-
Články
Top novinky
Reklama- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
Top novinky
Reklama- Kongresy
- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Top novinky
ReklamaQuality of Private and Public Ambulatory Health Care in Low and Middle Income Countries: Systematic Review of Comparative Studies
Background:
In developing countries, the private sector provides a substantial proportion
of primary health care to low income groups for communicable and
non-communicable diseases. These providers are therefore central to
improving health outcomes. We need to know how their services compare to
those of the public sector to inform policy options.Methods and Findings:
We summarised reliable research comparing the quality of formal private
versus public ambulatory health care in low and middle income countries. We
selected studies against inclusion criteria following a comprehensive
search, yielding 80 studies. We compared quality under standard categories,
converted values to a linear 100% scale, calculated differences
between providers within studies, and summarised median values of the
differences across studies. As the results for for-profit and not-for-profit
providers were similar, we combined them. Overall, median values indicated
that many services, irrespective of whether public or private, scored low on
infrastructure, clinical competence, and practice. Overall, the private
sector performed better in relation to drug supply, responsiveness, and
effort. No difference between provider groups was detected for patient
satisfaction or competence. Synthesis of qualitative components indicatesthe private sector is more client centred.
Conclusions:
Although data are limited, quality in both provider groups seems poor, with
the private sector performing better in drug availability and aspects of
delivery of care, including responsiveness and effort, and possibly being
more client orientated. Strategies seeking to influence quality in both
groups are needed to improve care delivery and outcomes for the poor,
including managing the increasing burden of non-communicable diseases.
: Please see later in the article for the Editors' Summary
Published in the journal: . PLoS Med 8(4): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000433
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000433Summary
Background:
In developing countries, the private sector provides a substantial proportion
of primary health care to low income groups for communicable and
non-communicable diseases. These providers are therefore central to
improving health outcomes. We need to know how their services compare to
those of the public sector to inform policy options.Methods and Findings:
We summarised reliable research comparing the quality of formal private
versus public ambulatory health care in low and middle income countries. We
selected studies against inclusion criteria following a comprehensive
search, yielding 80 studies. We compared quality under standard categories,
converted values to a linear 100% scale, calculated differences
between providers within studies, and summarised median values of the
differences across studies. As the results for for-profit and not-for-profit
providers were similar, we combined them. Overall, median values indicated
that many services, irrespective of whether public or private, scored low on
infrastructure, clinical competence, and practice. Overall, the private
sector performed better in relation to drug supply, responsiveness, and
effort. No difference between provider groups was detected for patient
satisfaction or competence. Synthesis of qualitative components indicatesthe private sector is more client centred.
Conclusions:
Although data are limited, quality in both provider groups seems poor, with
the private sector performing better in drug availability and aspects of
delivery of care, including responsiveness and effort, and possibly being
more client orientated. Strategies seeking to influence quality in both
groups are needed to improve care delivery and outcomes for the poor,
including managing the increasing burden of non-communicable diseases.
: Please see later in the article for the Editors' SummaryIntroduction
The private sector is the main provider of primary health care for the poor in many low and middle income countries (LMICs). For example, in South Asia about three quarters of children from the poorest income quintile with acute respiratory conditions seeking health care go to a private provider [1], and about 45% of sick children from the poorest income quintile across 26 African countries go to a formal or informal private provider rather than a public provider for health care [2]. Private providers are also increasingly important for providing ambulatory care as non-communicable diseases (NCDs) increase [3].
Private providers may be “formal”, i.e. recognised by law or by legally recognised regulatory authorities, or “informal”, i.e. not recognised [4]. Formal private providers include “for-profit” hospitals and self-employed practitioners, and “not-for-profit” non-governmental organizations (NGOs). NGOs include churches, and are particularly common in Africa, although the for-profit/not-for-profit dichotomy is not so clear cut in practice, with some NGOs simply representing private practitioners securing tax breaks [5],[6]. Informal allopathic providers include “quacks”, lay health workers, drug sellers, and ordinary shop keepers [7].
Advocating that formal for-profit private services are preferable to government provision raises considerable ideological debates [8]–[10]; equally, not-for-profit private providers such as those run by churches are seen by some as good and as providing value for money [11]. Whatever the debates, there is agreement that influencing the quality of both public and private providers could have a major impact on health outcomes. Adequate state stewardship and oversight of these mixed systems is widely advocated [9],[12], but the mechanisms to assure quality are not simple and are of unclear effectiveness [13],[14]. Improving stewardship and oversight is complex, involving resources, management, legislation, and approaches to influence the market [15],[16]. Thus, an understanding of how quality and performance in the formal private sector compares with that of the public sector would help governments to focus strategies to improve delivery. Putting this simply, if the private sector is generally providing poorer quality care than the public sector, then there is an imperative to improve the quality and outcomes; on the other hand, if the quality of private-sector care is good, the priority for policy is to influence the market somehow to further improve access for low income groups.
“Quality” has many dimensions [17], including structural quality, aspects of delivery, and the technical or professional content of care, all of which are likely to influence service use. Each dimension will have complex effects on patient satisfaction, patient use of the service, and outcomes for their health. In addition, each is interrelated: population health outcomes will depend on service use, technical quality, and drug availability, for example. A recent substantive analysis that examined the use of medicines in primary care reported poor quality prescribing for both sectors, with little change over time [18]. The authors also reported the relatively poor quality of data and the need for research assessing the difference between the public and private sector. Thus, our objective was to systematically identify and summarise the results of studies that directly compare the quality of private providers and public services in relation to ambulatory health care in LMICs.
Methods
Criteria for Inclusion
We included field-based studies that directly compared service quality in ambulatory care from private versus public medical health services. The purpose was to include studies using the same methods to measure the differences, and in the same countries, to avoid confounding factors related to overall differences in service quality between countries. We included studies conducted in LMICs that assessed ambulatory care, defined as the “delivery of personal health care services on an outpatient basis” [19]. We only included studies that compared private and public services in the same country, at the same time, using the same methods, and which met particular quality criteria (Table S1). “Private” refers to “all organizations and individuals working outside the direct control of the state” [20], and we included only those working within the allopathic medical systems. “Private for-profit providers” included individuals or groups of practitioners in privately owned clinics, hospitals, and pharmacies that operate on a for-profit basis, while “private not-for-profit providers” included practitioners in facilities that operate on a non-profit basis, such as various (missionary or non-missionary) NGOs and private voluntary organizations. Informal providers included those without formal health professional qualifications, such as street vendors and shop keepers. We included studies reported in English, French, or German and published from January 1970 to April 2009. We screened all titles/abstracts found by the search methods described below for potential inclusion, and then carefully applied the detailed inclusion criteria (Table S1) to the full text of those identified in the screening search. Studies using qualitative methods were identified and were included if they (a) used internationally accepted data collection methods (e.g., in-depth interviews, focus group discussion, or observation), (b) indicated the methods used in analysis (e.g., thematic analysis, content analysis, or grounded theory), and (c) presented data by theme or in the form of verbatim quotes.
Search Methods
The search strategy for Medline can be found in Table S2, and a list of the databases searched in Table S3. In addition, we searched all records of the World Health Organization's (WHO's) library database, WHOLIS (on 27 April 2009), all Service Availability Mapping reports published on the WHO Web site (http://www.who.int/healthinfo/systems/samdocs/en/index.html) (on 5 December 2010) [21], all Service Provision Assessment Survey reports published on the Measure DHS Web site (http://www.measuredhs.com/aboutsurveys/search/search_survey_main.cfm?SrvyTp=type&listtypes=3) (on 3 December 2010) [22], and all research studies published on the Core group Web site (http://www.coregroup.org/) (on 6 December 2010), and we examined reference lists of relevant reviews [23]–[25] and of the included studies.
The search strategies included indexed and free-text terms: health sector, health care, delivery of health care, primary health care, medical care, health clinic, outpatient service, ambulatory care, practitioner, health provider, health provision, hospital, pharmacy, drug vendor, drug seller, drug store, public sector, public, private sector, private, quality of health care, Africa, Asia, South America, developing countries, less developed countries, third world countries, underdeveloped country, low income country, low income nation, middle income country, middle income nation, low and middle income countries.
Data Collection and Analysis
We applied the inclusion criteria to all titles and abstracts. We retrieved full-text copies of potentially relevant records, and discussed each to resolve uncertainties. We then appraised potential studies against a set of basic minimum methodological criteria to exclude studies where data were unlikely to be reliable (Table S1).
We adapted Donabedian's [17] classification of quality of care using structural, delivery, and technical categories (Table 1). We incorporated “responsiveness” [26] to reflect aspects such as waiting time, communication quality, and dignity, as well as an assessment of the “effort” providers make, such as whether they examine the patient, and the length of the consultation time [27],[28], and we divided technical quality into measures of competence and clinical practice (Table 1).
Tab. 1. Quality categories, sub-categories, and indicators used. 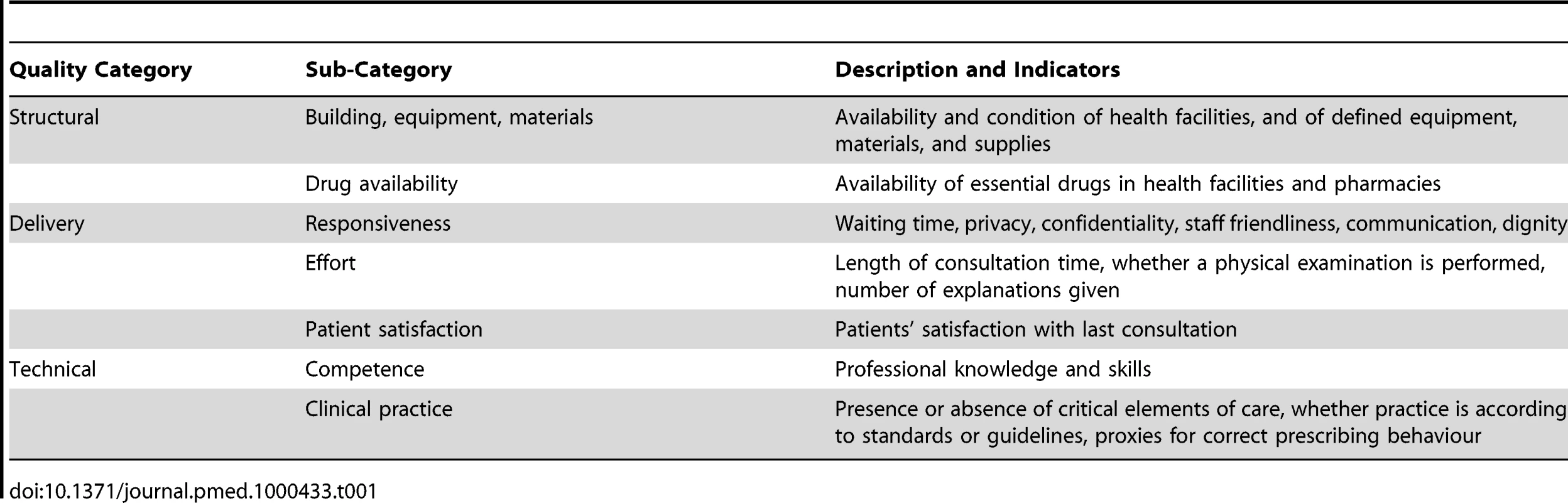
S. B. extracted data using a standard form, entered into an Access database, with about 80% verified by a second author to ensure standardisation of coding. We contacted 33 authors for further information, and all but nine authors responded. Standard data describing the study were extracted. If a study reported several comparisons, we selected groups that were most similar within the health system (e.g., public hospitals versus private hospitals, or public health centres versus private clinics). If results were presented separately for different cadres or levels of staff qualification, we chose the comparison group with the staff qualification levels that were most comparable and most frequented by the population. If the latter could not be established, we chose the highest qualified comparison group.
We then separately computed summary measures of (a) the overall level of quality of care in the private and in the public sector and (b) the difference of quality of care between both sectors stratified by quality categories and components. If there were several data measures for one component in a study, we computed the median for all reported measures to calculate a single measure for component quality for the provider. For example, in the case of a public-sector score (on a linear scale, with 100% being the maximum obtainable) of 45% for physical infrastructure, 50% for availability of basic diagnostic equipment, and 60% for availability of basic material, the median for the structural component “building, equipment, and material” would be 50%. The median was also computed for the quality score difference between private and public provider. For example, in case of a difference of +5% in physical infrastructure, +11% in availability of basic diagnostic equipment, and +14% in basic material, the median difference would be +11% for the given comparison in a study. After computing the medians for the overall quality of care and for the difference of care for each single comparison in each study, we computed medians and inter-quartile ranges (IQRs) across all comparisons. The size of the difference and the IQRs of the difference were used to judge whether a difference was evident.
Results
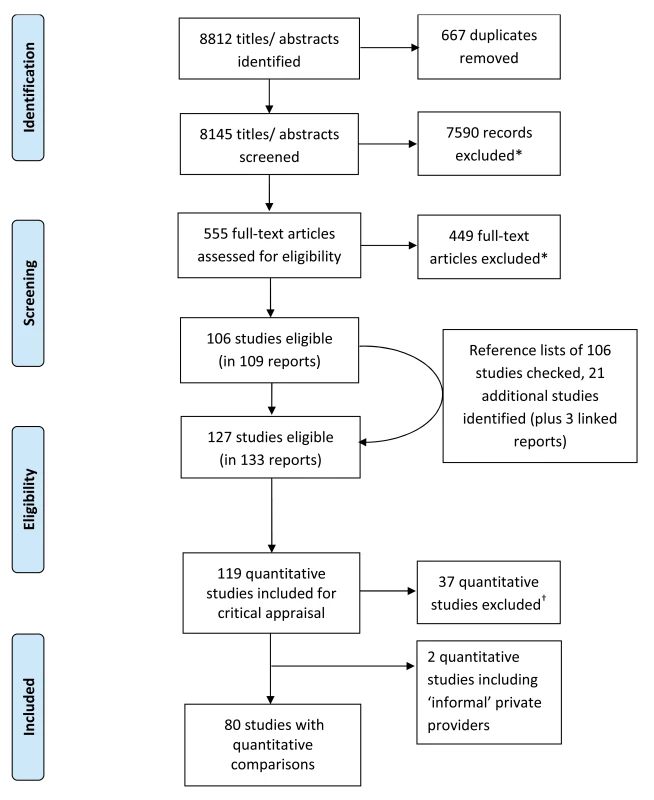
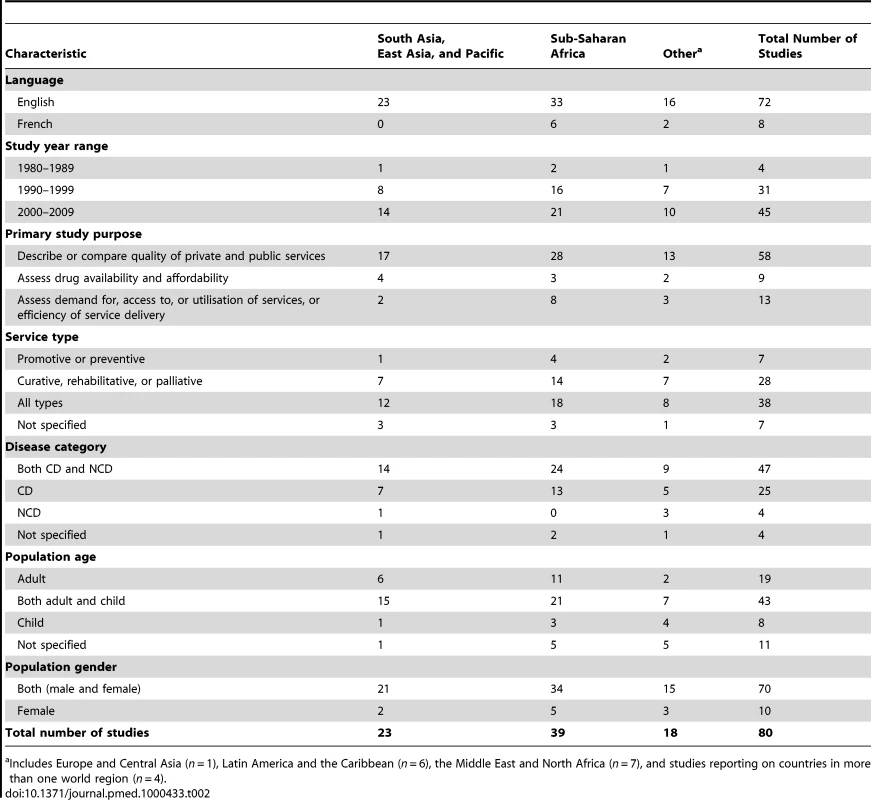
Of 8,812 titles and abstracts identified, 80 studies included direct quantitative comparisons of public and private formal providers (Figure 1, adapted from PRISMA 2009 flow diagram [29]; Tables S4 and S5 describe excluded studies). These yielded 133 comparisons, of which we were able to convert 101 to a 100% scale (Table S6). Most studies were carried out after 1990; they were mainly conducted in sub-Saharan Africa (n = 39) and in Asia and the Pacific (n = 23); and most were intended to compare quality, examining all types of primary service and disease category (Table 2; details in Table S9). Most studies did not report socio-economic status of public and private service users, and only five presented data by different wealth groups [30]–[34]. No study compared the same individual providers working in public and private care settings. For two studies [35],[36] that reported results separately for different cadres, we chose public versus private doctors rather than public versus private nurses or midwives as comparison groups, but it should be noted that for both groups results pointed in the same direction.
We found only two studies comparing public providers and private informal providers. The first [37] compared malaria-related knowledge and chloroquine availability in public dispensaries and informal drug vendors, and suggested that the public sector was slightly better. The second [38] mixed both formal and informal private providers together. These two studies were excluded from further analysis.
Of the 101 formal private versus public sector comparisons that were converted to a 100% scale, 57 compared government with private for-profit providers, 10 with a mix of for-profit and not-for-profit providers, and 34 with private not-for-profit providers. Of the last 34 comparisons, most (n = 29) were conducted in sub-Saharan Africa.
Study-level summary values for each quality component are presented in Table 3, along with the summary of the within-study differences. We also carried out an analysis that separated private for-profit and private not-for-profit providers (Table S7). As the results in the for-profit and not-for-profit providers were remarkably consistent, they are presented as combined.
In addition, ten studies included qualitative data that met our eligibility criteria, with a similar geographic spread to the quantitative data.
Structure
For buildings, equipment, materials, and supplies, no difference was detected. For the 26 comparisons, the IQR of the difference included 0. Respondents in two qualitative studies reporting on this category described private facilities as better [39],[40].
For drug availability, private-sector care was substantially better than public-sector care, from 14 comparisons. Nine studies used a standard method and referred to the WHO essential drug list [41],[42]. None of the quantitative studies compared the quality of drugs available in the public versus private sector. Qualitative studies reported that the private sector was more trusted for drug quality [43] and that the drugs were more readily available [39],[40],[44],[45].
Service Delivery
For responsiveness, private-sector care was better (see Table 1 for definition), from seven comparisons. Studies used patient interviews, observations, or simulated visits. In six of the seven comparisons measuring waiting time, the time was shorter in the private sector. Qualitative data in five studies indicated that the private sector provided more personalised, respectful [39],[40],[46],[47], listening [43], and client-centred service, as well as service that was more convenient [48] and quicker and easier to access [47],[49].
For effort, private-sector care was better, from three comparisons. A further four studies reported on average consultation times, which were longer in the private sector in all studies, although statistical significance was only computed and confirmed in two of them [6],[50]–[52]. Qualitative data were consistent with this finding. Studies consistently reported criticisms of the public sector (with providers showing favouritism for some patients and less respect for poorer clients [39],[40],[43],[44],[46],[48],[49]) and praise for the private sector [39],[40],[43],[48],[49].
For patient satisfaction, no difference between private and public sector was detected, from ten comparisons. None of the studies measuring “satisfaction” reported the use of a validated questionnaire. Only one took into account possible differences in expectations of public and private services [53].
Technical Quality
For competence, scores for private - versus public-sector care were similar, and generally poor, from 19 comparisons; competence was measured by case scenarios or vignettes, provider interviews, or a formal test. In qualitative studies the private sector was reported as quicker and easier to access, although the competence of some providers was questioned [40],[48]. The public sector was often perceived as technically competent but inconvenient and provider centred, with complex systems that took time and effort to negotiate [44],[47],[49],[54].
For clinical practice, private-sector care was marginally better, from 22 comparisons. Of those not convertible to a linear 100% scale, 14 studies used the same standard methods to assess prescribing behaviour, summarised in Table S8, with no obvious differences. In qualitative studies, respondents perceived public providers as qualified and well trained [43], although some were thought to overprescribe to raise their income [40],[48]. The private sector was also criticised for overprescribing and collusion between doctors and pharmacists [46], for suspected “fake” or unlabelled drugs, for “fake” doctors, and for nurses practicing illegally in private pharmacies in need of regulation [40],[46],[48].
We carried out a sensitivity analysis including only studies and comparisons (n = 67) classified as high quality because of their size (Table S1 provides the criteria); the results obtained were very similar to Table 3.
For-Profit and Not-for-Profit Providers
As mentioned above, most of the not-for-profit studies were carried out in sub-Saharan Africa (29 of 34 comparisons). Table S7 contains an analysis stratified by private for-profit and private not-for-profit. The direction of the difference is the same as for the aggregated value for all components. Notably, clinical practice was much better in the for-profit sector, and the difference was less marked for the not-for-profit sector, but the number of comparisons in the for-profit sector is limited.
Factors Contributing to a Quality Difference
Some of the qualitative studies (n = 8) sought to explain the quality difference between the two sectors. Factors perceived to be related to low public-sector quality included resource constraints, low salaries, high workload, and poor incentives and conditions of service [39],[40],[44], the lack of a public family/general practice system that enables patients to return to the doctor(s) of their choice and develop relationships of trust over longer periods of time [43], public-sector drugs being sold privately [39],[40], staff favouring particular patients [39],[47], and clients lacking sufficient information about the appropriate use of drugs, resistance to antibiotics, costs, and their rights to challenge poor service [39],[46],[49],[54].
Discussion
Summary
The results of our analyses indicate that, in both private and public sectors, median values for structure, competence, and clinical practice fall around or below scores of 50/100. Whilst these values depend on the instruments used and the stringency of the primary research studies in applying these standards, the trends provide some insight into absolute performance, with obvious problems with technical aspects of care in both sectors.
In comparative performance, the formal private sector was better for drug availability, responsiveness, and effort. Overall, the median differences were modest, so stereotyped opinions that one sector is clearly better than another are not supported by this review.
Qualitative data portrayed formal private services that, in contrast to the public sector, were more client centred. This is consistent with the differences in care delivery shown by the quantitative data.
Interpretation
In a formal private setting, drugs may be more available because funds are not restricted in the same way as in the public sector, and private providers are motivated to encourage patients to return, so responsiveness and effort are greater.
These results, combined with the fact that the private sector provides a substantial amount of health services, raise two further issues—the importance of paying attention to both sectors if overall quality is to be raised, and the need for governments to play a more active role in assuring quality of care.
Many efforts to improve the quality of ambulatory care are restricted to the public sector on the grounds that public funds should be reserved for the public sector because that is where the poor turn for their health care. But concentrating on the public sector misses a large proportion, the majority in some cases, of the providers used by the poor. Raising the quality of care delivered by private, as well as public, providers would, in fact, be a pro-poor intervention as it would improve the effectiveness of the money the poor spend on health care. A second argument advanced against spending public money on private providers is that because they provide a lower quality of care it is more effective to reserve funds for the public sector. The results of this review indicate that the overall quality of care from the two sets of providers is similar; if anything, the private sector is more responsive and drug availability is greater.
The overall low quality of care is likely to become even more so as the double burden of communicable disease (CD) and NCD becomes more prominent. Most health care providers, public or private, practicing today have been trained by institutions and work in health systems primarily oriented to CDs. Consequently, providers have only limited knowledge of NCDs, which demand a different set of clinical skills and a different approach to treatment. On most dimensions, effective treatment for NCDs requires approaches quite different to those that are available through the current health systems, and, contrary to views held by many, NCDs and associated risk factors are not the preserve of the rich; they are equally, if not more, prevalent among the poor [55]. Thus, it has to be considered that certain types of diseases, such as some NCDs, but also more complex CDs, such as AIDS, might require particularly high levels of structural quality, drug availability, and provider competence, while for other diseases, such as childhood diarrhoea, that are easy to diagnose and treat, it is most important to motivate providers to exert effort and practice what they already know [56].
Raising the quality of care in a health system is a long-term effort and requires attention to various aspects, including the incentive structure and training, both areas in which government has an important role, but to which it frequently pays little attention. Systematic and comprehensive traditional narrative reviews suggest a variety of strategies that can help increase quality. For example, supervision and audit with feedback, especially if combined with training, have been found to be effective [57]. However, an overall government bias against the private sector frequently means that too little attention is paid, and too few resources devoted, to overall supervision of the private sector. But setting standards, partly through ensuring standards of training, partly through licensing and accreditation of professionals (including emphasis on continuing education), and partly through consumer protection laws, is an important role of government [16],[58]. Researchers such as Leonard and colleagues [15] have provided useful theoretical frameworks for influencing the private sector based on the “principal-agent theory”. Others have proposed different ways of classifying the variety of strategies that have so far been used to improve the quality of private care, for example, classifying strategies according to the influence they have either on supply or demand or on the overall market environment [16],[59]. However, empirical evidence on the effectiveness of various approaches is somewhat limited, as the review by Peters et al. shows for reproductive health care [14].
Strengths and Weaknesses of This Review
The search was comprehensive, the inclusion criteria were applied carefully, and quality criteria were applied to ensure comparisons were valid and were direct comparisons using the same methods. Given that studies used a very varied set of tools to measure quality of care, results on the absolute level of quality of care have to be interpreted with caution. However, results on the difference in quality of care can be interpreted with more confidence, because, as mentioned above, we took care to include only those studies that directly compared quality of care in the same country at the same time, using the same methods. A further strength is that we were able to categorise the various quality components to allow comparisons between studies. A disadvantage is that small studies could contribute as much to the estimates as large studies, but the sensitivity analysis—excluding the smaller studies—did not alter the direction of the differences between the sectors.
Although this review fully assessed eligible comparative studies on quality, additional work is needed to compare costs and aspects of equity. Similar to the dispute on quality, there are controversial views on whether private or public care is more costly or more accessible to the poor.
The review also highlights the lack of comparative evidence between the public sector and the private informal sector, although the latter is widely used [2],[60].
Implications for Policy and Research
With the current evidence base, there is a clear need to consider quality of primary health services in both the public and private sector in order to improve health outcomes. There is a tendency for the private sector to provide better quality services, but further research on the overall quality and testing feasibility and effectiveness of mechanisms to improve quality will be critical for future health gains in LMICs.
Research needs to standardise outcomes and measures of socio-economic position across studies to improve comparability and to assist in between-country dialogue on effective quality assurance policies. Research on the effectiveness of market-led strategies to influence the private sector is important. Studies of dual practice, examining the same providers' behaviour in the two settings, could be useful specific studies in identifying factors in terms of the setting. Lastly, establishing minimum standards of care, and research to help identify effective approaches to achieve them, is central to achieving the health gains that are possible with current preventive and treatment medical technologies.
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. World Bank
2004
World development report: Making services work for poor people
Washington (District of Columbia)
World Bank and Oxford University Press
2. Marek
T
O'Farrell
C
Yamamoto
C
Zable
I
2005
Trends and opportunities in public-private partnerships to improve
health service delivery in Africa. Africa Region Human Development Working
Paper Series
Washington (District of Columbia)
World Bank
3. Murray
CJ
Lopez
AD
1997
Alternative projections of mortality and disability by cause
1990–2020: Global Burden of Disease Study.
Lancet
349
1498
1504
4. Bloom
G
Standing
H
Lloyd
R
2008
Markets, information asymmetry and health care: towards new
social contracts.
Soc Sci Med
66
2076
2087
5. Gilson
L
Sen
PD
Mohammed
S
Mujinja
P
1994
The potential of health sector non-governmental organizations:
policy options.
Health Policy Plan
9
14
24
6. Kanji
N
Kilima
P
Lorenz
N
Garner
P
1995
Quality of primary outpatient services in Dar-es-Salaam: a
comparison of government and voluntary providers.
Health Policy Plan
10
186
190
7. Waters
H
Hatt
L
Peters
D
2003
Working with the private sector for child health.
Health Policy Plan
18
127
137
8. Hanson
K
Gilson
L
Goodman
C
Mills
A
Smith
R
2008
Is private health care the answer to the health problems of the
world's poor?
PLoS Med
5
e233
doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0050233
9. Lagomarsino
G
de Ferranti
D
Pablos-Mendez
A
Nachuk
S
Nishtar
S
2009
Public stewardship of mixed health systems.
Lancet
374
1577
1578
10. Sauerborn
R
2001
Low quality of care in low income countries: is the private
sector the answer?
Int J Qual Health Care
13
281
282
11. Leonard
KL
2002
When both states and markets fail: asymmetric information and the
role of NGOs in African health care.
Int Rev Law Econom
22
61
80
12. Saltman
RB
Ferroussier-Davis
O
2000
The concept of stewardship in health policy.
Bull World Health Organ
78
732
739
13. Patouillard
E
Goodman
CA
Hanson
KG
Mills
AJ
2007
Can working with the private for-profit sector improve
utilization of quality health services by the poor? A systematic review of
the literature.
Int J Equity Health
6
17
14. Peters
DH
Mirchandani
GG
Hansen
PM
2004
Strategies for engaging the private sector in sexual and
reproductive health: how effective are they?
Health Policy Plan
19
Suppl 1
i5
i21
15. Leonard
DK
2003
Africa's changing markets for health and veterinary services: the
new institutional issues
Berkeley
University of California Press/University of California
International and Area Studies Digital Collection
16. Mills
A
Brugha
R
Hanson
K
McPake
B
2002
What can be done about the private health sector in low-income
countries?
World Hosp Health Serv
38
24
30, 41–24
17. Donabedian
A
1978
The quality of medical care.
Science
200
856
864
18. World Health Organization
2009
Medicines use in primary care in developing and transitional countries:
Fact Book summarizing results from studies reported between 1990 and
2006
Geneva
World Health Organization
19. Berman
P
2000
Organization of ambulatory care provision: a critical determinant
of health system performance in developing countries.
Bull World Health Organ
78
791
802
20. Bennett
S
1992
Promoting the private sector: a review of developing country
trends.
Health Policy Plan
7
97
110
21. World Health Organization
2010
Health statistics and health information systems: service availability
mapping (SAM)
Geneva
World Health Organization
22. Measure
DHS
ICF Macro
2010
Service provision assessment (SPA) surveys
Calverton (Maryland)
Measure DHS and ICF Macro
23. Madden
JM
Quick
JD
Ross-Degnan
D
Kafle
KK
1997
Undercover careseekers: simulated clients in the study of health
provider behavior in developing countries.
Soc Sci Med
45
1465
1482
24. World Health Organization
2004
The world medicines situation
Geneva
World Health Organization
25. Zurovac
D
Rowe
AK
2006
Quality of treatment for febrile illness among children at
outpatient facilities in sub-Saharan Africa.
Ann Trop Med Parasitol
100
283
296
26. World Health Organization
2000
The world health report 2000—health systems: improving
performance
Geneva
World Health Organization
27. Leonard
DK
2003
Lessons from the new institutional economics for the structural
reform of human health services in Africa.
Leonard
DK
Africa's changing markets for health and veterinary services: the
new institutional issues
Berkeley
University of California Press/University of California
International and Area Studies Digital Collection
28. Das
J
Gertler
PJ
2007
Variations in practice quality in five low-income countries: a
conceptual overview.
Health Aff (Millwood)
26
w296
w309
29. Moher
D
Liberati
A
Tetzlaff
J
Altman
DG
2009
Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and
meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement.
PLoS Med
6
e1000097
doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
30. Barber
SL
2006
Public and private prenatal care providers in urban Mexico: how
does their quality compare?
Int J Qual Health Care
18
306
313
31. Barber
SL
Bertozzi
SM
Gertler
PJ
2007
Variations in prenatal care quality for the rural poor in
Mexico.
Health Aff (Millwood)
26
w310
w323
32. Barber
SL
Gertler
PJ
Harimurti
P
2007
Differences in access to high-quality outpatient care in
Indonesia.
Health Aff (Millwood)
26
w352
w366
33. Boller
C
Wyss
K
Mtasiwa
D
Tanner
M
2003
Quality and comparison of antenatal care in public and private
providers in the United Republic of Tanzania.
Bull World Health Organ
81
116
122
34. Das
J
Hammer
J
2007
Location, location, location: residence, wealth, and the quality
of medical care in Delhi, India.
Health Aff (Millwood)
26
w338
w351
35. Barber
SL
Gertler
PJ
Harimurti
P
2007
Differences in access to high-quality outpatient care in
Indonesia.
Health Aff (Millwood)
26
w352
w366
36. Nahum
A
Akogbeto
M
2000
[Malaria and pregnancy: attitude of health care personnel
during prenatal care in Cotonou, Benin].
Med Trop (Mars)
60
251
255
37. Massele
AY
Sayi
J
Nsimba
SE
Ofori-Adjei
D
Laing
RO
1993
Knowledge and management of malaria in Dar es Salaam,
Tanzania.
East Afr Med J
70
639
642
38. Tuan
T
Dung
VT
Neu
I
Dibley
MJ
2005
Comparative quality of private and public health services in
rural Vietnam.
Health Policy Plan
20
319
327
39. Gilson
L
Alilio
M
Heggenhougen
K
1994
Community satisfaction with primary health care services: an
evaluation undertaken in the Morogoro region of Tanzania.
Soc Sci Med
39
767
780
40. Lindelow
M
Serneels
P
2006
The performance of health workers in Ethiopia: results from
qualitative research.
Soc Sci Med
62
2225
2235
41. World Health Organization, Health Action International
2003
Medicine prices—a new approach to measurement
Geneva
World Health Organization
42. World Health Organization
2005
WHO operational package for monitoring and assessing country
pharmaceutical situations
Geneva
World Health Organization
43. Russell
S
2005
Treatment-seeking behaviour in urban Sri Lanka: trusting the
state, trusting private providers.
Soc Sci Med
61
1396
1407
44. Deressa
W
Ali
A
Hailemariam
D
2008
Malaria-related health-seeking behaviour and challenges for care
providers in rural Ethiopia: implications for control.
J Biosoc Sci
40
115
135
45. Lewis
M
Eskeland
G
Traa-Valerezo
X
2004
Primary health care in practice: is it effective?
Health Policy
70
303
325
46. Hoa
NQ
Ohman
A
Lundborg
CS
Chuc
NT
2007
Drug use and health-seeking behavior for childhood illness in
Vietnam—a qualitative study.
Health Policy
82
320
329
47. Turan
JM
Bulut
A
Nalbant
H
Ortayli
N
Akalin
AA
2006
The quality of hospital-based antenatal care in
Istanbul.
Stud Fam Plann
37
49
60
48. Lim
MK
Yang
H
Zhang
T
Feng
W
Zhou
Z
2004
Public perceptions of private health care in socialist
China.
Health Aff (Millwood)
23
222
234
49. Paphassarang
C
Philavong
K
Boupha
B
Blas
E
2002
Equity, privatization and cost recovery in urban health care: the
case of Lao PDR.
Health Policy Plan
17
Suppl
72
84
50. Pongsupap
Y
Van Lerberghe
W
2006
Choosing between public and private or between hospital and
primary care: responsiveness, patient-centredness and prescribing patterns
in outpatient consultations in Bangkok.
Trop Med Int Health
11
81
89
51. Siddiqi
S
Hamid
S
Rafique
G
Chaudhry
SA
Ali
N
2002
Prescription practices of public and private health care
providers in Attock District of Pakistan.
Int J Health Plann Manage
17
23
40
52. Mbanefoh
GF
Soyibo
A
Anyanwu
JC
2004
Markets for health care in Nigeria.
Nwabu
G
Wang'ombe
J
Okello
D
Munishi
G
Improving health policy in Africa
Nairobi
University of Nairobi Press
431
441
53. Mahaprata
P
2003
Quality health care in private and public health care
institutions.
Abdo
S
Yazbeck
AS
Peters
DH
Health policy research in South Asia: building capacity for
reform
Washington (District of Columbia)
World Bank
333
367
54. Schneider
H
Palmer
N
2002
Getting to the truth? Researching user views of primary health
care.
Health Policy Plan
17
32
41
55. Strong
K
Mathers
C
Leeder
S
Beaglehole
R
2005
Preventing chronic diseases: how many lives can we
save?
Lancet
366
1578
1582
56. Das
J
Hammer
J
Leonard
K
2008
The quality of medical advice in low-income
countries.
J Econ Perspect
22
93
114
57. Rowe
AK
de Savigny
D
Lanata
CF
Victora
CG
2005
How can we achieve and maintain high-quality performance of
health workers in low-resource settings?
Lancet
366
1026
1035
58. Bhat
R
1996
Regulating the private health care sector: the case of the Indian
Consumer Protection Act.
Health Policy Plan
11
265
279
59. Brugha
R
Zwi
A
1998
Improving the quality of private sector delivery of public health
services: challenges and strategies.
Health Policy Plan
13
107
120
60. Das
J
Hammer
J
2005
Which doctor? Combining vignettes and item response to measure
clinical competence.
J Dev Econom
78
348
383
Štítky
Interní lékařství
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Medicine
Nejčtenější tento týden
2011 Číslo 4- Není statin jako statin aneb praktický přehled rozdílů jednotlivých molekul
- Magnosolv a jeho využití v neurologii
- Biomarker NT-proBNP má v praxi široké využití. Usnadněte si jeho vyšetření POCT analyzátorem Afias 1
- Moje zkušenosti s Magnosolvem podávaným pacientům jako profylaxe migrény a u pacientů s diagnostikovanou spazmofilní tetanií i při normomagnezémii - MUDr. Dana Pecharová, neurolog
- Antikoagulační léčba u pacientů před operačními výkony
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- Quality of Private and Public Ambulatory Health Care in Low and Middle Income Countries: Systematic Review of Comparative Studies
- A Multifaceted Intervention to Implement Guidelines and Improve Admission Paediatric Care in Kenyan District Hospitals: A Cluster Randomised Trial
- The Quality of Medical Care in Low-Income Countries: From Providers to Markets
- Neglect of Medical Evidence of Torture in Guantánamo Bay: A Case Series
- Improving Effective Surgical Delivery in Humanitarian Disasters: Lessons from Haiti
- Decline in Diarrhea Mortality and Admissions after Routine Childhood Rotavirus Immunization in Brazil: A Time-Series Analysis
- Effect of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccination on Serotype-Specific Carriage and Invasive Disease in England: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Effect of a Nutrition Supplement and Physical Activity Program on Pneumonia and Walking Capacity in Chilean Older People: A Factorial Cluster Randomized Trial
- Strategies and Practices in Off-Label Marketing of Pharmaceuticals: A Retrospective Analysis of Whistleblower Complaints
- A Call for Action: The Application of the International Health Regulations to the Global Threat of Antimicrobial Resistance
- Medical Complicity in Torture at Guantánamo Bay: Evidence Is the First Step Toward Justice
- A Public Health Emergency of International Concern? Response to a Proposal to Apply the International Health Regulations to Antimicrobial Resistance
- Global Health Philanthropy and Institutional Relationships: How Should Conflicts of Interest Be Addressed?
- Claims about the Misuse of Insecticide-Treated Mosquito Nets: Are These Evidence-Based?
- The African Women's Protocol: Bringing Attention to Reproductive Rights and the MDGs
- PLOS Medicine
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Global Health Philanthropy and Institutional Relationships: How Should Conflicts of Interest Be Addressed?
- A Call for Action: The Application of the International Health Regulations to the Global Threat of Antimicrobial Resistance
- Claims about the Misuse of Insecticide-Treated Mosquito Nets: Are These Evidence-Based?
- Neglect of Medical Evidence of Torture in Guantánamo Bay: A Case Series
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Vladimír Palička, CSc., Dr.h.c., doc. MUDr. Václav Vyskočil, Ph.D., MUDr. Petr Kasalický, CSc., MUDr. Jan Rosa, Ing. Pavel Havlík, Ing. Jan Adam, Hana Hejnová, DiS., Jana Křenková
Autoři: MUDr. Irena Krčmová, CSc.
Autoři: MDDr. Eleonóra Ivančová, PhD., MHA
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Eva Kubala Havrdová, DrSc.
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání