antiviral genes. Primary Ppm1a+/+ and Ppm1a–/—MEFs were transfected with ISD (2 μg/ml) for 6 h, followed by qRT-PCR analysis. The transcriptional levels of Cxcl10 (A), Ifnβ (B) Rantes (C), and Isg15 (D) were examined, the relative levels of the indicated mRNA in the control cells (Ppm1a+/+, mock) was assigned a value of 1. (E) The production of IFN-β protein induced by ISD was increased in Ppm1a-/- MEFs. Primary Ppm1a+/+ and Ppm1a-/- MEFs were left untreated or transfected with ISD (2 μg/ml) for 24 h, and then the supernatants were collected for measurement of IFN-β protein by ELISA.(F) ISD-induced IRF3 activation was increased in Ppm1a–/—MEFs. Primary Ppm1a+/+ and Ppm1a–/—MEFs were left untreated or transfected with ISD (2 μg/ml) for 4 h. The cell lysates were separated by native gel electrophoresis (upper panel) or SDS-PAGE (lower panels) and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (G) The phosphorylation of TBK1 induced by ISD was enhanced in Ppm1a–/—MEFs. Primary Ppm1a+/+ and Ppm1a–/—MEFs were left untreated or transfected with ISD (2 μg/ml) for the indicated times. The cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (H) Ppm1a-/- MEFs were first infected with retrovirus expressing PPM1A-WT or PPM1A-R147G, after 48 h infection, cells were then transfected with (or without) ISD (3 μg/ml) for 7 h and followed by qRT-PCR analysis. Ppm1a+/+ MEFs were used as positive control. The relative levels of Ifnβ mRNA in the control cells (Ppm1a+/+, mock) was assigned a value of 1. (I) PPM1A deficiency suppressed the amplification of HSV-1. Primary Ppm1a+/+ and Ppm1a–/—MEFs were infected with HSV-1 at MOI of 5 for 16 h. The genomic DNA was extracted and the relative HSV genome copy numbers were measured with qRT-PCR analysis. The data in A–E, H and I are from one representative experiment of at least three independent experiments (means ± SD of triplicate assays in A-D and H-I, or duplicate in E). A two-tailed Student’s t test was used to analyze statistical significance. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01versus the control groups. We next determined the biological function of PPM1A in regulating virus amplification. As shown in Fig. 4I, the copy numbers of HSV-1 genomic DNA were much lower in the Ppm1a–/—MEFs cells than in wild-type MEFs, suggesting that PPM1A is involved in regulating the amplification of DNA virus. Given that TBK1 also plays critical roles in anti-RNA-viral signaling, and that PPM1A suppresses TBK1 activity, we then sought to determine whether PPM1A also regulates the amplification of RNA virus. We measured the titer of the vesicular stomatitis mutant virus (VSVΔM51-GFP), a RNA virus which carries a single amino acid deletion (methionine 51) in the matrix (M) protein in VSV-GFP virus, in wild-type and Ppm1a–/—MEFs. As shown in S5A and S5B Fig, we observed much lower viral titers of VSVΔM51-GFP produced in Ppm1a–/—MEFs than in wild-type control cells. These results provide further biological evidence that PPM1A is a negative regulator of IRF3 activation, IFN-β production, and cellular antiviral response.
TBK1 promotes STING aggregation
It has previously been reported that STING acts as a scaffold to assemble the protein complex containing TBK1 and IRF3, thus specifying and promoting the phosphorylation of IRF3 by TBK1 [25]. Our results showed that PPM1A plays a role in regulating the activation of both STING and TBK1 in a manner that depends on the catalytic activity of PPM1A, suggesting a potential regulatory relationship among these proteins. Because of the important role of STING in transducing antiviral signaling against DNA virus, we investigated whether and how the dynamic status of STING phosphorylation is regulated by TBK1 and PPM1A. To test whether TBK1 regulates STING, we transfected HEK293 cells with plasmids expressing TBK1 and STING, as shown in Fig. 5A (top panel), the expression of TBK1 caused band shifts of the STING on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) in a dose-dependent manner. The shifted bands appeared to be phosphorylated forms of STING, since calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (CIAP) treatment abolished the band shifts (Fig. 5B), suggesting that TBK1 promotes STING phosphorylation. Interestingly, we noted that STING also formed high-molecular-weight products that stayed in the stacking gel on native PAGE (Fig. 5A, middle panel), when it was co-expressed with TBK1. These findings suggest that the TBK1-mediated phosphorylation of STING potentially promotes its polymerization.
Fig. 5. TBK1 promotes STING aggregation. 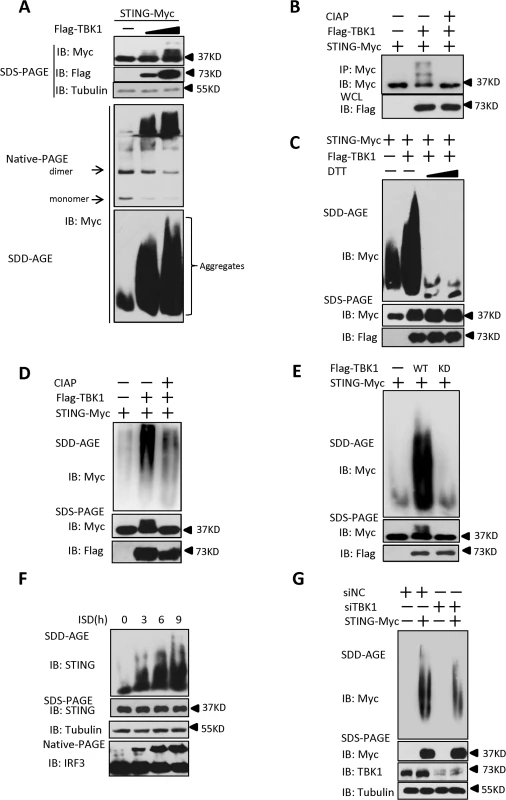
(A) TBK1 promoted STING aggregation in a dose-dependent manner. HEK293 cells were transfected with STING-Myc expression plasmids (0.2 μg) together with the empty vector (2 μg) or increased dose of Flag–TBK1 expression plasmids (0.5 μg, 2 μg). At 30 h after transfection, the cell lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE (top), native gel electrophoresis (middle), or SDD-AGE (bottom), and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (B) TBK1 induced STING phosphorylation. HEK293 cells were transfected with STING-Myc (0.5 μg) along with empty vector (2 μg) or Flag-TBK1 (2 μg), and 24 h later, cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc. The immunoprecipitates were treated with buffer or calf intestine phosphatase (CIAP) and analyzed by with SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting. (C) DTT treatment reduced STING aggregation. HEK293 cells were transfected with STING-Myc expression plasmids together with the empty vector or Flag–TBK1 expression plasmid. At 30 h after transfection, the cell lysates were untreated or treated with 5 mM or 20 mM DTT for 30 min at room temperature, and then resolved by SDD-AGE (upper panel) or SDS-PAGE (lower panels), followed by immunoblotting analysis with the indicated antibodies. (D) CIAP treatment reduced the STING aggregation induced by TBK1. HEK293 cells were transfected with STING-Myc expression plasmids along with empty vector or Flag–TBK1 expression plasmids. At 24 h after transfection, the cells were lysed and then left untreated or treated with CIAP for 30 min at 37°C as indicated and analyzed with SDD-AGE and SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting analysis. (E) TBK1 kinase activity was important for the induction of STING aggregation. HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids for 24 h. The cell lysates were separated with SDD-AGE and SDS-PAGE, and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (F) Endogenous STING formed aggregates in response to stimulation with ISD in THP-1 cells. THP-1 cells were transfected with ISD (2 μg/ml) using Lipofectamine 2000 for the indicated times and lysed. The proteins were resolved with SDD-AGE and SDS-PAGE, and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (G) Knockdown of endogenous TBK1 attenuated STING aggregation in HEK293 cells. HEK293 cells were transfected with NC (40 nM) or a TBK1 (40 nM) RNAi oligonucleotide. At 48 h after transfection, the cells were transfected with vector encoding STING-Myc or empty vector for 24 h. The cell lysates were prepared and resolved with SDD-AGE (upper panel) and SDS-PAGE assays (lower panel), followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Prion-like polymerization has recently been shown to be a conserved signal-transduction mechanism in both yeast and mammal [34,35]. Previous studies have suggested that in response to RNA viral infection, MAVS forms large prion-like aggregates that potently activate MAVS-mediated antiviral signaling [8]. A recent study [25] and our current study suggest that STING is potentially polymerized, and as demonstrated here, this polymerization of STING might be promoted directly by TBK1. Therefore, we examined whether STING aggregates behave like MAVS. To do so, we separated cell lysates with semi-denaturing detergent agarose gel electrophoresis (SDD-AGE), a method for detecting large protein polymers in studying prions [36]. As shown in S6A Fig, the overexpression of STING alone produced a smear of high-molecular weight aggregates at higher doses, albeit at a lower level. However, we found that levels of aggregation of STING were dramatically increased, when it was co-expressed with TBK1, suggesting that TBK1 promotes STING aggregation (Fig. 5A, bottom panel). Of note, STING aggregation required the N-terminal (amino acids 1–152) and C-terminal (amino acids 311–379) regions, since lacking either of these regions evidently affected the aggregation of STING (S6B and S6C Fig). Interestingly, we found that similar to MAVS [8], the aggregation of STING promoted by TBK1 was also very sensitive to Dithiothreitol (DTT) treatment (Fig. 5C), suggesting that STING aggregates are likely facilitated by the disulfide bond formation. Furthermore, we found that the aggregation of STING was also reduced when the lysates were treated with CIAP (Fig. 5D), revealing that the formation of STING aggregates is dependent on its phosphorylation. In a line with this, the kinase-dead form of TBK1 (TBK1-KD) failed to promote further STING aggregation (Fig. 5E). Taken together, these findings suggest that the TBK1-induced phosphorylation of STING promotes the aggregation of STING.
We next investigated whether STING aggregation occurs when THP-1 cells were stimulated with ISD. As shown in Fig. 5F, ISD treatment induced STING aggregation in a time-dependent manner. Consistently, similar results were obtained with HSV-1 infection (S6D Fig). Since overexpression of TBK1 promoted STING aggregation, we next tested whether TBK1 is necessary for the STING aggregation. As shown in an SDD-AGE assay, the knockdown of TBK1 appeared to attenuate STING aggregation in HEK293 cells (Fig. 5G). Collectively, these findings support the notion that TBK1 promotes STING aggregation, likely in a phosphorylation-dependent manner.
Identification of specific phosphorylation residues in STING that contribute to its aggregation
Having established that TBK1 promotes STING phosphorylation and aggregation, we then determined how TBK1-mediated STING phosphorylation and attempted to identify the putative phosphorylation residues in STING that are required for its activity and its aggregation as well. Based on the protein sequence of STING, we generated a library of human STING mutants in which serine (S) or threonine (T) residues were mutated to alanine (A) either individually, or two adjacent serine and/or threonine residues in combination, according to the method described previously [37]. Using this library, we performed luciferase reporter assays to test the potential roles of these serine and threonine residues in controlling STING function. As shown in luciferase reporter assays, mutation of S280, S358, or S366 to alanine remarkably reduced the activation of STING (Figs. 6A and B, and S7A-S7D), suggesting that these residues are critical for the STING activation to induce downstream signaling. Notably, further western blot analysis suggested that mutation of S280, S358, or S366 to alanine affected the TBK1-mediated phosphorylation of STING, since the shifted bands were apparently reduced (Fig. 6C). In addition to the above strategy, we also employed the HEK293 cells co-expressing TBK1 and STING to perform a mass spectrometric analysis and again identified the S358 site as the phosphorylated residue in STING (S8A–S8C Fig, S1 Text). We then asked whether the S358 residue in STING could be directly phosphorylated by TBK1 and performed an in vitro phosphorylation assay. As shown in S9 Fig, a stronger super-shift signal of wild-type STING induced by TBK1 could be detected, when compared to the STING-S358A mutant. Taken together, these findings support that S358 is one of the residues for phosphorylation targeted by TBK1 and the phosphorylation status of this site likely contributes to the full activation of STING.
Fig. 6. Identification of specific phosphorylation sites in STING that contribute to its aggregation. 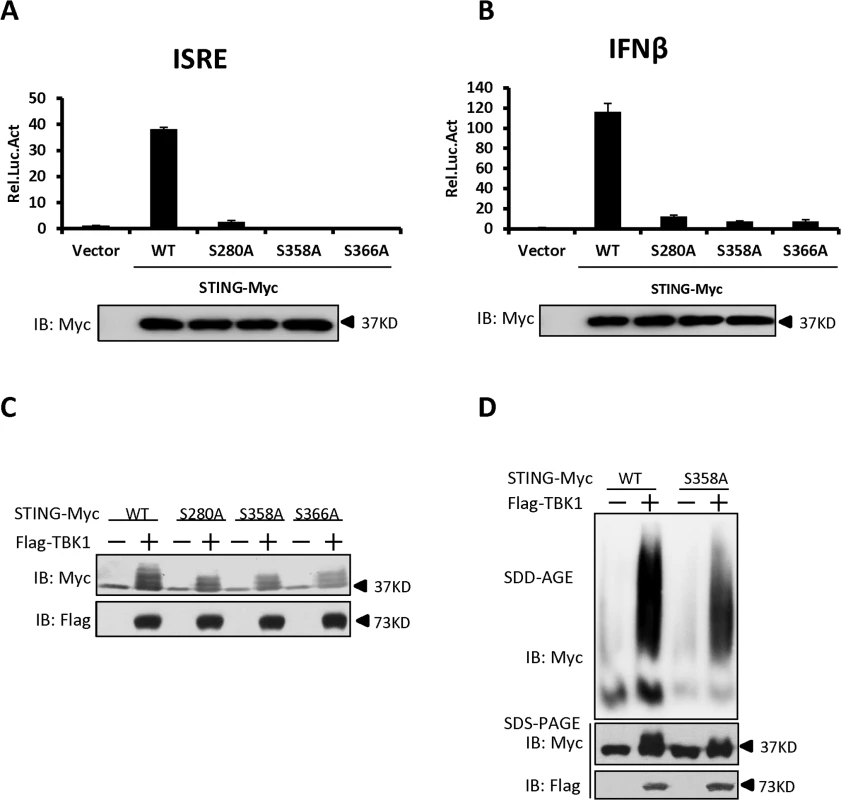
(A, B) The luciferase reporter assays showing activation of the ISRE (A) and IFN-β (B) promoter to different levels by that indicated STING Ser mutants. HEK293 cells were transfected with vectors encoding STING-WT or mutants as indicated. At 30 h after transfection, the cells were lysed for luciferase assays (upper panel) and immunoblotting assays (lower panel). (C) The phosphorylation of STING mediated by TBK1 was reduced in STING S280A, S358A, and S366A mutants. HEK293 cells were transfected with vectors encoding STING wild-type or its mutants, together with TBK1-encoding vector or empty vector, for 30 h. The cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (D) The residue S358 of STING was important for its aggregation. HEK293 cells were transfected with vector encoding STING-WT or STING-S358A together with TBK1 expression vector or empty vector. At 30 h after transfection, the cell lysates were resolved by SDD-AGE (upper panel) or SDS-PAGE (lower panel) and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. The data in A–B are from one representative experiment of at least three independent experiments (means ± SD of duplicate assays). We next tested whether the S358 residue contributes to the polymerization of STING by performing SDD-AGE assays. As shown in Fig. 6D, the S358A mutant of STING has a significant reduction in self-propagating polymer formation induced by TBK1, when compared to wild-type STING. These findings suggest that the S358 in STING is an important target residue phosphorylated by TBK1 and also contributes to the aggregation of STING.
PPM1A directly dephosphorylates STING and prevents STING aggregation
Having demonstrated that TBK1 plays an important role in controlling STING phosphorylation and aggregation, we next sought to ask whether PPM1A has an opposite effect in regulating STING phosphorylation and aggregation. Several lines of evidence suggest that PPM1A antagonizes TBK1 function and regulates STING phosphorylation and aggregation. First, PPM1A functions as a negative regulator of STING-induced antiviral signaling; second, PPM1A associates with both STING and TBK1; and third, PPM1A functions as a Ser/Thr phosphatase and its catalytic activity is required for regulating STING activation. To test this hypothesis, we first examined whether PPM1A affects the phosphorylation of STING induced by TBK1 in transfected cells. As shown in Fig. 7A, we found that PPM1A dramatically reduced the phosphorylation of STING in a phosphatase activity-dependent manner. Next we further determined whether STING is a direct target of PPM1A. We purified His–STING (amino acids 153–379), GST–PPM1A-WT and GST-PPM1A-R174G from bacteria, Flag–TBK1 from HEK293 cells, respectively, and performed in vitro phosphorylation and dephosphorylation assays. In these assays, His–STING (amino acids 153–379) was firstly used as the substrate to be phosphorylated by Flag–TBK1. Once the phosphorylation reaction was terminated, the reaction buffer was changed to phosphatase buffer and the GST–PPM1A-WT or GST-PPM1A-R174G was added for a subsequent phosphatase assay. As shown in Fig. 7B, GST–PPM1A-WT, but not GST-PPM1A-R174G, clearly reduced the levels of STING phosphorylation catalyzed by Flag-TBK1. To further test whether PPM1A target STING dephosphorylation through its S358 site, we used synthesized STING phosphopeptides corresponding to phospho-S358 as substrate, and performed an in vitro dephosphorylation assay, and found that GST-PPM1A-WT, but not GST-PPM1A-R174G, directly dephosphorylates pS358 peptide (S10A Fig). This finding provides direct biochemical evidence suggesting that PPM1A regulates de-phosphorylation of STING. Of note, we also found that the levels of TBK1 phosphorylation at Ser 172, were reduced by PPM1A both in the in vitro phosphatase assay (Fig. 7C) and in transfected cells (Fig. 7D), suggesting that TBK1 is also a direct target of PPM1A. By contrast, we found that PPM1A failed to dephosphorylate IRF3 at the Ser 396 residue, which is phosphorylated in response to TBK1 activation, under the same experimental conditions (S10B–S10C Fig).
Fig. 7. PPM1A directly dephosphorylates STING and TBK1 and prevents STING aggregation. 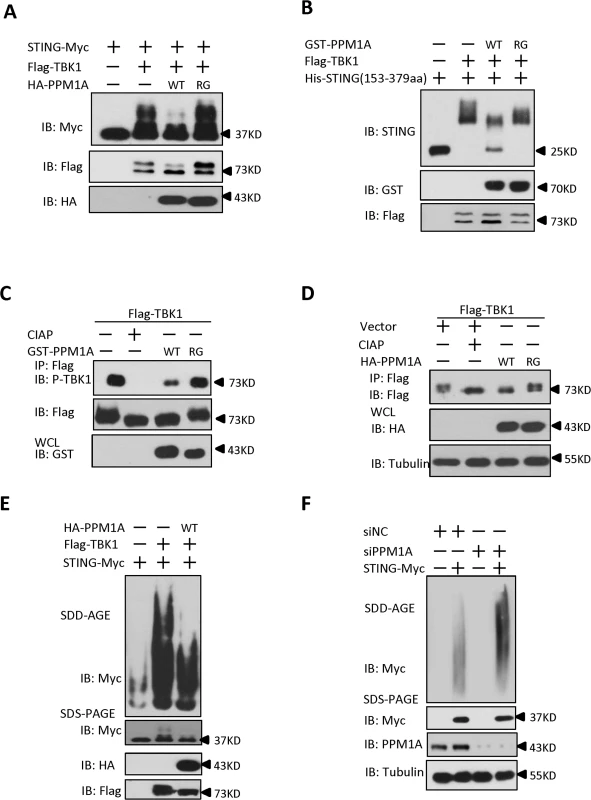
(A) STING phosphorylation induced by TBK1 was inhibited by PPM1A-WT, but not PPM1A-R174G. HEK293 cells were transfected with indicated plasmids for 24 h, and cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies. (B) STING was a direct target of PPM1A in an in vitro phosphatase assay. Purified His–STING (amino acids 153–379; 1 μg) and Flag–TBK1 (1 μg) were incubated in kinase buffer for 30 min at 30°C. After the samples were concentrated and the buffer was changed to phosphatase buffer, Purified GST–PPM1A-WT (1 μg) or GST-PPM1A-R174G protein (1 μg) was added, incubated for another 30 min at 30°C, and then analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (C) TBK1 was a direct target of PPM1A in an in vitro phosphatase assay. Purified Flag–TBK1 (1 μg) and GST–PPM1A–WT or GST-PPM1A-R174G (1 μg) were incubated in phosphatase buffer for 30 min at 30°C and then analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (D) PPM1A decreases phosphorylation of TBK1 in transfected HEK293 cells. HEK293 cells were transfected with Flag-TBK1 (0.5 μg) along with empty vector (2 μg) or HA-PPM1A-WT or HA-PPM1A-R174G (2 μg), and 24 h later, cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag beads. The immunoprecipitates were treated with buffer or CIAP as indicated and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Flag (upper panel). Expression of the transfected proteins was analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-HA (lower panel). (E) TBK1-induced STING aggregation was impaired by PPM1A. HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated expression plasmids. At 30 h after transfection, the cell lysates were resolved with SDD-AGE (upper panel) or SDS-PAGE (lower panel) and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (F) PPM1A knockdown enhances STING aggregation in HEK293 cells. HEK293 cells were transfected with siNC (40 nM) or siPPM1A-2 (40 nM). At 48 h after transfection, the cells were transfected with empty vector or STING expression vector for 20 h. the cell lysates were resolved with SDD-AGE (upper panel) or SDS-PAGE (lower panel) and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Because PPM1A targets both TBK1 and STING, we tested whether the PPM1A-mediated dephosphorylation of STING and TBK1 affects STING aggregation. HEK293 cells were transfected with epitope-tagged STING and TBK1, with or without PPM1A. Cell lysates were subjected to SDD-AGE assays to examine STING aggregation. As shown in Fig. 7E, PPM1A evidently impaired TBK1-induced STING aggregation in the transfected HEK293 cells. Consistent with this, knockdown of PPM1A significantly enhanced the STING aggregation in HEK293 cells (Fig. 7F). Importantly, we consistently found the STING aggregation induced by ISD was significantly enhanced in Ppm1a–/—MEFs, compared to Ppm1a+/+ MEFs (S11 Fig)
Taken together, these findings suggest that TBK1-mediated STING phosphorylation is important for STING function and its self-propagating polymerization, whereas PPM1A prevents STING aggregation by directly dephosphorylating both STING and TBK1.
Discussion
STING plays an important role in defending against DNA virus infection. Although the mechanism of STING activation has been studied extensively, much less is known about how the activation of STING is balanced to ensure the proper antiviral signal transduction, thereby avoiding deleterious effects on the host cells when responding to viral infection. In this study, we have demonstrated that PPM1A, a member of the PP2C family of Ser/Thr protein phosphatases, physically interacts with and dephosphorylates both STING and TBK1, thus negatively regulates antiviral signaling. Importantly, we found that whereas TBK1 promotes STING phosphorylation to induce a self-propagating polymerization, PPM1A antagonizes STING aggregation in a dephosphorylation-dependent manner. Thus, our study has established a novel mechanism by which PPM1A regulates antiviral signaling by antagonizing TBK1-mediated STING phosphorylation and aggregation, thereby maintaining innate immune homeostasis in the host cells.
Dynamic phosphorylation/dephosphorylation balances the antiviral signaling induced by STING
The activation of protein kinases and the subsequent substrate phosphorylation are critical to antiviral signaling pathways [31,38–40]_.Viral infection or stimulation by dsDNA activates STING by relocating it from the ER to the Golgi and causing its assembly into punctate structures, where STING associates with TBK1 [41]. The association between STING and TBK1 promotes TBK1 activation, which further phosphorylates IRF3 and induces downstream target genes expression[25]. This demonstrates the importance of TBK1-mediated phosphorylation events, which are regulated by STING during antiviral signaling transduction. However, how STING is regulated by the TBK1 kinase remains unclear. In this study, we have presented evidence that STING is directly phosphorylated by TBK1 in a kinase activity-dependent manner. The mutation of putative phosphorylation sites in STING reduced the antiviral signaling of STING, suggesting that the phosphorylation of STING, mediated by TBK1, contributes to the full activation of STING. Therefore, STING and TBK1 reciprocally regulate each other to promote the rapid induction of antiviral signal transduction.
How is this feed-forward regulation between STING and TBK1 balanced? In this study, we have shown that PPM1A, a Ser/Thr phosphatase, physically interacts with both STING and TBK1. As shown in reporter assays, whereas ectopic expression of PPM1A significantly suppressed the STING-induced activation of IRF3 and the expression of the IFNβ gene, the knockdown of PPM1A markedly increased STING-mediated antiviral signaling (Figs. 2A, B and 3C, D). Consistent with this, Ppm1a–/—MEFs showed increased IRF3 dimerization and Ifnβ gene transcription after ISD stimulation. Particularly, Ppm1a–/—MEFs also exhibited reduced viral replication after HSV-1 or VSVΔM51-GFP virus infection, demonstrating its biological importance. Furthermore, our study suggests that PPM1A not only dephosphorylates TBK1, but also targets STING for dephosphorylation. Thus, the question is that, apart from TBK1, whether the PPM1A-mediated STING dephosphorylation also contributes to the IFNβ signaling transduction. In an effort to address this issue, we performed several experiments and obtained evidence supporting the important role of the PPM1A-mediated STING dephosphorylation in regulating the IFNβ signaling. First, PPM1A directly dephosphorylated STING, likely via its S358 site (Figs. 7A-B and S10A). Second and importantly, PPM1A could still reduce the STING phosphorylation induced by TBK1-S172E, a phosphorylation/ dephosphorylation-resistant form of TBK1, providing evidence that PPM1A directly dephosphorylated STING in vivo (S10D Fig). Third, the levels of Ifnβ expression induced by ISD in Ppm1a-/- MEF cells ectopically expressing STING-S357A (corresponding to human STING-S358A mutant) were much lower than that in Ppm1a-/- MEF cells expressing the wild-type STING (S12 Fig). Taken together, these findings support the notion that PPM1A functions as a phosphatase to balance antiviral signaling by dephosphorylating both STING and TBK1.
Of note, we observed that PPM1A fails to remove all the phosphorylation of STING/TBK1 in vitro or in vivo assays, opening an interesting possibility of the existence of other phosphatases that are involved in regulating STING/TBK1 dephosphorlyation. A previous study has reported that PPM1B influences the IFNβ signaling against RNA virus through dephosphorlyation of TBK1 [31], our study also showed knockdown of PPM1B increased the levels of IFNβ expression induced by HSV-1 infection (S13A–S13B Fig). Thus, PPM1B might also contribute to regulating STING signaling by controlling its phosphorylation status.
PPM1A and TBK1 balance antiviral signaling by controlling STING aggregation
Two different mechanisms have been reported to explain the function of phosphorylation of STING in mediating the signaling transduction. Konno et al. previously reported that ULK1 phosphorylated STING at S366 to facilitate STING degradation and suppress IRF3 function [23]. However, a recent study provided evidence that STING phosphorylation at S366 by TBK1 is required for direct IRF3 recruitment and activation, but not for STING degradation [26]. In our study, we found that PPM1A dephosphorylated STING, but did not affect its degradation; since we didn’t observe that more stable STING proteins were present in Ppm1a-/- MEF cells after ISD treatments, compared to wild-type control (S14 Fig).
Given the opposite roles of PPM1A and TBK1 in regulating the phosphorylation status of STING, and the fact that TBK1 promotes STING aggregation, we investigated the molecular mechanism underlying the action of PPM1A by examining whether PPM1A antagonizes STING aggregation by dephosphorylating it. We found that alteration of PPM1A levels by either overexpression or knockdown reduced or potentiated the aggregation of STING, respectively, suggesting an important role for PPM1A in the regulation of STING aggregation. We also found that the mutation of STING at residue S358 not only reduced the level of STING phosphorylation, but also reduced its aggregation, thus attenuating the antiviral activity of STING. Consistent with this, the kinase activity of TBK1 is necessary and sufficient for STING aggregation. These lines of evidence not only support the idea that STING aggregation is controlled by its phosphorylation status, but also argue that aggregation of STING on the ER or other membranes provide an ideal platform for the efficient downstream TBK1-mediated phosphorylation and activation of IRF3. This argument offers a better explanation of why the activation of TBK1 is not efficient to induce IRF3 activation in the absence of STING in response to cytosolic DNA.
Recent studies have suggested that both MAVS and ASC undergo a process of self-propagating polymerization upon induction by innate immune or inflammasome stimulators [34,35]. The present study suggests that STING also forms high-molecular-weight self-polymers, which is regulated by TBK1-mediated phosphorylation and PPM1A-mediated dephosphorylation. It will be interesting to investigate whether a phosphorylation/dephosphorylation balance also controls MAVS and ASC aggregation in the future.
Materials and Methods
Ethics statements
All animal studies were carried out in strict accordance with the recommendations in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China. The protocols for animal studies were approved by the Committee on the Ethics of Animal Experiments of the Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Approval number: IOZ15001).
Cell culture and animals
HEK293, Hela, and Vero cells were obtained from Shanghai Cell Bank of Chinese Academy of Sciences, and maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 1% penicillin, and 1% streptomycin. Ppm1a+/+ and Ppm1a–/—MEFs (the detailed information regarding this KO mouse has been described in the reference[42]) were generated from 13.5-day embryos and maintained in complete DMEM (described above) with 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 10 μM l-glutamine, 10 μM β-mercaptoethanol and 1% nonessential amino acids. THP-1 cells were maintained in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 1% penicillin, 1% streptomycin, 10 μM β - mercaptoethanol, and 5 mM HEPES. Bone marrow-derived macrophages were prepared as previously described with modification [43]. Briefly, bone marrow cells were harvested from femurs and tibiae of mice, and cultured in complete DMEM containing conditioned media from L929 cell culture for five days, and then cells are collected for experiments.
Antibodies
Rabbit anti-phospho-TBK1, anti-phospho-IRF3 and anti-TBK1 antibodies were from Cell Signaling Technology; rabbit anti-Tubulin and anti-IRF3 antibodies were from Santa Cruz Biotechnology; mouse anti-GAPDH antibody was from Sungene Biotechnology; mouse anti-PPM1A antibody was from Abcam; mouse anti-Flag and rabbit anti-HA antibodies were from Sigma; rabbit anti-Myc antibody was from MBL. Mouse or rabbit anti-STING antiserum was raised against recombinant human STING (amino acids 221–379). Mouse polyclonal antibody recognizing mouse STING was kindly provided by Dr. Zhengfan Jiang (Peking University) [44]
Plasmids
Mammalian expression plasmids encoding Myc-tagged STING, hemagglutinin (HA)-tagged PPM1A, Flag-tagged TBK1, HA-tagged TBK1 and Flag-tagged IRF3 were constructed with standard molecular biology techniques. Various mutants, including STING mutants, PPM1A-R174G, Flag-TBK1-KD (K38A), Flag-IRF3-5D (S396D, S398D, S402D, T404D, S405D), were generated by PCR using Pfu Turbo DNA polymerase. The IFNβ-Luc and ISRE-Luc have been described previously [45].
Transfection and luciferase reporter analysis
HEK293 cells were seeded in 24-well plates at a density of 1.0 × 105 cells per well and transfected on the following day with the standard calcium phosphate transfection method. A pRSV/LacZ reporter plasmid (50 ng) and a firefly luciferase reporter plasmid (50 ng) were transfected together with the indicated expression plasmids. In the same experiment, empty control plasmid was added to ensure that the same amount of total DNA was transfected. Luciferase activity was measured at the indicated time point, and normalized to the LacZ activity. All reporter assays were repeated at least three times.
RNA interference (RNAi) and lentiviral infection
HEK293 cells were transfected with siRNA at a final concentration of 40 nM with the standard calcium phosphate transfection method. After 48 h, the cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) for 20 h and then harvested for analysis. THP-1 cells were infected with a pLL3.7 lentiviral vector carrying a target PPM1A sequence or the non-targeting sequence (shRNA-NC) for 72 h, and then cells were untreated or infected with HSV-1 for 6 h. The knockdown efficiency was determined with a qRT-PCR analysis. The siRNA sequences were as follows (only the sense strand is shown): NC (non-targeting), TTCTCCGAACGTGTCACGT; PPM1A-1, GAGGAATGTTATTGAAGCC; PPM1A-2, GTACCTGGAATGCAGAGTA; TBK1, TCAAGAACTTATCTACGAA. The sequences for shRNA PPM1A were the same as siPPM1A-1 and siPPM1A-2. The sequences for shRNA PPM1B were as follows: PPM1B-1: GGGAAAAGGAGCGAATCCA; PPM1B-2: GCTCTGTGAATATGTTAAA.
Co-immunoprecipitation, immunoblotting analysis, confocal microscopy, native PAGE, virus plaque assay and ELISA assay
These experiments were performed as previously described [45]. Briefly, for virus plaque assays, confluent Vero cells were used for infection with the diluted virus of VSVΔM51-GFP for 1 hour. Culture medium containing 2% methylcellulose was overlaid and incubated for about 36 h. Cells were then fixed for 15 min with methanol and further stained with 1% crystal violet to display plaques. Plaques were counted to determine the viral titer as plaque-forming units per ml.
SDD-AGE assay
The cells were transfected as indicated and then washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), the cells were resuspended with lysis buffer (0.5% Triton X-100, 50mM Tris-HCl, 150mM NaCl, 10% Glycerol,). The supernatants were separated by 1.5% SDD-AGE as previously described [45].
Measurement of HSV-1 genomic DNA copy numbers
MEFs were plated in six-well plates and grown to 80% confluence overnight. The cells were washed with PBS and infected with HSV at 5 MOI at 37°C in serum-free DMEM for 1 h. The cells were then washed with warm PBS, cultured in complete DMEM for 16 h, and their genomic DNA was extracted. The HSV-1 genomic DNA copy numbers were determined with real-time qRT-PCR with HSV-1-specific primers with the following sequence: 5′-TGGGACACATGCCTTCTTGG-3′ and 5′-ACCCTTAGTCAGACTCTGTTACTTACCC-3′.
Purification of GST - and His-tagged recombinant proteins
GST-PPM1A was cloned into the pGEX-4T-1 vector, and construct encoding His-tagged STING (amino acids 153–379) was cloned into the pET-28a vector. The fusion proteins were purified from the cell lysates using glutathione–Sepharose beads (Sigma) or Ni–Sepharose beads (GE), according to protocols of the manufacturers. The protein concentrations were measured with a Bradford Protein Assay (Bio-Rad).
In vitro pull-down
Purified STING (amino acids 153–379; 1 μg) and purified PPM1A (1 μg) or GST (1 μg) were incubated with glutathione–Sepharose beads at 4°C overnight with rotation. The glutathione–Sepharose beads were washed three times with washing buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH7.5, 200 mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, 0.1% Triton X-100) for 5 min at 4°C with rotation. The association between STING and PPM1A was assayed by immunoblotting.
Phosphatase assays in vitro
HEK293 cells were transfected with the Flag–TBK1 expression plasmid using the standard calcium phosphate transfection method. The Flag–TBK1 protein was immunoprecipitated from cell extracts with anti-Flag beads. After the immunoprecipitated Flag–TBK1 was washed three times with washing buffer, and incubated with the Flag peptide at 4°C for 30 min with rotation for three times. The collected supernatants were concentrated with centrifugal filter units (Millipore) and the protein concentrations were measured with a Bradford protein assay (Bio-Rad). Flag–TBK1 (1 μg) and purified STING (amino acids 153–379; 1 μg) were incubated in kinase buffer (25 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 5 mM ATP, 1 mM DTT) for 30 min at 30°C. The proteins were then left untreated or concentrated with centrifugal filter units and exchanged with phosphatase buffer (250 mM imidazole, 1 mM EGTA, 2 mM DTT, 25 mM MgCl2, 0.1% BSA). Purified GST-PPM1A-WT or GST-PPM1A-R174G (1 μg) was added and incubated for 30 min at 30°C. The phosphatase reaction was then terminated by boiling it in protein sample buffer and followed with an immunoblotting analysis.
Malachite green phosphatase assay
The sequence of synthetic phosphopeptide was as follow: STINGp358S(STSTMpSQEPEL). The phosphorylated amino acid is indicated in bold. The peptide was synthesized by Sangon Biotech, phosphopeptide phosphatase assay was performed with malachite green phosphatase assay kit (BioAssay Systems, POMG-048) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Yeast two-hybrid screening
To perform the yeast two-hybrid screening, we cloned STING (amino acids 153–379) into the bait vector. A human spleen DNA library (Agilent) was screened according to the recommendations of the manufacturer.
Quantitative RT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted using TRIZOL reagent (Invitrogen). cDNA was synthesized using SuperScript III First-Strand cDNA Synthesis kit (Invitrogen). Real-time PCR was performed using SYBR Green Master Mix (Thermo) in triplicate on a Bio-Rad iCycler iQ5 PCR Thermal Cycler. Relative levels of mRNA were normalized to the GAPDH RNA levels in each sample. 2-ΔΔCt method was used to calculate relative expression changes. Data shown are the relative abundance of the mRNA as indicated to that of control groups. The primers used were as follows (5′–3′):
hGAPDH-S: ATGACATCAAGAAGGTGGTG
hGAPDH-AS: CATACCAGGAAATGAGCTTG
hIFN-β-S: AGGACAGGATGAACTTTGAC
hIFN-β-AS: TGATAGACATTAGCCAGGAG
hPPM1A-S: AGGGGCAGGGTAATGGGTT
hPPM1A-AS: GATCACAGCCGTATGTGCATC
mGAPDH-S: AACTTTGGCATTGTGGAAGG
mGAPDH-AS: ACACATTGGGGGTAGGAACA
mCxcl-10-S: GAATCCGGAATCTAAGACCATCAA
mCxcl-10-AS: GTGCGTGGCTTCACTCCAGT
mIFN-β-S: ATGGTGGTCCGAGCAGAGAT
mIFN-β-AS: CCACCACTCATTCTGAGGCA
mISG15-S: GGTGTCCGTGACTAACTCCAT
mISG15-AS: TGGAAAGGGTAAGACCGTCCT
mRANTES-S: CTCACCATATGGCTCGGACA
mRANTES-AS: ACAAACACGACTGCAAGATTGG
Statistical analyses
All statistical analyses are shown as means ± SD. Significant differences between values under different experimental conditions were carried out using two-tailed Student’s t-test. For all tests, a p value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Accession numbers
The mRNA sequence data for genes described in this study can be found in the NCBI under the following accession numbers: Homo sapiens PPM1A (NM_021003.4), Homo sapiens STING(NM_198282.3), Mus musculus STING (NM_028261.1), Homo sapiens TBK1 (NM_013254.3), Homo sapiens IRF3 (NM_001571.5).
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. Barber GN (2011) Cytoplasmic DNA innate immune pathways. Immunol Rev 243 : 99–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01051.x 21884170
2. Kawai T, Akira S (2008) Toll-like receptor and RIG-I-like receptor signaling. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1143 : 1–20. doi: 10.1196/annals.1443.020 19076341
3. Seth RB, Sun L, Chen ZJ (2006) Antiviral innate immunity pathways. Cell Res 16 : 141–147. 16474426
4. Seth RB, Sun L, Ea CK, Chen ZJ (2005) Identification and characterization of MAVS, a mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein that activates NF-kappaB and IRF 3. Cell 122 : 669–682. 16125763
5. Kawai T, Takahashi K, Sato S, Coban C, Kumar H, et al. (2005) IPS-1, an adaptor triggering RIG-I - and Mda5-mediated type I interferon induction. Nat Immunol 6 : 981–988. 16127453
6. Xu LG, Wang YY, Han KJ, Li LY, Zhai Z, et al. (2005) VISA is an adapter protein required for virus-triggered IFN-beta signaling. Mol Cell 19 : 727–740. 16153868
7. Meylan E, Curran J, Hofmann K, Moradpour D, Binder M, et al. (2005) Cardif is an adaptor protein in the RIG-I antiviral pathway and is targeted by hepatitis C virus. Nature 437 : 1167–1172. 16177806
8. Hou F, Sun L, Zheng H, Skaug B, Jiang QX, et al. (2011) MAVS forms functional prion-like aggregates to activate and propagate antiviral innate immune response. Cell 146 : 448–461. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.041 21782231
9. Hornung V, Ablasser A, Charrel-Dennis M, Bauernfeind F, Horvath G, et al. (2009) AIM2 recognizes cytosolic dsDNA and forms a caspase-1-activating inflammasome with ASC. Nature 458 : 514–518. doi: 10.1038/nature07725 19158675
10. Burckstummer T, Baumann C, Bluml S, Dixit E, Durnberger G, et al. (2009) An orthogonal proteomic-genomic screen identifies AIM2 as a cytoplasmic DNA sensor for the inflammasome. Nat Immunol 10 : 266–272. doi: 10.1038/ni.1702 19158679
11. Fernandes-Alnemri T, Yu JW, Datta P, Wu J, Alnemri ES (2009) AIM2 activates the inflammasome and cell death in response to cytoplasmic DNA. Nature 458 : 509–513. doi: 10.1038/nature07710 19158676
12. Roberts TL, Idris A, Dunn JA, Kelly GM, Burnton CM, et al. (2009) HIN-200 proteins regulate caspase activation in response to foreign cytoplasmic DNA. Science 323 : 1057–1060. doi: 10.1126/science.1169841 19131592
13. Takaoka A, Wang Z, Choi MK, Yanai H, Negishi H, et al. (2007) DAI (DLM-1/ZBP1) is a cytosolic DNA sensor and an activator of innate immune response. Nature 448 : 501–505. 17618271
14. Unterholzner L, Keating SE, Baran M, Horan KA, Jensen SB, et al. (2010) IFI16 is an innate immune sensor for intracellular DNA. Nat Immunol 11 : 997–1004. doi: 10.1038/ni.1932 20890285
15. Zhang Z, Yuan B, Bao M, Lu N, Kim T, et al. (2011) The helicase DDX41 senses intracellular DNA mediated by the adaptor STING in dendritic cells. Nat Immunol 12 : 959–965. doi: 10.1038/ni.2091 21892174
16. Sun L, Wu J, Du F, Chen X, Chen ZJ (2013) Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway. Science 339 : 786–791. doi: 10.1126/science.1232458 23258413
17. Zhong B, Yang Y, Li S, Wang YY, Li Y, et al. (2008) The adaptor protein MITA links virus-sensing receptors to IRF3 transcription factor activation. Immunity 29 : 538–550. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.09.003 18818105
18. Sun W, Li Y, Chen L, Chen H, You F, et al. (2009) ERIS, an endoplasmic reticulum IFN stimulator, activates innate immune signaling through dimerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106 : 8653–8658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900850106 19433799
19. Ahn J, Gutman D, Saijo S, Barber GN (2012) STING manifests self DNA-dependent inflammatory disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109 : 19386–19391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1215006109 23132945
20. Gall A, Treuting P, Elkon KB, Loo YM, Gale M Jr., et al. (2012) Autoimmunity initiates in nonhematopoietic cells and progresses via lymphocytes in an interferon-dependent autoimmune disease. Immunity 36 : 120–131. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.11.018 22284419
21. Zhong B, Zhang L, Lei C, Li Y, Mao AP, et al. (2009) The ubiquitin ligase RNF5 regulates antiviral responses by mediating degradation of the adaptor protein MITA. Immunity 30 : 397–407. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.01.008 19285439
22. Saitoh T, Fujita N, Hayashi T, Takahara K, Satoh T, et al. (2009) Atg9a controls dsDNA-driven dynamic translocation of STING and the innate immune response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106 : 20842–20846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911267106 19926846
23. Konno H, Konno K, Barber GN (2013) Cyclic dinucleotides trigger ULK1 (ATG1) phosphorylation of STING to prevent sustained innate immune signaling. Cell 155 : 688–698. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.09.049 24119841
24. Zhang L, Mo J, Swanson KV, Wen H, Petrucelli A, et al. (2014) NLRC3, a member of the NLR family of proteins, is a negative regulator of innate immune signaling induced by the DNA sensor STING. Immunity 40 : 329–341. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.01.010 24560620
25. Tanaka Y, Chen ZJ (2012) STING specifies IRF3 phosphorylation by TBK1 in the cytosolic DNA signaling pathway. Sci Signal 5: ra20. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002521 22394562
26. Liu S, Cai X, Wu J, Cong Q, Chen X, et al. (2015) Phosphorylation of innate immune adaptor proteins MAVS, STING, and TRIF induces IRF3 activation. Science.
27. Takekawa M, Maeda T, Saito H (1998) Protein phosphatase 2Calpha inhibits the human stress-responsive p38 and JNK MAPK pathways. EMBO J 17 : 4744–4752. 9707433
28. Cheng A, Ross KE, Kaldis P, Solomon MJ (1999) Dephosphorylation of cyclin-dependent kinases by type 2C protein phosphatases. Genes Dev 13 : 2946–2957. 10580002
29. Sun W, Yu Y, Dotti G, Shen T, Tan X, et al. (2009) PPM1A and PPM1B act as IKKbeta phosphatases to terminate TNFalpha-induced IKKbeta-NF-kappaB activation. Cell Signal 21 : 95–102. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.09.012 18930133
30. Lu X, An H, Jin R, Zou M, Guo Y, et al. (2014) PPM1A is a RelA phosphatase with tumor suppressor-like activity. Oncogene 33 : 2918–2927. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.246 23812431
31. Zhao Y, Liang L, Fan Y, Sun S, An L, et al. (2012) PPM1B negatively regulates antiviral response via dephosphorylating TBK1. Cell Signal 24 : 2197–2204. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.06.017 22750291
32. Jackson MD, Fjeld CC, Denu JM (2003) Probing the function of conserved residues in the serine/threonine phosphatase PP2Calpha. Biochemistry 42 : 8513–8521. 12859198
33. Lin X, Duan X, Liang YY, Su Y, Wrighton KH, et al. (2006) PPM1A functions as a Smad phosphatase to terminate TGFbeta signaling. Cell 125 : 915–928. 16751101
34. Cai X, Chen J, Xu H, Liu S, Jiang QX, et al. (2014) Prion-like polymerization underlies signal transduction in antiviral immune defense and inflammasome activation. Cell 156 : 1207–1222. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.01.063 24630723
35. Lu A, Magupalli VG, Ruan J, Yin Q, Atianand MK, et al. (2014) Unified polymerization mechanism for the assembly of ASC-dependent inflammasomes. Cell 156 : 1193–1206. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.02.008 24630722
36. Alberti S, Halfmann R, King O, Kapila A, Lindquist S (2009) A systematic survey identifies prions and illuminates sequence features of prionogenic proteins. Cell 137 : 146–158. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.044 19345193
37. Xia L, Jia S, Huang S, Wang H, Zhu Y, et al. (2010) The Fused/Smurf complex controls the fate of Drosophila germline stem cells by generating a gradient BMP response. Cell 143 : 978–990. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.11.022 21145463
38. Vitour D, Dabo S, Ahmadi Pour M, Vilasco M, Vidalain PO, et al. (2009) Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) regulates interferon (IFN) induction by MAVS. J Biol Chem 284 : 21797–21809. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.018275 19546225
39. Fitzgerald KA, McWhirter SM, Faia KL, Rowe DC, Latz E, et al. (2003) IKKepsilon and TBK1 are essential components of the IRF3 signaling pathway. Nat Immunol 4 : 491–496. 12692549
40. Galati D, Srinivasan S, Raza H, Prabu SK, Hardy M, et al. (2009) Role of nuclear-encoded subunit Vb in the assembly and stability of cytochrome c oxidase complex: implications in mitochondrial dysfunction and ROS production. Biochem J 420 : 439–449. doi: 10.1042/BJ20090214 19338496
41. Ishikawa H, Ma Z, Barber GN (2009) STING regulates intracellular DNA-mediated, type I interferon-dependent innate immunity. Nature 461 : 788–792. doi: 10.1038/nature08476 19776740
42. Yang X, Teng Y, Hou N, Fan X, Cheng X, et al. (2011) Delayed re-epithelialization in Ppm1a gene-deficient mice is mediated by enhanced activation of Smad2. J Biol Chem 286 : 42267–42273. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.292284 21990361
43. Sun Q, Sun L, Liu HH, Chen X, Seth RB, et al. (2006) The specific and essential role of MAVS in antiviral innate immune responses. Immunity 24 : 633–642. 16713980
44. Chen H, Sun H, You F, Sun W, Zhou X, et al. (2011) Activation of STAT6 by STING is critical for antiviral innate immunity. Cell 147 : 436–446. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.022 22000020
45. Zhao Y, Sun X, Nie X, Sun L, Tang TS, et al. (2012) COX5B regulates MAVS-mediated antiviral signaling through interaction with ATG5 and repressing ROS production. PLoS Pathog 8: e1003086. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003086 23308066
Štítky
Hygiena a epidemiologie Infekční lékařství Laboratoř
Článek A Phospholipase Is Involved in Disruption of the Liver Stage Parasitophorous Vacuole MembraneČlánek Host ESCRT Proteins Are Required for Bromovirus RNA Replication Compartment Assembly and FunctionČlánek Enhanced CD8 T Cell Responses through GITR-Mediated Costimulation Resolve Chronic Viral Infection
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Pathogens
Nejčtenější tento týden
2015 Číslo 3- Stillova choroba: vzácné a závažné systémové onemocnění
- Perorální antivirotika jako vysoce efektivní nástroj prevence hospitalizací kvůli COVID-19 − otázky a odpovědi pro praxi
- Diagnostika virových hepatitid v kostce – zorientujte se (nejen) v sérologii
- Jak souvisí postcovidový syndrom s poškozením mozku?
- Familiární středomořská horečka
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- To Be or Not IIb: A Multi-Step Process for Epstein-Barr Virus Latency Establishment and Consequences for B Cell Tumorigenesis
- Is Antigenic Sin Always “Original?” Re-examining the Evidence Regarding Circulation of a Human H1 Influenza Virus Immediately Prior to the 1918 Spanish Flu
- The Great Escape: Pathogen Versus Host
- Coping with Stress and the Emergence of Multidrug Resistance in Fungi
- Catch Me If You Can: The Link between Autophagy and Viruses
- Bacterial Immune Evasion through Manipulation of Host Inhibitory Immune Signaling
- Evidence for Ubiquitin-Regulated Nuclear and Subnuclear Trafficking among Matrix Proteins
- BILBO1 Is a Scaffold Protein of the Flagellar Pocket Collar in the Pathogen
- Production of Anti-LPS IgM by B1a B Cells Depends on IL-1β and Is Protective against Lung Infection with LVS
- Virulence Regulation with Venus Flytrap Domains: Structure and Function of the Periplasmic Moiety of the Sensor-Kinase BvgS
- α-Hemolysin Counteracts the Anti-Virulence Innate Immune Response Triggered by the Rho GTPase Activating Toxin CNF1 during Bacteremia
- Induction of Interferon-Stimulated Genes by IRF3 Promotes Replication of
- Intracellular Growth Is Dependent on Tyrosine Catabolism in the Dimorphic Fungal Pathogen
- HCV Induces the Expression of Rubicon and UVRAG to Temporally Regulate the Maturation of Autophagosomes and Viral Replication
- Spatiotemporal Analysis of Hepatitis C Virus Infection
- Subgingival Microbial Communities in Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency and Their Relationship with Local Immunopathology
- Interaction between the Type III Effector VopO and GEF-H1 Activates the RhoA-ROCK Pathway
- Attenuation of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Using Large-Scale Random Codon Re-encoding
- Establishment of HSV1 Latency in Immunodeficient Mice Facilitates Efficient Reactivation
- XRN1 Stalling in the 5’ UTR of Hepatitis C Virus and Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus Is Associated with Dysregulated Host mRNA Stability
- γδ T Cells Confer Protection against Murine Cytomegalovirus (MCMV)
- Rhadinovirus Host Entry by Co-operative Infection
- A Phospholipase Is Involved in Disruption of the Liver Stage Parasitophorous Vacuole Membrane
- Dermal Neutrophil, Macrophage and Dendritic Cell Responses to Transmitted by Fleas
- Elucidation of Sigma Factor-Associated Networks in Reveals a Modular Architecture with Limited and Function-Specific Crosstalk
- A Conserved NS3 Surface Patch Orchestrates NS2 Protease Stimulation, NS5A Hyperphosphorylation and HCV Genome Replication
- Host ESCRT Proteins Are Required for Bromovirus RNA Replication Compartment Assembly and Function
- Disruption of IL-21 Signaling Affects T Cell-B Cell Interactions and Abrogates Protective Humoral Immunity to Malaria
- Compartmentalized Replication of R5 T Cell-Tropic HIV-1 in the Central Nervous System Early in the Course of Infection
- Diminished Reovirus Capsid Stability Alters Disease Pathogenesis and Littermate Transmission
- Characterization of CD8 T Cell Differentiation following SIVΔnef Vaccination by Transcription Factor Expression Profiling
- Visualization of HIV-1 Interactions with Penile and Foreskin Epithelia: Clues for Female-to-Male HIV Transmission
- Sensing Cytosolic RpsL by Macrophages Induces Lysosomal Cell Death and Termination of Bacterial Infection
- PKCη/Rdx-driven Phosphorylation of PDK1: A Novel Mechanism Promoting Cancer Cell Survival and Permissiveness for Parvovirus-induced Lysis
- Metalloprotease NleC Suppresses Host NF-κB/Inflammatory Responses by Cleaving p65 and Interfering with the p65/RPS3 Interaction
- Immune Antibodies and Helminth Products Drive CXCR2-Dependent Macrophage-Myofibroblast Crosstalk to Promote Intestinal Repair
- Adenovirus Entry From the Apical Surface of Polarized Epithelia Is Facilitated by the Host Innate Immune Response
- The RNA Template Channel of the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase as a Target for Development of Antiviral Therapy of Multiple Genera within a Virus Family
- Neutrophils: Between Host Defence, Immune Modulation, and Tissue Injury
- CD169-Mediated Trafficking of HIV to Plasma Membrane Invaginations in Dendritic Cells Attenuates Efficacy of Anti-gp120 Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies
- Japanese Encephalitis Virus Nonstructural Protein NS5 Interacts with Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein and Impairs Fatty Acid β-Oxidation
- Yip1A, a Novel Host Factor for the Activation of the IRE1 Pathway of the Unfolded Protein Response during Infection
- TRIM26 Negatively Regulates Interferon-β Production and Antiviral Response through Polyubiquitination and Degradation of Nuclear IRF3
- Parallel Epigenomic and Transcriptomic Responses to Viral Infection in Honey Bees ()
- A Crystal Structure of the Dengue Virus NS5 Protein Reveals a Novel Inter-domain Interface Essential for Protein Flexibility and Virus Replication
- Enhanced CD8 T Cell Responses through GITR-Mediated Costimulation Resolve Chronic Viral Infection
- Exome and Transcriptome Sequencing of Identifies a Locus That Confers Resistance to and Alters the Immune Response
- The Role of Misshapen NCK-related kinase (MINK), a Novel Ste20 Family Kinase, in the IRES-Mediated Protein Translation of Human Enterovirus 71
- Chitin Recognition via Chitotriosidase Promotes Pathologic Type-2 Helper T Cell Responses to Cryptococcal Infection
- Activates Both IL-1β and IL-1 Receptor Antagonist to Modulate Lung Inflammation during Pneumonic Plague
- Persistence of Transmitted HIV-1 Drug Resistance Mutations Associated with Fitness Costs and Viral Genetic Backgrounds
- An 18 kDa Scaffold Protein Is Critical for Biofilm Formation
- Early Virological and Immunological Events in Asymptomatic Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in African Children
- Human CD8 T-cells Recognizing Peptides from () Presented by HLA-E Have an Unorthodox Th2-like, Multifunctional, Inhibitory Phenotype and Represent a Novel Human T-cell Subset
- Decreased HIV-Specific T-Regulatory Responses Are Associated with Effective DC-Vaccine Induced Immunity
- RSV Vaccine-Enhanced Disease Is Orchestrated by the Combined Actions of Distinct CD4 T Cell Subsets
- Concerted Activity of IgG1 Antibodies and IL-4/IL-25-Dependent Effector Cells Trap Helminth Larvae in the Tissues following Vaccination with Defined Secreted Antigens, Providing Sterile Immunity to Challenge Infection
- Structure of the Low pH Conformation of Chandipura Virus G Reveals Important Features in the Evolution of the Vesiculovirus Glycoprotein
- PPM1A Regulates Antiviral Signaling by Antagonizing TBK1-Mediated STING Phosphorylation and Aggregation
- Lipidomic Analysis Links Mycobactin Synthase K to Iron Uptake and Virulence in .
- Roles and Programming of Arabidopsis ARGONAUTE Proteins during Infection
- Impact of Infection on Host Macrophage Nuclear Physiology and Nucleopore Complex Integrity
- The Impact of Host Diet on Titer in
- Antimicrobial-Induced DNA Damage and Genomic Instability in Microbial Pathogens
- Herpesviral G Protein-Coupled Receptors Activate NFAT to Induce Tumor Formation via Inhibiting the SERCA Calcium ATPase
- The Causes and Consequences of Changes in Virulence following Pathogen Host Shifts
- Small GTPase Rab21 Mediates Fibronectin Induced Actin Reorganization in : Implications in Pathogen Invasion
- Positive Role of Promyelocytic Leukemia Protein in Type I Interferon Response and Its Regulation by Human Cytomegalovirus
- NEDDylation Is Essential for Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Latency and Lytic Reactivation and Represents a Novel Anti-KSHV Target
- β-HPV 5 and 8 E6 Disrupt Homology Dependent Double Strand Break Repair by Attenuating BRCA1 and BRCA2 Expression and Foci Formation
- An O Antigen Capsule Modulates Bacterial Pathogenesis in
- Variable Processing and Cross-presentation of HIV by Dendritic Cells and Macrophages Shapes CTL Immunodominance and Immune Escape
- Probing the Metabolic Network in Bloodstream-Form Using Untargeted Metabolomics with Stable Isotope Labelled Glucose
- Adhesive Fiber Stratification in Uropathogenic Biofilms Unveils Oxygen-Mediated Control of Type 1 Pili
- Vaccinia Virus Protein Complex F12/E2 Interacts with Kinesin Light Chain Isoform 2 to Engage the Kinesin-1 Motor Complex
- Modulates Host Macrophage Mitochondrial Metabolism by Hijacking the SIRT1-AMPK Axis
- Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 (HTLV-1) Tax Requires CADM1/TSLC1 for Inactivation of the NF-κB Inhibitor A20 and Constitutive NF-κB Signaling
- Suppression of RNAi by dsRNA-Degrading RNaseIII Enzymes of Viruses in Animals and Plants
- Spatiotemporal Regulation of a T4SS Substrate by the Metaeffector SidJ
- Antigenic Properties of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus Envelope Glycoprotein Gp120 on Virions Bound to Target Cells
- Dependence of Intracellular and Exosomal microRNAs on Viral Oncogene Expression in HPV-positive Tumor Cells
- Identification of a Peptide-Pheromone that Enhances Escape from Host Cell Vacuoles
- Impaired Systemic Tetrahydrobiopterin Bioavailability and Increased Dihydrobiopterin in Adult Falciparum Malaria: Association with Disease Severity, Impaired Microvascular Function and Increased Endothelial Activation
- Transgenic Expression of the Dicotyledonous Pattern Recognition Receptor EFR in Rice Leads to Ligand-Dependent Activation of Defense Responses
- Comprehensive Antigenic Map of a Cleaved Soluble HIV-1 Envelope Trimer
- Low Doses of Imatinib Induce Myelopoiesis and Enhance Host Anti-microbial Immunity
- Impaired Systemic Tetrahydrobiopterin Bioavailability and Increased Oxidized Biopterins in Pediatric Falciparum Malaria: Association with Disease Severity
- PLOS Pathogens
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Bacterial Immune Evasion through Manipulation of Host Inhibitory Immune Signaling
- BILBO1 Is a Scaffold Protein of the Flagellar Pocket Collar in the Pathogen
- Antimicrobial-Induced DNA Damage and Genomic Instability in Microbial Pathogens
- Attenuation of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Using Large-Scale Random Codon Re-encoding
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Vladimír Palička, CSc., Dr.h.c., doc. MUDr. Václav Vyskočil, Ph.D., MUDr. Petr Kasalický, CSc., MUDr. Jan Rosa, Ing. Pavel Havlík, Ing. Jan Adam, Hana Hejnová, DiS., Jana Křenková
Autoři: MUDr. Irena Krčmová, CSc.
Autoři: MDDr. Eleonóra Ivančová, PhD., MHA
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Eva Kubala Havrdová, DrSc.
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



