-
Články
- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
- Kongresy
- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Strong Epistatic Selection on the RNA Secondary Structure of HIV
Epistasis is an evolutionary process in which the effect of a nucleotide at one site in the genome is dependent on the presence or absence of particular nucleotides at other sites in the genome. One of the simplest types of epistasis occurs between Watson-Crick (WC) nucleotides in RNA secondary structures, which are under constraint to maintain base-pairing. In this study, I examine the effects of mutations at WC sites in the RNA secondary structure of HIV-1. I show that while epistasis plays a major role in the evolution of the HIV-1 secondary structure, different types of mutations have variable effects on fitness. Therefore, by favoring certain mutational trajectories, HIV-1 can evolve rapidly despite strong epistatic constraint on its RNA secondary structure.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Pathog 10(9): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004363
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1004363Summary
Epistasis is an evolutionary process in which the effect of a nucleotide at one site in the genome is dependent on the presence or absence of particular nucleotides at other sites in the genome. One of the simplest types of epistasis occurs between Watson-Crick (WC) nucleotides in RNA secondary structures, which are under constraint to maintain base-pairing. In this study, I examine the effects of mutations at WC sites in the RNA secondary structure of HIV-1. I show that while epistasis plays a major role in the evolution of the HIV-1 secondary structure, different types of mutations have variable effects on fitness. Therefore, by favoring certain mutational trajectories, HIV-1 can evolve rapidly despite strong epistatic constraint on its RNA secondary structure.
Introduction
Epistasis is an evolutionary phenomenon whereby the fitness effect of a mutation is conditional on the genetic background in which it arises [1], [2]. One of the simplest forms of epistasis occurs between WC sites of RNA secondary structures. Replacement of a nucleotide at one site of a WC pair is often deleterious because it disrupts binding, decreasing the stability of the RNA secondary structure. However, a second-site replacement in the modified genetic background may be beneficial, or compensatory, if it restores binding by creating a new WC pair [3]. Due to these complex interactions, RNA secondary structures evolve along rugged, or multi-peaked, adaptive landscapes [4], on which certain mutational trajectories may be inaccessible due to highly deleterious intermediate states. Thus, understanding how a population navigates from one peak to another on an epistatic adaptive landscape is a fundamental problem in evolutionary biology.
Selection to maintain WC pairing in RNA secondary structures leaves distinct evolutionary footprints. For one, theoretical work shows that evolutionary rates should be lower at WC than at unpaired sites [5], [6], a pattern that has been observed in noncoding and synonymous regions of many viral RNA secondary structures, including those of influenza A [7], hepatitis C [8], [9], and HIV-1 [10]–[12]. The negative correlation between extent of WC pairing and amino acid variability in HIV-1 suggests that selection to maintain WC pairing may also decrease evolutionary rates at nonsynonymous WC sites [13]. Moreover, because transitions occur more frequently and are thus compensated more rapidly than transversions, transition-to-transversion ratios are elevated at WC sites of RNA secondary structures [14]. Thus, epistatic selection can significantly alter the genomic landscape by modulating the numbers and types of mutations at WC sites of RNA secondary structures. These signatures of epistatic selection have been used both to predict and evaluate RNA secondary structures [14]–[16].
Epistatic interactions between WC sites have been studied in a variety of RNA molecules, including mRNAs [3], [17], rRNAs [18]–[20], tRNAs [21], [22], and RNA viruses [7], [23]–[41]. These analyses have uncovered several key evolutionary principles. First, constraint to maintain WC pairing can result in strong long-term conservation of RNA secondary structures, yet weak conservation at the nucleotide level [18], [24]. A striking example of this phenomenon involves the nearly identical secondary structures of the R regions of HIV-2 and simian immunodeficiency virus in mandrills, which have highly conserved WC pairing interactions despite a sequence homology of only 40% [24]. Second, introduction of a mutation at a WC site typically results in impaired function, decreased thermodynamic stability, and lower fitness of a RNA secondary structure [3], [5], [7], [17], [20]–[23], [25]–[41]. Third, compensatory replacements at WC sites often fully restore the function, thermodynamic stability, and fitness of a RNA secondary structure [3], [17], [21]–[23], [27], [28], [30], [32]–[35], [38]–[41]. Fourth, second-site compensatory replacements may be preferred over back mutations [23], an intriguing finding that is also supported by studies of compensatory evolution in other interaction schemes [42]–[44]. Finally, compensatory evolution often proceeds through GU wobble intermediates [3], [19], [22], [23], which are nearly as thermodynamically stable as WC pairs and are ubiquitous in RNAs from organisms in all three domains of life [23], [45]. In some cases, GU wobbles may even confer higher fitness than WC pairs, resulting in their long-term retention [18], [19].
While the dynamics of WC pairing have been extensively studied in HIV-1 [24]–[41], previous analyses primarily focused on secondary structures located in the 5′LTR, which regulates the transcription of viral genes. Little is known about the evolution of secondary structures across the HIV-1 genome. Recently, the RNA secondary structure of the entire HIV-1 subtype B NL4-3 genome was experimentally derived with high confidence via high-throughput selective 2′-hydroxyl acylation analyzed by primer extension (SHAPE) reactivity [46]. The availability of this structure provides a novel opportunity to study the evolution of WC pairing in HIV-1 on a genome-wide scale.
HIV-1 is an ideal model system in which to study epistasis at WC sites for a number of reasons. First, there is an abundance of publicly available sequence data for HIV-1. Second, HIV-1 has one of the highest observed spontaneous mutation rates and a relatively small genome and, thus, the waiting time for new mutations is short [47]. Third, experimental analyses of HIV-1 have demonstrated the importance of its RNA secondary structure at all stages of the viral life cycle, including reverse transcription [33], [35], frameshifting [36]–[38], mRNA splicing [39], [41], and viral packaging and transport [26], [31], [33]. Mutations that disrupt WC pairing in important domains often have severe phenotypic consequences [25]–[41], and site-directed mutagenesis studies have shown that compensatory mutations that re-establish WC pairing can restore wild type functions [27], [28], [30], [32]–[35], [38]–[41]. Finally, HIV-1 is a virus of great clinical significance, and knowledge about its evolutionary dynamics at the structural level may inform public health studies.
Results and Discussion
To investigate epistatic interactions between WC sites of HIV-1, I utilized the subtype B NL4-3 genomic sequence and RNA secondary structure [38] as a reference, 197,863 subtype B sequences (1,867 genomic) for intra-population comparison, and 66 subtype D (closest relative to subtype B) genomic sequences as an outgroup. Pairing probabilities associated with the RNA secondary structure [38] were not used because they were computed via phylogenetic analyses of covariation between sites. I restricted my analysis to sites at which reference nucleotides are ancestral, i.e., conserved in all 66 outgroup sequences, both enabling polarization of mutations in the subtype B population and ensuring that reference nucleotides have been under long-term selective constraint and are therefore likely important to the RNA secondary structure. Additionally, I only considered noncoding and synonymous sites so as not to confound selection on pairing with selection on amino acid composition, though nonsynonymous sites were also analyzed separately (see Materials and Methods). Using these criteria, I identified 562 WC sites (281 pairs) and 2,868 non-WC (nWC) sites in the secondary structure of the HIV-1 reference genome.
Stems utilized in this analysis have a median length of 4 bp and are distributed across the HIV-1 genome (Table 1). Most stems are located in Pol, which is the gene responsible for transcribing viral RNA into double-stranded DNA, and which also contains the greatest number of ancestral WC sites. Surprisingly, while most studies of WC pairing interactions in HIV-1 have focused on the 5′LTR, this region contains the fewest number of stems, indicating that much information may be gained from studying the evolution of WC pairing across the entire HIV-1 genome.
Tab. 1. Number of stems, median stem size, and number of ancestral WC sites in different regions of the HIV-1 genome. 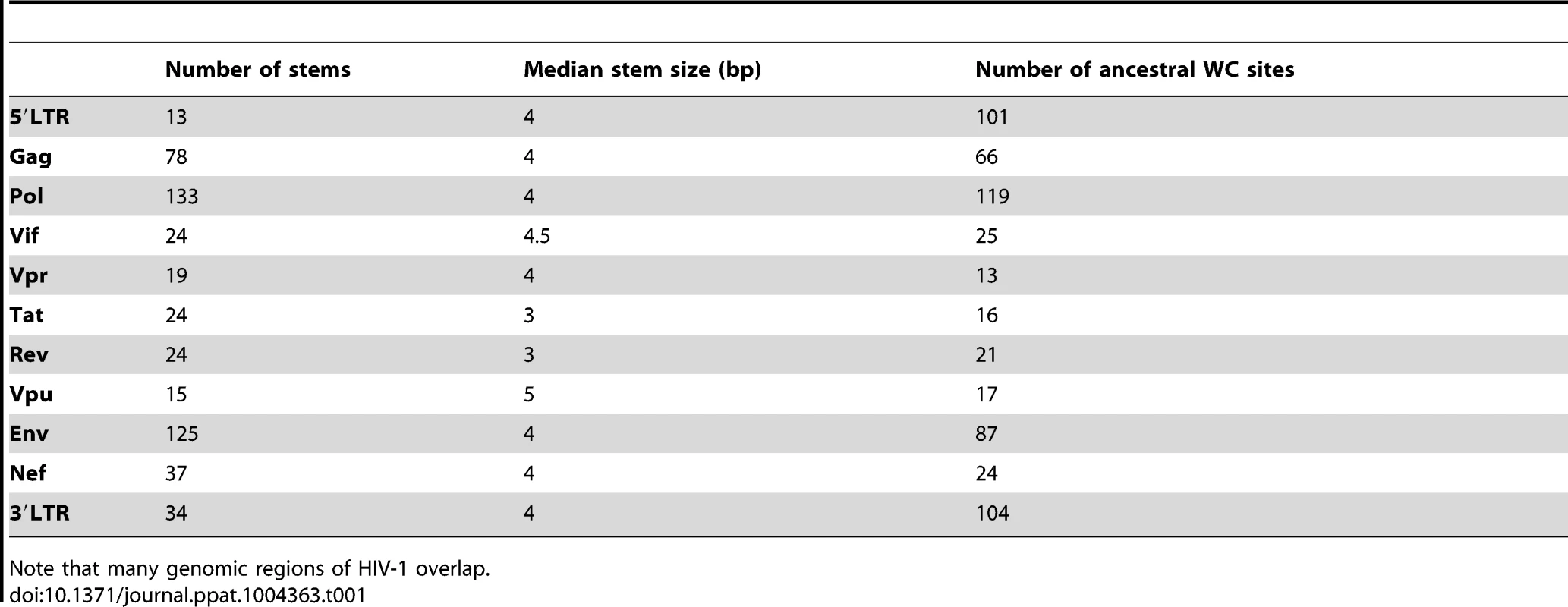
Note that many genomic regions of HIV-1 overlap. Comparisons of subtype B sequences to the reference sequence yielded 1,105 polymorphisms at WC sites and 7,723 polymorphisms at nWC sites. These counts indicate that there are, on average, 1.97 polymorphisms per WC site and 2.69 polymorphisms per nWC site. Thus, because there are three possible replacement nucleotides per site, WC sites are ∼66% saturated and nWC sites are ∼90% saturated, and this difference is highly significant (p<2.20×10−16, Binomial test; see Materials and Methods for details). Additionally, of the 1,105 WC polymorphisms, only 306 occur as single-site replacements; the remaining 799 polymorphisms correspond to 669 double-site replacements (see Materials and Methods). Together, the lower mutational saturation at WC sites and tendency for polymorphisms at interacting WC sites to co-segregate highlight the importance of epistasis in the evolution of the HIV-1 secondary structure.
If conservation of WC interactions in the HIV-1 secondary structure is important, destruction of WC pairing should result in a significant fitness loss. Comparison of the intra-population frequencies of single-site WC polymorphisms to those of nWC polymorphisms revealed that this is indeed the case (Figure 1). WC polymorphisms segregate at frequencies that are ∼82% lower than those of nWC polymorphisms, and this difference is highly significant (p = 1.07×10−8, Mann-Whitney U test), indicating that there is strong selection against destruction of WC pairing in the HIV-1 secondary structure. To estimate the strength of this constraint, I computed selection coefficients against WC and nWC polymorphisms by s = μ/pmed [48], where μ is mutation rate, which has been estimated as 3.0×10−5 replacements/site/replication cycle [47], and pmed is the median frequency of the segregating polymorphism (Table 2). Differences between selection coefficients against WC and nWC polymorphisms indicate that ∼63% of constraint at WC sites, and ∼46% of genome-wide constraint, is due to epistatic interactions between nucleotides in the RNA secondary structure of HIV-1 (see Materials and Methods for details).
Fig. 1. Intra-population frequencies of nWC and single-site WC replacement polymorphisms in the HIV-1 genome. 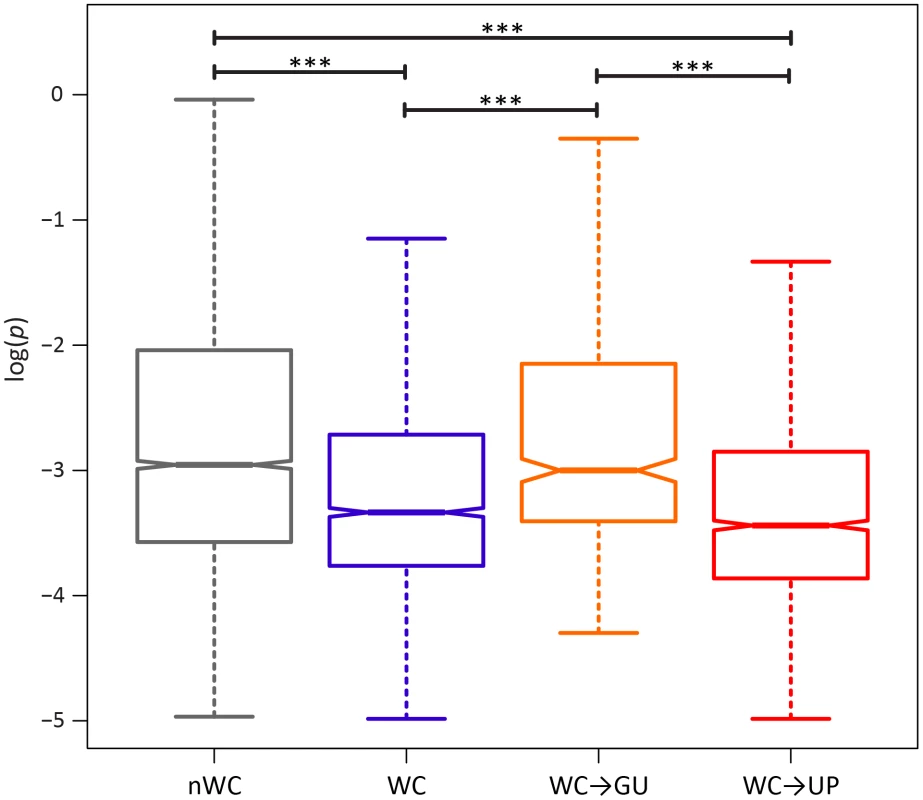
Frequencies are normalized to enable comparisons among classes (see Materials and Methods for details) and plotted on a log10-scale. Asterisks indicate p<0.05 (*), p<0.01 (**), and p<0.001 (***). Tab. 2. Median frequencies, selection coefficients, and relative fitnesses of nWC and single-site WC replacement polymorphisms in the HIV-1 genome. 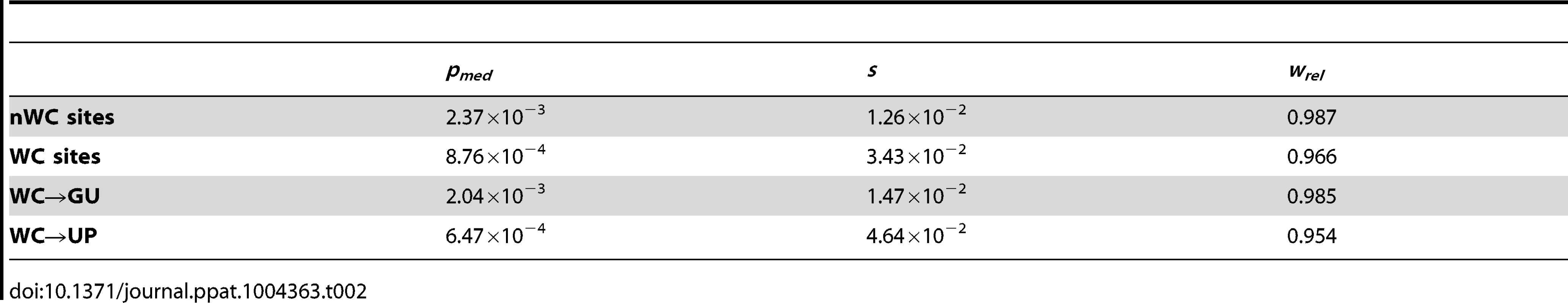
A single replacement at a WC site can either result in two unpaired nucleotides (WC→UP) or in a GU pair (WC→GU). Because previous studies have demonstrated that WC→GU replacements are typically slightly deleterious, and can sometimes even be beneficial, selection against WC→GU replacements should be weaker than selection against WC→UP replacements [3], [19], [22], [23], [45]. Consistent with this expectation, WC→GU polymorphisms segregate at significantly higher frequencies than WC→UP polymorphisms (p = 3.75×10−6, Mann-Whitney U test; Figure 1), such that selection against WC→UP replacements is approximately three times stronger than selection against WC→GU replacements (Table 2). Moreover, frequencies of WC→GU polymorphisms are comparable to those of nWC polymorphisms (p = 0.86, Mann-Whitney U test), and selection against WC→GU replacements is marginally stronger than selection against replacements at nWC sites (see Table 2), indicating that WC→GU replacements are slightly deleterious in the HIV-1 secondary structure.
A potential factor in the effect of a mutation at a WC site is location. In particular, location-specific effects of replacements may be due to position within a stem or within the HIV-1 genome. Surprisingly, frequencies of both WC→GU and WC→UP polymorphisms are similar for interior and exterior stem sites (p = 0.65, p = 0.97, Mann-Whitney U tests; Figure 2). However, frequencies of both replacement classes differ among sites located in 5′LTR, protein-coding, and 3′LTR regions of the HIV-1 genome (Figure 3). In particular, WC→GU and WC→UP polymorphisms segregate at significantly higher frequencies in 5′LTR than in either protein-coding (p = 8.01×10−3, p = 5.49×10−7, Mann-Whitney U tests) or 3′LTR (p = 5.20×10−3, p = 7.05×10−8, Mann-Whitney U tests) regions, which contain similar distributions of polymorphism frequencies (p = 0.94, p = 0.33, Mann-Whitney U tests). Thus, WC sites in the 5′LTR are less constrained than those in any other genomic region, underlining the importance of regulatory changes in the evolution of HIV-1.
Fig. 2. Intra-population frequencies of single-site WC replacement polymorphisms at interior and exterior stem positions. 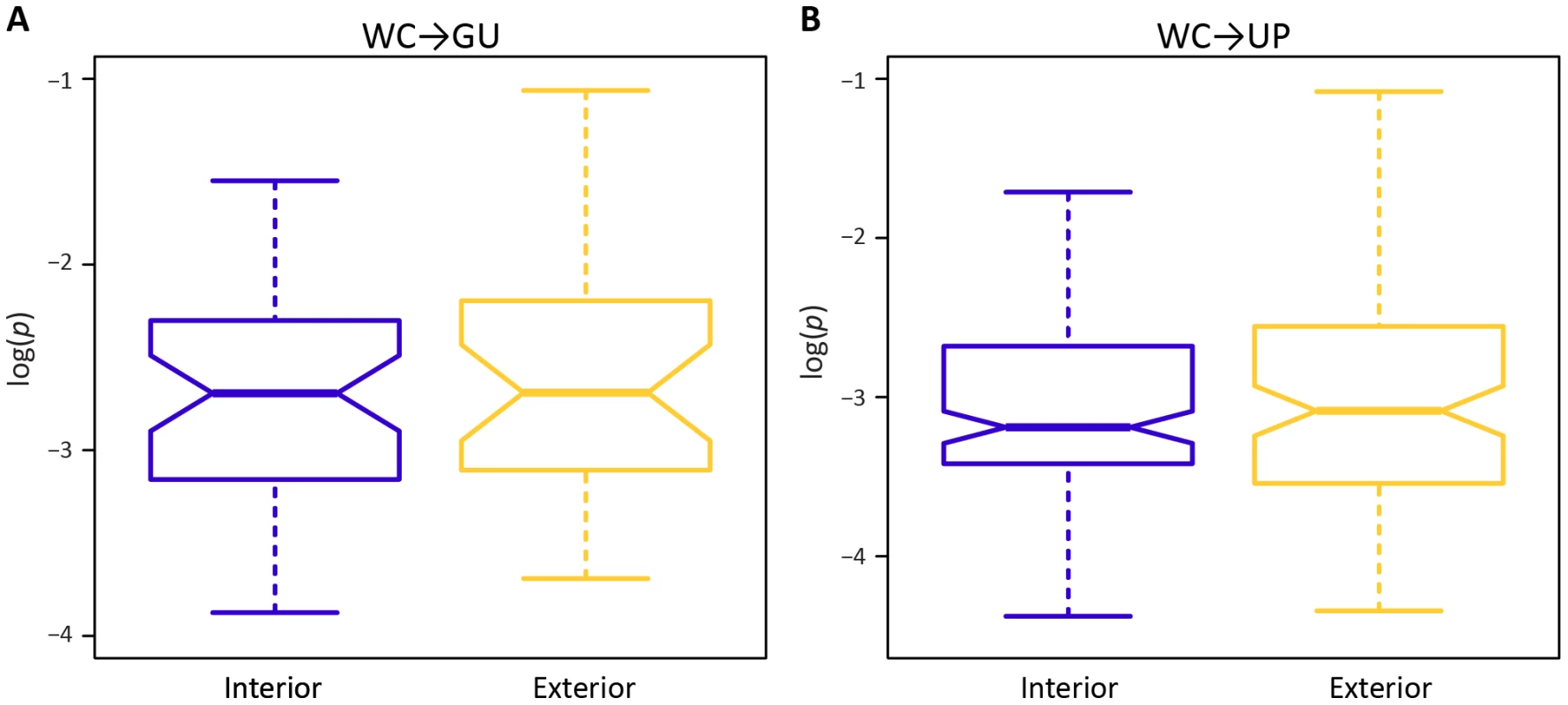
A) Frequencies of WC→GU polymorphisms. B) Frequencies of WC→UP polymorphisms. Frequencies are normalized to enable comparisons among classes (see Materials and Methods for details) and plotted on a log10-scale. Asterisks indicate p<0.05 (*), p<0.01 (**), and p<0.001 (***). Fig. 3. Intra-population frequencies of single-site WC replacement polymorphisms in 5′LTR, protein-coding, and 3′LTR regions of the HIV-1 genome. 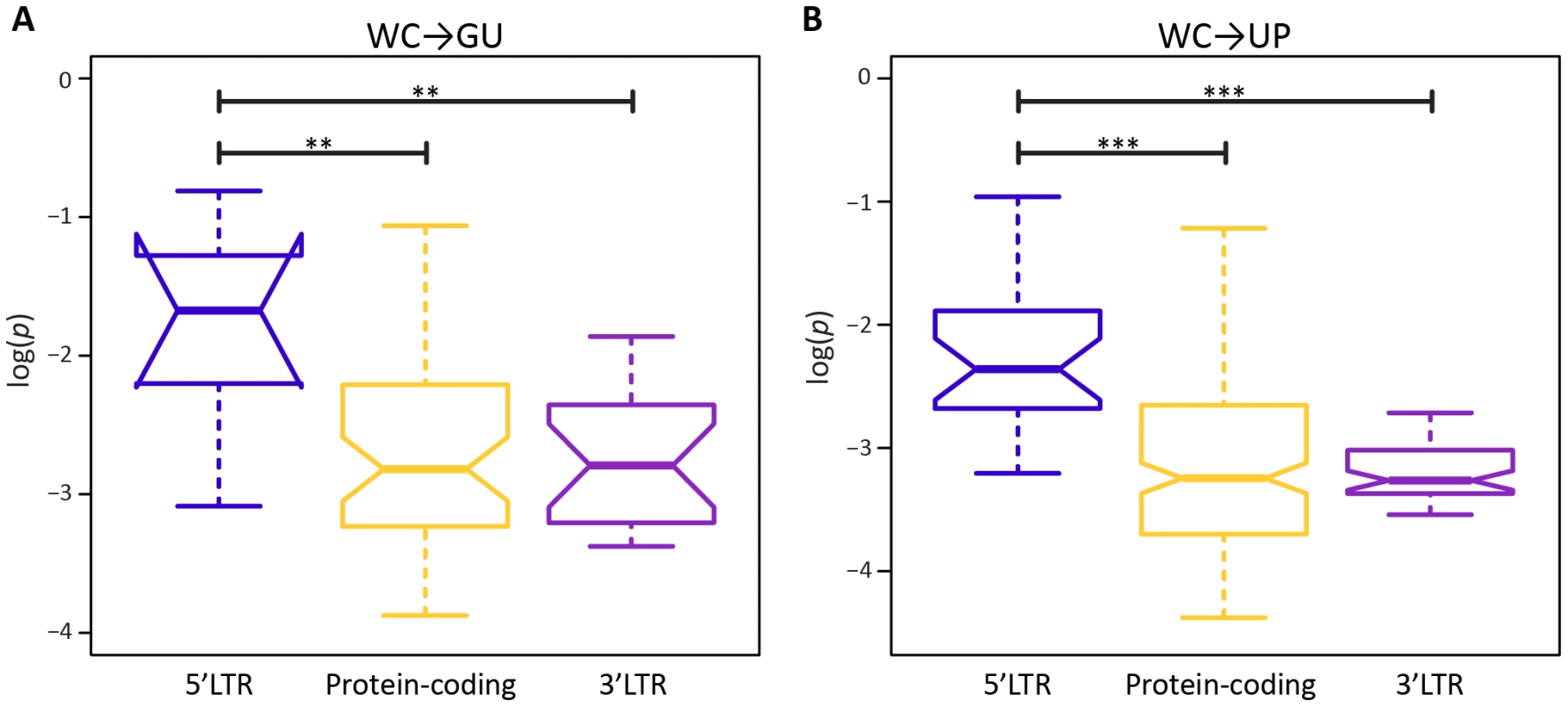
A) Frequencies of WC→GU polymorphisms. B) Frequencies of WC→UP polymorphisms. Frequencies are normalized to enable comparisons among classes (see Materials and Methods for details) and plotted on a log10-scale. Asterisks indicate p<0.05 (*), p<0.01 (**), and p<0.001 (***). To further elucidate the nature of epistatic interactions at WC sites of the HIV-1 secondary structure, I investigated the fitness effects of second-site WC replacements. A second-site replacement after an initial WC→GU replacement can result in a WC pair (GU→WC) or unpaired nucleotides (GU→UP), while a second-site replacement after an initial WC→UP replacement can result in a WC pair (UP→WC), a GU wobble (UP→GU), or unpaired nucleotides (UP→UP). Consistent with the prediction that restoration of WC pairing is compensatory, GU→WC polymorphisms segregate at significantly higher frequencies than GU→UP polymorphisms (p = 2.44×10−5, Mann-Whitney U test), and UP→WC polymorphisms segregate at significantly higher frequencies than either UP→GU (p = 0.04, Mann-Whitney U test) or UP→UP (p = 8.21×10−7, Mann-Whitney U test) polymorphisms (Figure 4). However, frequencies of UP→WC polymorphisms are also significantly greater than those of GU→WC polymorphisms (p = 4.07×10−3, Mann-Whitney U test; Figure 4). Moreover, while UP→WC replacements increase median fitness by ∼4.2% relative to initial WC→UP replacements, GU→WC replacements only increase median fitness by ∼0.3% relative to initial WC→GU replacements (see Materials and Methods for details). This difference indicates that conversion of a GU wobble back to a WC pair results in a small fitness gain that is comparable to the small fitness loss from an initial WC→GU replacement.
Fig. 4. Intra-population frequencies of second-site WC replacement polymorphisms in the HIV-1 genome. 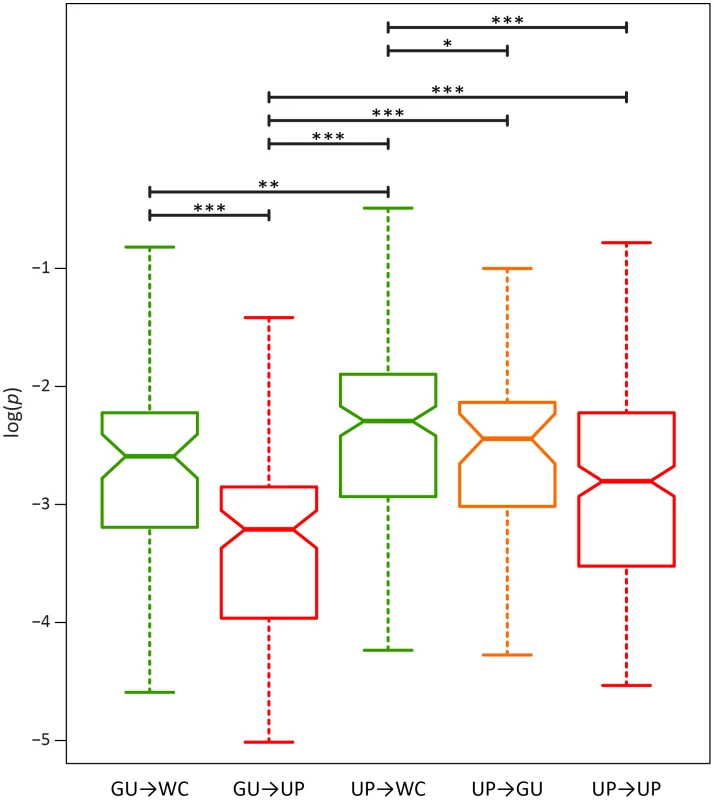
Frequencies are normalized to enable comparisons among classes (see Materials and Methods for details) and plotted on a log10-scale. Asterisks indicate p<0.05 (*), p<0.01 (**), and p<0.001 (***). Because GU wobbles confer higher fitness than UP nucleotides in the HIV-1 secondary structure, the difference between frequencies of second-site GU→WC and GU→UP polymorphisms may be due not only to the compensatory nature of second-site GU→WC replacements, but also to fitness losses from second-site GU→UP replacements. To test this hypothesis, I compared the frequencies of second-site GU→UP and UP→UP polymorphisms, since the latter second-site replacement should not result in a fitness loss relative to the initial WC→UP replacement. Indeed, GU→UP polymorphisms segregate at significantly lower frequencies than UP→UP polymorphisms (p = 2.42×10−5, Mann-Whitney U test), such that selection against GU→UP replacements is ∼2.6 times stronger than selection against UP→UP replacements (see Table 3). Moreover, second-site GU→UP replacements result in a median fitness loss of ∼3.5% relative to initial WC→GU replacements (see Materials and Methods for details), illustrating the highly deleterious effect of losing all complementarity at ancestral WC sites in the HIV-1 secondary structure.
Tab. 3. Median frequencies, selection coefficients, and relative fitnesses of second-site WC replacement polymorphisms in the HIV-1 genome. 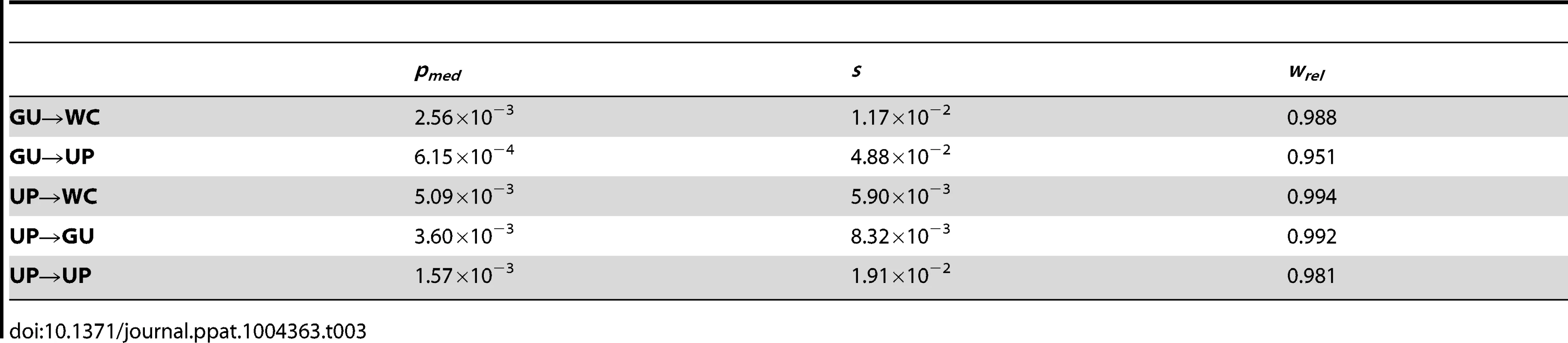
While restoration of WC pairing is thought to be the only mechanism for compensatory evolution, the findings from this study prompt a key question: Are second-site UP→GU replacements also compensatory in the HIV-1 secondary structure? Examination of frequencies of UP→GU polymorphisms shows that they are intermediate to those of UP→UP and UP→WC polymorphisms (Figure 4). Thus, second-site UP→GU replacements are indeed compensatory, though not to the degree of UP→WC replacements. In particular, UP→GU replacements result in a ∼4% fitness gain relative to initial WC→UP replacements, in contrast to the ∼4.2% fitness gain conferred by UP→WC replacements (see Materials and Methods for details). Hence, as expected given the small fitness losses from initial WC→GU replacements and large fitness losses from second-site GU→UP replacements, second-site UP→GU replacements are nearly as compensatory as GU→WC replacements at ancestral WC sites in the HIV-1 secondary structure.
This analysis highlights the complexities of epistatic interactions between WC sites in the HIV-1 secondary structure. In particular, although epistatic selection is strong and accounts for nearly half of all constraint on the HIV-1 secondary structure, it primarily targets replacements that completely abolish pairing interactions. In contrast, GU wobbles are typically slightly deleterious and can even compensate for the loss of fitness from initial WC→UP replacements. While the GU wobble as an intermediate is not a novel theme in the evolution of RNA secondary structures, these findings suggest that the GU wobble may play a more central role in compensatory evolution via its ability to “rescue” a RNA secondary structure after an initially deleterious WC→UP replacement. Thus, GU wobbles act not just as intermediates, but also as compensators. Moreover, this study provides the first numerical analysis of the fitness effects of various initial and second-site replacements, including those involving GU wobbles, at WC sites in the RNA secondary structure of HIV-1.
Together, these findings suggest that epistatic selection on the RNA secondary structure of HIV-1 operates under a fitness hierarchy in which , and the ability of a new state to increase in frequency is based on its position in the hierarchy relative to that of the previous state. Because the fitness of a GU wobble is nearly equivalent to that of a WC pair, a GU wobble can be maintained stably at a relatively high frequency in the population, likely until fitness is completely restored by a replacement that re-establishes WC pairing. Thus, GU wobbles compose ridges that connect WC peaks in the epistatic adaptive landscape of the HIV-1 secondary structure, forming relatively flat high-fitness mutational paths to distant peaks. Moreover, while the HIV-1 population will inevitably fall into UP valleys as it traverses the adaptive landscape, it can be rescued from such a valley by a mutation that lifts it to either a WC peak or a GU ridge. Because of the high mutation rate and small genome of HIV-1, such a mutation will arise quickly, preventing the population from becoming trapped in a UP valley and enabling its rapid evolution along the epistatic adaptive landscape.
Materials and Methods
Sequence retrieval and analysis
HIV-1 sequences were downloaded from the HIV Sequence Database at http://www.hiv.lanl.gov/ and aligned by HMMER [49] using the HIVAlign [50] tool. The subtype B NL4-3 genome sequence (accession M19921) and corresponding positions of WC pairs in the RNA secondary structure [46] were used as a reference set for all analyses. Protein-coding nonsynonymous sites were removed from analyses to minimize confounding effects of selection on amino acids. However, as expected, findings for a separate analysis of nonsynonymous sites (Figures S1 and S2) are generally consistent with those obtained with their exclusion (Figures 1 and 4). Also, it is important to note that splice sites, which may be under additional selective constraint, were not removed from analyses, although these should not affect overall patterns observed. A site in the reference genome was considered ancestral if it is conserved in all 66 subtype D genomic sequences, and a replacement mutation was inferred when an ancestral site is polymorphic in the subtype B population. WC sites were considered to have undergone a single-site replacement when a polymorphism at one site segregates with the ancestral nucleotide at the interacting site, and a double-site replacement when polymorphisms at both sites segregate together in the population. In cases of double-site replacements, polymorphism frequencies were used to distinguish between initial and second-site replacements. In particular, the polymorphism segregating at a higher frequency (with the ancestral nucleotide at the interacting site) was designated as the initial replacement.
Normalization of polymorphism frequencies
Selection coefficients were inferred from polymorphism frequencies and the average spontaneous mutation rate of HIV-1. However, mutation rates and effects of selection may vary among different classes of nucleotide replacements. Thus, to enable comparisons of polymorphism frequencies among different classes of replacements, I normalized polymorphism frequencies by multiplying the frequency of each nucleotide replacement by its observed/expected ratio. The expected number of a particular nucleotide replacement (e.g., A→U) was computed by multiplying the number of sites with the ancestral state (e.g., A) by the corresponding nucleotide replacement rate (e.g., A→U), which was estimated from replacements at nWC sites. For example, the A→U replacement rate was computed by dividing the total number of A→U replacements at nWC sites by the total number of nWC sites with replacements of an A (A→U+A→G+A→C). The rates for all replacement types are given in Table S1. As expected, transitions are more common than transversions at nWC sites.
Also shown in Table S1 are replacement rates computed for experimentally derived mutation data from Mansky and Temin (1995) [51]. These rates were not appropriate for the current analysis for two reasons. First, Mansky and Temin did not observe any transversions at three of the four ancestral nucleotides (G, C, and A; see Table S1), which may have been due to their small sample size (42 replacements), and is an unrealistic expectation for the current dataset (7,723 replacements at nWC sites). Second, and more importantly, replacements observed by Mansky and Temin reflect mutation rates, while nWC replacements were likely affected by non-epistatic selection. Thus, I was able to use replacement rates at nWC sites to compare and quantify epistatic and non-epistatic components of selection on the HIV-1 secondary structure, which were major objectives of the current study.
Additionally, because WC→GU polymorphisms segregate at much higher frequencies than WC→UP polymorphisms, and the probability (and frequency) of a particular second-site replacement is proportional to the probability (and frequency) of the initial replacement polymorphism, I normalized frequencies of second-site replacements by median frequencies of single-site replacements.
Estimation of the proportion of constraint due to epistasis
Selective constraint against replacements at nWC and WC sites are given in Table 1 as snwc = 1.26×10−2 and swc = 3.43×10−2. Because swc cannot solely be attributed to epistasis, I estimated the epistatic component of swc by . Then, the proportion of swc that is due to epistasis can be estimated by , and the proportion of constraint at all HIV-1 sites that is due epistasis can be estimated by , where () represents total constraint.
Estimation of fitness changes
Assuming that the optimal genotype has a fitness of 1, the relative fitness (wrel) of each replacement class can be estimated by 1−s, where s is the estimated selection coefficient of the respective replacement class that was derived from normalized polymorphism frequencies (see above). Thus, wrel is the relative median fitness of a particular replacement class based on normalized nucleotide polymorphism frequencies, rather than an experimentally derived fitness value based on viral replication capacity. This estimation enables the comparison of median, but not absolute, fitness effects between replacement classes. The change in relative fitness due to conversion from state 1 to state 2, , was computed as the difference between the relative fitnesses of the two states (), divided by . For example, if state 1 is an initial WC→GU replacement and state 2 is a second-site GU→WC replacement, the change in relative fitness due to the second-site replacement is given by
Statistical analyses
All statistical analyses were performed in the R software environment [52]. An exact binomial test was used to compare mutation saturation levels at WC and non-WC sites by setting x to the number of observed polymorphisms at WC sites (1,105), n to the total number of possible polymorphisms at WC sites (1,686), and p to the proportion of non-WC sites that are saturated by mutation (0.898). Mann-Whitney U tests were used to compare all pairs of frequency distributions.
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. KimuraM (1985) The role of compensatory neutral mutations in molecular evolution. J Genet 64 : 7–19.
2. PhillipsPC (2008) Epistasis—the essential role of gene interactions in the structure and evolution of genetic systems. Nat Rev Genet 9 : 855–867.
3. KirbyDA, MuseSV, StephanW (1995) Maintenance of pre-mRNA secondary structure by epistatic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92 : 9047–9051.
4. HuynenMA, HogewegP (1994) Pattern generation in molecular evolution: exploitation of the variation in RNA landscapes. J Mol Evol 39 : 71–79.
5. StephanW (1996) The rate of compensatory evolution. Genetics 144 : 419–426.
6. InnanH, StephanW (2001) Selection intensity against deleterious mutations in RNA secondary structures and the rate of compensatory nucleotide substitutions. Genetics 159 : 389–399.
7. GarcíaM, CrawfordJM, LatimerJW, Rivera-CruzE, PerdueML (1996) Heterogeneity in the haemagglutinin gene and emergence of the highly pathogenic phenotype among recent H5N2 avian influenza viruses from Mexico. J Gen Virol 77 : 1493–1504.
8. ContrerasAM, HiasaY, HeW, TerellaA, SchmidtEV, et al. (2002) Viral RNA mutations are region specific and increased by ribavirin in a full-length hepatitis C virus replication system. J Virol 76 : 8505–8517.
9. TuplinA, WoodJ, EvansDJ, PatelAH, SimmondsP (2002) Thermodynamic and phylogenetic prediction of RNA secondary structures in the coding region of hepatitis C virus. RNA 8 : 824–841.
10. LeSY, ChenJH, BraunMJ, GondaMA, MaizelJV (1988) Stability of RNA stem-loop structure and distribution of non-random structure in the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1). Nucleic Acids Res 16 : 5153–5168.
11. LeSY, ChenJH, ChatterjeeD, MaizelJV (1989) Sequence divergence and open regions of RNA secondary structures in the envelope regions of the 17 human immunodeficiency isolates. Nucleic acids Res 17 : 3275–3288.
12. YoshidaK, NakamuraM, OhnoT (1997) Mutations of the HIV type 1 V3 loop under selection pressure with neutralizing monoclonal antibody NM-01. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 13 : 1283–1290.
13. SanjuánR, BorderíaAV (2011) Interplay between RNA structure and protein evolution in HIV-1. Mol Biol Evol 28 : 1333–1338.
14. KniesJL, DangKK, VisionTJ, HoffmanNG, SwanstromR, et al. (2008) Compensatory evolution in RNA secondary structures increases substitution rate variation among sites. Mol Biol Evol 25 : 1778–1787.
15. MuseSV (1995) Evolutionary analyses of DNA sequences subject to constraints on secondary structure. Genetics 139 : 1429–1439.
16. PedersonJ, MeyerI, ForsbergR, SimmondsP, HeinJ (2004) A comparative method for finding and folding RNA secondary structures within protein-coding regions. Nucleic Acids Res 32 : 4925–4936.
17. ChenY, StephanW (2003) Compensatory evolution of a precursor messenger RNA secondary structure in the Drosophila melanogaster Adh gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100 : 11499–11504.
18. WoeseCR, GutellR, GuptaR, NollerHF (1983) Detailed analysis of the higher-order structure of 16S-like ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Microbiol Rev 47 : 621.
19. RoussetF, PelandakisM, SolignacM (1991) Evolution of compensatory substitutions through G.U intermediate states in Drosophila rRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88 : 10032–10036.
20. DutheilJY, JossinetF, WestofE (2010) Base pairing constraints drive structural epistasis in ribosomal RNA sequences. Mol Biol Evol 27 : 1868–1876.
21. KernAD, KondrashovFA (2004) Mechanisms and convergence of compensatory evolution in mammalian mitochondrial tRNAs. Nature Genet 36 : 1207–1212.
22. MeerMV, KondrashovAS, Artzy-RandrupY, KondrashovFA (2010) Compensatory evolution in mitochondrial tRNAs navigates valleys of low fitness. Nature 464 : 279–282.
23. OlsthoornRCL, LicisN, van DuinJ (1994) Leeway and constraints in the forced evolution of a regulatory RNA helix. EMBO J 13 : 2660–2668.
24. BerkhoutB (1991) Structural features in TAR RNA of human and simian immunodeficiency viruses: a phylogenetic approach. Nucleic Acids Res 20 : 27–31.
25. BerkhoutB, JeangKT (1991) Detailed mutational analysis of TAR RNA: critical spacing between the bulge and loop recognition domains. Nucleic Acids Res 19 : 6169–6176.
26. HarrisonGP, LeverAM (1992) The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 packaging signal and major splice donor region have a conserved stable secondary structure. J Virol 66 : 4144–4153.
27. KlaverB, BerkhoutB (1994) Evolution of a disrupted TAR RNA hairpin structure in the HIV-1 virus. EMBO J 13 : 2650–2659.
28. EmilianiS, Van LintC, FischleW, ParasPJr, OttM, et al. (1996) A point mutation in the HIV-1 Tat responsive element is associated with postintegration latency. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93 : 6377–6381.
29. McBrideMS, PanganibanAT (1996) The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 encapsidation site is a multipartite RNA element composed of functional hairpin structures. J Virol 70 : 2963–2973.
30. BerkhoutB, KlaverB, DasAT (1997) Forced evolution of a regulatory RNA helix in the HIV-1 genome. Nucleic Acids Res 25 : 94–947.
31. CleverJL, ParslowTG (1997) Mutant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genomes with defects in RNA dimerization or encapsidation. J Virol 71 : 3407–3414.
32. DasAT, KlaverB, BerkhoutB (1999) A hairpin structure in the R region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA genome is instrumental in polyadenylation site selection. J Virol 73 : 81–91.
33. HarrichD, HookerCW, ParryE (2000) The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 TAR RNA upper stem-loop plays distinct roles in reverse transcription and RNA packaging. J Virol 74 : 5639–5646.
34. KulinskiT, OlejniczakM, HuthoffH, BieleckiL, Pachulska-WieczorekK, et al. (2003) The apical loop of the HIV-1 TAR RNA hairpin is stabilized by a cross-loop base pair. J Biol Chem 278 : 38892–38901.
35. CobrinikD, SoskeyL, LeisJA (1988) Retroviral RNA secondary structure required for efficient initiation of reverse transcription. J Virol 62 : 3622–3630.
36. WilsonW, BraddockM, AdamsSE, RathjenPD, KingsmanSM, et al. (1988) HIV expression strategies: ribosomal frameshifting is directed by a short sequence in both mammalian and yeast systems. Cell 55 : 1159–1169.
37. CassanM, BerteauxV, AngrandPO, RoussetJP (1990) Expression vectors for quantifying in vivo translational ambiguity: their potential use to analyze frameshifting at the HIV gag-pol junction. Res Virol 141 : 597–610.
38. ParkinNT, ChamorroM, VarmusHE (1992) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gag-pol frameshifting is dependent on downstream mRNA secondary structure: demonstration by expression in vivo. J Virol 66 : 5147–5151.
39. JacquenetS, RopersD, BilodeauPS, DamierL, MouginA, et al. (2001) Conserved stem-loop structures in the HIV-1 RNA region containing the A3 3′ splic site and its cis-regulatory element: possible involvement in RNA splicing. Nucleic Acids Res 29 : 464–478.
40. GarciaJA, HarrichD, SoultanakisE, WuF, MitsuyasuR, et al. (1989) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 LTR TATA and TAR region sequences required for transcriptional regulation. EMBO J 8 : 765–778.
41. AbbinkTEM, BerkhoutB (2008) RNA structure modulates splicing efficiency at the human immunodeficiency virus type I major splice donor. J Virol 82 : 3090–3098.
42. SchragSJ, PerrotV, LevinBR (1997) Adaptation to the fitness costs of antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 264 : 1287–1291.
43. Maisnier-PatinS, BergOG, LiljasL, AndersonDI (2002) Compensatory adaptation to the deleterious effect of antibiotic resistance in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Microbiol 46 : 355–366.
44. HoffmanNG, SchifferCA, SwanstromR (2005) Covariation of amino acid positions in HIV-1 protease. Virology 331 : 206–207.
45. VaraniG, McClainWH (2000) The GU wobble base pair. EMBO Rep 1 : 18–23.
46. WattsJM, DangKK, GorelickRJ, LeonardCW, BessCWJr, et al. (2009) Architecture and secondary structure of an entire HIV-1 RNA genome. Nature 460 : 711–719.
47. PerelsonAS, RibeiroRM (2008) Estimating drug efficacy and viral dynamic parameters: HIV and HCV. Statist Med 27 : 4647–4657.
48. SunyaevS, RamenskyV, KochI, LatheW3rd, KondrashovAS, et al. (2001) Prediction of deleterious human alleles. Hum Mol Genet 10 : 591–597.
49. EddySR (1995) Multiple alignment using hidden Markov models. ISMB 3 : 114–120.
50. GaschenB, KuikenC, KorberB, FoleyB (2001) Retrieval and on-the-fly alignment of sequence fragments from the HIV database. Bioinformatics 17 : 415–418.
51. ManskyLM, TeminHM (2005) Lower in vivo mutation rate of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 than predicted from the fidelity of purified reverse transcriptase. J Virol 69 : 5087.
52. R Development Core Team (2009) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria.
Štítky
Hygiena a epidemiologie Infekční lékařství Laboratoř
Článek Out-of-Sequence Signal 3 as a Mechanism for Virus-Induced Immune Suppression of CD8 T Cell ResponsesČlánek RNF26 Temporally Regulates Virus-Triggered Type I Interferon Induction by Two Distinct MechanismsČlánek Mouse, but Not Human, ApoB-100 Lipoprotein Cholesterol Is a Potent Innate Inhibitor of Pneumolysin
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Pathogens
Nejčtenější tento týden
2014 Číslo 9- Stillova choroba: vzácné a závažné systémové onemocnění
- Perorální antivirotika jako vysoce efektivní nástroj prevence hospitalizací kvůli COVID-19 − otázky a odpovědi pro praxi
- Diagnostika virových hepatitid v kostce – zorientujte se (nejen) v sérologii
- Jak souvisí postcovidový syndrom s poškozením mozku?
- Familiární středomořská horečka
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- Virus Control Goes Epigenetic
- The Role of Iron in Prion Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases
- The Ins and Outs of Rust Haustoria
- Prion Strains and Amyloid Polymorphism Influence Phenotypic Variation
- Teaching Fido New ModiFICation Tricks
- Can Enhance Infection in Mosquitoes: Implications for Malaria Control?
- MIF Contributes to Associated Immunopathogenicity Development
- Persistence of Virus Reservoirs in ART-Treated SHIV-Infected Rhesus Macaques after Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant
- Bacillus Calmette-Guerin Infection in NADPH Oxidase Deficiency: Defective Mycobacterial Sequestration and Granuloma Formation
- EhCoactosin Stabilizes Actin Filaments in the Protist Parasite
- Molecular Insights Into the Evolutionary Pathway of O1 Atypical El Tor Variants
- LprG-Mediated Surface Expression of Lipoarabinomannan Is Essential for Virulence of
- Structural Correlates of Rotavirus Cell Entry
- Multivalent Adhesion Molecule 7 Clusters Act as Signaling Platform for Host Cellular GTPase Activation and Facilitate Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction
- The Effects of Vaccination and Immunity on Bacterial Infection Dynamics
- Myeloid Derived Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1-alpha Is Required for Protection against Pulmonary Infection
- Functional Characterisation of Germinant Receptors in and Presents Novel Insights into Spore Germination Systems
- Global Analysis of Neutrophil Responses to Reveals a Self-Propagating Inflammatory Program
- Host Cell Invasion by Apicomplexan Parasites: The Junction Conundrum
- Comparative Phenotypic Analysis of the Major Fungal Pathogens and
- Unravelling the Multiple Functions of the Architecturally Intricate β-galactosidase, BgaA
- Sialylation of Prion Protein Controls the Rate of Prion Amplification, the Cross-Species Barrier, the Ratio of PrP Glycoform and Prion Infectivity
- Symbionts Commonly Provide Broad Spectrum Resistance to Viruses in Insects: A Comparative Analysis of Strains
- Ontogeny of Recognition Specificity and Functionality for the Broadly Neutralizing Anti-HIV Antibody 4E10
- Identification and Characterisation of a Hyper-Variable Apoplastic Effector Gene Family of the Potato Cyst Nematodes
- Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus Entry into Host Cells Occurs through the Multivesicular Body and Requires ESCRT Regulators
- Age-Dependent Enterocyte Invasion and Microcolony Formation by
- CD160-Associated CD8 T-Cell Functional Impairment Is Independent of PD-1 Expression
- Functional Fluorescent Protein Insertions in Herpes Simplex Virus gB Report on gB Conformation before and after Execution of Membrane Fusion
- The Tudor Domain Protein Spindlin1 Is Involved in Intrinsic Antiviral Defense against Incoming Hepatitis B Virus and Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1
- Transgenic Analysis of the MAP Kinase MPK10 Reveals an Auto-inhibitory Mechanism Crucial for Stage-Regulated Activity and Parasite Viability
- Evidence for a Transketolase-Mediated Metabolic Checkpoint Governing Biotrophic Growth in Rice Cells by the Blast Fungus
- Incomplete Deletion of IL-4Rα by LysM Reveals Distinct Subsets of M2 Macrophages Controlling Inflammation and Fibrosis in Chronic Schistosomiasis
- Identification and Functional Expression of a Glutamate- and Avermectin-Gated Chloride Channel from , a Southern Hemisphere Sea Louse Affecting Farmed Fish
- Out-of-Sequence Signal 3 as a Mechanism for Virus-Induced Immune Suppression of CD8 T Cell Responses
- Strong Epistatic Selection on the RNA Secondary Structure of HIV
- Hematopoietic but Not Endothelial Cell MyD88 Contributes to Host Defense during Gram-negative Pneumonia Derived Sepsis
- Delineation of Interfaces on Human Alpha-Defensins Critical for Human Adenovirus and Human Papillomavirus Inhibition
- Exploitation of Reporter Strains to Probe the Impact of Vaccination at Sites of Infection
- RNF26 Temporally Regulates Virus-Triggered Type I Interferon Induction by Two Distinct Mechanisms
- Helminth Infections Coincident with Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis Inhibit Mono- and Multifunctional CD4 and CD8 T Cell Responses in a Process Dependent on IL-10
- MHC Class II Restricted Innate-Like Double Negative T Cells Contribute to Optimal Primary and Secondary Immunity to
- Reactive Oxygen Species Regulate Caspase-11 Expression and Activation of the Non-canonical NLRP3 Inflammasome during Enteric Pathogen Infection
- Evolution of Plastic Transmission Strategies in Avian Malaria
- A New Human 3D-Liver Model Unravels the Role of Galectins in Liver Infection by the Parasite
- Translocates into the Myocardium and Forms Unique Microlesions That Disrupt Cardiac Function
- Mouse, but Not Human, ApoB-100 Lipoprotein Cholesterol Is a Potent Innate Inhibitor of Pneumolysin
- The Cofilin Phosphatase Slingshot Homolog 1 (SSH1) Links NOD1 Signaling to Actin Remodeling
- Kaposi's Sarcoma Herpesvirus MicroRNAs Induce Metabolic Transformation of Infected Cells
- Reorganization of the Endosomal System in -Infected Cells: The Ultrastructure of -Induced Tubular Compartments
- Distinct Dictation of Japanese Encephalitis Virus-Induced Neuroinflammation and Lethality via Triggering TLR3 and TLR4 Signal Pathways
- Exploitation of the Complement System by Oncogenic Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus for Cell Survival and Persistent Infection
- The Secreted Peptide PIP1 Amplifies Immunity through Receptor-Like Kinase 7
- Structural Insight into Host Recognition by Aggregative Adherence Fimbriae of Enteroaggregative
- The CD14CD16 Inflammatory Monocyte Subset Displays Increased Mitochondrial Activity and Effector Function During Acute Malaria
- Infection Induces Expression of a Mosquito Salivary Protein (Agaphelin) That Targets Neutrophil Function and Inhibits Thrombosis without Impairing Hemostasis
- PLOS Pathogens
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- The Secreted Peptide PIP1 Amplifies Immunity through Receptor-Like Kinase 7
- Symbionts Commonly Provide Broad Spectrum Resistance to Viruses in Insects: A Comparative Analysis of Strains
- MIF Contributes to Associated Immunopathogenicity Development
- The Ins and Outs of Rust Haustoria
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Vladimír Palička, CSc., Dr.h.c., doc. MUDr. Václav Vyskočil, Ph.D., MUDr. Petr Kasalický, CSc., MUDr. Jan Rosa, Ing. Pavel Havlík, Ing. Jan Adam, Hana Hejnová, DiS., Jana Křenková
Autoři: MUDr. Irena Krčmová, CSc.
Autoři: MDDr. Eleonóra Ivančová, PhD., MHA
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Eva Kubala Havrdová, DrSc.
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání




