-
Články
- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
- Kongresy
- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
HCMV Spread and Cell Tropism are Determined by Distinct Virus Populations
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) can infect many different cell types in vivo. Two gH/gL complexes are used for entry into cells. gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) shows no selectivity for its host cell, whereas formation of a gH/gL/gO complex only restricts the tropism mainly to fibroblasts. Here, we describe that depending on the cell type in which virus replication takes place, virus carrying the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex is either released or retained cell-associated. We observed that virus spread in fibroblast cultures was predominantly supernatant-driven, whereas spread in endothelial cell (EC) cultures was predominantly focal. This was due to properties of virus released from fibroblasts and EC. Fibroblasts released virus which could infect both fibroblasts and EC. In contrast, EC released virus which readily infected fibroblasts, but was barely able to infect EC. The EC infection capacities of virus released from fibroblasts or EC correlated with respectively high or low amounts of gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) in virus particles. Moreover, we found that focal spread in EC cultures could be attributed to EC-tropic virus tightly associated with EC and not released into the supernatant. Preincubation of fibroblast-derived virus progeny with EC or beads coated with pUL131A-specific antibodies depleted the fraction that could infect EC, and left a fraction that could predominantly infect fibroblasts. These data strongly suggest that HCMV progeny is composed of distinct virus populations. EC specifically retain the EC-tropic population, whereas fibroblasts release EC-tropic and non EC-tropic virus. Our findings offer completely new views on how HCMV spread may be controlled by its host cells.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Pathog 7(1): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1001256
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1001256Summary
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) can infect many different cell types in vivo. Two gH/gL complexes are used for entry into cells. gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) shows no selectivity for its host cell, whereas formation of a gH/gL/gO complex only restricts the tropism mainly to fibroblasts. Here, we describe that depending on the cell type in which virus replication takes place, virus carrying the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex is either released or retained cell-associated. We observed that virus spread in fibroblast cultures was predominantly supernatant-driven, whereas spread in endothelial cell (EC) cultures was predominantly focal. This was due to properties of virus released from fibroblasts and EC. Fibroblasts released virus which could infect both fibroblasts and EC. In contrast, EC released virus which readily infected fibroblasts, but was barely able to infect EC. The EC infection capacities of virus released from fibroblasts or EC correlated with respectively high or low amounts of gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) in virus particles. Moreover, we found that focal spread in EC cultures could be attributed to EC-tropic virus tightly associated with EC and not released into the supernatant. Preincubation of fibroblast-derived virus progeny with EC or beads coated with pUL131A-specific antibodies depleted the fraction that could infect EC, and left a fraction that could predominantly infect fibroblasts. These data strongly suggest that HCMV progeny is composed of distinct virus populations. EC specifically retain the EC-tropic population, whereas fibroblasts release EC-tropic and non EC-tropic virus. Our findings offer completely new views on how HCMV spread may be controlled by its host cells.
Introduction
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is ubiquitously distributed in the human population. In immunocompetent adults infections are mainly asymptomatic, but in immunocompromised patients like transplant recipients or AIDS patients life threatening infections occur at a high rate. HCMV is also the leading cause of birth defects among congenitally transmitted viral infections. HCMV replicates in vivo and in vitro in many different host cells including epithelial cells, connective tissue cells, hepatocytes, various leukocyte populations and vascular endothelial cells (reviewed in [1]). The broad host cell range implicates that either an ubiquitous cellular receptor, recognized by one protein or protein complex in the viral envelope, mediates entry, or that HCMV uses elaborate combinations of different viral envelope proteins to employ different cellular receptors. More than 10 glycoproteins have been identified in HCMV particles [2], including the essential glycoproteins gB, gH, gL, gM and gN, which all play a role in the virus entry process [3]–[7]. Although a number of cellular surface proteins have been identified to bind these envelope proteins and play a role in virus particle attachment or promoting intracellular signaling after binding [8]–[13], none of them is currently considered to be a functional entry receptor.
The best candidates for binding to entry receptors are the HCMV gH/gL complexes. The gH/gL complex has been shown to promote fusion of cellular membranes [7] and can either form a gH/gL/gO [14], [15] or a gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex [16]–[18]. HCMV isolates from patients are consistently able to form both gH/gL complexes [19], [20]. In contrast, many HCMV laboratory strains express only the gH/gL/gO complex, which restricts virus entry to few cell types like fibroblasts and neuronal cells [21], [22]. Leukocytes, dendritic, epithelial and endothelial cells (EC) can only be infected by virus expressing the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex [16], [17], [22], [23], which can also promote infection of fibroblasts [24]. Virus strains expressing only gH/gL/gO enter fibroblasts through fusion at the plasma membrane [25]. When fibroblast infection is promoted by gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) only, then entry is through pH-sensitive endocytosis [26].
It is currently not clear whether gH/gL/gO complexes exert their function by directly initiating entry [27]. gO has been shown to be incorporated in the virus envelope of the HCMV strain AD169, a laboratory strain which does not express the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex [2], [27], but not in the envelope of the clinical isolate TR [27]. Deletion of gO in a virus background, which still allows formation of the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex, strongly impairs release of infectious virus particles from infected cells. Virus spread becomes focal and dependent on the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex [24], [26], [28].
In contrast to the gH/gL/gO complex, the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex has been found to be consistently incorporated into virions [16]–[18], [29]. The exact roles of the individual proteins of the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex are not known, but pUL128, pUL130 and pUL131A are all needed to form a functional complex with gH/gL and to have this complex incorporated into virions [16]–[18]. Although the data are controversal, the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex very likely promotes entry into endothelial and epithelial cells through an endocytotic pathway [30]–[33]. There is also good evidence for epithelial cells that binding and uptake of virus is promoted through a cell type-specific receptor for the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex [34].
Viruses lacking both, gO and pUL(128,130,131A), are not viable, indicating that at least one of the two gH/gL complexes is needed for infection [24]. It is not known whether both gH/gL complexes are incorporated in one particle or whether they are incorporated into distinct particles, and how the usage of the complexes for entry is regulated.
The formation of distinct gH/gL complexes is not restricted to HCMV and has also been described for EBV and HHV-6 [35], [36]. For EBV, a gH/gL/gp42 and a gp42-negative gH/gL complex have been described. The latter binds to integrins αvß6 and αvß8 and promotes entry into epithelial cells by fusion at the plasma membrane [37]–[39]. The gH/gL/gp42 complex binds to HLA-DR ß and promotes entry into B-cells by an endocytotic route [38]–[40]. During virus production in B-cells, gp42 is intracellularly targeted to HLA-DR ß, where it is vulnerable for degradation. Consequently, B-cells release virus particles, which are low in gH/gL/gp42. This virus is directed towards epithelial cells. Epithelial cells on the other hand do not express HLA-DR ß and produce virus which is high in gH/gL/gp42 and is directed to B-cells [35]. Thus, the EBV host cell tropism is switched by alternate replication in B - or epithelial cells. For HHV-6 a gH/gL/gO and a gH/gL/Q1/Q2 complex have been identified [36], [41], [42]. The latter has a high affinity for the HHV-6 cellular receptor CD46 [41], whereas the gH/gL/gO complex does not bind CD46 [36].
Here, we show that, similar to EBV, also HCMV progenies derived from different cell types differ in their cell tropism. Fibroblast-derived virus progeny could readily infect fibroblasts and EC, whereas EC-derived virus progeny was barely able to infect EC, and this difference in tropism was reflected by a respectively high or low content of the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex in virus particles. EC-tropism could be depleted from fibroblast-derived virus progeny, indicating that this progeny is composed of distinct populations of virus particles with different EC infection capacities. Spread patterns in culture and cell disruption experiments indicated that fibroblasts readily released EC-tropic and non EC-tropic virus particles, whereas EC selectively retained the EC-tropic population.
Results
HCMV shows different spread patterns in fibroblast and EC cultures
When fibroblasts and EC are infected with HCMV in vitro, virus homogeneously spreads in fibroblast cultures whereas spread in endothelial cell cultures stays focal [17], [43]. Here, we infected fibroblasts and EC with the HCMV strains VR1814 and TB40/E, two clinical isolates passaged on endothelial cells, and vTB40-BAC4, a virus derived from TB40/E and cloned as a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC). Infections were performed at a low multiplicity of infection (m.o.i.), and 2 or 8 days after infection cells were stained for HCMV immediate early 1 (ie1) protein expression. Numbers of initially infected HFF or EC were comparable (Fig. 1A, VR1814, day 2 and data not shown). When fibroblasts were infected, HCMV homogeneously spread throughout the culture indicating release of virus from infected cells and infection via free supernatant virus (Fig. 1A, day 8). In contrast, EC infection remained focal indicating virus transmission which delivers virus particles from cell-to-cell, without releasing it. This spread pattern in EC cultures was comparable for all HCMV strains tested and independent of whether a microvascular cell line (TIME) or primary macrovascular endothelial cells (HUVEC) were infected (Fig. 1A, day 8, lower panels). Focal spread in EC cultures could be completely inhibited by neutralizing anti-HCMV antibodies in human serum or anti-pUL131A antibodies (Fig. S1), indicating that virus spread in EC cultures was not due to direct cell-to-cell spread. Spread in fibroblast cultures was restricted from supernatant-driven spread to focal spread by human antiserum and not inhibited at all by anti-pUL131A antibodies (Fig. S1).
Fig. 1. HCMV spread in fibroblast and EC cultures. 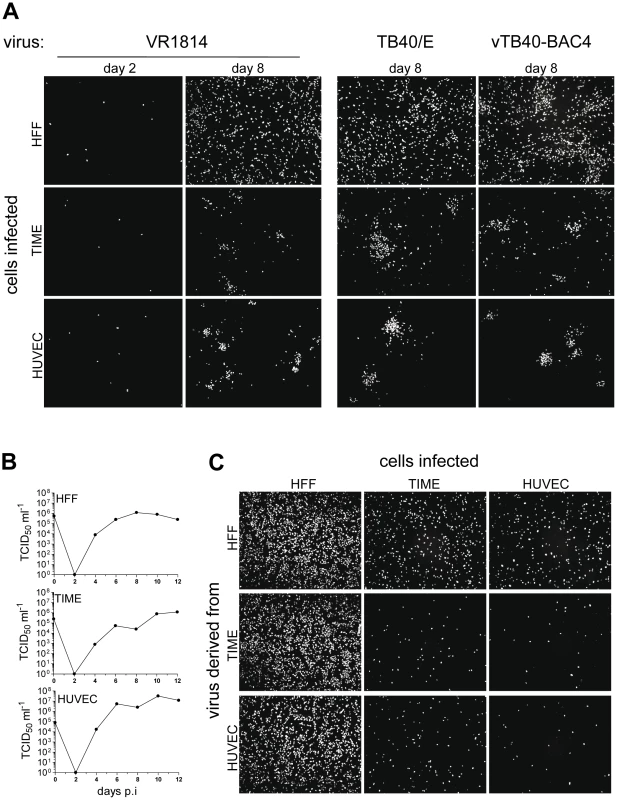
(A) HFF, TIME cells and HUVEC were infected with VR1814, TB40/E and vTB40-BAC4 as described in Materials and Methods to obtain equal numbers of initially infected cells (m.o.i. on HFF: 0.1). The initial infection (day 2) as well as virus spread (day 8) were monitored by staining for HCMV ie1 protein expression. (B) Growth curves of vTB40-BAC4 on HFF, TIME cells and HUVEC. Cells were infected as described in Materials and Methods to obtain equal numbers of initially infected cells (m.o.i. on HFF: 1). Cell culture supernatants were harvested at the indicated time points post infection and virus titers determined by a TCID50 assay performed on HFF. (C) Infection capacities of supernatant-derived vTB40-BAC4. HFF, TIME cells and HUVEC were infected at an m.o.i. of 1 with day 8 supernatants obtained from the growth curves under (B). Infection capacities were monitored by staining for ie1 protein expression 48 hours post infection. Except where indicated, supernatants used for infection were titrated by a TCID50 assay on HFF. To test whether the focal spread could be attributed to differences in release of infectious virus, we performed growth curves of vTB40-BAC4 on HFF, TIME cells and HUVEC, and measured virus release into the supernatants by titration on fibroblasts. HFF and EC equally released high amounts of virus into their supernatants (Fig. 1B). As spread of infection in EC cultures was focal although EC released virus in abundance, focal spread might be due to the inability of EC supernatant virus to infect EC. Indeed, although HFF and EC supernatants comparably infected fibroblasts, the capacities of EC-derived supernatants to infect EC were very low (Fig. 1C). In the experiment shown, spread in HUVEC cultures appeared more cell-associated than in TIME cell cultures, where also single cells in between foci were ie1-positive (Fig. 1A). This correlated with the lower HUVEC infection capacity of EC-derived supernatants when compared to the TIME cell infection capacity (Fig. 1C).
Quantification of HCMV infection capacities using a TB40-BAC4-derived virus expressing firefly luciferase
Infection capacities on different cell types are often compared by methods, which depend on counting infected cells which are either stained for viral antigen or GFP - expression. These methods reach their technical limits, when the infection capacities strongly differ on the cell types to be tested. It is very difficult to obtain reliable cell counts on the less permissive cell type, without at the same time saturating infection on the more permissive cells. Saturation yet, would lead to an overestimation of the infection capacity on the less permissive cells, when related to the more permissive cells.
To circumvent these problems and to simplify the analysis, we used a luciferase reporter virus to monitor infection. An SV40 promoter-driven luciferase expression cassette was inserted into BAC4-FRT5-9, a TB40-BAC4-derived BACmid lacking the genes UL5 to UL9 and carrying an FRT site at the position of the deleted locus (Fig. S2A). Virus was reconstituted from BAC4-FRT5-9 (vBAC4-FRT5-9) and BAC4-luc (vBAC4-luc). Virus growth of these mutants in HFF and EC was comparable to growth of the parental vTB40-BAC4 (Fig. S2B). Both, vBAC4-FRT5-9 and vBAC4-luc, also showed comparable spread patterns in HFF and EC cultures (Fig. S2C).
We used vBAC4-luc to evaluate EC and fibroblast infection capacities of virus preparations on HFF and TIME cells. The luciferase signals obtained from HFF and TIME cell infections were related to each other and expressed as TIME/HFF infection ratios, and thus, represent relative EC infection capacities. After infection, phosphono acetic acid (PAA) was added to block the viral DNA replication and the further amplification of the luciferase signal. Thus, the luciferase activity evaluates infection of cells in a fashion analogous to staining cells for HCMV ie1 protein expression. Indeed, when infection with one and the same virus preparation was evaluated either by counting ie1-positive cells or by measuring the luciferase activity in cell lysates, both methods always gave comparable results (Fig. 2A and data not shown). The assay proved to be linear over a wide range of m.o.i and highly sensitive (Fig. 2B).
Fig. 2. vBAC4-luc as a tool to study infection capacities. 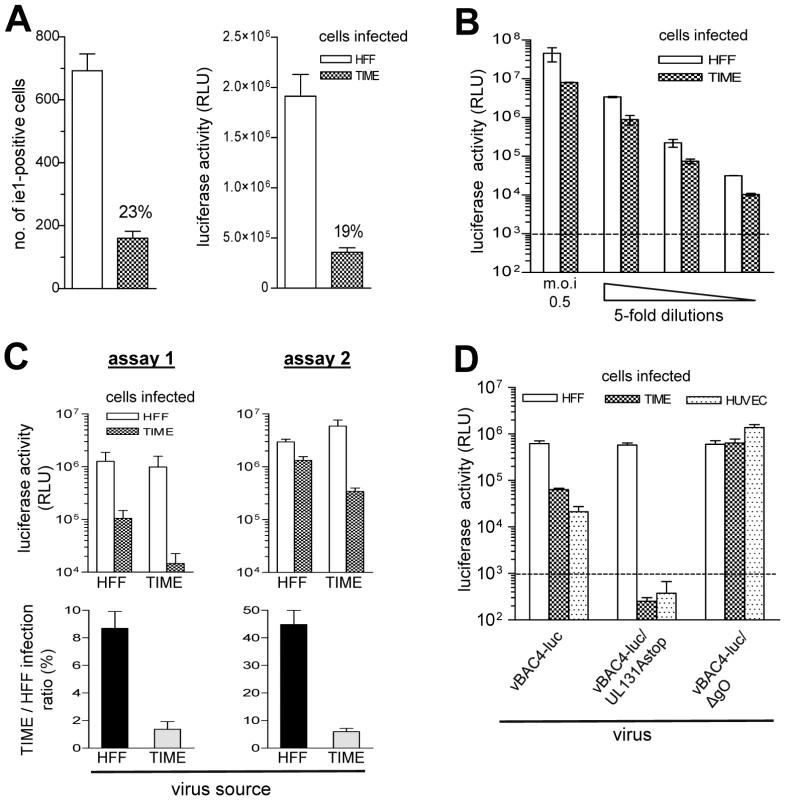
(A) HFF and in parallel TIME cells were infected on 96 well plates at an m.o.i. of 0.3 with a cell culture supernatant derived from HFF infected with vBAC4-luc. After infection, PAA was added and 48 hours later cells either stained for HCMV ie1 protein expression or lysed and subjected to a luciferase assay. The experiment was performed in triplicates. For ie1 staining, three independent wells were infected and one microscopic field per well was counted. For the luciferase assay, lysates from three wells were analysed. Shown are means +/− SD of these triplicates. The TIME cell infection capacity was related to the HFF infection capacity which was set to 100%, and the ratio expressed in percent. (B) HFF and TIME cells were infected with serial 5-fold dilutions of a supernatant derived from HFF infected with vBAC4-luc starting at an m.o.i of 0.5 and 48 hours later analysed by a luciferase assay performed in triplicates. The background level of the luciferase assay is indicated by the dotted line. (C) Two independent luciferase assays using different batches of HFF and TIME cells. Three TIME cell and three HFF supernatants from three independent infections with vBAC4-luc were assayed. For the luciferase assay, cells were infected at an m.o.i. of 0.1 and analysed in triplicates 48 hours after infection. Shown are means +/− SD of three supernatants tested in triplicates. (D) HFF, TIME cells and HUVEC were infected at an m.o.i. of 0.02 (centrifugal enhancement) with supernatants from vBAC4-luc, vBAC4-luc/UL131Astop and vBAC4-luc/ΔgO infections of HFF. 48 hours after infection cells were subjected to a luciferase assay. Shown are means +/− SD of luciferase activities determined in triplicates. It is a standard observation in the field that one and the same HCMV preparation yields variable results, when repeatedly titrated on different target cell batches. When we tested HFF - and TIME cell-derived supernatants in independent luciferase assays, the results strongly depended on the quality of the cells used and varied with e.g. passage number and time after passage (Fig. 2C). Virus preparations derived from infected HFF and TIME cells (virus source) were tested twice, using different batches of HFF and TIME cells (assay 1 and 2). In assay one, the infection capacities of the supernatants on HFF and TIME cell differed much more than in assay two (Fig. 2C, upper panel), and consequently, the TIME/HFF infection ratios were in the range of 8 and 1.5% in assay one and in the range of 40 and 6% in assay two. (Fig. 2C, lower panel). Yet, when the TIME/HFF infection ratios of the HFF supernatants were divided by the TIME/HFF infection ratios of the TIME cell supernatants, the quotients were comparable in both assays (assay one: 6.9, assay two: 7.5). Therefore, the properties of virus preparations to be compared to each other were always tested in parallel.
EC infection strictly depends on the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex [16], [17]. The mutant vBAC4-luc/UL131Astop does not express pUL131A. The gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex is not formed, and the mutant cannot infect EC. The mutant vBAC4-luc/ΔgO does not express gO and promotes entry into EC and also HFF via the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex [24], [26]–[28]. We compared both mutants and the parental vBAC4-luc in the luciferase assay. Confirming the data from Figure 1C, supernatant from a vBAC4-luc infection of HFF showed a lower capacity to infect EC, when compared to the capacity to infect HFF (Fig. 2D). vBAC4-luc/UL131Astop infected HFF, whereas the luciferase signals obtained from infected HUVEC and TIME cells remained below the detection limit. vBAC4-luc/ΔgO equally well infected HFF, TIME cells and HUVEC and thus showed an infection pattern clearly different from the parental vBAC4-luc. Taken together, the luciferase assay proved to be highly sensitive, to allow quantitative measurements over a wide range of m.o.i., and to reflect what is seen, when infection is detected by staining cells for ie1 protein expression.
With the luciferase assay described above, we could compare the properties of virus progenies from HFF and EC. Supernatants of infected HFF and EC were harvested 6 days after infection, titrated on HFF, and the viral DNA content determined by real-time PCR. The ratios of infectious virus to viral DNA copy numbers were comparable for HFF - and EC-derived supernatants (data not shown). These supernatants were then used to infect HFF and TIME cells. Forty-eight hours later, infection was monitored by the luciferase assay. Although virus derived from all three cell types showed a comparable infection of HFF (data not shown), EC-derived virus was significantly less capable in infecting EC than fibroblast-derived virus (Fig. 3). On average, the TIME/HFF infection ratios were about fourfold lower for virus released from EC than for virus released from HFF.
Fig. 3. Virus released from EC shows a lower capability to infect EC than virus released from fibroblasts. 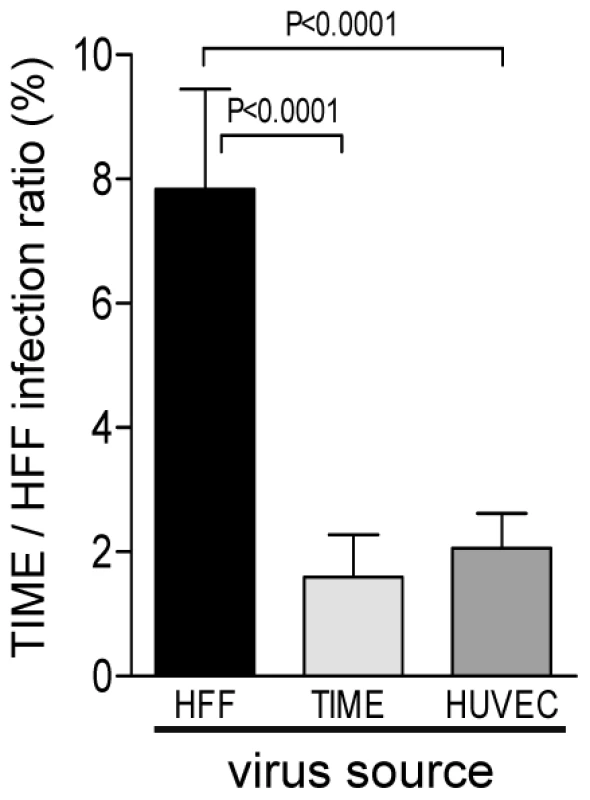
HFF, TIME cells and HUVEC were infected with vBAC4-luc as described in Materials and Methods to obtain equal numbers of initially infected cells (m.o.i. on HFF: 1). Supernatants from these infections were harvested 6 days after infection and titrated. HFF and TIME cells were then infected with these supernatants at an m.o.i. of 0.1. After infection, PAA was added to the cultures, and 48 h later, cells were lysed and subjected to a luciferase assay. The capacity of supernatant virus to infect EC was expressed as the ratio of TIME cell infection to HFF infection. HFF infection was set to 100%. Shown are means +/−SD of at least five independent experiments. EC-derived supernatants were significantly less capable to infect EC than fibroblast-derived supernatants (Student's t test). The capacity of supernatant virus to infect EC correlates with UL128 protein content in virions
Incorporation of gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) glycoprotein complexes into virions [16], [17] is a prerequisite to infect endothelial cells. As virus released from EC was less capable in infecting EC than virus released from fibroblasts, we asked whether this difference can be associated with the abundance of gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complexes incorporated into virions. We determined the gB and gH levels, and, representative for the presence of the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex, the pUL128 content in EC - and HFF-derived virions. Virus particles were pelleted from EC - or HFF-derived supernatants, lysed, and their gB, gH and pUL128 protein content determined by Western blot analysis. The amounts of gB and gH in virus pellets from HFF and EC supernatants always showed a constant relation (data not shown). Yet, HFF-derived virus particles contained more pUL128 protein than EC-derived virus particles (Fig. 4A). This could be quantitatively analysed by measuring the gB band intensities of the lysates, which reflect the particle amounts loaded, and then, relating the pUL128 band intensities to the respective gB bands (Fig. 4A, middle panel). Remarkably, the pUL128/gB ratios mirror the TIME/HFF infection ratios (Fig. 4B, lower panel). Thus, a low EC infection capacity correlated with a low level of gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complexes in virions. Interestingly, total cell lysates of the respective infected cells showed that EC and HFF expressed comparable amounts of pUL128 (Fig. 4B). This indicated that the differences in EC infection capacities observed are created at a late stage during maturation or release of virus progeny. To exclude that the observed differences between EC - and HFF-derived supernatants are due to non-infectious particles or contaminations with cell membrane components, gradient-purified virus from infections of HFF and HUVEC were analysed in the Western blot as described above (Fig. 4C). The pUL128/gB ratios again mirrored the TIME/HFF infection ratios of the supernatants, the virus was purified from.
Fig. 4. EC infection capacities correlate with pUL128 protein content of virus particles. 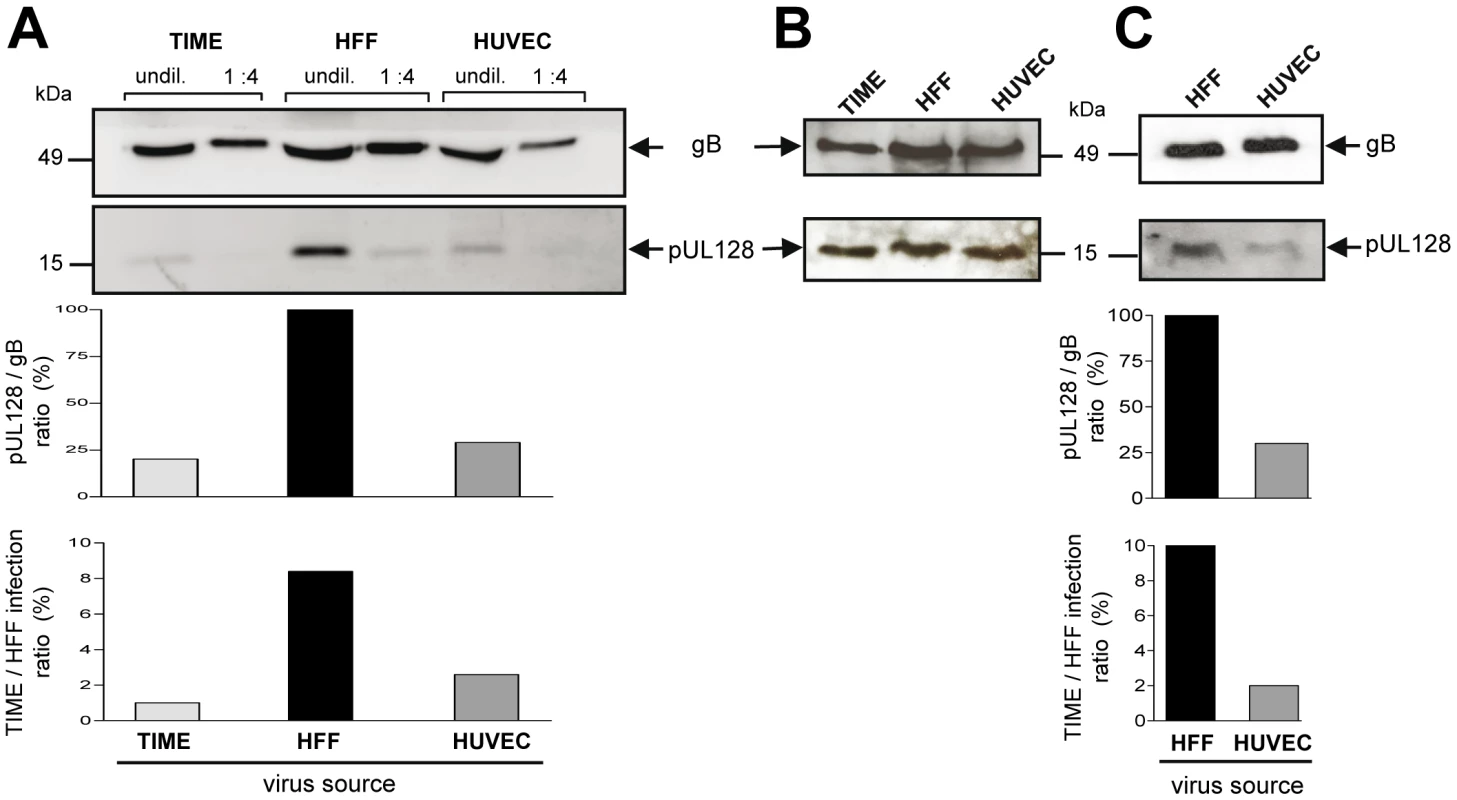
HFF, TIME cells and HUVEC were infected with vTB40-BAC4 or vBAC4-luc for the gradient purified virus as described in Materials and Methods to obtain equal numbers of initially infected cells (m.o.i. on HFF: 1). Supernatants were harvested, when cells showed about 80% CPE. (A) Supernatant-derived particles were concentrated by ultracentrifugation and pUL128 and gB protein levels detected by Western blot analysis of undiluted or 1∶4 diluted lysates. The pUL128 band intensities of undiluted samples are expressed as ratios of pUL128 band intensities to gB band intensities. This ratio was set to 100% for the HFF-derived particles and the ratios for HUVEC and TIME cell-derived particles expressed relative to the HFF value (middle panel). The virus preparations were additionally tested for their TIME/HFF infection ratios by staining infected HFF and TIME cells for ie1 protein expression 48 h after infection (lower panel). (B) Cellular expression levels of gB and pUL128 were monitored by Western blot analysis of total cell lysates of infected cells. (C) Analysis of gradient-purified virus derived from HFF and HUVEC infections. Cells were infected as described above. Virus was purified from the supernatants on glycerol/tartrate gradients as described in Materials and Methods and virus preparations analysed as described under (A). Endothelial cells produce, but not readily release EC-tropic HCMV
Whereas the virus released by EC is low in gH/gL/pUL(128,130,13A) complexes, focal spread in EC cultures was highly efficient. Like EC infection by supernatant virus, it can be blocked by anti-pUL128, anti-pUL130 and anti-pUL131A antibodies [16], [17], [44], [45]. This indicates that pUL(128,130,131A) are accessible to antibodies and promote infection of neighboring cells. We tested different cellular preparations for the presence of cell-associated EC-tropic virus. HUVEC and as a control HFF were infected with vBAC4-luc, and 6 days after infection supernatants were harvested. Cells were washed to remove loosely bound virus and then homogenized using cell douncers. Aliquots of the total homogenates, containing the disrupted cells and virus freed by cell disruption, were saved. Homogenates were then cleared by centrifugation at 3,500×g to separate supernatants containing virus, which can be released by physical disruption. The pellets of cell debris, containing virus which is not released from cells, were also resuspended. These four preparations were then tested on HFF and TIME cells by the luciferase assay. Virus supernatants from HFF and HUVEC showed a high and a low EC infection capacity, respectively (Fig. 5A). All three homogenate preparations from HFF showed a reduced EC infection capacity, when compared to HFF supernatant virus. Notably, the two HUVEC preparations, which contained cell debris showed an about tenfold higher EC infection capacity than the HUVEC supernatants (Fig. 5A). Thus, the progeny able to infect EC is released by HFF, but remained tightly associated with cellular structures in the case of EC. The differences observed are not due to different quantities of virus in the different preparations, because all HFF - and HUVEC-derived preparations showed high luciferase values, when tested on HFF (Fig. 5B). The tenfold differences between HUVEC-derived preparations, containing broken cells, and those without cells are due to high and low luciferase values on TIME cells, respectively (Fig. 5B). Highly EC-tropic virus could neither be released from EC by sonication nor by several rounds of freezing and thawing (data not shown). Taken together, the data show that HFF readily release, whereas HUVEC tightly retain EC-tropic virus.
Fig. 5. Endothelial cells retain EC-tropic virus particles. 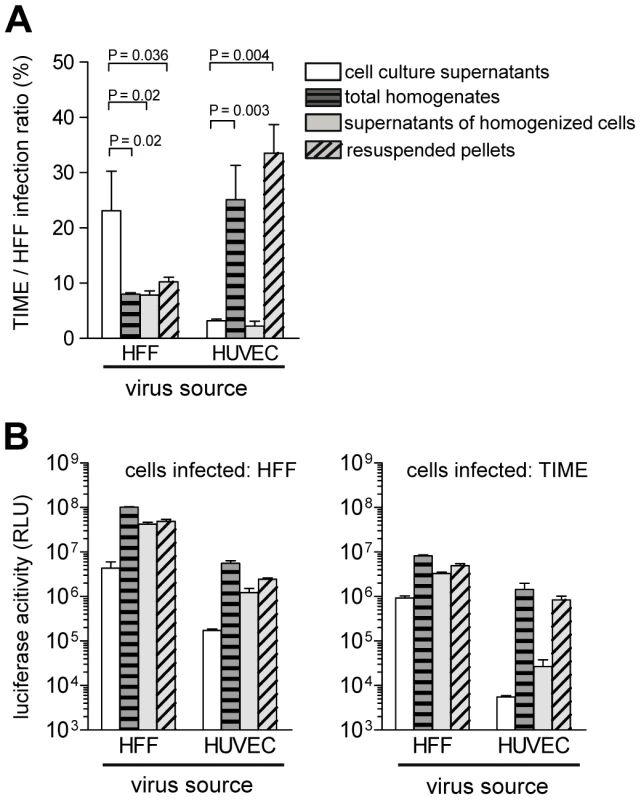
HFF were infected with vBAC4-luc as described in Materials and Methods to obtain equal numbers of initially infected cells (m.o.i. on HFF: 0.2). Six days after infection supernatants were harvested, cells homogenized as described in Materials and Methods and different fractions of the homogenates tested on HFF and TIME cells for their infection capacities by luciferase assay. (A) shows the TIME/HFF infection ratios and (B) the absolute luciferase activities of the different cell preparations on HFF and TIME cells. Shown are means +/− SD of three independent experiments assayed in triplicates. For HFF all homogenate preparations were significantly less EC-tropic than the cell culture supernatants. For HUVEC the total homogenates and the resuspended pellets were significantly more EC-tropic than the cell culture supernatants (Student's t test). HFF release virus progeny, which is not homogeneous
Virus released from EC is only poorly tropic for EC, whereas virus associated with EC shows a much higher tropism for EC. Virus released from HFF is highly EC-tropic and virus found in the particulate fraction of disrupted HFF rather shows a lower tropism for EC. One explanation would be that HCMV progeny is heterogeneous and consists of distinct virus populations with regard to their EC-tropism. EC show a propensity to retain EC-tropic virus and release non EC-tropic virus, whereas HFF readily release both, EC-tropic and non EC-tropic virus. The hypothesis, that HFF progeny is a mixture of EC-tropic and non EC-tropic virus is testable by separation of EC-tropic and non EC-tropic virus. As HUVEC strongly retain EC-tropic virus, they might serve to specifically bind EC-tropic virus and deplete HFF virus progeny of its EC-tropic fraction. We preincubated HFF-derived supernatant virus with HUVEC or with HFF, pelleted the cells, and analysed the HFF and TIME cell infectivity of virus remaining in the supernatants (Fig. 6A). Preincubation with HUVEC removed about 30 to 90% and preincubation with HFF about 99% of the infectious virus from supernatants, when tested on HFF (data not shown). The TIME/HFF infection ratios of the non-bound virus in supernatants preincubated with HUVEC was drastically and significantly reduced to the level observed in supernatants of HCMV-infected HUVEC (Fig. 6A). Preincubation with HFF in contrast, although it removed the bulk of infectivity, only weakly reduced the EC infection propensity of the non-bound virus (Fig. 6A). Thus, HUVEC, which retained EC-tropic virus in infection, were a good matrix for binding EC-tropic virus, whereas HFF, which readily released EC-tropic virus into the supernatant, were a weak matrix for EC-tropic virus. The depletion of EC-tropism strongly suggested that HFF virus progeny was heterogeneous and composed of distinct virus populations, which could be sorted. To find out whether the depletion of EC-tropism is based on removing virus particles expressing the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex, we coincubated HFF-derived virus progeny with protein G sepharose beads to which we had bound anti-pUL131A antibodies. Beads coated with antibodies specific for pUL131A, but not uncoated beads or beads coated with preimmune serum, depleted about 70% of the EC-tropism (Fig. 6B). This strongly implied that depletion of EC-tropism is through retaining virions, expressing the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex.
Fig. 6. HFF virus progeny can be depleted of EC-tropic virus by coincubation with endothelial cells and beads coated with anti-pUL131A antibodies. 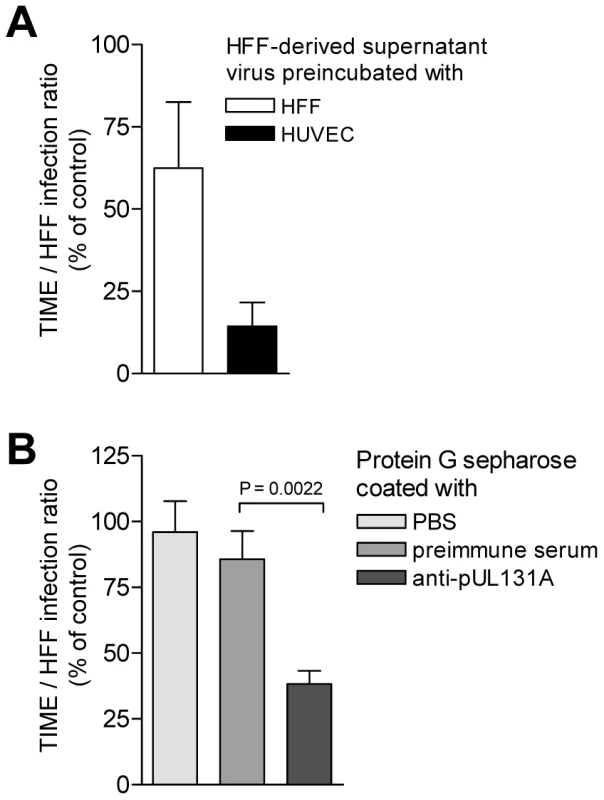
(A) 2×106 HFF or HUVEC were incubated (90 min, 37°C) with 130,000 TCID50 vBAC4-luc diluted in 30 µl DMEM (5% FCS). Then 500 µl of DMEM (5% FCS) was added, the cells pelleted by centrifugation at 300×g for 5 min and the supernatants cleared at 3,500×g for 15 min. As a control 130,000 TCID50 vBAC4-luc diluted in 30 µl DMEM (5% FCS) were mock-incubated and mock-treated as described above. HFF and TIME cells were infected with the supernatants from the coincubations and the controls and subjected to a luciferase assay. TIME/HFF infection ratios of the supernatants after coincubation were expressed as % of the TIME/HFF infection ratios of the control. Shown are the means of TIME/HFF infection ratios +/− SD determined in six independent experiments each assayed in triplicates. (B) 30 µl of a 50% protein G sepharose preparation (GE Healthcare, Germany) were coincubated overnight with 300 µl rabbit anti-pUL131A antiserum (1∶10 diluted in PBS) or as controls preimmune serum (1∶10 diluted in PBS) or PBS. Then, beads were washed 3 times with PBS and coincubated for 2 hours at RT with 130,000 TCID50 vBAC4-luc diluted in 500 µl DMEM without serum. After coincubation beads were pelleted and 5% FCS added to the supernatants. Then, HFF and TIME cells were infected with these supernatants and subjected to a luciferase assay. Shown are the means of TIME/HFF infection ratios +/− SD determined in triplicates. The TIME/HFF infection ratios of virus coincubated with anti-UL131A antibody coated beads was significantly different from the values obtained from virus coincubated with preimmune serum-coated beads. Discussion
The use of different receptor binding proteins to mediate entry into different cell types, and the use of different entry pathways even into one cell type is a common feature of herpesvirus entry. Herpesviruses have additionally developed strategies, which may route infection in vivo. For EBV, the group of L. Hutt-Fletcher has pioneered the paradigm that epithelial cells produce a virus progeny high in gH/gL/gp42 complexes, which promotes B-cell infection. B-cells in turn, produce virus progeny low in gH/gL/gp42 complexes which efficiently infect epithelial cells, but not B-cells. Although not absolute, this relative switch of cell tropism after alternate replication in epithelial and B-cells directs infection from one cell type to the other.
Here, we propose that also different producer cells of HCMV may direct the infection. gH/gL/gO complex formation is needed for release of infectious virus from any infected cell type tested so far [24], [28]. Incorporation of gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complexes into virions is essential for infection of e.g. endothelial, epithelial, and dendritic cells, and for leukocytes [16], [17], [22], [23]. If gO is missing, then the infection spreads predominantly focal and depends on the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex, even in cell types, which usually do not depend on this complex for infection [24], [26].
Our initial observation was that virus spread in fibroblast cultures differed from virus spread in EC cultures [17]. Spread in fibroblast cultures appeared supernatant - driven, whereas spread in EC cultures was focal. A strictly cell-associated virus spread in EC cultures had also been observed by the group of G. Gerna, who reported that propagation in HUVEC strictly depended on passage of cells and could not be achieved by supernatant virus [43]. We offer an explanation for the focal spread in EC cultures by showing that EC predominantly release virus, which is not EC-tropic, but at the same time tightly retain EC-tropic virus which may then be transferred to neighboring cells only. Virus transfer was accessible to neutralizing antibodies and dependent on the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex, as we could show in Figure S1. Focal spread was completely blocked by a neutralizing human antiserum and by anti-pUL131A antibodies. Interestingly, when infected HFF cultures were treated in a similar way, a neutralizing human antiserum blocked infection by free virus, but left a focal spread of virus, indicating that for HFF a direct cell-to-cell spread mechanism may be possible [46]. Anti-pUL131A antibodies could not at all inhibit spread in HFF cultures. These data confirmed earlier studies by our group, which showed that only gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) dependent virus spread, like spread in EC cultures, or spread of a delta gO mutant in fibroblast cultures could be inhibited by anti-pUL131A antibodies [17], [26].
Similar to the EBV model, supernatants from infected HFF showed a higher capacity to infect EC than EC-derived supernatants, and we could show that the biochemical basis for that is a respectively high and low content of gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex in virions.
The question, which arose then, was, what causes the observed difference in gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) content. For EBV it has been described that in infected B-cells HLA-DR ß binds the gp42 protein of the gH/gL/gp42 complex, which promotes B-cell infection, holds it back intracellularly, and thus, makes it vulnerable for degradation. As a consequence, B-cells release mainly virions containing a two-part gH/gL complex, which cannot infect B-cells. Epithelial cells, which do not express HLA-DR ß, do not retain gp42 and thus, release virus, which contains more of the three-part gH/gL/gp42 complex. The mechanisms, by which the differences in the released populations of virions in HCMV are achieved, appear to be different. For HCMV, we found that EC and fibroblasts produce heterogeneous virus progenies. EC release a virus progeny, which is not EC-tropic, and retain a progeny, which is highly EC-tropic. HFF release an EC-tropic progeny. which can be depleted of its EC-tropism by using HUVEC or protein G sepharose beads coated with antibodies directed against pUL131A. This strongly suggested that HFF progeny is composed of distinct EC-tropic and non EC-tropic virus populations, and that the EC-tropic population most likely is a population with a high gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) content. If HFF-derived virus progeny was homogeneous, a specific depletion only of EC-tropic virus would not be possible. Interestingly, HUVEC, which retain EC-tropic virus in infection experiments, were a good matrix to retain EC-tropic virus in the test tube, whereas HFF, which readily release EC-tropic virus in infections, were a bad matrix.
Thus, we propose that the difference in cell tropism of virus released from EC and fibroblasts is the result of a sorting process. EC strongly and specifically retain EC-tropic virus through the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex. HFF release EC-tropic and non EC-tropic virus. Thus, for HCMV, not protein components of gH/gL complexes are retained in a cell-type specific manner, but rather mature virions carrying the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex in their envelopes. Figure 7 depicts the EBV and HCMV models for virus spread side by side.
Fig. 7. HCMV and EBV models for virus spread in cell culture. 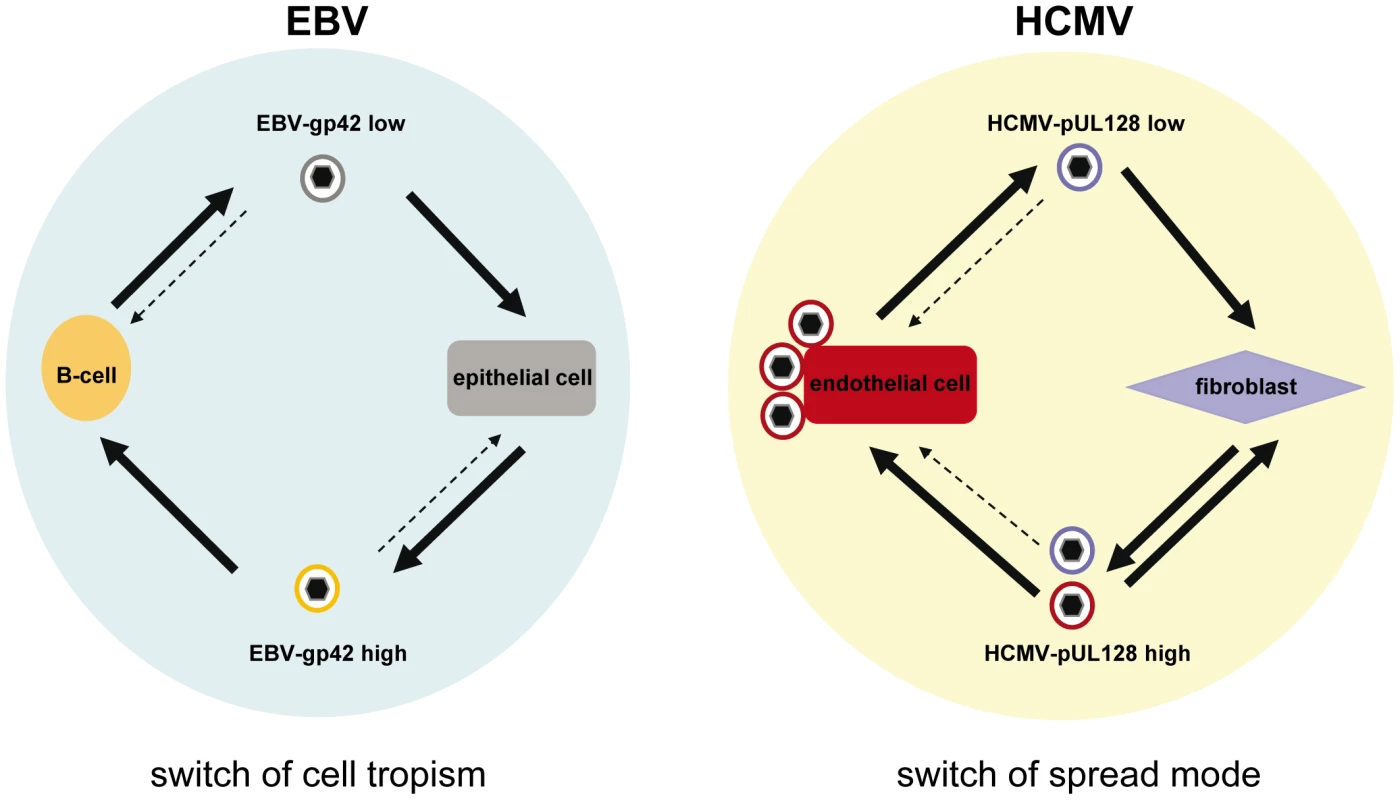
The EBV model proposes a switch of cell tropism through depletion of gp42 from B-cell derived virus progeny resulting in a gp42low progeny versus a gp42high progeny released from epithelial cells. The HCMV model proposes the production of a heterogeneous virus progeny from fibroblasts and EC. Fibroblasts release EC-tropic and non-EC tropic viruses which results in a pUL128high progeny, whereas EC release a non EC-tropic pUL128low progeny and retain the EC-tropic virus. This results in a switch of the spread mode. The tropism of virus progenies is indicated by color codes. Future experiments will have to show where and how EC-tropic virus is held back. It has recently been shown that overexpression of gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) in epithelial cells interferes with HCMV infection. It has been postulated that this reflects binding of the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex to the respective entry receptor [34]. This was not observed for fibroblasts and thus, an HCMV entry receptor binding to gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) and expressed on EC would be a good candidate also for retaining EC-tropic virus by infected EC. How virus is then transferred to neighboring cells, will also have to be investigated in the future. An attractive model would be a mechanism as described for MHV-68, for which it has been shown that virus particles attached to and moving on plasma membrane fronds are directly transferred to neighboring cells [47].
Assuming that gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complexes are incorporated into virus progeny at random, EC-tropism of a virus particle might be defined by a threshold level of gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complexes. Accordingly, high levels of gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complexes in turn could also block release from EC. Thus, the levels of gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complexes could define whether a particle is EC-tropic or not, whether it is retained by EC during infection, and whether it can be depleted from supernatants by EC-preincubation. This could also explain, why progeny of a ΔgO virus, which expresses only the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex, readily spreads cell-associated and can barely be released from EC [24], [28]. ΔgO virus progeny can equally well infect EC and HFF (Fig 2D). Wildtype TB40-BAC4 virus progeny, in contrast, shows a higher propensity to infect HFF (Fig. 2D), which could be explained by being a mixture of EC-tropic and non EC-tropic particles.
For EBV, it has been observed that virus bound to the surface of resting B cells is 103-104 times more infectious for epithelial cells than cell-free virus [48]. For HCMV it has not yet been tested whether surface-bound virus could promote a switch of cell tropism.
We restricted our experiments to endothelial cells and fibroblasts. Macrophages, dendritic cells, and epithelial cells also strictly depend on the gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) complex for their infection. Whether their infection also follows the pattern of the EC infection shown here, will have to be investigated in the future. Recently, it has been published by Wang et al. [30] that HCMV progenies derived from epithelial cells and fibroblast also differ. They reported that both cell types release progenies which can readily infect epithelial cells and fibroblasts, but differ with respect to the pathway they use to enter epithelial cells. They found a twofold higher gH/gL/pUL(128,130,131A) content in epithelial cell-derived particles, which they considered as marginal. As they used an AD169 mutant, in which UL131A had been repaired, it will have to be clarified, whether their findings reflect that epitheliotropic virus produced in epithelial cells is, in contrast to our findings in EC, not retained, or whether the observed differences are due to differences of the HCMV strains used. It has recently been shown that AD169 incorporates gO into virions, whereas HCMV strain TR does not [27]. This suggests that strain-specific differences may indeed affect gH/gL-dependent processes.
Whether our observations made in cell culture, reflect features valid for all HCMV strains, and what role a switch in tropism and spread patterns may play in vivo, will be the subject of future research. It will be of particular interest to find out whether the relative propensity of different cell types to release virus plays a crucial role in establishment of infection and transfer of virus to new hosts or the fetus. For HCMV, it has been shown that primary isolation of EC-tropic virus depends on infected cells as a source of virus, whereas fibroblast infection can also be achieved with cell-free virus sources like throat washes and amniotic fluid [43]. This might already be an indication that cells lining the compartments, where these fluids are produced, do not release EC-tropic virus.
Materials and Methods
Cells and viruses
Primary human foreskin fibroblasts (HFF) (PromoCell, Germany) were used from passage 12 to 22 and maintained in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum, 2 mM L-glutamine, 100 units/ml penicillin and 100 µg/ml streptomycin. Primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) (LONZA, USA) were used from passage 1 to 6. HUVEC and TIME (telomerase-immortalized human microvascular endothelial) cells [49] were maintained in an EGM-2 MV BulletKit medium system (LONZA, USA).
The HCMV strains used were VR1814 [19], TB40/E [50] and TB40/E cloned as a BAC (TB40-BAC4) [51].
BAC mutagenesis and construction of recombinant HCMV
The HCMV strain TB40/E cloned as a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) (TB40-BAC4) [51] was used for HCMV BAC mutagenesis. A 48 bp FRT site was inserted into the TB40-BAC4, thereby disrupting the open reading frames (ORFs) UL5, UL6, UL7, UL8 and UL9. Briefly, a linear PCR fragment containing a kanamycin-resistance gene flanked by two 48 bp FRT sites and sequences homologous to the HCMV UL5 and UL9 coding regions was generated using the primers UL5pcp15for (5′-ATGTTTCTAGGCTACTCTGACTGTGTAGATCCCGGCTTTGCTGTATATCGTGTATCTAGACGGGGGTGTCCAGGGTTTTCCC-3′) and UL9pcp15rev (5′-ATTGTTGTAACGATAACTAAGGGTATGATCCACATTGTATGTGGGGTGGCAGTATCGTGTCTTCCGGCTCGTATGTTGTGTGG-3) and pCP15 as template [52]. The PCR product was inserted into TB40-BAC4 by homologous recombination in E. coli, thereby deleting 3,066 kb. The kanamycin-resistance gene was subsequently excised by FLP-mediated site-directed recombination [53], and the resulting BAC mutant called BAC4-FRT5-9.
To generate a luciferase reporter HCMV, the SV40-driven firefly luciferase expression cassette was excised from pGL3-promoter (Promega) with Sal I and Bgl II, filled in by Klenow polymerase and inserted into the pOriR6K-zeo plasmid linearized by EcoR V. The resulting plasmid pO6-Luc was inserted into BAC4-FRT5-9 via FLP-mediated FRT recombination mutagenesis using the temperature-sensitive expression plasmid pCP20 [54]. The resulting BAC mutant was called BAC4-Luc.
The BAC mutants BAC4-Luc/ΔgO and BAC4-Luc/UL131Astop were cloned into the BAC4-Luc background as described previously [24], [26].
Deletions and insertions were controlled by restriction pattern analysis and subsequent sequencing.
Reconstitution of virus from recombinant BACmids
BACmids were reconstituted to virus by transfection of BAC DNA into HFF using FugeneHD transfection reagent (Roche Diagnostics) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Transfected cells were propagated until viral plaques appeared and the supernatants from these cultures used for further propagation of virus.
Preparation of virus stocks, concentration of virus particles, virus titration and infections
Virus stocks were prepared from supernatants of infected HFF, HUVEC or TIME cells. Supernatants were cleared of cellular debris by centrifugation for 15 min at 3,500×g and stored at −80°C.
For Western Blot analysis of HCMV particles, virus was concentrated from cell culture supernatants. Briefly, 200 ml supernatant from infected cells showing about 90% CPE was cleared of cellular debris by centrifugation at 3,500×g for 15 min. Then, virus was pelleted from cleared supernatant by ultracentrifugation at 80,000×g for 70 min. Virus pellets were resuspended in 1.5 ml 0.04 mol/l sodium phosphate pH 7.4.
Virus titers of cleared supernatants were determined by a TCID50 assay performed on 96 well plates on HFF.
To infect cells, medium was removed from 90% confluent cell monolayers and replaced by virus diluted in DMEM containing 5% FCS. For some experiments, virus infection was enhanced by a centrifugation step (30 min, 860×g at room temperature), followed by incubation at 37°C for 90 min. To compare infectivity of virus derived from fibroblasts and endothelial cells, subsequent infections were performed in DMEM 5% FCS/EGM-2 mixed at a ratio of 1∶1, to exclude medium effects. During infections, medium was exchanged every second day in a way that supernatants harvested contained virus released during the preceding 48 hours.
As HCMV in general more readily infects fibroblasts than EC, in all experiments, where infections of EC and fibroblasts (spread patterns and growth curves) were compared, the infections were adapted in a way that EC were infected with more virus than fibroblasts to achieve comparable numbers of ie1-positive cells after 48 hours.
Gradient purification of virions
For gradient purification of virions, supernatants from infected cell cultures showing approximately 100% late-stage CPE were cleared of cell debris by centrifugation for 10 min at 2,800×g. Supernatants were then ultracentrifuged for 70 min at 80,000×g. Pellets containing virions were resuspended in 1 ml PBS and transferred onto a preformed, linear glycerol/tartrate gradient (15–35% sodium tartrate and 30–40% glycerol in 0.04 mol/l sodium phosphate pH 7.4), which was ultracentrifuged for 45 min at 80,000×g. The virion-containing band was harvested with a syringe and the virions were washed and pelleted by an additional ultracentrifugation for 70 min at 80,000×g. The pellet was resuspended in 0.04 mol/l sodium phosphate.
Indirect immunofluorescence
HCMV-infected cells were fixed in 50% acetone/50% methanol, stained using a mouse anti-ie1 antibody (anti-ie1; Perkin Elmer) and detected with a Cy3-coupled goat anti-mouse antibody (Dianova). For counterstaining of cell nuclei, cells were incubated in PBS containing 5 µg/ml Hoechst 333258 (Invitrogen) for 1 min.
Luciferase assay
HFF and TIME cells were grown in 96 well plates (20,000 cells/well) and infected in triplicates at an m.o.i. between 0.02 and 0.5 for 90 min. Inoculi were then replaced by medium supplemented with 300 µg/ml phosphono acetic acid (PAA). 48 h after infection cells were lysed in 50 µl lysis buffer (25 mM Tris/H3PO4, 2 mM CDTA, 2 mM DTT, 10% glycerol, 5% Triton-X 100) and luciferase activity was determined for 20 µl of lysate with a luciferase assay system (Promega) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Western blot analysis
Virus particles or infected cells were lysed in 6× sample buffer (300 mM Tris-HCl (pH 6.8), 10% SDS, 30% glycerol, 5% ß-mercaptoethanol, 0.01% (w/v) bromphenolblue, 0.01% (w/v) phenolred), separated on 15% polyacrylamide gels and transferred onto nitrocellulose (Amersham Biosciences). Membranes were blocked with 5% low-fat milk in TBS and stained for gB or pUL128 using mouse anti-gB antibody (2F12; Abcam) or mouse anti-pUL128 antibody (4B10, kindly provided by T. Shenk, University of Princeton, USA), respectively. The specific protein bands were detected by using an peroxidase-coupled anti-mouse antibody (Dianova) and the SuperSignal West Dura Extended Duration Kit (Perbio).
The intensities of protein bands were quantified using the Fujifilm Intelligent Light Box LAS-300 and the Image reader LAS-300. Non-saturated light signals were analysed to determine the protein amounts using ImageQuant 5.0 software. The pUL128 levels were related to gB levels of the respective samples.
Homogenization of cells
Cells were infected in 6 cm dishes, and 6 days after infection the supernatants (4 ml) harvested and cleared of cellular debris (3,500×g, 15 min). Cell monolayers were washed with cold PBS, scraped and cells dounced in 4 ml DMEM medium supplemented with 5% FCS using tight fit hand homogenizers (Sartorius-Stedium). 3.5 ml of the total homogenized cells were pelleted (3,500×g, 15 min), the supernatant removed (supernatant of homogenized cells) and the pellets resuspended in fresh 3.5 ml DMEM medium supplemented with 5% FCS.
Accession numbers
GeneBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession number for TB40-BAC4 is EF999921.
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. SinzgerC
DigelM
JahnG
2008 Cytomegalovirus cell tropism. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 325 63 83
2. VarnumSM
StreblowDN
MonroeME
SmithP
AuberryKJ
2004 Identification of proteins in human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) particles: the HCMV proteome. J Virol 78 10960 10966
3. BrittWJ
1984 Neutralizing antibodies detect a disulfide-linked glycoprotein complex within the envelope of human cytomegalovirus. Virology 135 369 378
4. IsaacsonMK
ComptonT
2009 Human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B is required for virus entry and cell-to-cell spread but not for virion attachment, assembly, or egress. J Virol 83 3891 3903
5. MachM
KropffB
Dal MonteP
BrittW
2000 Complex formation by human cytomegalovirus glycoproteins M (gpUL100) and N (gpUL73). J Virol 74 11881 11892
6. ComptonT
2004 Receptors and immune sensors: the complex entry path of human cytomegalovirus. Trends Cell Biol 14 5 8
7. KinzlerER
ComptonT
2005 Characterization of human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein-induced cell-cell fusion. J Virol 79 7827 7837
8. WrightJF
KuroskyA
WasiS
1994 An endothelial cell-surface form of annexin II binds human cytomegalovirus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 198 983 989
9. PietropaoloRL
ComptonT
1997 Direct interaction between human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B and cellular annexin II. J Virol 71 9803 9807
10. KeayS
BaldwinB
1992 The human fibroblast receptor for gp86 of human cytomegalovirus is a phosphorylated glycoprotein. J Virol 66 4834 4838
11. WangX
HuongSM
ChiuML
Raab-TraubN
HuangES
2003 Epidermal growth factor receptor is a cellular receptor for human cytomegalovirus. Nature 424 456 461
12. SoroceanuL
AkhavanA
CobbsCS
2008 Platelet-derived growth factor-alpha receptor activation is required for human cytomegalovirus infection. Nature 455 391 395
13. WangX
HuangDY
HuongSM
HuangES
2005 Integrin alphavbeta3 is a coreceptor for human cytomegalovirus. Nat Med 11 515 521
14. LiL
NelsonJA
BrittWJ
1997 Glycoprotein H-related complexes of human cytomegalovirus: identification of a third protein in the gCIII complex. J Virol 71 3090 3097
15. HuberMT
ComptonT
1998 The human cytomegalovirus UL74 gene encodes the third component of the glycoprotein H-glycoprotein L-containing envelope complex. J Virol 72 8191 8197
16. WangD
ShenkT
2005 Human cytomegalovirus virion protein complex required for epithelial and endothelial cell tropism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102 18153 18158
17. AdlerB
ScrivanoL
RuzcicsZ
RuppB
SinzgerC
2006 Role of human cytomegalovirus UL131A in cell type-specific virus entry and release. J Gen Virol 87 2451 2460
18. RyckmanBJ
RainishBL
ChaseMC
BortonJA
NelsonJA
2008 Characterization of the human cytomegalovirus gH/gL/UL128-131 complex that mediates entry into epithelial and endothelial cells. J Virol 82 60 70
19. GraziaRM
BaldantiF
PercivalleE
SarasiniA
De GiuliL
2001 In vitro selection of human cytomegalovirus variants unable to transfer virus and virus products from infected cells to polymorphonuclear leukocytes and to grow in endothelial cells. J Gen Virol 82 1429 1438
20. BaldantiF
PaolucciS
CampaniniG
SarasiniA
PercivalleE
2005 Human cytomegalovirus UL131A, UL130 and UL128 genes are highly conserved among field isolates. Arch Virol 151 1225 1233
21. WangD
ShenkT
2005 Human cytomegalovirus UL131 open reading frame is required for epithelial cell tropism. J Virol 79 10330 10338
22. HahnG
RevelloMG
PatroneM
PercivalleE
CampaniniG
2004 Human cytomegalovirus UL131-128 genes are indispensable for virus growth in endothelial cells and virus transfer to leukocytes. J Virol 78 10023 10033
23. GernaG
PercivalleE
LilleriD
LozzaL
FornaraC
2005 Dendritic-cell infection by human cytomegalovirus is restricted to strains carrying functional UL131-128 genes and mediates efficient viral antigen presentation to CD8+ T cells. J Gen Virol 86 275 284
24. JiangXJ
AdlerB
SampaioKL
DigelM
JahnG
2008 UL74 of human cytomegalovirus contributes to virus release by promoting secondary envelopment of virions. J Virol 82 2802 2812
25. ComptonT
NepomucenoRR
NowlinDM
1992 Human cytomegalovirus penetrates host cells by pH-independent fusion at the cell surface. Virol 191 387 395
26. ScrivanoL
EsterlechnerJ
MuhlbachH
EttischerN
HagenC
2010 The m74 gene product of murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV) is a functional homolog of human CMV gO and determines the entry pathway of MCMV. J Virol 84 4469 4480
27. RyckmanBJ
ChaseMC
JohnsonDC
2009 HCMV TR strain glycoprotein O acts as a chaperone promoting gH/gL incorporation into virions, but is not present in virions. J Virol 84 2597 2609
28. WillePT
KnocheAJ
NelsonJA
JarvisMA
JohnsonDC
2009 An HCMV gO-null mutant fails to incorporate gH/gL into the virion envelope and is unable to enter fibroblasts, epithelial, and endothelial cells. J Virol 84 2585 2596
29. SchuesslerA
SampaioKL
ScrivanoL
SinzgerC
2010 Mutational mapping of UL130 of human cytomegalovirus defines peptide motifs within the C-terminal third as essential for endothelial cell infection. J Virol 84 9019 9026
30. WangD
YuQC
SchroerJ
MurphyE
ShenkT
2007 Human cytomegalovirus uses two distinct pathways to enter retinal pigmented epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104 20037 20042
31. BodaghiB
Slobbe-van DrunenME
TopilkoA
PerretE
VossenRC
1999 Entry of human cytomegalovirus into retinal pigment epithelial and endothelial cells by endocytosis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 40 2598 2607
32. RyckmanBJ
JarvisMA
DrummondDD
NelsonJA
JohnsonDC
2006 Human cytomegalovirus entry into epithelial and endothelial cells depends on genes UL128 to UL150 and occurs by endocytosis and low-pH fusion. J Virol 80 710 722
33. SinzgerC
2008 Entry route of HCMV into endothelial cells. J Clin Virol 41 174 179
34. RyckmanBJ
ChaseMC
JohnsonDC
2008 HCMV gH/gL/UL128-131 interferes with virus entry into epithelial cells: evidence for cell type-specific receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105 14118 14123
35. BorzaCM
Hutt-FletcherLM
2002 Alternate replication in B cells and epithelial cells switches tropism of Epstein-Barr virus. Nat Med 8 594 599
36. MoriY
AkkapaiboonP
YonemotoS
KoikeM
TakemotoM
2004 Discovery of a second form of tripartite complex containing gH-gL of human herpesvirus 6 and observations on CD46. J Virol 78 4609 4616
37. ChesnokovaLS
NishimuraSL
Hutt-FletcherLM
2009 Fusion of epithelial cells by Epstein-Barr virus proteins is triggered by binding of viral glycoproteins gHgL to integrins alphavbeta6 or alphavbeta8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106 20464 20469
38. MillerN
Hutt-FletcherLM
1992 Epstein-Barr virus enters B cells and epithelial cells by different routes. J Virol 66 3409 3414
39. Hutt-FletcherLM
2007 Epstein-Barr virus entry. J Virol 81 7825 7832
40. SpriggsMK
ArmitageRJ
ComeauMR
StrockbineL
FarrahT
1996 The extracellular domain of the Epstein-Barr virus BZLF2 protein binds the HLA-DR beta chain and inhibits antigen presentation. J Virol 70 5557 5563
41. MoriY
YangX
AkkapaiboonP
OkunoT
YamanishiK
2003 Human herpesvirus 6 variant A glycoprotein H-glycoprotein L-glycoprotein Q complex associates with human CD46. J Virol 77 4992 4999
42. AkkapaiboonP
MoriY
SadaokaT
YonemotoS
YamanishiK
2004 Intracellular processing of human herpesvirus 6 glycoproteins Q1 and Q2 into tetrameric complexes expressed on the viral envelope. J Virol 78 7969 7983
43. GernaG
PercivalleE
SarasiniA
RevelloMG
2002 Human cytomegalovirus and human umbilical vein endothelial cells: restriction of primary isolation to blood samples and susceptibilities of clinical isolates from other sources to adaptation. J Clin Microbiol 40 233 238
44. MacagnoA
BernasconiNL
VanzettaF
DanderE
SarasiniA
2010 Isolation of human monoclonal antibodies that potently neutralize human cytomegalovirus infection by targeting different epitopes on the gH/gL/UL128-131A complex. J Virol 84 1005 1013
45. GernaG
SarasiniA
PatroneM
PercivalleE
FiorinaL
2008 Human cytomegalovirus serum neutralizing antibodies block virus infection of endothelial/epithelial cells, but not fibroblasts, early during primary infection. J Gen Virol 89 853 865
46. DigelM
SampaioKL
JahnG
SinzgerC
2006 Evidence for direct transfer of cytoplasmic material from infected to uninfected cells during cell-associated spread of human cytomegalovirus. J Clin Virol 37 10 20
47. GillMB
EdgarR
MayJS
StevensonPG
2008 A gamma-herpesvirus glycoprotein complex manipulates actin to promote viral spread. PLoS ONE 3 e1808
48. Shannon-LoweCD
NeuhierlB
BaldwinG
RickinsonAB
DelecluseHJ
2006 Resting B cells as a transfer vehicle for Epstein-Barr virus infection of epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103 7065 7070
49. VenetsanakosE
MirzaA
FantonC
RomanovSR
TlstyT
2002 Induction of tubulogenesis in telomerase-immortalized human microvascular endothelial cells by glioblastoma cells. Exp Cell Res 273 21 33
50. SinzgerC
SchmidtK
KnappJ
KahlM
BeckR
1999 Modification of human cytomegalovirus tropism through propagation in vitro is associated with changes in the viral genome. J Gen Virol 80 2867 2877
51. SinzgerC
HahnG
DigelM
KatonaR
SampaioKL
2008 Cloning and sequencing of a highly productive, endotheliotropic virus strain derived from human cytomegalovirus TB40/E. J Gen Virol 89 359 368
52. CherepanovPP
WackernagelW
1995 Gene disruption in Escherichia coli: TcR and KmR cassettes with the option of Flp-catalyzed excision of the antibiotic-resistance determinant. Gene 158 9 14
53. BubicI
WagnerM
KrmpoticA
SauligT
KimS
2004 Gain of virulence caused by loss of a gene in murine cytomegalovirus. J Virol 78 7536 7544
54. BubeckA
WagnerM
RuzsicsZ
LotzerichM
IglesiasM
2004 Comprehensive mutational analysis of a herpesvirus gene in the viral genome context reveals a region essential for virus replication. J Virol 78 8026 8035
Štítky
Hygiena a epidemiologie Infekční lékařství Laboratoř
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Pathogens
Nejčtenější tento týden
2011 Číslo 1- Stillova choroba: vzácné a závažné systémové onemocnění
- Diagnostika virových hepatitid v kostce – zorientujte se (nejen) v sérologii
- Perorální antivirotika jako vysoce efektivní nástroj prevence hospitalizací kvůli COVID-19 − otázky a odpovědi pro praxi
- Choroby jater v ordinaci praktického lékaře – význam jaterních testů
- Diagnostický algoritmus při podezření na syndrom periodické horečky
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- Salivary Gland NK Cells Are Phenotypically and Functionally Unique
- Genetic Epidemiology of Tuberculosis Susceptibility: Impact of Study Design
- Early Target Cells of Measles Virus after Aerosol Infection of Non-Human Primates
- Multiple Plant Surface Signals are Sensed by Different Mechanisms in the Rice Blast Fungus for Appressorium Formation
- Biofilm Development on by Is Facilitated by Quorum Sensing-Dependent Repression of Type III Secretion
- Distinct Patterns of IFITM-Mediated Restriction of Filoviruses, SARS Coronavirus, and Influenza A Virus
- Molecular Basis of Increased Serum Resistance among Pulmonary Isolates of Non-typeable
- A Helminth Immunomodulator Exploits Host Signaling Events to Regulate Cytokine Production in Macrophages
- HCMV Spread and Cell Tropism are Determined by Distinct Virus Populations
- Characteristics of the Earliest Cross-Neutralizing Antibody Response to HIV-1
- Induction of a Peptide with Activity against a Broad Spectrum of Pathogens in the Salivary Gland, following Infection with Dengue Virus
- Structural Basis for the Recognition of Cellular mRNA Export Factor REF by Herpes Viral Proteins HSV-1 ICP27 and HVS ORF57
- Identification and Characterization of the Host Protein DNAJC14 as a Broadly Active Flavivirus Replication Modulator
- Dual-Use Research and Technological Diffusion: Reconsidering the Bioterrorism Threat Spectrum
- Pathogenesis of the 1918 Pandemic Influenza Virus
- A Cardinal Role for Cathepsin D in Co-Ordinating the Host-Mediated Apoptosis of Macrophages and Killing of Pneumococci
- Critical Role of IRF-5 in the Development of T helper 1 responses to infection
- The Pel Polysaccharide Can Serve a Structural and Protective Role in the Biofilm Matrix of
- Selective C-Rel Activation via Malt1 Controls Anti-Fungal T-17 Immunity by Dectin-1 and Dectin-2
- Imaging Single Retrovirus Entry through Alternative Receptor Isoforms and Intermediates of Virus-Endosome Fusion
- Aerosols Transmit Prions to Immunocompetent and Immunodeficient Mice
- PLOS Pathogens
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Dual-Use Research and Technological Diffusion: Reconsidering the Bioterrorism Threat Spectrum
- Pathogenesis of the 1918 Pandemic Influenza Virus
- Critical Role of IRF-5 in the Development of T helper 1 responses to infection
- A Cardinal Role for Cathepsin D in Co-Ordinating the Host-Mediated Apoptosis of Macrophages and Killing of Pneumococci
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Vladimír Palička, CSc., Dr.h.c., doc. MUDr. Václav Vyskočil, Ph.D., MUDr. Petr Kasalický, CSc., MUDr. Jan Rosa, Ing. Pavel Havlík, Ing. Jan Adam, Hana Hejnová, DiS., Jana Křenková
Autoři: MUDr. Irena Krčmová, CSc.
Autoři: MDDr. Eleonóra Ivančová, PhD., MHA
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Eva Kubala Havrdová, DrSc.
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



