-
Články
- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
- Kongresy
- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Clinical Features and Serum Biomarkers in HIV Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome after Cryptococcal Meningitis: A Prospective Cohort Study
Background:
Although antiretroviral therapy (ART) improves survival in persons with cryptococcal meningitis (CM) and AIDS, ART frequently elicits HIV immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS), an exaggerated and frequently deadly inflammatory reaction that complicates recovery from immunodeficiency. The pathogenesis of IRIS is poorly understood and prediction of IRIS is not possible.Methods and Findings:
We prospectively followed 101 ART-naïve Ugandans with AIDS and recent CM for one year after initiating ART, and used Luminex multiplex assays to compare serum cytokine levels in participants who did or did not develop IRIS. IRIS occurred in 45% of participants with recent CM on ART, including 30% with central nervous system (CNS) manifestations. The median time to CM-IRIS was 8.8 wk on ART. Overall mortality on ART was 36% with IRIS and 21% without IRIS. CM-IRIS was independently associated with death (HR = 2.3, 95% CI 1.1–5.1, p = 0.04). Patients experiencing subsequent CM-IRIS had 4-fold higher median serum cryptococcal antigen (CRAG) levels pre-ART (p = 0.006). Higher pre-ART levels of interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-17 as well as lower tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) predicted future IRIS in multivariate analyses (area under the curve [AUC] = 0.82). An algorithm based on seven pre-ART serum biomarkers was a robust tool for stratifying high (83%), moderate (48%), and low risk (23%) for IRIS in the cohort. After ART was initiated, increasing levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), D-dimer, IL-6, IL-7, IL-13, G-CSF, or IL-1RA were associated with increasing hazard of IRIS by time-to-event analysis (each p≤0.001). At the time of IRIS onset, multiple proinflammatory cytokine responses were present, including CRP and IL-6. Mortality was predicted by pre-ART increasing IL-17, decreasing GM-CSF, and CRP level >32 mg/l (highest quartile). Pre-ART CRP level >32 mg/l alone was associated with future death (OR = 8.3, 95% CI 2.7–25.6, p<0.001).Conclusions:
Pre-ART increases in Th17 and Th2 responses (e.g., IL-17, IL-4) and lack of proinflammatory cytokine responses (e.g., TNF-α, G-CSF, GM-CSF, VEGF) predispose individuals to subsequent IRIS, perhaps as biomarkers of immune dysfunction and poor initial clearance of CRAG. Although requiring validation, these biomarkers might be an objective tool to stratify the risk of CM-IRIS and death, and could be used clinically to guide when to start ART or use prophylactic interventions.
: Please see later in the article for the Editors' Summary
Published in the journal: . PLoS Med 7(12): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1000384
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000384Summary
Background:
Although antiretroviral therapy (ART) improves survival in persons with cryptococcal meningitis (CM) and AIDS, ART frequently elicits HIV immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS), an exaggerated and frequently deadly inflammatory reaction that complicates recovery from immunodeficiency. The pathogenesis of IRIS is poorly understood and prediction of IRIS is not possible.Methods and Findings:
We prospectively followed 101 ART-naïve Ugandans with AIDS and recent CM for one year after initiating ART, and used Luminex multiplex assays to compare serum cytokine levels in participants who did or did not develop IRIS. IRIS occurred in 45% of participants with recent CM on ART, including 30% with central nervous system (CNS) manifestations. The median time to CM-IRIS was 8.8 wk on ART. Overall mortality on ART was 36% with IRIS and 21% without IRIS. CM-IRIS was independently associated with death (HR = 2.3, 95% CI 1.1–5.1, p = 0.04). Patients experiencing subsequent CM-IRIS had 4-fold higher median serum cryptococcal antigen (CRAG) levels pre-ART (p = 0.006). Higher pre-ART levels of interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-17 as well as lower tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) predicted future IRIS in multivariate analyses (area under the curve [AUC] = 0.82). An algorithm based on seven pre-ART serum biomarkers was a robust tool for stratifying high (83%), moderate (48%), and low risk (23%) for IRIS in the cohort. After ART was initiated, increasing levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), D-dimer, IL-6, IL-7, IL-13, G-CSF, or IL-1RA were associated with increasing hazard of IRIS by time-to-event analysis (each p≤0.001). At the time of IRIS onset, multiple proinflammatory cytokine responses were present, including CRP and IL-6. Mortality was predicted by pre-ART increasing IL-17, decreasing GM-CSF, and CRP level >32 mg/l (highest quartile). Pre-ART CRP level >32 mg/l alone was associated with future death (OR = 8.3, 95% CI 2.7–25.6, p<0.001).Conclusions:
Pre-ART increases in Th17 and Th2 responses (e.g., IL-17, IL-4) and lack of proinflammatory cytokine responses (e.g., TNF-α, G-CSF, GM-CSF, VEGF) predispose individuals to subsequent IRIS, perhaps as biomarkers of immune dysfunction and poor initial clearance of CRAG. Although requiring validation, these biomarkers might be an objective tool to stratify the risk of CM-IRIS and death, and could be used clinically to guide when to start ART or use prophylactic interventions.
: Please see later in the article for the Editors' SummaryIntroduction
Cryptococcal meningitis (CM), caused by the fungal organism Cryptococcus neoformans (commonly termed simply “cryptococcus”) is the most common fatal central nervous system (CNS) infection in persons with AIDS and is the initial AIDS-defining illness in 20%–30% of AIDS patients in Africa, causing 20%–40% of AIDS-attributable mortality [1]–[4]. The US Centers for Disease Control (CDC) estimates approximately 1 million CM cases occur annually, with 70% in sub-Saharan Africa [5]. The incidence of CM among Ugandans with CD4 counts <200 cells/µl is 10% annually without antiretroviral therapy (ART) [1], and without ART, almost all persons with CM die within 6 mo [6]. Although ART availability has led to improved CM survival in Africa [7]–[9], mortality after CM is still high, in part due to paradoxical HIV immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS), an exaggerated inflammatory response causing a subset of persons with recent CM to paradoxically deteriorate on ART in the presence of improving immune function [10]–[14]. Paradoxical CM-IRIS incidence has been reported as 10%–42% among ART-naïve persons with CM, with a pooled average of 18% (95% CI 14%–23%) [7],[14]–[17]. CM-IRIS is of grave concern because of its high incidence and mortality (33%–66%) [7],[14],[17],[18]. In many resource-limited regions, particularly sub-Saharan Africa where CM is the second most common AIDS-defining opportunistic infection [1]–[4], CM-IRIS is a major clinical problem.
The pathophysiology of paradoxical IRIS is largely unknown, but IRIS is hypothesized to be due to dysregulated reconstitution of antigen-specific immunity, leading to an exaggerated immune response to persisting antigens despite microbiologic treatment success [19]–[22]. The antigens, which may be present as intact organisms, dead organisms, or debris [23], evoke pathological inflammatory responses that cause paradoxical clinical deterioration [24]–[26].
A healthy immune response in non-immunocompromised hosts to cryptococcal infection depends on coordinated interactions between antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and effector T cells, thereby generating an effective type-1 helper T cell (Th1) immune response that clears the infection. Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) induces classical activation of macrophages to destroy phagocytosed cryptococcus (Figure 1) [27]–[30]. In contrast, Th2 responses are not protective and allow intracellular proliferation of cryptococcus within macrophages, resulting in disseminated infection [31],[32]. Colony-stimulating factors, such as granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), also up-regulate anti-cryptococcal activity of the innate immune system [33]–[36]. We hypothesize that an ineffectual immune response to cryptococcus occurs in a subset of AIDS patients, and these abnormal responses predispose to the development of IRIS.
Fig. 1. Normal Immunology of Cryptococcosis. 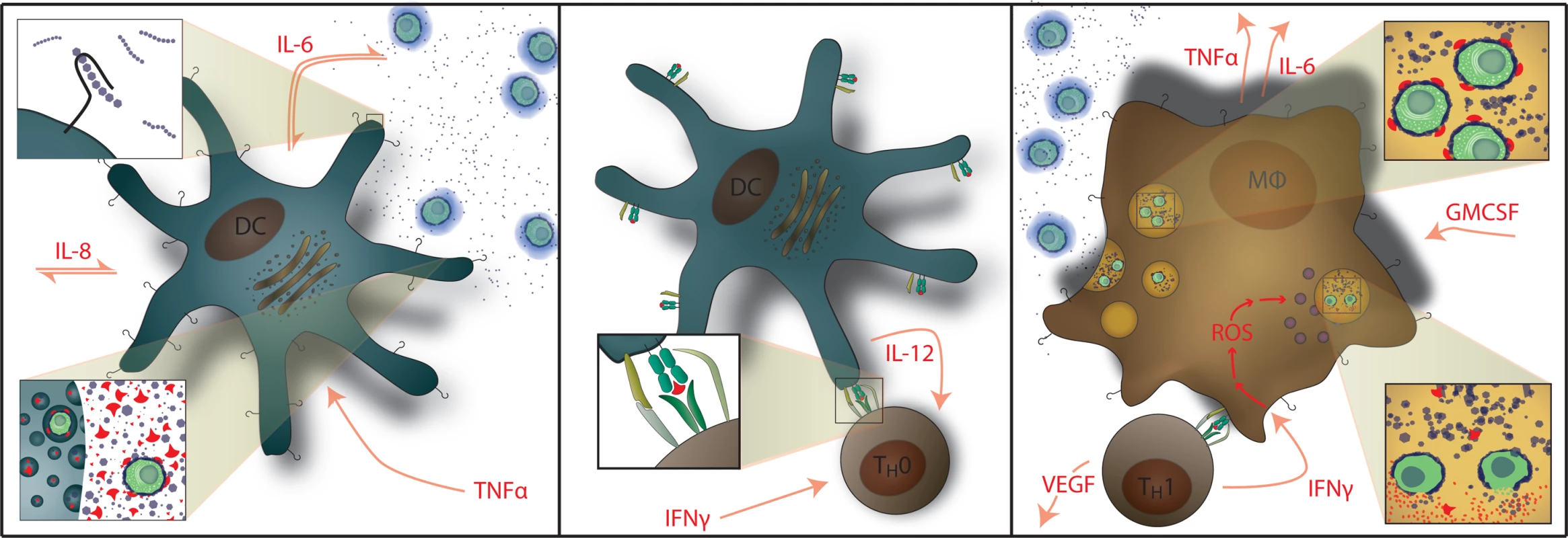
Left: Myeloid dendritic cells serve as APCs that recognize and phagocytose C. neoformans and generate cytokine signals of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. GXM polysaccharide capsule (i.e. CRAG) activates APCs via Toll-like receptor 4 and CD14. Center: Activated dendritic cells migrate to lymphatic tissue and present cryptococcal mannoprotein antigen to naïve T cells via MHC-II receptors. This coupled with CD28 costimulation results in Th1 differentiation. Right: Antigen-specific Th1 T cell recognition results in IFN-γ secretion causing classical activation of macrophages with up-regulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production; IL-6, TNF-α, IL-8 (CXCL8), CXCL10, fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-2 secretion by macrophages. T cells also secrete additional inflammatory mediators of GM-CSF and VEGF. Th2 T cell responses are not protective. Macrophages also release G-CSF which up-regulates leukotriene synthesis and anticryptococcal activity of neutrophils. We prospectively studied the incidence, clinical presentations, outcomes, and cytokine profiles of CM-IRIS in a cohort of HIV-infected Ugandans initiating ART in order to identify serum biomarkers of inflammation that can be used to predict and diagnose CM-IRIS. Characterizing the abnormal inflammatory responses associated with IRIS will enable the future selection of rational IRIS treatment strategies targeting specific inflammatory pathways.
Methods
Participants
One hundred two ART-naïve patients with AIDS and recent CM were enrolled for 12 mo of longitudinal evaluation after ART initiation. One participant was lost to follow up at <2 wk and excluded. Participants with CM were enrolled from May 2006 through September 2009 at Mulago Hospital in Kampala, Uganda [7]. Patients were treated with 0.7–1.0 mg/kg/day of amphotericin for 14 doses, then fluconazole 400 mg daily, and subsequently started on ART as outpatients at the Infectious Disease Institute clinic. ART was initiated at a median of 34 d (interquartile range [IQR] 24–41 d) after CM diagnosis and consisted of: zidovudine, lamivudine, and efavirenz or stavudine, lamivudine, and nevirapine. After ART initiation, participants attended clinic visits biweekly for 3 mo then monthly through 12 mo. Evaluation for IRIS was performed at each scheduled visit and when participants presented acutely. When IRIS was suspected, alternative diagnoses were evaluated by history, examination, laboratory, lumbar puncture, and/or radiological investigations. The International Network for the Study of HIV-associated IRIS (INSHI) consensus working case definition for CM-IRIS was used [37]. Suspected but unconfirmed IRIS events were considered non-IRIS. Each participant provided written informed consent for protocols approved by the institutional review boards at the University of Minnesota, Makerere University, and Uganda National Council for Science and Technology.
Laboratory Testing
CD4+ T cell and plasma HIV RNA measurements were made every 12 wk and at suspected IRIS events. From 2007 onward, CD4+ T cells were also measured at 4 and 8 wk of ART. Serum was frozen at −80°C at visits (0, 2, 4, 8, 12, 24 wk and suspected IRIS events). We measured 27 serum cytokines/chemokines in duplicate (Human 27-Plex Panel, Bio-Rad, Hercules, California) according to manufacturer protocol via a Luminex 100 system (Austin, Texas). Plasma D-dimer was measured in 1∶25 dilution by IMUCLONE D-Dimer ELISA (America Diagnostics, Stamford, Connecticut). Serum C-reactive protein (CRP) was measured by reflectance spectrophotometry at the University of Minnesota clinical laboratory. Baseline specimens, collected on the day of ART initiation, were missing from nine patients. Serum cryptococcal antigen (CRAG) titers were batched with each patient's specimens being tested simultaneously in parallel (Immuno-Mycologics, Norman, Oklahoma). At the time of CM-IRIS onset, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis excluded alternative diagnoses. Investigations included: Gram and acid-fast bacilli (AFB) stains, bacterial and fungal cultures, 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for bacteria [38], and viral culture in Vero cells and RT-PCR amplification for arboviruses performed at the Centers for Disease Control–Fort Collins, Colorado. Patients presenting with pneumonitis were offered bronchoalveolar lavage with separate consent. Histopathology or autopsy specimens always included AFB staining to exclude tuberculosis (TB).
Statistical Analysis
The primary comparison was between CM patients developing IRIS and control CM patients without IRIS. Non-normally distributed variables (e.g., cytokines, CD4) were tested at baseline by Mann-Whitney U and presented as median with IQR. p-Values are two-sided with α<0.05 (SPSS 18.0.1, Chicago, IL). Cytokine p-values were adjusted for multiple comparisons via Benjamini-Hochberg methods [39]. To determine the risk of future CM-IRIS, pre-ART demographic variables, standard HIV parameters, and log2-transformed cytokines were analyzed. A training model was developed in October 2008 after the first 65 participants were enrolled [40], which narrowed the selection from all 29 possible biomarkers to consideration of: CRP, interleukin (IL)-4, IL-8, IL-12, IL-17, G-CSF, GM-CSF, CCL2 (MCP-1), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). To evaluate the additive predictive power of the above cytokine set, we fitted penalized logistic regression models with penalty parameters specified by the Lasso method [41]. Cross-validation was used to estimate the penalty parameters in the model, with 10% of the data removed for each subset estimate. Models were fitted using the “penalized” package in R [42]. The unadjusted models look at the serum biomarkers alone. Six participants were a priori excluded during model development (four suspected IRIS, two TB-IRIS). We also considered an adjusted model including CD4 and the time from CM to ART initiation as unpenalized regression coefficients.
To describe the degree of inflammation occurring at CM-IRIS events, two methods were used. First, cytokine profiles at IRIS events were compared with CM controls time-matched from 4–12 wk of ART (corresponding to the approximate IQR of IRIS timing). Second, we modeled the longitudinal within-patient cytokine changes by Cox regression with a time-dependent covariate to represent each cytokine profile and the profile's evolution over time on ART [43],[44]. The outcome variable in the Cox model was the time to first IRIS event. The “survival package” in R fitted the model on log2-transformed data [42]. Sandwich estimates determined the variance of regression coefficients, and the relative IRIS risk was portrayed as the hazard ratio (HR). The p-values resulting from each cytokine test were adjusted for multiple comparisons [39]. The Cox model allowed the use of the full longitudinal cytokine profile in order to test for association with the hazard of CM-IRIS events. The HR measures the relative risk of CM-IRIS for each two-fold change in the cytokine expression at any given time point through the first 6 mo of ART.
Results
Clinical Features of Cryptococcal IRIS
In this cohort, 57 paradoxical IRIS events occurred in 45 persons (45%; 95% CI 35%–55%; see Figure S1), of whom 35 persons had one event, nine persons had two events, and one person had three events. The median pre-ART CD4 count was 19 (IQR 7–38) cells/µl. Baseline demographic features and both virologic and CD4+ T cell responses to ART were similar in patients who did and did not develop cryptococcal IRIS (Table 1). The most frequent clinical manifestation of paradoxical cryptococcal IRIS was aseptic meningitis, which occurred in 30% (30/101) after appropriate clinical responses to initial amphotericin therapy. In these 30 patients, CM-IRIS manifested as headache (87%), photophobia (33%), vomiting (30%), meningismus (27%), papilledema (27%) and seizures (20%). Analysis of CSF showed elevated WBCs in 75% (median 50, range 5–200/µl, lymphocytic predominance), elevated protein in 88% (median 80, range 40–150 mg/dl), and sterile cultures in 96% (27/28, missing two). Each variable was increased compared with pre-ART values (p<0.001). Six patients with CM-IRIS presented with seizures that were accompanied by cryptococcoma(s) on CT and/or postmortem exam; three of these patients had concomitant aseptic meningitis. Other paradoxical cryptococcal IRIS events included: pneumonitis with nonproductive cough and radiologic infiltrate (n = 14), CNS cryptococcoma without meningitis (n = 3), sepsis syndrome with sterile cultures (n = 2), and single episodes each of marked lymphadenopathy, retinitis, optic neuritis, and phlyctenular keratoconjunctivitis. CM-IRIS events are summarized and additional clinical details are provided in Text S1. Overall, our results suggest that IRIS occurs in a large percentage of AIDS patients with CM who start ART, and the manifestations of IRIS can be severe, often involving aseptic meningitis and other CNS manifestations.
Tab. 1. Demographic and laboratory parameters in comparison to occurrence of IRIS events. 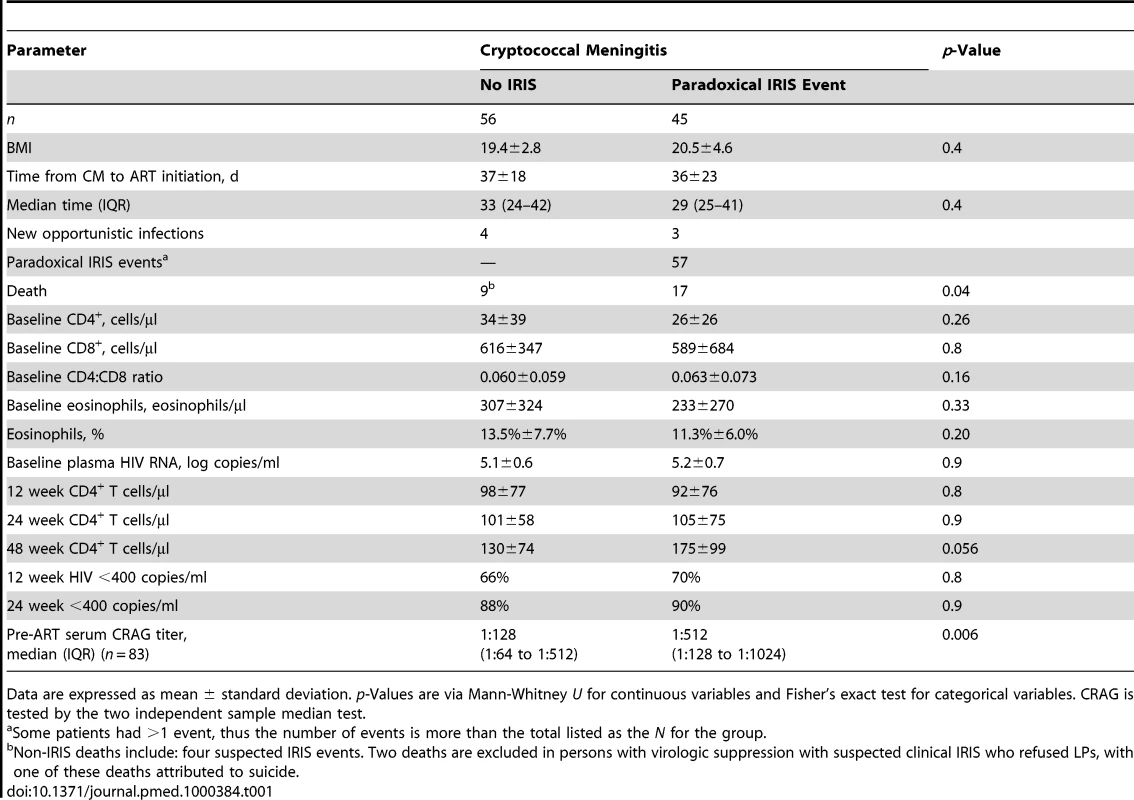
Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. p-Values are via Mann-Whitney U for continuous variables and Fisher's exact test for categorical variables. CRAG is tested by the two independent sample median test. Association between IRIS and Death
In the absence of ART, CM in Africa is associated with high mortality [6],[45]. We analyzed mortality data in our cohort to determine whether the development of IRIS was associated with increased mortality. Overall, 28 of 101 CM patients died (27%) after initiating ART. Mortality was 36% (16/45) in patients with IRIS and 21% (12/56) in those without IRIS (Figure 2). Causes of death were cryptococcal IRIS (n = 16), virologic failure and CM relapse (n = 1), paradoxical TB-IRIS (n = 1), aspiration after AZT-induced severe anemia and lactic acidosis (non-IRIS) (n = 1), renal failure (n = 1), cerebrovascular event (n = 1), suspected but unverified cases of CM-IRIS (n = 4), suspected pulmonary emboli (n = 2), and one unknown cause of death occurring at home. By time-to-event analysis, mortality was higher among those experiencing cryptococcal IRIS (HR = 2.3, 95% CI 1.1–5.1, p = 0.04) than the remainder of the cohort, alone or after adjustment for baseline CD4 (p = 0.11 for CD4). Our findings suggest that the development of IRIS is associated with an increased risk for death in patients with recent CM.
Fig. 2. Cumulative survival in persons with prior cryptococcal meningitis newly initiating HIV therapy in Uganda is stratified by the occurrence of cryptococcal IRIS. 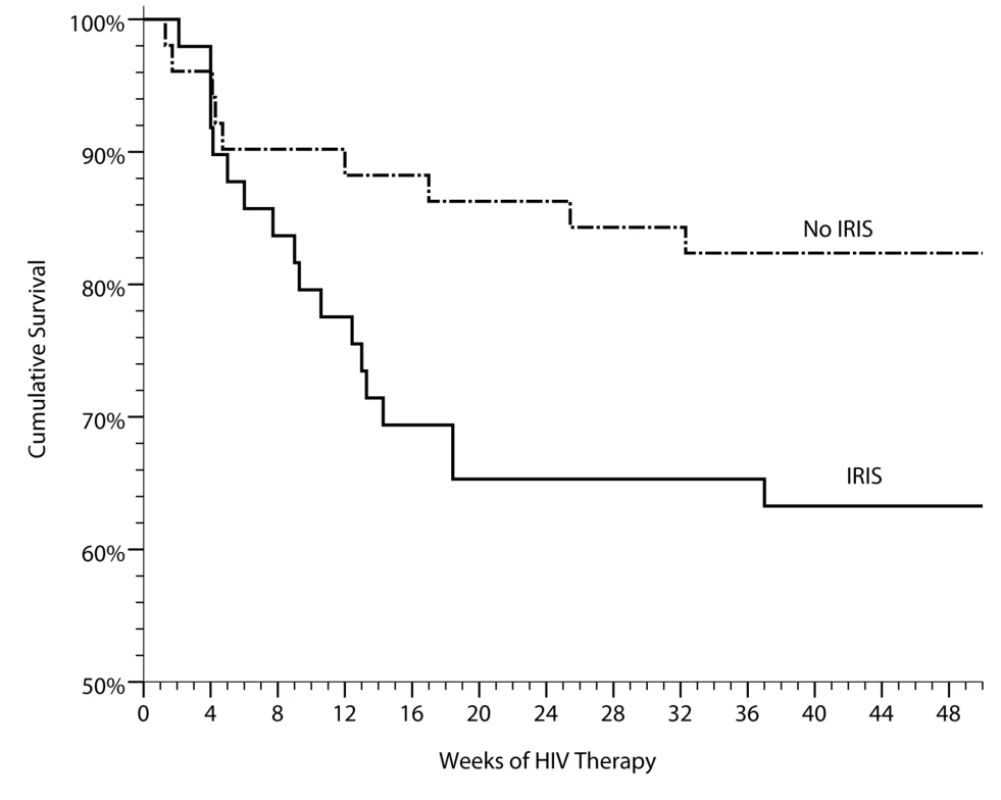
IRIS was associated with increased mortality (HR = 2.4, 95% CI 1.1–5.3, p = 0.035). Included with the controls are three suspected, but unproven cases of CM-IRIS, three unknown causes of death (two suspected pulmonary emboli). Two deaths have been excluded of persons with known virologic suppression with clinical IRIS who refused lumbar punctures to exclude alternative etiologies of their deterioration, of which one of these deaths was attributed to suicide. Demographic Risk Factors for IRIS
We sought to determine the risks for IRIS by analyzing demographic and standard HIV parameters. For participants with recent CM, we identified no statistically significant difference among those who did or did not develop IRIS in baseline number or change in CD4+ T cell number, in baseline plasma HIV RNA, nor in virologic suppression at 12, 24, 36, or 48 wk (Table1). CD4 recovery is displayed in Figure S2. The lack of differences in these variables pertained to univariate or multivariate analyses, controlling for CRP, body mass index (BMI), cytokine profiles, as well as time-to-event analysis or comparison of quartiles. Thus, the degree of immunosuppression, rate of immune recovery after ART, level of viremia, and degree of viral suppression on ART were not predictors of CM-IRIS in this prospective cohort with very severe immunosuppression.
Median serum CRAG titers when starting ART were 4-fold higher in participants with IRIS (1∶512 cases versus 1∶128 controls, p = 0.006). This result is in marked contrast to our previous CSF report from 85 members of this cohort, in whom there were no differences in CSF CRAG titer at time of their initial CM diagnosis between IRIS cases and controls (median CRAG 1∶1024 for both groups) [46]. A pre-ART serum CRAG ≥1∶512 was associated with later CM-IRIS (OR = 4.2, 95% CI 1.7–10.3; p = 0.002). Though serum was not available for direct comparison at time of their initial CM diagnosis, the implication is that patients with IRIS likely had poorer antigen clearance in the 5-wk median interval between CM diagnosis and ART initiation.
A concern among many clinicians is that early initiation of ART in patients with CM could lead to an increased incidence of IRIS and increased mortality [47]. We identified no statistical significant difference in the incidence of IRIS in those initiating ART 11–28 d from CM-diagnosis compared with those who waited ≥28 d, (44% versus 55% respectively; p = 0.4) nor a statistical difference in survival (p = 0.9). Thus, earlier initiation of ART following the diagnosis of CM was not a risk factor for IRIS.
Predictive IRIS Model
Based on a training set derived from pilot data through 2008 [40], we considered nine possible biomarkers to incorporate into a predictive IRIS model. We used penalized logistic regression with penalties defined by the lasso method to develop a classification model with the best overall fit. Applying this model to our cohort, we were able to stratify persons into high-, moderate-, and low-risks groups with IRIS incidences of 82%, 47%, and 22%, respectively (Figure 3), based on seven serum biomarkers collected on the day of ART initiation (IL-4, IL-17, G-CSF, GM-CSF, CCL2 [MCP-1], TNF-α, and VEGF). The predictive performance (i.e. C-statistic) as quantified by the area under the curve (AUC) of a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve is 0.82 for correct prediction (p<0.001).
Fig. 3. Cumulative incidence of cryptococcal IRIS. 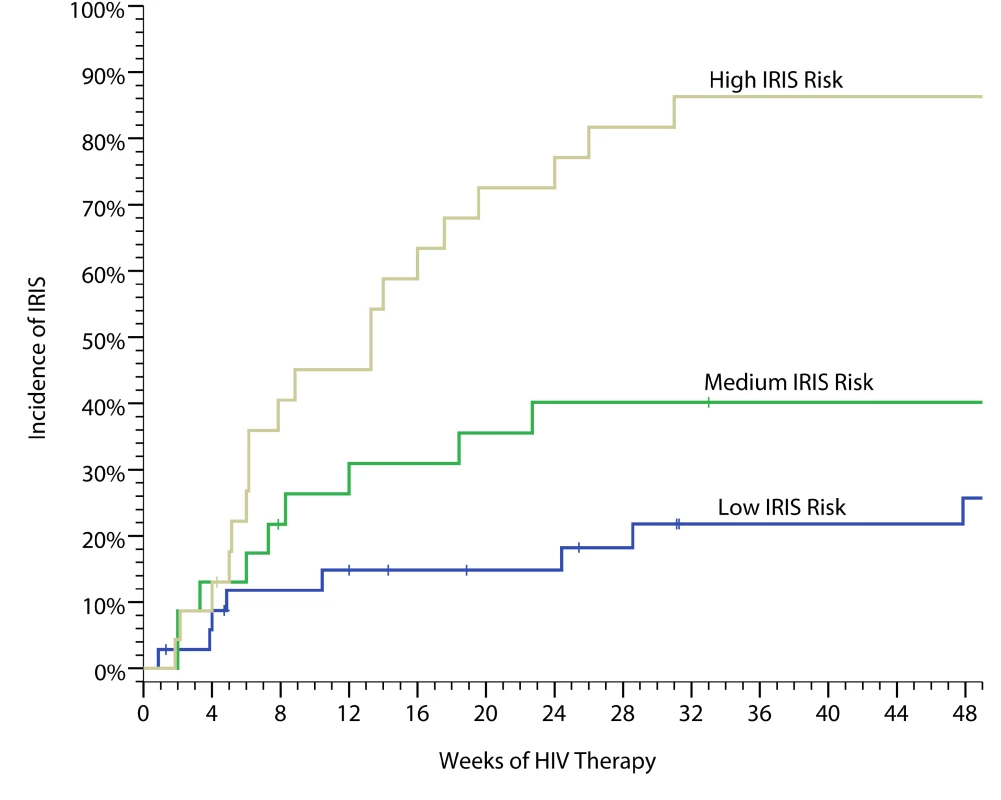
The data are based on a weighed predictive biomarker score composed of pre-ART serum levels of seven biomarkers—IL-4, IL-17, G-CSF, GM-CSF, CCL2 (MCP-1), TNF-α, and VEGF—calculated as follows. Probability of IRIS = where:Probability risk is scored from 0 to 1.0 with the categorical classification being defined for low risk (0–0.40), moderate risk (0.41–0.60), and high risk (0.61–1.0). The performance as quantified by the AUC is 0.82 for correct prediction (i.e. C-statistic). The predictive model had better predictive performance than CRP (AUC = 0.58, p = 0.25) or CRAG titer (AUC = 0.67, p = 0.004). We considered an adjusted model including the pre-ART CD4 count and the delay from CM to ART initiation. Adjustment did not improve prediction (AUC = 0.83). We also considered the effect on predictive performance by using a more parsimonious model with fewer predictors (Figure S3). The AUC decreased in a linear fashion with inclusion of fewer predictors, such that the AUC was 0.72 for a four-variable model of IL-17, GM-CSF, TNF-α, and VEGF. Although these biomarkers are associated with prediction of IRIS, these factors alone or in aggregate may not be causative of IRIS. However, the roles of these cytokines in immune responses to cryptococcus (Figure 1) suggest that these cytokines may play a role in IRIS pathogenesis. Overall, our results suggest that the risk of IRIS could be stratified on the basis of pre-ART biomarker levels in persons with cryptococcosis.
Biomarkers Associated with Cryptococcal IRIS
Since predictive models have a different goal and interpretation than do models of association, we also tested for association. We considered the seven biomarkers identified above in a multivariate logistic model to determine their statistical association with IRIS (Table 2). In a multivariate model, future CM-IRIS was associated with increased pre-ART levels of CRP, IL-4, and IL-17 (each p<0.05). Since Th1, rather than Th2 responses, are protective in cryptococcosis [28], a Th2 response to cryptococcus characterized by increased IL-4 production by T cells might be associated with ineffective antigen clearance, leading to a predisposition to the subsequent development of IRIS. Notably, increased pre-ART levels of IL-17, often viewed as a proinflammatory cytokine, were also associated with future IRIS. Moreover, pre-ART levels of the inflammatory marker CRP were increased among patients who subsequently developed IRIS (mean 2.3-fold higher, 95% CI 1.2–3.5, p = 0.03). Persons with CRP >32 mg/l levels (highest quartile) experienced IRIS with an increased incidence of 74% (OR = 3.9, 95% CI 1.3-11.3, p = 0.01) and shorter time-to-event (HR = 3.4, 95% CI 1.8–6.6, p<0.001) compared with persons with CRP<32 mg/l, independent of CD4+ count. Our data suggest that not only is the presence of pre-ART inflammation associated with risk for IRIS, but the type of inflammation is important, with the closest association of IL-4 (Th2) and IL-17 (Th17) responses with a predisposition toward CM-IRIS development.
Tab. 2. Pre-ART serum biomarkers associated with subsequent paradoxical cryptococcal IRIS. 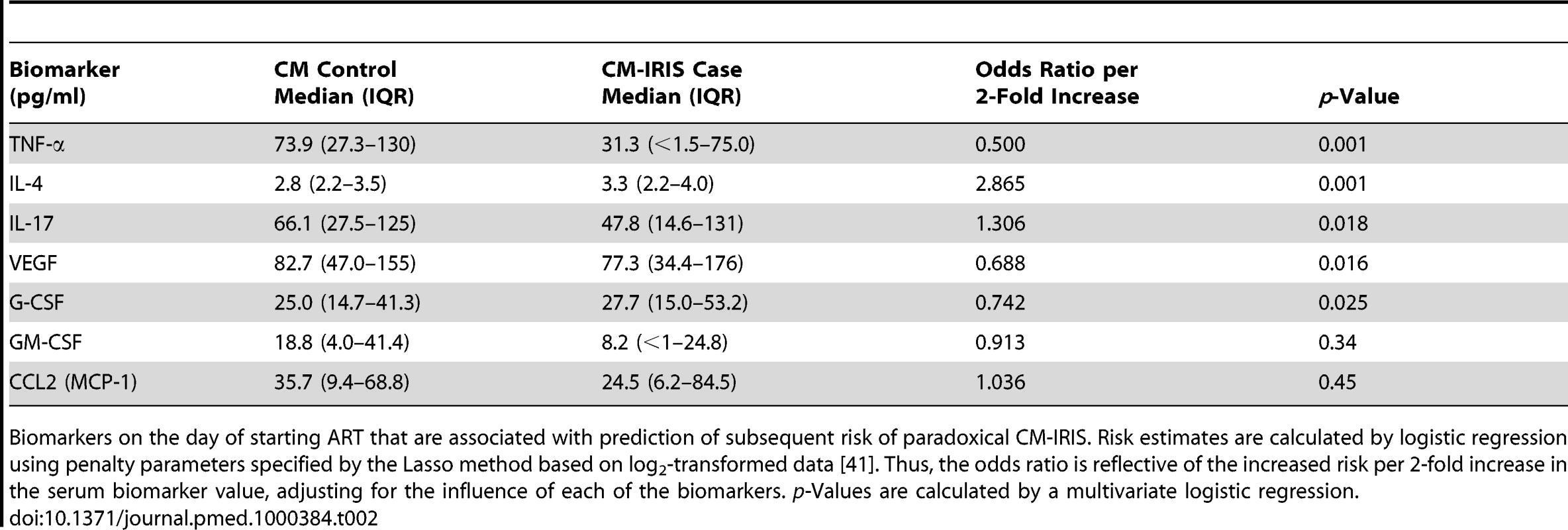
Biomarkers on the day of starting ART that are associated with prediction of subsequent risk of paradoxical CM-IRIS. Risk estimates are calculated by logistic regression using penalty parameters specified by the Lasso method based on log2-transformed data [41]. Thus, the odds ratio is reflective of the increased risk per 2-fold increase in the serum biomarker value, adjusting for the influence of each of the biomarkers. p-Values are calculated by a multivariate logistic regression. Although high pre-ART levels of IL-4, IL-17, and CRP were associated with increased risk of IRIS, lower pre-ART levels of VEGF, G-CSF, and TNF-α were also associated with increased risk (p<0.05 each). IRIS developed in 79% (11/14) of patients with undetectable serum levels of TNF-α when starting ART, but only 35% (27/78) with detectable TNF-α (OR = 4.9, 95% CI 1.3 to 19.0, p = 0.019). TNF-α is involved in innate immunity by activating phagocytosis of cryptococcus by macrophages, antigen processing, and proinflammatory recruitment of additional leukocytes [48],[49], resulting in improved clearance of the organism. Thus, lack of these protective proinflammatory responses at baseline may be associated with subsequent IRIS. In summary, a predisposition to developing IRIS is associated with a paucity of cytokines involved in antigen processing and macrophage function, such as TNF-α, coupled with increased generalized inflammation (e.g., increased CRP, IL-17), lack of antigen recognition by CD4+ T cells (e.g., decreased VEGF), and inappropriate Th2 responses (e.g., increased IL-4) before ART.
Biomarkers on ART
In addition to identifying pre-ART predictors of CM-IRIS, we performed a time-to-event analysis to identify additional predictors of IRIS that evolved in patients while on ART. After ART initiation, analysis of changes in biomarkers during all time points through the first 24 wk of ART showed a significant divergence in inflammatory profiles associated with immune reconstitution between cases and controls that was evident in blood weeks before IRIS events. Increasing levels of CRP, D-dimer, IL-1RA, IL-6, IL-7, IL-13, or G-CSF following initiation of ART were associated with increasing hazard of IRIS (each p≤0.001) (Table 3). The pattern of inflammation indicated increasing levels of biomarkers of generalized inflammation such as CRP, IL-6, and D-dimer; inappropriate Th2 responses characterized by elevated IL-13 levels; and elevated levels of growth factors such as G-CSF and the T cell growth and differentiation factor IL-7. The anti-inflammatory mediator IL-1RA increased following ART initiation and before IRIS. The clinical implication of these findings is that these biomarkers could be used to indicate risk for CM-IRIS before the development of IRIS events, providing an opportunity for intervention before clinical deterioration occurs.
Tab. 3. Time-to-event analysis of the hazard of CM-IRIS by serum cytokine profile evolving during ART. 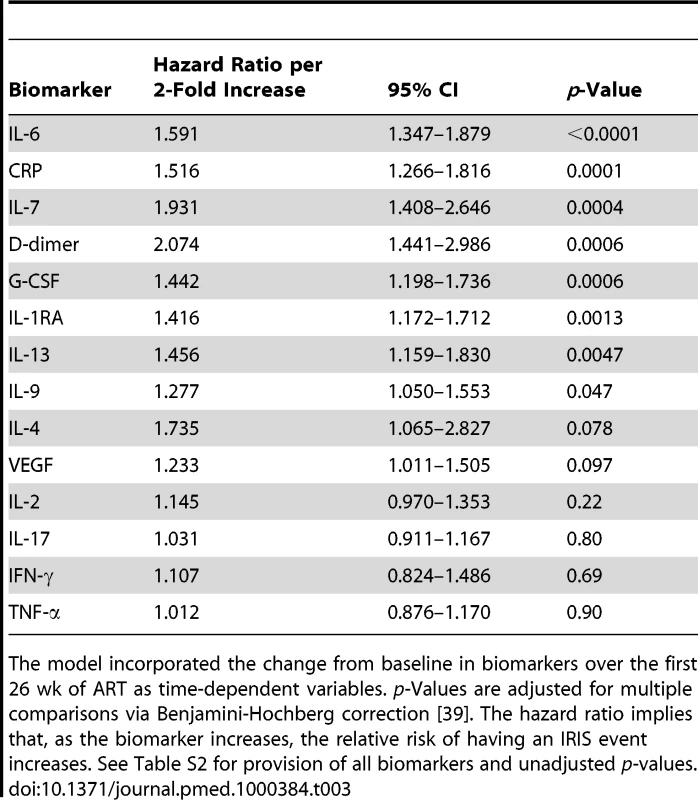
The model incorporated the change from baseline in biomarkers over the first 26 wk of ART as time-dependent variables. p-Values are adjusted for multiple comparisons via Benjamini-Hochberg correction [39]. The hazard ratio implies that, as the biomarker increases, the relative risk of having an IRIS event increases. See Table S2 for provision of all biomarkers and unadjusted p-values. Biomarkers of Inflammation at IRIS Events
At time of cryptococcal IRIS, serum biomarkers of inflammation were elevated in almost all IRIS patients over those in time-matched controls (Table 4). However, the pattern of inflammation was heterogeneous with individual variation (Table S1). Early IRIS events were associated with more systemic inflammation than were events occurring after 24 wk. IL-6 was most frequently elevated at time of IRIS events (median 5-fold increase compared with time-matched control participants). CRP levels often correlated with IL-6 levels, as CRP is stimulated by IL-6; and CRP levels were most often increased at IRIS diagnosis compared with levels pre-ART or pre-event (Figure 4; p<0.001). In comparing IRIS events with CNS manifestations versus non-CNS IRIS events, there were no statistical differences in any biomarker (each p>0.1) with the possible exception of D-dimer being more elevated in non-CNS events (median 3.68 versus 2.22 µg/ml, unadjusted p = 0.031). Interestingly, the inflammatory profile distinguished relapse from CM-IRIS in the four cases of culture-positive CM relapse. In the relapse cases, CRP was normal (<8 mg/l), whereas CRP was elevated in 76% of participants with cryptococcal IRIS. These results confirm that IRIS is associated with elevations in markers of inflammation that are large enough to be measured in the serum and can help distinguish patients with CM-IRIS from those with CM relapse before culture results are available.
Fig. 4. Individual longitudinal increases in CRP and IL-6 from baseline pre-ART, to the time point before IRIS, and at time of IRIS event. 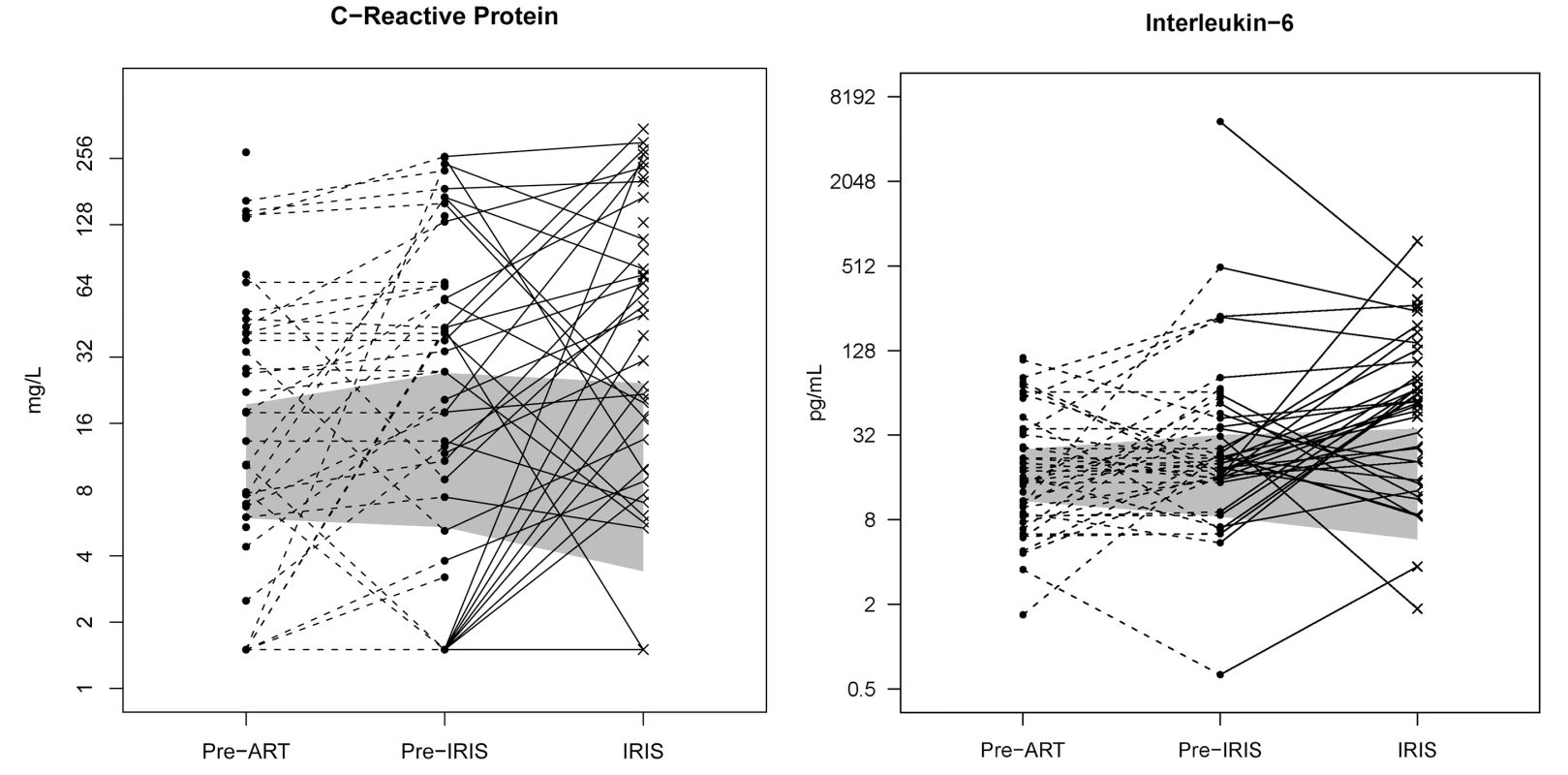
The gray shading represents the interquartile range (25th to 75th percentile) of the CM cohort controls without IRIS over the first 8 wk of ART. The median time of IRIS was 8.8 wk. IL-6 and CRP are increased before the IRIS event (p<0.001) and at time of IRIS (p<0.001). Tab. 4. Increase in serum biomarkers at the time of first IRIS event compared to time-matched controls. 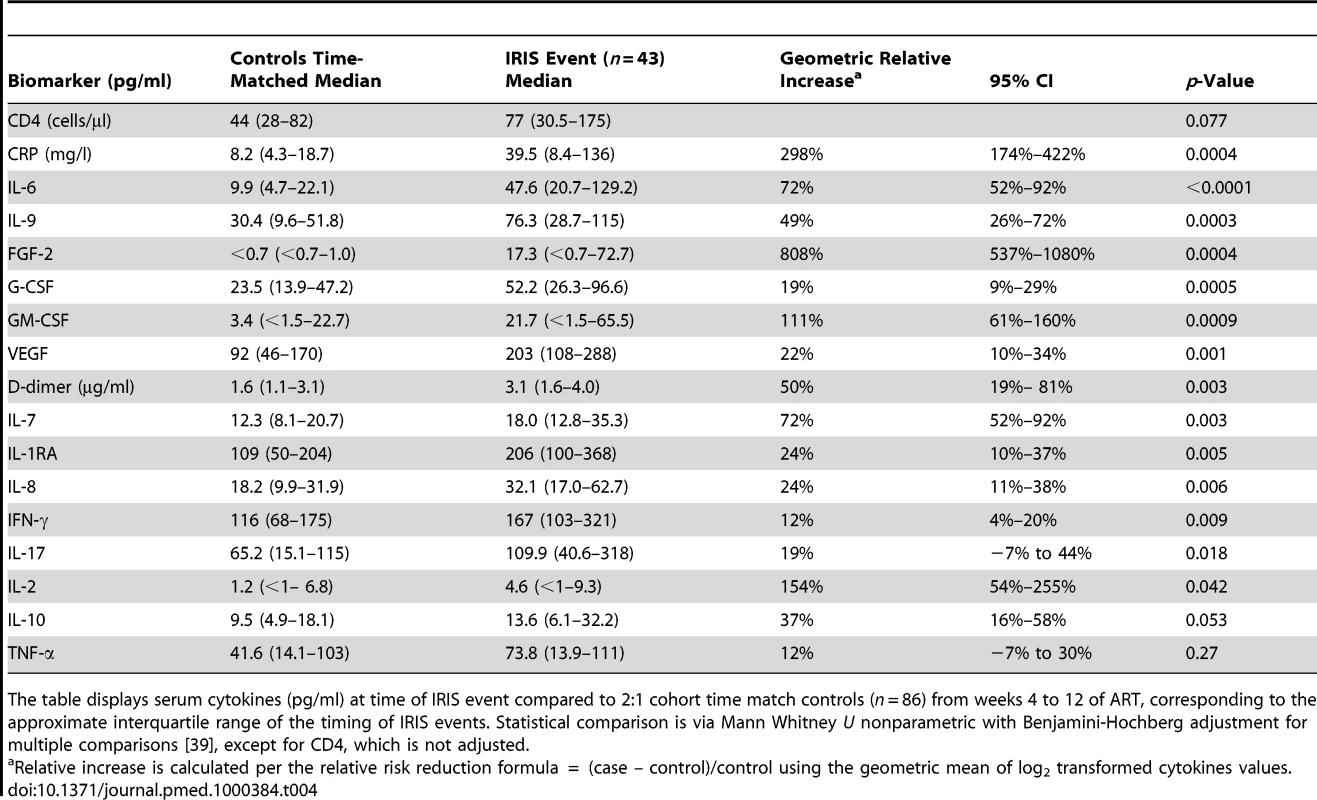
The table displays serum cytokines (pg/ml) at time of IRIS event compared to 2:1 cohort time match controls (n = 86) from weeks 4 to 12 of ART, corresponding to the approximate interquartile range of the timing of IRIS events. Statistical comparison is via Mann Whitney U nonparametric with Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment for multiple comparisons [39], except for CD4, which is not adjusted. Biomarkers Predictive of or Associated with Mortality
In addition to evaluating predictors of IRIS, we performed analyses to determine if inflammatory profiles could predict death. Using penalized logistic regression with Lasso estimates, we identified baseline pre-ART serum biomarkers that were associated with subsequent mortality on ART. The best fit model consisted of: IL-17, GM-CSF, IL-8, CXCL10, TNF-α, VEGF, and CRP >32 mg/l with an AUC of 0.84 for correct classification with 78% sensitivity, 81% specificity, 60% positive predictive value, and 91% negative predictive value. A more parsimonious three-biomarker model of increasing IL-17 or CRP >32 mg/l, and decreasing GM-CSF, predicted increasing mortality (AUC = 0.76). A weighted score based on these three biomarkers was used to classify high - and low-risk mortality groups (Figure 5). Persons scored as high risk had 69% mortality (i.e., 69% positive predictive value) whereas those with low risk had 83% survival (i.e. 83% negative predictive value), demonstrating the potential clinical utility of the tool to identify patients at increased and decreased risk for death. CRP alone was also clinically useful for predicting risk of death (Figure 5). Participants with a CRP >32 mg/l had 8-fold higher odds of all-cause mortality compared to those with CRP<32 mg/l (OR = 8.3, 95% CI 2.7–25.6, p<0.001). Using these biomarkers as clinical tools at the time of ARV initiation could be useful to identify high-risk patients and to monitor them for early therapeutic intervention.
Fig. 5. Survival on ART in persons with prior cryptococcosis stratified by their mortality biomarker risk score. 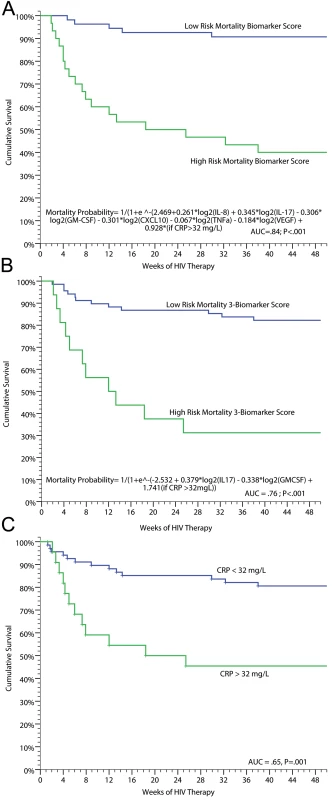
(A) Full predictive model (AUC = 0.84). (B) Parsimonious three-biomarker model based on IL-17 (p = 0.015), GM-CSF (p = 0.022), and categorical CRP >32 mg/l (p = 0.004) (AUC = 0.76). With a categorical cutoff point for the model with high risk of probability >0.5 to 1.0, the positive predictive value was 69% and negative predictive value 83% with 48% sensitivity and 92% specificity. (C) Survival stratified by baseline, pre-ART CRP level of<32 or ≥32 mg/l (AUC = 0.65). The three respective ROC curves are presented in Figure S4. We also performed analyses to determine if levels of biomarkers at time of IRIS events were associated with mortality. Among persons experiencing CM-IRIS, mortality after an IRIS event was associated with increased IL-10 levels (OR = 2.8 per 2-fold change, 95% CI 1.3–5.9, p = 0.007) and decreased IL-17 levels (OR = 0.59 per 2-fold change, 95% CI 0.40–0.86, p = 0.006) at event compared to persons with IRIS who survived.
Discussion
In this prospective cohort study of patients with AIDS and recent CM in Uganda, we characterized the incidence and clinical features of CM-IRIS and identified serum biomarkers that can diagnose IRIS and can stratify the risk for IRIS or death. CM-IRIS is a common complication of ART in sub-Saharan Africa, with an incidence reported in the literature ranging from 10% to 31% [11],[14]–[18],[50]. In our cohort with <1% loss to follow up, the incidence of CM-IRIS was 45%, two-thirds of whom experienced characteristic CNS manifestations (30%). Unlike many other forms of IRIS, which produce less dramatic consequences, CM-IRIS is exceptional for its substantial morbidity and mortality [11],[50]–[52]. The 36% CM-IRIS mortality in our study is consistent with other CM-IRIS studies [14],[15],[17],[18],[52],[53]. Such dire outcomes may derive from the increased inflammation that accompanies CM-IRIS in the anatomically constrained compartment of the CNS.
Before this study, it was not possible to predict risk for CM-IRIS. Epidemiologic factors, that were identified in retrospective studies, were not predictive of CM-IRIS in our study, and have not been found consistently across other studies [14],[15],[17],[52]. Similar to a recent ACTG (AIDS Clinical Trial Group) a5164 trial, in our study timing of ART initiation was not associated with IRIS [54]. In contrast, however, we identified specific patterns of biomarkers that were predictive of the development of IRIS and death at initiation of ART, after initiation of ART, and at IRIS event.
Based on our identification of biomarkers that predict CM-IRIS, our theoretical model is one whereby persons predisposed to IRIS have more dysfunctional immune systems that fail to effectively clear antigens from cryptococcus before ART-associated immune restoration. Indeed, persons with IRIS had higher median serum CRAG titers when initiating ART than controls without IRIS (p = 0.006), but they had identical 1∶1024 median CSF CRAG titers at their initial CM diagnosis [46]. This result may have implications for customization of timing of ART based on initial induction antifungal therapy prescribed with a longer delay required for less active antifungal therapy (e.g., fluconazole monotherapy).
Further failures of antigen clearance may result from an imbalance in immune regulation, initially characterized by increased production of Th2 cytokines (IL-4, IL-13) and a lack of the proinflammatory mediators (VEGF, TNF-α, G-CSF, GM-CSF) that are required to recruit lymphocytes and activate macrophages and other innate cells to clear C. neoformans. Specifically, in neutrophils and macrophages, G-CSF and GM-CSF promote phagocytosis, up-regulation of reactive oxygen species, and intracellular destruction of cryptococcus [33]–[36]. Decreased pre-ART levels of G-CSF, GM-CSF, and TNF-α should result in decreased phagocytosis and promotion of a fertile intracellular environment within macrophages for cryptococcus [36],[49]. Based on our model of CM-IRIS pathogenesis, this inappropriate or ineffective macrophage activation leads to failure to clear cryptococcal organisms and predisposes toward the development of CM-IRIS. In this respect, CM-IRIS pathogenesis may parallel the proposed mechanism of TB-IRIS [55].
A failure of antigen clearance promotes generalized inflammatory signaling to then occur, specifically with IL-6. Compared with time-matched control participants, persons who developed IRIS had elevated levels of CRP before ART initiation, and elevated levels of CRP and IL-6 before and at the time of IRIS events. Our results indicate that the inflammatory signaling response involving IL-6 progressively increased on ART until the development of IRIS. Since IL-6 is the primary stimulant of hepatic CRP production, it is unsurprising that these biomarkers had similar patterns. French and colleagues reported similar increases in plasma IL-6 after a variety of IRIS events or before herpesvirus-related IRIS events, and they verified by flow cytometry experiments that activated macrophages were the primary source of IL-6 [56],[57].
We hypothesize that the abnormal cytokine profiles we observed before CM-IRIS, including elevations of Th2 cytokine (e.g., IL-4, IL-13) and lack of proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, indicate ineffective or inappropriate alternative macrophage activation. In contrast to Th1 responses, which promote IFN-γ–mediated killing of cryptococcus by macrophages [28],[32], IL-4 produced in Th2 cells causes alternative activation of macrophages—typically a response to parasite infections—promoting fibrosis [58]. Alternative activation of macrophages allows for intracellular growth, proliferation, and dissemination of C. neoformans [28],[29]. In other fungal processes, IL-4 reverses GM-CSF–mediated macrophage killing of yeast in vitro [59]. In our results, small quantitative increases in IL-4 were associated with large statistical increases in IRIS risk. Since Th1 and Th2 responses are often mutually exclusive, inappropriate increases in Th2 responses (e.g., IL-4, IL-10, IL-13) generate ineffective inflammation and inhibit the protective Th1 responses necessary for efficient antigen clearance. The association of a Th2 bias and risk for IRIS was evident with elevated IL-4 levels at baseline, elevated IL-13 levels on ART before IRIS events, and elevated IL-10 levels at IRIS events as well as an association between increased IL-10 levels at IRIS and subsequent death. The Th2 responses that limit clearance of C. neoformans may be driven by preexisting Th2 biases to other concomitant coinfections, such as intestinal helminths or schistosomiasis. This phenomenon might underlie the higher overall incidence of IRIS in our cohort compared to cohorts from temperate regions [14],[15],[17],[50]. Unexplained absolute eosinophilia (>500 cells/µl) was present in over one-quarter of the cohort; however there were not statistical differences in eosinophils or total serum IgE between cases and controls. Overall, our data suggest that Th2 responses to cryptococcus are associated with poor outcomes, including increased risk for IRIS and death.
Risk factors for IRIS extend beyond the Th1:Th2 paradigm. Increased Th17 responses (i.e. IL-17) were a pre-ART risk for both IRIS and mortality on ART. Proinflammatory Th17 cells have been previously hypothesized as important in IRIS pathogenesis [60],[61]. In normal immune homeostasis, a balance between Th17 cells and regulatory T cells (Treg) is crucial. A Th17 imbalance can cause autoimmune diseases. In this balance, IL-6 plays a key role in naïve T cell differentiation inducing Th17 differentiation and inhibiting Treg differentiation in the presence of TGF-β [62]. The copious IL-6 present before IRIS events may alter the balance between Treg and Th17 cells, suppressing Treg differentiation or function during ART-related immune reconstitution.
Additionally, other cytokines that we identified may play a role in IRIS pathogenesis by contributing to ineffective macrophage activation. For example, low pre-ART levels of TNF-α or VEGF were associated with increased IRIS risk. TNF-α, secreted by macrophages and T cells, is particularly important in activating antigen-presenting cells. Absence of TNF-α causes failure of mature dendritic cell activation and recruitment, thereby blunting further recruitment of T cells [63]. Lack of TNF-α could indicate failure to present and/or process antigen and could contribute to ineffective macrophage activation in patients at risk for IRIS. In cryptococcosis, VEGF is secreted by a variety of leukocytes but especially by CD4+ T cells during antigen-specific responses to cryptococcal mannoprotein being presented by MHC-II molecules [64]. Decreased VEGF may reflect greater immune dysfunction due to failure of CD4+ T cell antigen recognition from antigen-presenting cells. The downstream effects of decreased VEGF would further diminish both chemotaxis and the costimulatory activity of VEGF on IFN-γ–secreting Th1 memory T cells [65]. Thus, decreased VEGF may then diminish the Th1 response and shift the Th1:Th2 balance toward Th2 responses. The decreased levels of TNF-α and VEGF in patients at risk for IRIS may be causes or reflections of impaired macrophage function. Overall, the inappropriate Th2 responses and IL-4 production, coupled with ineffective macrophage activation, suggest that a failure in pathogen recognition and clearance could set the stage for paradoxical IRIS by promoting antigen persistence. Upon eventual immune restoration of more appropriate antigen-specific responses, these responses are exaggerated because of the abundance of uncleared foreign antigen and promotion by IL-6 of a proinflammatory state.
Study Strengths
Strengths of this study include its prospective design, careful and complete follow-up, and integration of pathophysiologic analyses in the context of characterizing clinical phenotypes. As such, we believe the results reported here are generalizable to cryptococcal IRIS as a pathophysiologic entity. In general, the diagnoses of other forms of IRIS are somewhat subjective, but in CM-IRIS, the identification of IRIS in the CNS is very objective due to the ability to examine the CSF, where the inflammation occurs. A problem arises with non-CNS manifestations of IRIS, which often represent diagnoses of exclusion and depend on the diagnostic capabilities available. In this cohort, we identified several (n = 20) non-CNS IRIS events, of which 60% were associated with later CNS-IRIS events or with supportive/definitive histopathology (Text S1). Eight cases (retinitis, optic neuritis, keratoconjunctivitis, pneumonitis; n = 5) were probable IRIS diagnoses and unsupported by histopathology or culture (17% of total IRIS cases). Although cryptococcus most often causes meningitis, cryptococcosis is a disseminated disease with systemic CRAG measurable for months in peripheral blood [66]. In our experience here, dead C. neoformans causing IRIS reactions were identified in tissue by histopathology of brain, lymphatics, gut, skin, and tongue and were isolated via bronchoalveolar lavage. Thus, non-CNS cryptococcal IRIS events do occur, allowing these “probable events” as likely, but not definitely, attributable to IRIS. In separately considering these non-CNS IRIS events, there were no statistical differences in the inflammatory profiles observed at time of IRIS as compared to CNS-IRIS events, except for possibly D-dimer. In Uganda, there is likely high and ongoing environmental exposure to cryptococcus [1],[4], thus pneumonitis-IRIS could equally be triggered by persisting original antigen or by environmental re-exposure manifesting effectively as an acute hypersensitivity pneumonitis reaction. Pulmonary cryptococcosis often goes unrecognized and/or is suspected as smear-negative TB [67].
Study Limitations
This prospective observational study has allowed us to characterize the statistical association between cytokine profiles and IRIS. Of course, this does not prove causality; however, the anomalies we report are biologically plausible within the known immunology of responses to cryptococcus. A challenge in pathogenesis studies such as ours is that the inflammatory profiles associated with IRIS are heterogeneous, representing a continuum that is likely dependent on the duration of symptoms, the antigen, and the robustness of the event. In cytokine profiling, six of our participants had minimal immunologic perturbation in peripheral blood even though they clinically deteriorated, presenting with headache and elevated intracranial pressure several months into ART. Thus, some patients fulfilling the IRIS clinical case definition either have localized immune responses that were not detectable in peripheral blood, or they may not have had true immunologic IRIS but instead had delayed complications of CM that were clinically indistinguishable from CM-IRIS. This heterogeneity may have implications for IRIS management and the response to anti-inflammatory therapies. Although this prospective study of CM-IRIS is the largest to date, our biomarker data should be viewed as hypothesis-generating and will require validation in future cohorts. We plan to validate these biomarkers in subjects enrolled in the multi-site Cryptococcal Optimal ART Timing (COAT) trial (NCT 01075152; http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01075152) and investigate these biomarkers with regard to timing of ART initiation after CM diagnosis. This validation will give insight on whether altering the timing of ART initiation is a potential intervention to alter high risk or whether other strategies should be pursued. Once validated, creating diagnostics such as multiplex ELISAs or bead-based techniques could move this into clinical use.
Conclusions
Given the high incidence, morbidity, and mortality associated with CM-IRIS, identifying patients at risk for IRIS may enable interventions to improve management. Three distinct phases of IRIS pathogenesis can be identified (Table 5). First, before ART, a paucity of innate inflammatory responses or inappropriate (Th2) responses promote ineffective antigen clearance. Second, after ART initiation, copious antigen presentation promotes proinflammatory signaling (e.g., IL-6, CRP, IL-7). Third, at the time of IRIS, a generalized cytokine storm occurs. The biomarkers identified here, although requiring validation, may help target interventions to decrease IRIS risk, such as (1) early adjunctive GM-CSF or IFN-γ to increase macrophage function, (2) antiparasitic therapy to eliminate coinfections that promote inappropriate Th2 bias, (3) anti-IL-6 receptor antibody (tocilizumab) therapy to blunt inflammatory signaling, or (4) delaying ART initiation. This study suggests that prediction of IRIS or death may be possible with measurement of pre-ART serum biomarkers.
Tab. 5. Summary of paradoxical cryptococcal-IRIS pathogenesis hypothesis. 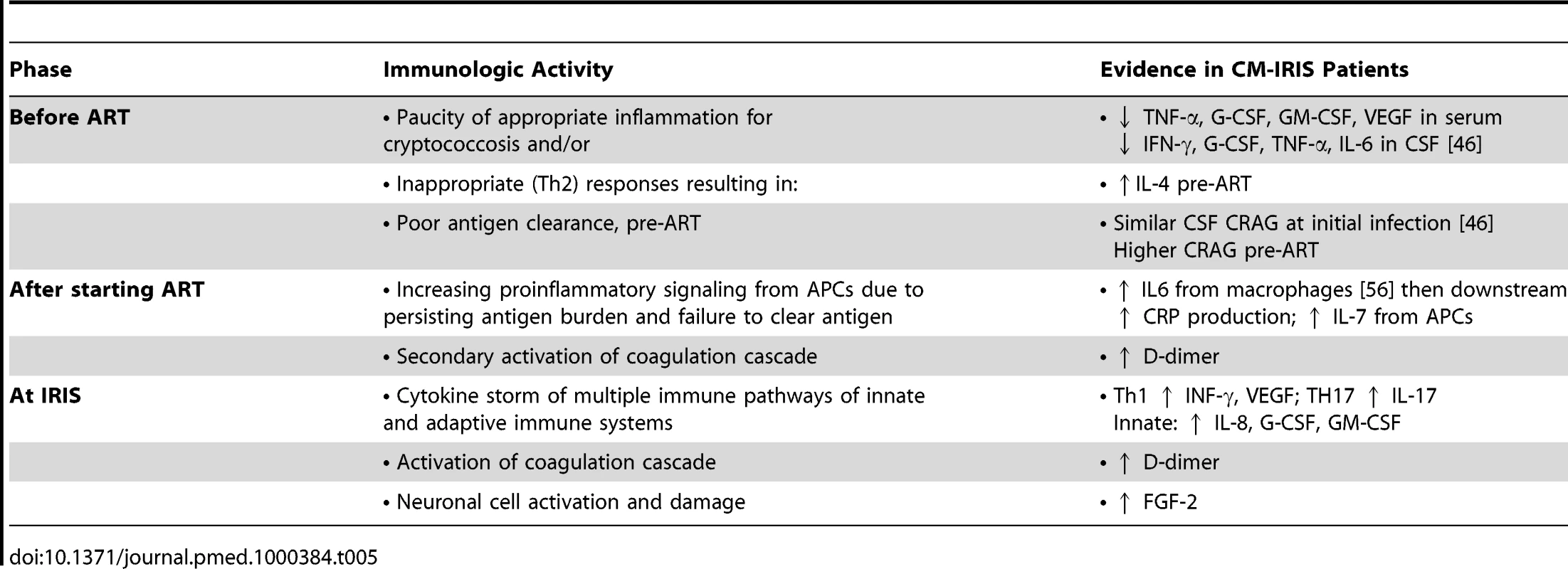
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. FrenchN
GrayK
WateraC
NakiyingiJ
LugadaE
2002 Cryptococcal infection in a cohort of HIV-1-infected Ugandan adults. AIDS 16 1031 1038
2. HakimJG
GangaidzoIT
HeydermanRS
MielkeJ
MushangiE
2000 Impact of HIV infection on meningitis in Harare, Zimbabwe: a prospective study of 406 predominantly adult patients. AIDS 14 1401 1407
3. CorbettEL
ChurchyardGJ
CharalambosS
SambB
MoloiV
2002 Morbidity and mortality in South African gold miners: impact of untreated disease due to human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Infect Dis 34 1251 1258
4. LiechtyCA
SolbergP
WereW
EkwaruJP
RansomRL
2007 Asymptomatic serum cryptococcal antigenemia and early mortality during antiretroviral therapy in rural Uganda. Trop Med Int Health 12 929 935
5. ParkBJ
WannwmuehlerKA
MarstonBJ
GovenderN
PappasPG
2009 Estimation of the current global burden of cryptococcal meningitis among persons living with HIV/AIDS. AIDS 23 525 530
6. Mayanja-KizzaH
OishiK
MitaraiS
YamashitaH
NalongoK
1998 Combination therapy with fluconazole and flucytosine for cryptococcal meningitis in Ugandan patients with AIDS. Clin Infect Dis 26 1362 1366
7. KambuguA
MeyaDB
RheinJ
O'BrienM
JanoffEN
2008 Outcomes of cryptococcal meningitis in Uganda before and after the availability of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis 46 1694 1701
8. BicanicT
MeintjesG
WoodR
HayesM
RebeK
2007 Fungal burden, early fungicidal activity, and outcome in cryptococcal meningitis in antiretroviral-naive or antiretroviral-experienced patients treated with amphotericin B or fluconazole. Clin Infect Dis 45 76 80
9. BissonGP
NthobatsongR
ThakurR
LesetediG
VinekarK
2008 The use of HAART is associated with decreased risk of death during initial treatment of cryptococcal meningitis in adults in Botswana. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 49 227 229
10. StoneSF
PriceP
FrenchMA
2004 Immune restoration disease: a consequence of dysregulated immune responses after HAART. Curr HIV Res 2 235 242
11. ShelburneSA
VisnegarwalaF
DarcourtJ
GravissEA
GiordanoTP
2005 Incidence and risk factors for immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome during highly active antiretroviral therapy. Aids 19 399 406
12. BonhamS
MeyaDB
BohjanenPR
BoulwareDR
2008 Biomarkers of HIV immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. Biomark Med 2 349 361
13. ManabeYC
CampbellJD
SydnorE
MooreRD
2007 Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome: risk factors and treatment implications. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 46 456 462
14. BicanicT
MeintjesG
RebeK
WilliamsA
LoyseA
2009 Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis: a prospective study. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 51 130 134
15. DarcourtJ
GreenbergSB
HamillRJ
Shelburne SA3rdWhite AC Jr. 2005 The role of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in AIDS-related Cryptococcus neoformans disease in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis 40 1049 1052
16. SungkanuparphS
JongwutiwesU
KiertiburanakulS
2007 Timing of cryptococcal immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome after antiretroviral therapy in patients with AIDS and cryptococcal meningitis. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 45 595 596
17. LortholaryO
FontanetA
MemainN
MartinA
SitbonK
2005 Incidence and risk factors of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome complicating HIV-associated cryptococcosis in France. AIDS 19 1043 1049
18. LawnSD
BekkerLG
MyerL
OrrellC
WoodR
2005 Cryptococcocal immune reconstitution disease: a major cause of early mortality in a South African antiretroviral programme. AIDS 19 2050 2052
19. ElliottJH
VohithK
SaramonyS
SavuthC
DaraC
2009 Immunopathogenesis and diagnosis of tuberculosis and tuberculosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome during early antiretroviral therapy. J Infect Dis 200 1736 1745
20. TieuHV
AnanworanichJ
AvihingsanonA
ApateerapongW
SirivichayakulS
2009 Immunologic markers as predictors of tuberculosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in HIV and tuberculosis coinfected persons in Thailand. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 25 1083 1089
21. MurdochDM
SuchardMS
VenterWD
MhlanguP
OttingerJS
2009 Polychromatic immunophenotypic characterization of T cell profiles among HIV-infected patients experiencing immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS). AIDS Res Ther 6 16
22. AntonelliLR
MahnkeY
HodgeJN
PorterBO
BarberDL
2010 Elevated frequencies of highly activated CD4+ T cells in HIV+ patients developing immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. Blood 116 3818 3827
23. FrenchMA
PriceP
StoneSF
2004 Immune restoration disease after antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 18 1615 1627
24. AutranB
CarcelainG
LiTS
BlancC
MathezD
1997 Positive effects of combined antiretroviral therapy on CD4+ T cell homeostasis and function in advanced HIV disease. Science 277 112 116
25. DeaytonJR
SabinCA
BrittWB
JonesIM
WilsonP
2002 Rapid reconstitution of humoral immunity against cytomegalovirus but not HIV following highly active antiretroviral therapy. Aids 16 2129 2135
26. ChengVC
YuenKY
ChanWM
WongSS
MaES
2000 Immunorestitution disease involving the innate and adaptive response. Clin Infect Dis 30 882 892
27. BeenhouwerDO
ShapiroS
FeldmesserM
CasadevallA
ScharffMD
2001 Both Th1 and Th2 cytokines affect the ability of monoclonal antibodies to protect mice against Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun 69 6445 6455
28. VoelzK
LammasDA
MayRC
2009 Cytokine signaling regulates the outcome of intracellular macrophage parasitism by Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun 77 3450 3457
29. MullerU
StenzelW
KohlerG
WernerC
PolteT
2007 IL-13 induces disease-promoting Type 2 cytokines, alternatively activated macrophages and allergic inflammation during pulmonary infection of mice with Cryptococcus neoformans. J Immunol 179 5367 5377
30. PerfectJR
SteeleC
CoxGM
Wormley FLJr. 2007 Protection against cryptococcosis by using a murine gamma interferon-producing Cryptococcus neoformans strain. Infect Immun 75 1453 1462
31. HernandezY
AroraS
Erb-DownwardJR
McDonaldRA
ToewsGB
2005 Distinct roles for IL-4 and IL-10 in regulating T2 immunity during allergic bronchopulmonary mycosis. J Immunol 174 1027 1036
32. StenzelW
MullerU
KohlerG
HeppnerFL
BlessingM
2009 IL-4/IL-13-dependent alternative activation of macrophages but not microglial cells is associated with uncontrolled cerebral cryptococcosis. Am J Pathol 174 486 496
33. VecchiarelliA
MonariC
BaldelliF
PietrellaD
RetiniC
1995 Beneficial effect of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on fungicidal activity of polymorphonuclear leukocytes from patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis 171 1448 1454
34. CoffeyMJ
PhareSM
GeorgeS
Peters-GoldenM
KazanjianPH
1998 Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor administration to HIV-infected subjects augments reduced leukotriene synthesis and anticryptococcal activity in neutrophils. J Clin Investigat 102 663 670
35. TasciniC
VecchiarelliA
PreziosiR
FrancisciD
BistoniF
1999 Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and fluconazole enhance anti-cryptococcal activity of monocytes from AIDS patients. AIDS 13 49 55
36. ChillerT
FarrokhshadK
BrummerE
StevensDA
2002 Effect of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor on polymorphonuclear neutrophils, monocytes or monocyte-derived macrophages combined with voriconazole against Cryptococcus neoformans. Medical Mycol 40 21 26
37. HaddowLJ
ColebundersR
MeintjesG
LawnSD
ElliottJH
2010 Cryptococcal immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome: literature review and proposed clinical case definitions. Lancet Infect Dis 10 791 802
38. Welinder-OlssonC
DotevallL
HogevikH
JungneliusR
TrollforsB
2007 Comparison of broad-range bacterial PCR and culture of cerebrospinal fluid for diagnosis of community-acquired bacterial meningitis. Clin Microbiol Infect 13 879 886
39. BenjaminiY
HochbergY
1995 Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B 57 289 300
40. BoulwareDR
MeyaDB
BergemannTL
WiesnerD
BonhamS
2009 Serum inflammatory biomarkers predict HIV immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome and death after cryptococcal meningitis. Abstract 774. 16th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI). Montreal, Canada
41. TibshiraniR
1996 Regression shrinkage and selection via the Lasso. J R Statist Soc B 58 267 288
42. R Development Core Team 2009 R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Available: http://www.r-project.org
43. FisherLD
LinDY
1999 Time-dependent covariates in the Cox proportional-hazards regression model. Annual Review of Public Health 20 145 157
44. KalbfleischJD
PrenticeRL
1980 The statistical analysis of failure time data. New York Wiley 321
45. HeydermanRS
GangaidzoIT
HakimJG
MielkeJ
TaziwaA
1998 Cryptococcal meningitis in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients in Harare, Zimbabwe. Clin Infect Dis 26 284 289
46. BoulwareDR
BonhamSC
MeyaDB
WiesnerDL
ParkGS
2010 Paucity of initial cerebrospinal fluid inflammation in cryptococcal meningitis is associated with subsequent Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome. J Infect Dis 202 962 970
47. MakadzangeAT
NdhlovuCE
TakarindaK
ReidM
KurangwaM
2010 Early versus delayed initiation of antiretroviral therapy for concurrent HIV infection and cryptococcal meningitis in Sub-Saharan Africa. Clin Infect Dis 50 1532 1538
48. ChenGH
OlszewskiMA
McDonaldRA
WellsJC
Paine R 3rd, et al. 2007 Role of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in host defense against pulmonary Cryptococcus neoformans infection during murine allergic bronchopulmonary mycosis. Am J Pathol 170 1028 1040
49. CollinsHL
BancroftGJ
1992 Cytokine enhancement of complement-dependent phagocytosis by macrophages: synergy of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor for phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans. Eur J Immunol 22 1447 1454
50. ZolopaA
AndersenJ
PowderlyW
SanchezA
SanneI
2009 Early antiretroviral therapy reduces AIDS progression/death in individuals with acute opportunistic infections: a multicenter randomized strategy trial. PLoS One 4 e5575
51. BretonG
DuvalX
EstellatC
PoalettiX
BonnetD
2004 Determinants of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in HIV type 1-infected patients with tuberculosis after initiation of antiretroviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis 39 1709 1712
52. SungkanuparphS
FillerSG
ChetchotisakdP
PappasPG
NolenTL
2009 Cryptococcal immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome after antiretroviral therapy in AIDS patients with cryptococcal meningitis: a prospective multicenter study. Clin Infect Dis 49 931 934
53. Jenny-AvitalER
AbadiM
2002 Immune reconstitution cryptococcosis after initiation of successful highly active antiretroviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis 35 e128 133
54. GrantPM
KomarowL
AndersenJ
SeretiI
PahwaS
2010 Risk factor analyses for immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in a randomized study of early vs. deferred ART during an opportunistic infection. PLoS One 5 e11416
55. Van den BerghR
VanhamG
RaesG
De BaetselierP
ColebundersR
2006 Mycobacterium-associated immune reconstitution disease: macrophages running wild? Lancet Infect Dis - 6 2 3; author reply 4-5
56. StoneSF
PriceP
KeaneNM
MurrayRJ
FrenchMA
2002 Levels of IL-6 and soluble IL-6 receptor are increased in HIV patients with a history of immune restoration disease after HAART. HIV Med 3 21 27
57. StoneSF
PriceP
BrochierJ
FrenchMA
2001 Plasma bioavailable interleukin-6 is elevated in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients who experience herpesvirus-associated immune restoration disease after start of highly active antiretroviral therapy. J Infect Dis 184 1073 1077
58. MartinezFO
HelmingL
GordonS
2009 Alternative activation of macrophages: an immunologic functional perspective. Annu Rev Immunol 27 451 483
59. WintersMS
ChanQ
CarusoJA
Deepe GS Jr. 2010 Metallomic analysis of macrophages infected with Histoplasma capsulatum reveals a fundamental role for zinc in host defenses. J Infect Dis 202 1136 1145
60. KestensL
SeddikiN
BohjanenPR
2008 Immunopathogenesis of immune reconstitution disease in HIV patients responding to antiretroviral therapy. Curr Opin HIV AIDS 3 419 424
61. FrenchMA
2009 HIV/AIDS: Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome: a reappraisal. Clin Infect Dis 48 101 107
62. KimuraA
KishimotoT
2010 IL-6: Regulator of Treg/Th17 balance. Eur J Immunol 40 1830 1835
63. BaumanSK
HuffnagleGB
MurphyJW
2003 Effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha on dendritic cell accumulation in lymph nodes draining the immunization site and the impact on the anticryptococcal cell-mediated immune response. Infect Immun 71 68 74
64. CoenjaertsFA
van der FlierM
MwinziPNM
Brouwer AnnemarieE
ScharringaJ
2004 Intrathecal production and secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor during cryptococcal meningitis. J Infect Dis 190 1310 1317
65. BasuA
HoerningA
DattaD
EdelbauerM
StackMP
2010 Cutting edge: Vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated signaling in human CD45RO+ CD4+ T cells promotes Akt and ERK activation and costimulates IFN-gamma production. J Immunol 184 545 549
66. AbergJA
WatsonJ
SegalM
ChangLW
2000 Clinical utility of monitoring serum cryptococcal antigen (sCRAG) titers in patients with AIDS-related cryptococcal disease. HIV Clin Trials 1 1 6
67. Deok-jong YooS
WorodriaW
DavisJL
CattamanchiA
den BoonS
2010 The prevalence and clinical course of HIV-associated pulmonary cryptococcosis in Uganda. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 54 269 274
Štítky
Interní lékařství
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Medicine
Nejčtenější tento týden
2010 Číslo 12- Není statin jako statin aneb praktický přehled rozdílů jednotlivých molekul
- Magnosolv a jeho využití v neurologii
- Moje zkušenosti s Magnosolvem podávaným pacientům jako profylaxe migrény a u pacientů s diagnostikovanou spazmofilní tetanií i při normomagnezémii - MUDr. Dana Pecharová, neurolog
- Biomarker NT-proBNP má v praxi široké využití. Usnadněte si jeho vyšetření POCT analyzátorem Afias 1
- Antikoagulační léčba u pacientů před operačními výkony
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- Clinical Features and Serum Biomarkers in HIV Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome after Cryptococcal Meningitis: A Prospective Cohort Study
- Scaling Up the 2010 World Health Organization HIV Treatment Guidelines in Resource-Limited Settings: A Model-Based Analysis
- Toward a Consensus on Guiding Principles for Health Systems Strengthening
- Association of Secondhand Smoke Exposure with Pediatric Invasive Bacterial Disease and Bacterial Carriage: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- The Health Crisis of Tuberculosis in Prisons Extends beyond the Prison Walls
- A Longitudinal Study of Medicaid Coverage for Tobacco Dependence Treatments in Massachusetts and Associated Decreases in Hospitalizations for Cardiovascular Disease
- Participatory Epidemiology: Use of Mobile Phones for Community-Based Health Reporting
- Nuclear Receptor Expression Defines a Set of Prognostic Biomarkers for Lung Cancer
- Antibiotic Selection Pressure and Macrolide Resistance in Nasopharyngeal A Cluster-Randomized Clinical Trial
- Clinical Benefits, Costs, and Cost-Effectiveness of Neonatal Intensive Care in Mexico
- Tuberculosis Incidence in Prisons: A Systematic Review
- PLOS Medicine
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Clinical Features and Serum Biomarkers in HIV Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome after Cryptococcal Meningitis: A Prospective Cohort Study
- Participatory Epidemiology: Use of Mobile Phones for Community-Based Health Reporting
- Clinical Benefits, Costs, and Cost-Effectiveness of Neonatal Intensive Care in Mexico
- Scaling Up the 2010 World Health Organization HIV Treatment Guidelines in Resource-Limited Settings: A Model-Based Analysis
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Vladimír Palička, CSc., Dr.h.c., doc. MUDr. Václav Vyskočil, Ph.D., MUDr. Petr Kasalický, CSc., MUDr. Jan Rosa, Ing. Pavel Havlík, Ing. Jan Adam, Hana Hejnová, DiS., Jana Křenková
Autoři: MUDr. Irena Krčmová, CSc.
Autoři: MDDr. Eleonóra Ivančová, PhD., MHA
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Eva Kubala Havrdová, DrSc.
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



