-
Články
Top novinky
Reklama- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
Top novinky
Reklama- Kongresy
- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Top novinky
ReklamaLymph-Node Resident CD8α Dendritic Cells Capture Antigens from Migratory Malaria Sporozoites and Induce CD8 T Cell Responses
Malaria is responsible for the deaths of 0.5–2 million people each year. A safe and effective vaccine is likely needed for the control or eradication of malaria. Immunization with irradiated sporozoites, the infectious stage of the parasite transmitted by mosquitoes, protects people against malaria through the activation of specialized effector cells called CD8+ T cells, which can eliminate live parasites. The induction of such malaria-specific CD8+ T cells is critically dependent on dendritic cells, a diverse population of antigen-presenting cells. It was previously unclear how dendritic cells acquire sporozoite antigens to induce the protective CD8+ T cell response. Using a combination of functional studies and high-resolution imaging, we report here that live sporozoites access skin-draining lymph nodes after infection and directly provide antigens to resident dendritic cells that in turn activate CD8+ T cells. These results underscore the importance of live, motile sporozoites in the induction of protective CD8+ T cell responses and provide a mechanistic understanding for the superior immunogenicity of whole parasite vaccines.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Pathog 11(2): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004637
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1004637Summary
Malaria is responsible for the deaths of 0.5–2 million people each year. A safe and effective vaccine is likely needed for the control or eradication of malaria. Immunization with irradiated sporozoites, the infectious stage of the parasite transmitted by mosquitoes, protects people against malaria through the activation of specialized effector cells called CD8+ T cells, which can eliminate live parasites. The induction of such malaria-specific CD8+ T cells is critically dependent on dendritic cells, a diverse population of antigen-presenting cells. It was previously unclear how dendritic cells acquire sporozoite antigens to induce the protective CD8+ T cell response. Using a combination of functional studies and high-resolution imaging, we report here that live sporozoites access skin-draining lymph nodes after infection and directly provide antigens to resident dendritic cells that in turn activate CD8+ T cells. These results underscore the importance of live, motile sporozoites in the induction of protective CD8+ T cell responses and provide a mechanistic understanding for the superior immunogenicity of whole parasite vaccines.
Introduction
Sterile immunity against live sporozoite challenge is elicited by immunization with radiation-attenuated sporozoites [1] and is, in part, mediated by CD8+ T cells specific for the Plasmodium circumsporozoite (CS) antigen [2, 3]. Using a model mimicking natural exposure to sporozoite-infected mosquitoes, we previously demonstrated that CS-specific CD8+ T cell responses are primed by DCs in the skin-draining lymph nodes (DLNs) of mice [4]. Following activation in the DLNs, CS-specific CD8+ T cells migrate to the liver where they eliminate parasite-infected hepatocytes [4, 5]. Subsequently, others have shown that immune responses generated in the DLNs are sufficient for sterile protection against live sporozoites [6]. These findings challenged the prevalent idea that CD8+ T cell responses against malaria liver stages originate exclusively in hepatic tissues.
How do skin-deposited sporozoites elicit cell-mediated immune responses in the DLNs? The induction of malaria-specific CD8+ T cells is critically dependent on dendritic cells (DCs) [4, 7–11], a diverse population of specialized antigen-presenting cells (APCs). The phenotypic diversity of DCs is exemplified in murine skin-DLNs which contain lymphoid-tissue resident DCs (composed of CD8α+ and CD11b+ subsets), B220+ plasmacytoid DCs, and three distinct subsets of skin-derived migratory DCs [12]. In addition, DCs differ in their ability to present antigen to CD4+ and CD8+ T cells [12, 13] and are located within different compartments in the DLN [14, 15]. For any cutaneously-deposited pathogen or vaccine, this phenotypic and spatial heterogeneity raises the question of how antigen is transported to the secondary lymphoid tissue and which DCs are responsible for priming CD8+ T cells. This issue is especially important for malaria given that immunization with sporozoites represents the gold-standard for malaria vaccination and understanding the factors that contribute to efficient antigen presentation may aid vaccine design [16].
Several studies have examined T cell, APC, and parasite interactions in infections other than malaria [17,18]; however, the role of different DC subsets in the transport and presentation of parasite antigens is not well understood or, in the case of Leishmania infection, is controversial [19, 20]. In contrast, these questions have been well studied in viral models. In infections with tissue-tropic viruses, such as influenza virus and Herpes simplex virus (HSV), tissue-derived DCs play prominent roles in either the transport of antigen to lymph node (LN)-resident DCs or the direct presentation of antigen to CD8+ T cells [21, 22]. In other infections such as vaccinia virus in which the virus can infect dendritic cells, direct presentation of antigen to CD8+ T cells has been observed just beneath the subcapsular sinus [23] and within the LN parenchyma [24, 25].
Based on these viral paradigms, there are several potential routes by which antigen might be presented to malaria-specific CD8+ T cells after skin delivery of sporozoites. One possibility is that sporozoite antigen is acquired in the dermis by skin-resident migratory DCs, trafficked to the DLNs, and presented directly to CD8+ T cells. Alternatively, skin-emigrant DCs may transfer antigens to LN-resident DCs for presentation and CTL activation. These models are supported by the fact that sporozoites are injected and, in some cases, develop in the skin after mosquito inoculation (reviewed in [26]). However, these models fail to take into account the sporozoites’ exquisite motility and the superior immunogenicity of live, irradiated sporozoites versus dead sporozoites. Therefore, we investigated a third possibility: that CD8+ T cell priming does not require skin-derived DCs, but instead, depends on antigen delivery to lymphoid tissues by migratory parasites. To acquire insight into these issues, we used genetically manipulated parasites, advanced imaging technologies, and transgenic mice with constitutive or conditional loss of distinct APC subsets. We found that skin-derived DCs are not needed for CD8+ T cell priming; rather the ability of parasites to actively traverse out of the skin is critical for the induction of CD8+ T cell responses by LN-resident DCs. Our data provide the most complete picture to date of the events required for the development of an adaptive cell-mediated immune response against skin-deposited malaria liver stages.
Results
Langerhans cells and langerin+ dermal DCs are not required for priming CS-specific CD8+ T cells in the DLN
Given the prolonged residence and development of parasites in the skin after inoculation [27, 28], we hypothesized that migratory skin DCs may be critically involved in CD8+ T cell priming, either by direct presentation of sporozoite antigens or via transfer of such antigens to LN-resident DCs. To evaluate the contribution of skin-derived migratory DCs we used a knock-in mouse model in which the diphtheria toxin receptor (DTR) is expressed under the control of the murine langerin promoter [15]. Administration of diphtheria toxin (DT) to these animals rapidly depletes Langerhans cells in the epidermis (which only recover after ~2 weeks), langerin+ CD103+ DCs in the dermis (which begin to recover after ~ 5 days), and langerin-expressing skin-emigrant DCs in the DLN [15, 29–31] and S1A-C Fig. Though langerin is expressed by a population of LN-resident CD8α+ DCs [15, 30], this subset is missing on the C57BL/6 background [32]. Therefore, MuLangerin-DTR/EGFP mice on the C57BL/6 background allow us to examine the role of Langerhans cells and langerin+ dermal DCs in CD8+ T cell priming without affecting LN-resident CD8α+ DCs. Following depletion of these subsets with DT, we transferred OT-1 TCR transgenic T cells specific for the H-2Kb-SIINFEKL ligand into treated animals and immunized these mice with P. berghei CS5M sporozoites, a transgenic parasite expressing SIINFEKL within the CS protein [7]. To mimic the natural situation as closely as possible, mice were immunized through the bites of P. berghei CS5M-infected mosquitoes and the magnitude of the OT-1 response was examined in the DLNs, spleens, and livers 10 days later. There was no difference in the expansion nor antigen-specific IFN-γ production of OT-1 cells recovered from WT and MuLangerin-DTR/EGFP mice treated with DT (Fig. 1 and S1D Fig.). These data demonstrate that Langerhans cells and langerin+ dermal DCs are dispensable for the transport and/or presentation of sporozoite antigens to CD8+ T cells in the DLN.
Fig. 1. Langerhans cells and langerin+ dermal DCs are dispensable for anti-CS CD8+ T cell responses. 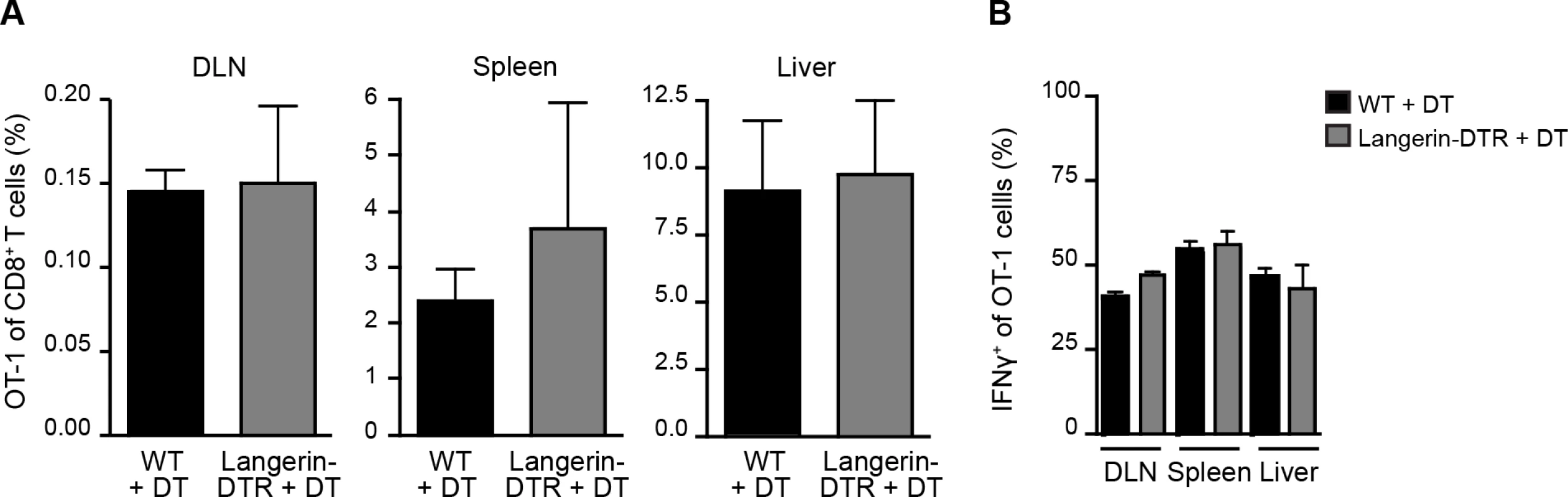
MuLangerin-DTR/EGFP and C57BL/6 mice received a single IP injection of DT (1 μg). 24 hours after DT treatment, 5×103 naive OT-1 cells were adoptively transferred to recipient mice. Mice were immunized through the bites of 20 irradiated P. berghei CS5M-infected mosquitoes 1 day after cell transfer and 2 days after DT treatment. A. Percentage of OT-1 cells of total CD8+ T cells recovered 10 days after sporozoite inoculation. B. Percentage of OT-1 cells producing IFN-γ as determined by intracellular staining and flow cytometry 10 days after inoculation by irradiated P. berghei CS5M–infected mosquito bites (mean ± SEM; n = 4–5/group). Data representative of 2 similar experiments. Sporozoite migration to the DLN is required for CD8+ T cell priming
Having established a nonessential role for Langerhans cells and langerin+ dermal DCs in sporozoite antigen presentation to CD8+ T cells, we hypothesized that the parasites themselves may deliver antigens to LN-resident DCs. To investigate the contribution of direct parasite access to the DLN for T cell activation, we applied two approaches. First, we limited parasite motility by antibody-mediated immobilization [33–35]. To this end, we pre-treated sporozoites with a CS-specific mAb before intradermal (ID) injection of the parasites. Additionally, we used monovalent Fab fragments in these experiments to avoid potential opsonization of the organism. We then assessed the parasite burden in the DLNs at 2 and 5 hours post-inoculation, as this is when we have previously detected the highest numbers of sporozoites in this organ [4]. Strikingly, both full-length CS-specific mAb (3D11) and monovalent Fab fragments (3D11:Fab) significantly reduced parasite burden in the DLN as compared to parasites incubated with a control mAb (Fig. 2A). Such a reduction in direct parasite access to the DLN was accompanied by a dramatic reduction in the clonal expansion of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells in the DLN as well as the spleen and liver (Fig. 2B), two sites of effector T cell migration after initial priming in the DLN [4].
Fig. 2. Sporozoite migration to the DLN is required for robust CD8+ T cell priming. 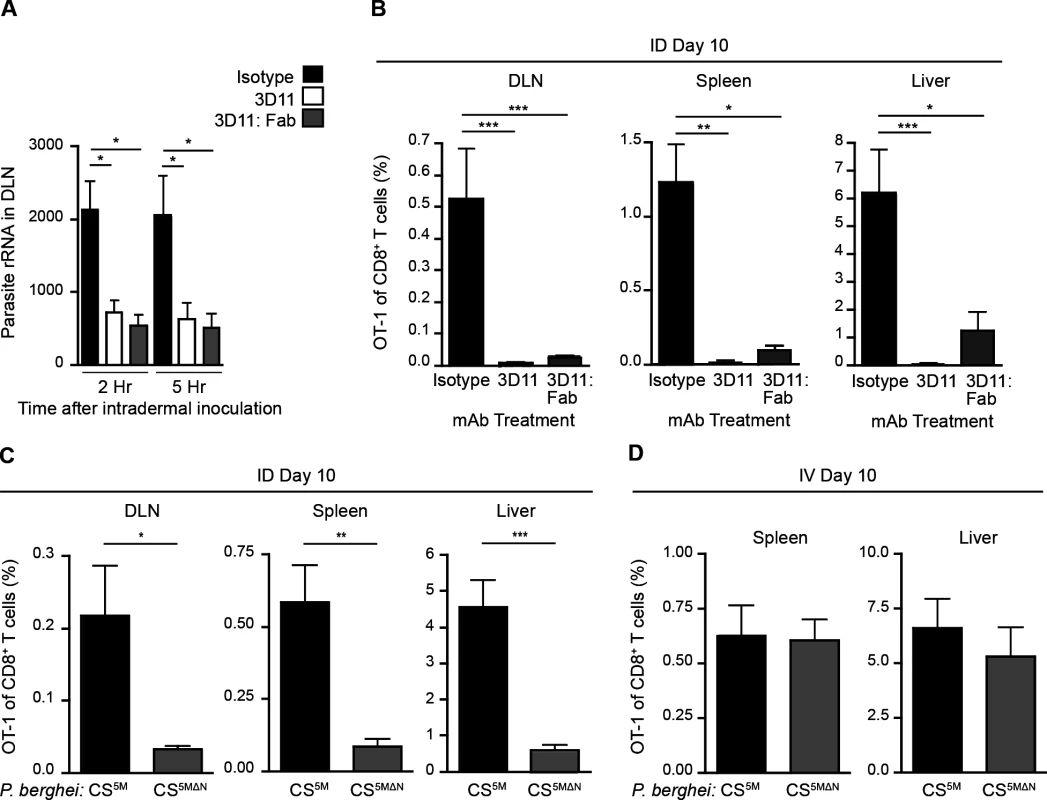
A. Naïve mice were injected ID with 2×104 P. berghei CS5M sporozoites treated for 20 minutes with 25 ug/ml of mAb, 2G3 (isotype control) or anti-P. berghei CS (3D11), or 16 ug/ml of Fab fragments prepared from the 3D11 antibody. Total RNA was isolated from DLNs at the indicated times. Parasite burdens were quantified by RT-PCR and pooled from 2 similar experiments; mean ± SEM, n = 10/group. B. 5×103 naïve OT-1 cells were transferred to mice. 24 hours later, mice were injected ID with 2×104 irradiated P. berghei CS5M sporozoites treated with 25 ug/ml 2G3 or 3D11 mAb or 16 ug/ml 3D11:Fab. Proportion of CD8+ T cells of OT-1 origin recovered 10 days post-inoculation; n = 5/group, mean ± SEM. Data representative of 2 similar experiments. C. 5×103 naïve OT-1 cells were transferred to mice. Mice were injected ID with 2×104 irradiated P. berghei CS5M or P. berghei CS5MΔN sporozoites 1 day after cell transfer. Proportion of CD8+ T cells of OT-1 origin recovered 10 days post-inoculation; n = 5/group, mean ± SEM. Data are representative of 4 similar experiments. D. 5×103 naive OT-1 cells were transferred to mice. 1 day after transfer mice were immunized IV with 2×104 irradiated P. berghei CS5M sporozoites or P. berghei CS5MΔN sporozoites. Expansion of OT-1 cells was measured 10 days after inoculation; mean ± SEM, n = 4–6/group. Data representative of 3 similar experiments. As a second approach, we generated mutant parasites that expressed the SIINFEKL epitope in a CS-restricted manner and were unable to migrate out of the skin due to a deletion in the N-terminal third of the CS protein [36], P. berghei CS5MΔN (S2A-C Fig.). In further agreement with the hypothesis that sporozoite motility is required for parasite entry into the lymphatics, P. berghei CS5MΔN sporozoites exhibited a severe impairment in their migration to the DLN (S2D Fig.). To evaluate the effect of these changes in DLN access on the development of cell-mediated immunity, mice were given CFSE-labeled OT-1 cells, injected ID with P. berghei CS5M or P. berghei CS5MΔN sporozoites, and OT-1 proliferation was examined 3 days later in the DLN. OT-1 proliferation was significantly reduced in mice injected with P. berghei CS5MΔN sporozoites (S2E and F Fig.). To determine whether the diminished CD8+ T cell response observed at day 3 was due to a delay in sporozoite migration to the DLN, rather than an absolute reduction, we measured the expansion of OT-1 cells in the DLN, spleen, and liver 10 days after ID inoculation of P. berghei CS5M or P. berghei CS5MΔN sporozoites. In line with our previous findings, we found that ID immunization with P. berghei CS5MΔN sporozoites led to drastically reduced OT-1 responses 10 days after immunization as compared to P. berghei CS5M sporozoites (Fig. 2C). Importantly, when injected IV, P. berghei CS5MΔN sporozoites were fully infectious (S2G Fig.) and induced similar OT-1 responses in the spleen and liver as compared to control parasites (P. berghei CS5M) (Fig. 2D). These findings demonstrate that the SIINFEKL epitope is expressed by the mutant parasite and is efficiently presented by APCs upon sporozoite access to lymphoid organs. Together, our studies with Fab-treated and transgenic parasites establish a critical role for sporozoite migration to the DLN in CD8+ T cell priming after ID inoculation.
Early acquisition of sporozoite-derived antigens by LN-resident DCs
The requirement for sporozoite-mediated delivery of antigen to the DLN was unexpected and led us to further characterize the location and behavior of parasites in this organ. P. berghei CS5M sporozoites were injected ID into footpads and the popliteal LNs were harvested at various times after sporozoite inoculation, fixed, sectioned, and stained for confocal analysis. We detected sporozoites in the DLN as early as 30 minutes after sporozoite inoculation with the majority of sporozoites in close association with CD169+ macrophages populating the subcapsular sinus (SCS) (Fig. 3A). By 1 hour after ID inoculation, sporozoites were still present in, or immediately adjacent to, the subcapsular or medullary sinuses and displayed the characteristic crescent shape of intact sporozoites (Fig. 3B). Higher magnification revealed the presence of particulate CS staining around sporozoites in the DLN (Fig. 3B), reminiscent of the CS vesicles first detected by transmission electron microscopy [37]. The presence of intact sporozoites peaked at around 2 hours post-inoculation but declined over the next few hours (Fig. 3C). The remaining intact sporozoites were enriched in deeper interfollicular LN areas and could be found in association with DCs (Fig. 3C and D). In contrast to intact parasites, particulate CS antigen was frequently observed in the LN parenchyma and underneath the B cell follicles (Fig. 3E), with the proportion of CS-positive events associated with DCs increasing with time (Fig. 3F).
Fig. 3. Localization, quantification, and dynamics of sporozoites in the DLN. 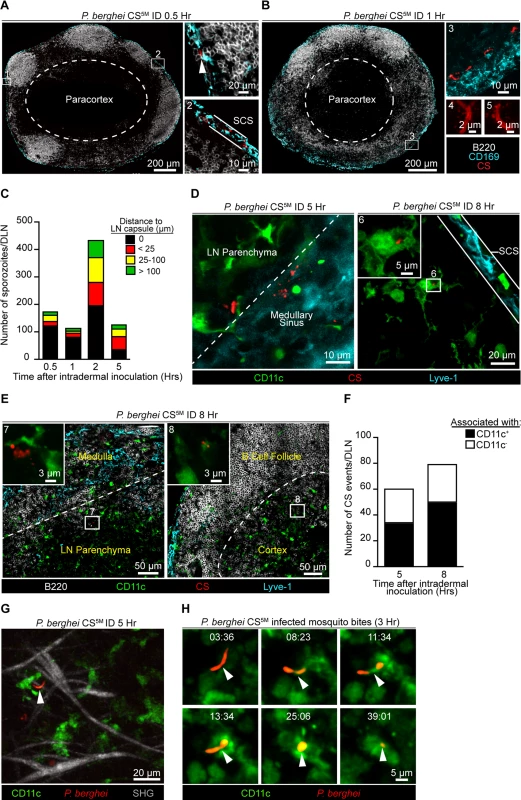
Immunofluorescence (IF) images depicting sporozoites and CS protein in the DLNs at various time points after ID inoculation with 1×105 P. berghei CS5M sporozoites. A. IF images of a DLN 30 minutes post-inoculation. Box 1 and 2 indicate enlarged areas of a DLN montage. Arrowhead denotes a sporozoite in the subcapsular sinus. Subcapsular sinus abbreviated as SCS. Colors of the word labels correspond to the colors of the stains here and throughout. White dotted line demarcates the paracortex. B. IF images of a DLN 1 hour post-inoculation. Box 3 indicates a maximum intensity projection of a 30 μm z stack. Box 4 and 5 are higher magnification images of sporozoites in the DLN 1 hour after ID inoculation. C. Number of sporozoites in whole DLNs at various time points after ID inoculation. The mean from one experiment is shown and is representative of 8 similar experiments. D. IF image of whole parasites interacting with DCs 5 and 8 hours post-inoculation. White dotted line marks boundary between the medullary sinus and LN parenchyma. Box 6 is an enlarged image of a DC-associated sporozoite. E. IF images of CS-positive events in a DLN 8 hours post-inoculation. White dotted line indicates boundary between the medullary sinus and LN parenchyma or the B cell follicle and cortex. Box 7 and 8 are higher magnification images of CS-positive events associated with DCs. F. Number of CS-positive events associated with DCs in the DLNs at 5 and 8 hours post-inoculation. Mean from one experiment is shown and is representative of 2 similar experiments. G. Maximum intensity projection of a 2-photon image from a CD11c-EYFP DLN 5 hours after ID inoculation with 1×105 P. berghei GFP sporozoites (pseudo-colored red). Second-harmonic generation (SHG, capsule); z stack of 30 μm. H. Time course of sporozoite uptake by a DC taken 3 hours after injection by infectious mosquito bites. Time, min:sec. See also S1 and S2 Movies. To observe the behavior and fate of sporozoites in the DLN in vivo, we injected GFP-expressing P. berghei CS5M sporozoites into the footpads of CD11c-EYFP reporter mice [38]. Using multiphoton intravital microscopy (MP-IVM) we were able to observe motile P. berghei CS5M GFP sporozoites in the superficial 100 μm of the DLN 5 hours after ID injection (Fig. 3G and S1 Movie). The sporozoites we observed in the DLN did not display gliding motility and moved more slowly than what has been reported in the skin [39]. The reduced motility we observed in the DLN is likely a constraint of the tissue microenvironment because sporozoites in the salivary glands of mosquitoes also exhibit decreased speeds as compared to sporozoites in the skin [39]. In agreement with our static imaging results showing DC-associated sporozoites, dynamic imaging revealed internalization of a live sporozoite by a DC after inoculation by infectious mosquito bites (Fig. 3H and S2 Movie). Together, these findings provide direct evidence for the migration of viable sporozoites to the DLN, their access to the parenchymal region after ID deposition, and direct uptake by LN-resident DCs.
CD8α+ DCs present sporozoite antigens to CD8+ T cells in the DLN
Our observations demonstrating the early acquisition of sporozoite-derived antigens by LN-resident DCs prompted us to evaluate the kinetics of CD8+ T cell priming in the DLN. To study antigen presentation in the DLN, we examined CD8+ T cell cluster formation around CD11c+ antigen-presenting cells (APCs) in situ, an established surrogate for antigen presentation [24, 25, 40–42]. In these studies, a large number of precursor cells (2.5–10×106 cells) was required to visualize antigen presentation by microscopy [24, 25, 40–42]. Accordingly, we fluorescently labeled and transferred 2×106 OT-1 cells to recipient mice before ID inoculation of sporozoites into the footpads. DLNs were fixed, sectioned, and stained for confocal analysis at 8, 16, 24, and 48 hours after ID inoculation (Fig. 4A). We detected OT-1 clusters in the paracortex and the boundary between the paracortex and follicles known as the cortical ridge [43] as early as 8 hours after parasite injection and these clusters increased in size and number by 16 hours. By 24 and 48 hours, the fluorescence intensity of the labeled OT-1 cells was substantially reduced, an effect likely due to dilution of the cytoplasmic label following OT-1 proliferation. Importantly, we did not observe cluster formation, nor reduced fluorescence of the labeled and transferred OT-1 cells, in mice injected with control parasites lacking the SIINFEKL epitope in CS (S3 Fig.).
Fig. 4. CD8α+ DCs present sporozoite antigens to CD8+ T cells in the LN cortex. 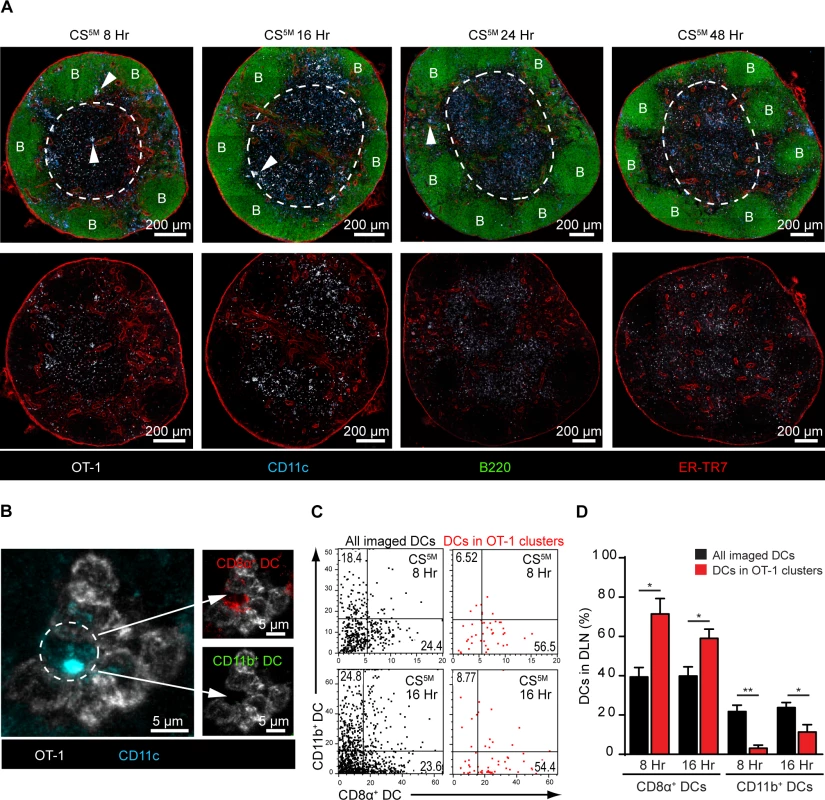
A. 2×106 naïve OT-1 cells were transferred to mice 1 day before ID inoculation with 1×105 irradiated P. berghei CS5M sporozoites. Popliteal LNs were harvested at the indicated time points and confocal images of popliteal LNs were prepared from 30 μm thick sections. White dotted line demarcates the cortex. B stands for B cell follicle. White arrowheads indicate examples of CD8+ T cell clusters. Representative images from 4 independent experiments with 2 mice per time point. B. Representative OT-1 cluster 8 hours after ID inoculation of P. berghei CS5M sporozoites. The phenotype of the DC within the cluster (depicted with a white dotted circle) was determined by histo-cytometry; CD8α+ DC signal (top panel) and CD11b+ DC signal (bottom panel) within the cluster. C. Representative histo-cytometry scatter plots depicting the percentage of all imaged DCs (black dots) and DCs associated with OT-1 clusters (red dots) in DLNs 8 and 16 hours after ID inoculation of sporozoites. D. The percentages of OT-1 cluster-associated CD8α+ or CD11b+ DCs (red bars) vs. all imaged DCs (black bars) were quantified from 3 independent experiments with 4 DLNs/time point (mean ± SEM). To examine directly the DC subset(s) involved in the presentation of sporozoite antigens, we employed histo-cytometry, an analytical microscopy method that provides quantitatively similar results to flow cytometry but additionally gathers spatial information, allowing for the quantification of cellular interactions in situ [14]. Because our results indicated a critical role for LN-resident DCs in CD8+ T cell responses against malaria sporozoites, we designed a 6-color panel to discriminate between CD8α+ and CD11b+ LN-resident DCs on stained LN sections (S4A and B Fig.). As before, we relied on OT-1 cluster formation as a surrogate for antigen presentation and quantified DCs in direct association with OT-1 clusters (S4B Fig.). Histo-cytometric analysis revealed the presence of CD8α+ DCs in direct physical contact with OT-1 clusters at 8 and 16 hours after ID inoculation of sporozoites (Fig. 4B-D). At these early time points, the great majority of OT-1 clusters were associated with CD8α+ DCs but not CD11b+ DCs, indicating CD8+ T cell activation by the LN-resident CD8α+ DC subset (Fig. 4C and D). By 24 hours, OT-1 clusters were smaller but still enriched for the presence of CD8α+ DCs (S4C-E Fig.), whereas OT-1 clusters were nearly absent at 48 hours (S4F Fig. and Fig. 4A). These results demonstrate activation of naïve antigen-specific CD8+ T cells by CD8α+ DCs in the DLN and are fully consistent with the accepted model of temporally distinct phases of T cell priming [41].
The early-sustained interactions between sporozoite antigen-bearing DCs and CD8+ T cells correlate with CD8+ T cell activation
It is well established that effector formation requires long-lasting, stable interactions between T cells and DCs bearing cognate antigen [41, 44]. We therefore utilized dynamic MP-IVM to examine the duration of CD8+ T clusters in the DLN. OT-1 cells and polyclonal CD8+ T cells expressing distinct fluorescent proteins were purified and transferred to recipient mice 1–4 days prior to sporozoite injection and imaging. The superficial 200 μm of the popliteal LN accessible to 2P imaging was imaged 7–12 hours after ID inoculation of P. berghei CS5M sporozoites (S3 Movie). The dynamic behavior of OT-1 cells differed from polyclonal CD8+ T cells in the same DLN 12 hours after ID inoculation (Fig. 5A), with OT-1 cells exhibiting a significantly reduced mean speed (Fig. 5B) and confinement ratio (Fig. 5C) as compared to polyclonal CD8+ T cells.
Fig. 5. CD8+ T cell activation correlates with durable interactions between CD8+ T cells and DCs. 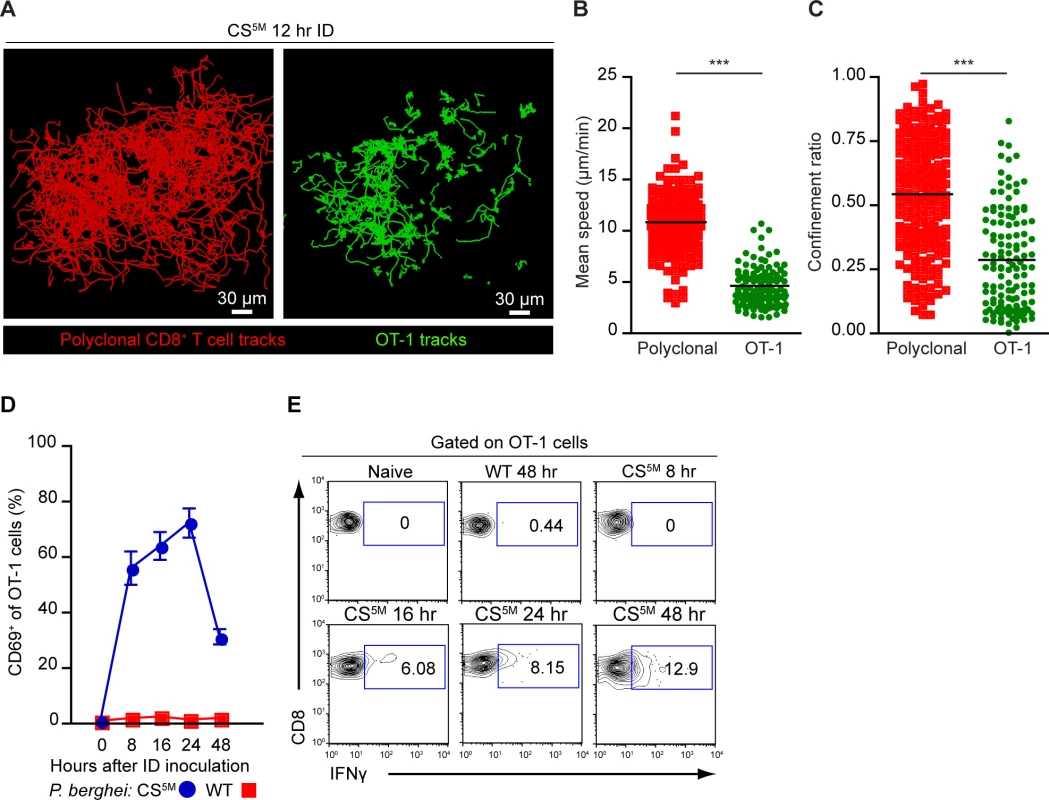
A-C. TdTomato-expressing polyclonal CD8+ T cells and GFP-expressing OT-1 cells were transferred to CD11c-YFP mice 1 day before ID inoculation with 1×105 irradiated P. berghei CS5M sporozoites. A. Tracks of polyclonal and OT-1 cells in the popliteal LN acquired by MP-IVM 12 hours after ID inoculation of sporozoites. Mean speed analysis (B) and confinement ratio (C) of TdTomato polyclonal CD8+ T cells and GFP OT-1 cells in situ, mean ± SEM. Data points represent individual cells from one experiment, representative of four similar experiments with mean value indicated. D and E. 1×106 OT-1 cells were transferred to naïve mice before ID inoculation with 1×105 irradiated P. berghei CS5M or P. berghei ANKA (WT) sporozoites. Single cell suspensions were prepared from popliteal LNs at the indicated time points. D. Proportion of OT-1 cells expressing CD69 based on a gate drawn on naïve OT-1 cells as controls. E. Percentage of OT-1 cells expressing IFN-γ at the indicated time points after ID inoculation. Data are representative of 2 similar experiments; mean ± SEM, n = 6/group. See also S3 Movie. To ascertain whether these physical interactions were correlated with OT-1 activation, we transferred OT-1 cells to recipient mice and injected mice ID with P. berghei CS5M sporozoites or P. berghei ANKA (WT) sporozoites that do not carry the SIINFEKL epitope in CS. Following sporozoite inoculation, DLNs were harvested and the up-regulation of CD69, an early activation marker, and the production of IFN-γ were examined on OT-1 cells by flow cytometry. By 8 hours post-inoculation with P. berghei CS5M sporozoites, the majority of OT-1 cells were CD69+. The proportion of CD69+ OT-1 cells steadily increased by 16 hours and decreased 24 hours after sporozoite inoculation (Fig. 5D). Antigen-stimulated OT-1 cells produced detectable levels of IFN-γ 16 hours after P. berghei CS5M injection with the proportion of IFN-γ-producing cells increasing modestly with time (Fig. 5E). In contrast, we did not observe up-regulation of CD69 or IFN-γ production by OT-1 cells in mice injected with parasites lacking the SIINFEKL epitope, P. berghei ANKA (WT) (Fig. 5D and E). These studies indicate that the early-sustained interactions between sporozoite antigen-bearing DCs and CD8+ T cells occurs under the conditions in which we observe robust T cell priming and activation.
LN-resident CD8α+ DCs are necessary for CD8+ T cell priming
Given the enrichment of CD8α+ DCs in OT-1 clusters at time points corresponding to CD8+ T cell activation, we next examined the contribution of these DCs to sporozoite-specific T cell activation in Batf3−/− mice that possess substantial defects in the numbers of CD8α+ DCs [45], [46]. CFSE-labeled OT-1 cells were transferred to WT and Batf3−/− C57BL/6 mice 1 day before ID inoculation with P. berghei CS5M sporozoites. The number of divided OT-1 cells was diminished by 50% in Batf3−/− C57BL/6 mice at day 3 in the DLN (Fig. 6A and B). To further investigate the requirement for CD8α+ DCs in the presentation of sporozoite antigens, we examined the OT-1 response in Batf3−/− C57BL/6 mice at several time points after exposure to P. berghei CS5M-infected mosquito bites. A significant reduction in OT-1 expansion was observed in the DLN, spleen, and liver of Batf3−/− C57BL/6 mice at day 8, 14, and 17 (Fig. 6C and S5A Fig.). Following a report demonstrating the potential presence of CD8α+ DCs in the DLNs of Batf3−/− C57BL/6 mice at steady state and in additional organs after administration of IL-12 [47], we repeated the priming experiments in Batf3−/− mice on the 129/SvEV background in which CD8α+ DCs and langerin+ dermal DCs are largely absent and observed a 75% reduction in OT-1 expansion (S5B and C Fig.). Besides the important role for CD8α+ DCs in the activation of CS-specific CD8+ T cells, we also found a reduction in CD8+ T cell priming in the absence of CD169+ macrophages (S6 Fig.). Despite a reduction in OT-1 expansion in DT-treated CD169-DTR mice, we did not observe OT-1 cluster formation around CD169+ macrophages lining the subcapsular or medullary sinuses (Fig. 4) and therefore conclude that CD169+ sinus-associated macrophages may play an indirect role in the generation of optimal CD8+ T cell responses.
Fig. 6. CD8α+ DCs are necessary for the presentation of sporozoite antigens to CD8+ T cells. 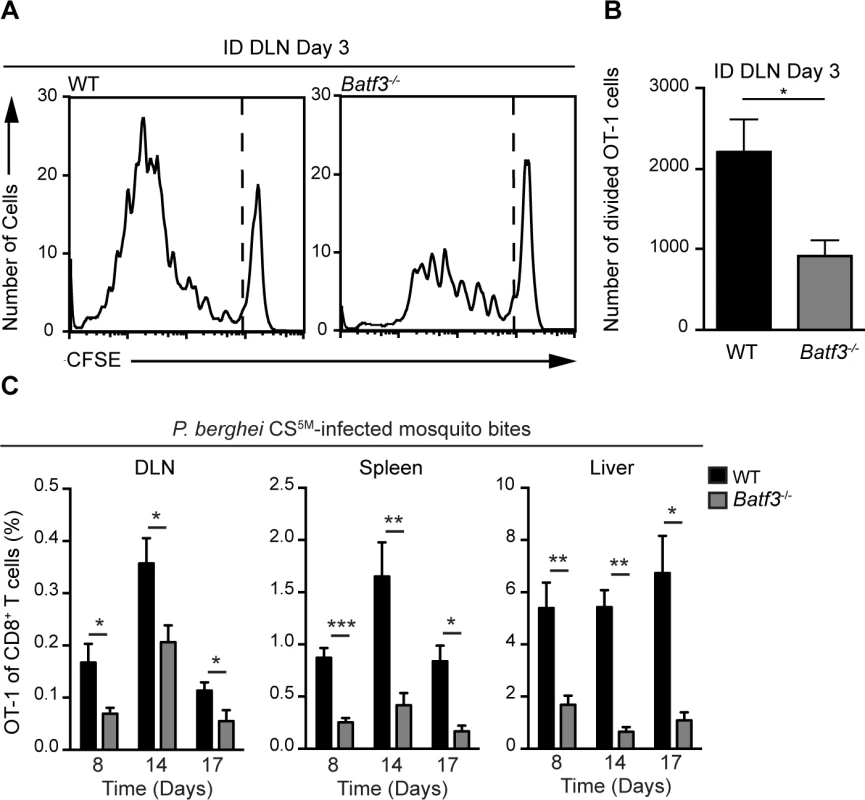
A and B. WT and Batf3−/− mice received 1×106 CFSE-labeled OT-1 cells 1 day prior to ID injection of 2×104 irradiated P. berghei CS5M sporozoites. DLNs were collected 3 days post-inoculation. A. Representative CFSE profiles of OT-1 cells from 1 of 3 similar experiments. B. Expansion of OT-1 cells in the DLN; mean ± SEM, n = 7/group. Data are representative of 3 similar experiments. C. 0.5–1×104 naive OT-1 cells were transferred to WT and Batf3−/− mice 1 day before immunization via 20 irradiated P. berghei CS5M-infected mosquito bites. Responses were examined 8, 14, and 17 days post-inoculation. Proportion of CD8+ T cells of OT-1 origin after P. berghei CS5M-infected mosquito bites. Data are pooled from 2 similar experiments mean ± SEM; n = 9/group (day 8) and n = 6/group (day 14 and 17). Discussion
Plasmodium sporozoites are introduced into the dermis of their mammalian host by infectious mosquito bites (reviewed in [26]), and a proportion of these sporozoites enter the lymphatics early after inoculation [4, 39, 48]. Following this natural route of parasite delivery, CS-specific CD8+ T cells are primed in the LNs draining the site of sporozoite inoculation [4]. Here, we present clear evidence indicating that direct parasite access to the DLN is required for the induction of CD8+ T cells directed against P. berghei CS (Fig. 7). Two independent experimental approaches were used to establish the immunological significance of parasites in the DLN. First, immobilization of sporozoites through pre-treatment with a CS-specific mAb, or monovalent Fab fragments derived from this antibody, resulted in reduced parasite burdens in the DLN and severely diminished CD8+ T cell responses directed against an antigenic determinant in CS. Second, mutant parasites with a defect in their ability to exit the skin and enter the DLNs also generated poor CD8+ T cell responses when injected ID. The relationship between live, motile sporozoites and the induction of robust CD8+ T cell responses is further supported by the observation that when dead sporozoites are injected ID they do not reach the DLN [39] and do not induce CD8+ T cell responses [4]. Reduced CS-specific CD8+ T cell responses were also observed in the spleen following IV injection of dead sporozoites [49]. This was surprising because IV injected sporozoites have direct access to the spleen, the site of CTL activation after IV immunization [50]. Therefore, the importance of live sporozoites in the development of CD8+ T cells likely extends beyond efficient drainage to lymphoid organs and may indicate a requirement for sporozoite motility within these organs.
Fig. 7. Summarizes Figs. 1–6 as a model. 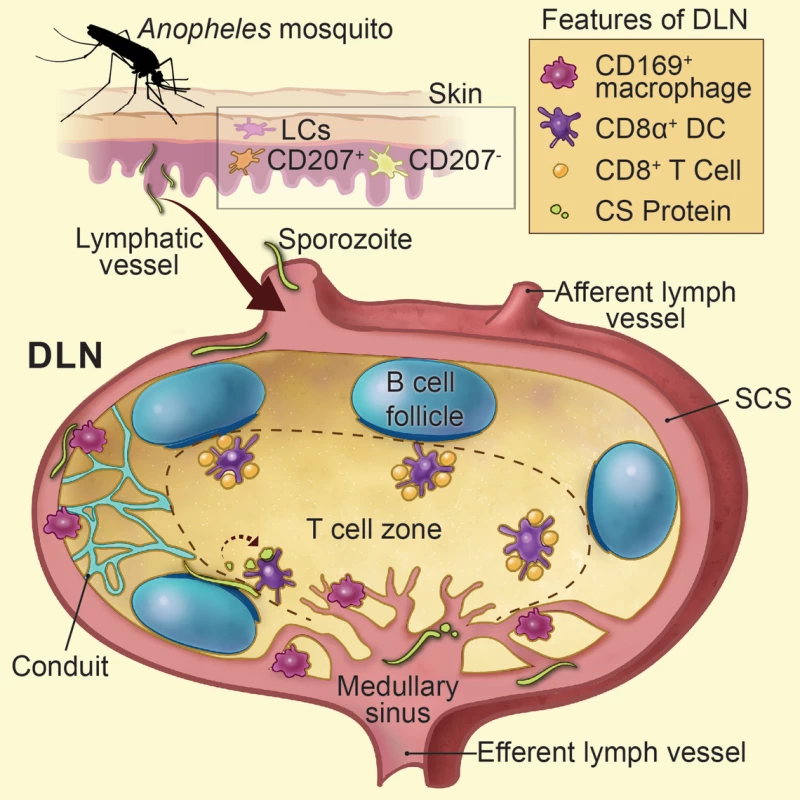
Sporozoite-mediated delivery of malaria antigens to the DLNs is required for CD8+ T cell priming. Anopheline mosquitoes inject sporozoites into the skin of their mammalian host, a tissue populated by epidermal Langerhans cells, langerin+ dermal DCs (CD207+), and langerin- dermal DCs (CD207-). Following sporozoite inoculation into the dermis, a proportion of sporozoites enter the DLNs via the afferent lymphatic vessel and are found in close association with CD169+ macrophages lining the subcapsular and medullary sinuses. LN-resident DCs directly sample and phagocytose sporozoites and sporozoite-derived CS particles within the LN parenchyma. Sporozoite-specific CD8+ T cells are primed by LN-resident CD8α+ DCs residing along the cortical ridge and the T cell zone of the DLN as early as 8 hours after immunization. Printed with permission from Heidi Sinsel, 2014. Sporozoites are renowned for their ability to migrate through many different cell types [51–54]. As sporozoites glide they release trails of CS comprised of 25–90 nm beadlike particles [37]. Our confocal analysis revealed the accumulation of particulate CS around intact parasites 1 to 2 hours after sporozoite injection. Based on the nature of CS staining and the timing of our in vivo observations, we hypothesize that particulate CS is actively shed by motile sporozoites in the DLN and may represent a source of antigen for cross-presentation by LN-resident DCs. In addition, we frequently observed sporozoites underneath the B cell follicles and immediately adjacent to the cortical ridge of the DLN. Therefore, live sporozoites may provide a source of CS that can be directly sampled and presented by DCs in the cortical ridge and paracortex of the DLN, the location of CD8+ T cell priming in our model. In further support of this idea, we visualized abundant stores of DC-associated CS in the DLN, which could derive from internalization of shed CS or direct uptake of live sporozoites as shown in S2 Movie.
The observation of CD8+ T cell cluster formation and IFN-γ production as early as 8 and 16 hours post-immunization, respectively, is in agreement with a limited role for migratory skin-DCs since these cells require anywhere from 16 hours to 5 days to migrate to the DLN [15, 55]. In addition, we observed robust CD8+ T cell priming in the absence of langerin+ dermal DCs and Langerhans cells using the MuLangerin-DTR/EGFP mouse model. However, it should be noted that migratory langerin- dermal DCs remain in the skin of DT-treated MuLangerin-DTR/EGFP mice [15] and two vaccine models have demonstrated the involvement of these cells in the presentation of skin-derived antigens to CD8+ T cells [56, 57]. Nonetheless, the location of CD8+ T cell cluster formation complements the diminished priming we observed in Batf3-deficient mice because CD8α+ DCs are known to populate the cortical ridge and paracortex of the DLN [14, 43]. Importantly, histo-cytometric analysis of LN sections revealed a significant enrichment of CD8α+ DCs in association with OT-1 clusters at time points corresponding to T cell activation. Although sporozoites can invade and develop within LN-resident CD11b+ myeloid cells [58], our studies demonstrate a pivotal role for CD8α+ DCs in the presentation of sporozoite antigens to CD8+ T cells.
The reduced CD8+ priming we observed in mice lacking CD169+ macrophages further emphasizes the importance of LN-resident APCs in liver stage immunity. Because OT-1 clusters were not directly associated with CD169+ macrophages, we conclude that these cells play an indirect role in CD8+ T cell priming. CD169+ macrophages may facilitate CD8+ T cell priming via the capture and transfer of antigen to cross-presenting DCs, a phenomenon shown to take place in the spleen following delivery of blood-borne antigens [59], or in a cytokine-dependent manner as demonstrated for LN-resident innate lymphoid cells [60]. Regardless of the mechanism, elucidating the contribution of CD169+ macrophages to liver stage immunity remains a key direction for future research.
Others have shown a requirement for CD8α+ DCs in the presentation of Plasmodium blood and liver stage antigens [8, 9, 61–62]. Our study now documents the presentation of sporozoite antigens by LN-resident CD8α+ DCs in situ while providing a potential explanation—direct parasite access to these DC subsets—for the superior immunogenicity of live versus dead parasites. We have based our analysis on the immunodominant CS protein [63]; however, it is possible that CD8α+ DCs present additional liver stage antigens in the liver draining lymph nodes or the liver site of infection, as shown previously [9]. Because liver stage antigens elicit broad, cross-stage protection [64–65], an important future direction will be to evaluate the contribution of CD8α+ DCs to the generation of CD8+ T cells against these antigens. The recent success of the IV administered live, attenuated P. falciparum sporozoite vaccine (PfSPZ) [16], along with the discovery of a human homologue of murine CD8α+ DCs [66–68], suggests that antigen delivery to this DC subset may also be critical for CTL responses in humans. Because large-scale vaccination with the IV administered PfSPZ vaccine is likely infeasible, there is a growing need to improve the efficacy of non-IV routes, which have been shown to be inefficient in mice [6, 69], and suboptimal in humans [70]. One promising strategy is to use adjuvants to reduce the number of irradiated sporozoites required to confer sterile immunity after ID immunization [69]. Given the vital role for CD8α+ DCs in the presentation of malaria antigens, and the unique expression of pattern recognition receptors among different DC subsets [71–72], it will be interesting to determine whether adjuvant activation of CD8α+ DCs can provide better protection after ID immunization.
The antagonistic effect of anti-sporozoite antibodies on CD8+ T cell priming reported here and elsewhere [7] suggests that humoral immunity may be generated at the expense of cellular immunity. Therefore, it may be difficult to generate robust CD8+ T cell responses in individuals with high-titer anti-CS antibodies. This assertion is based on the following observations: (1) antibody-treated parasites are immobilized in the skin [35]; (2) immobilized parasites are cleared by CD11b+ leukocytes in the skin [51]; and (3) skin-resident CD11b+ leukocytes are largely dispensable for CS-specific CD8+ T cell responses (reported here). Thus, a major challenge for the malaria vaccine effort will be to incorporate the very behaviors required for successful parasite infection—cell traversal and cell invasion—into a vaccine that elicits long-lasting, protective immunity.
A critical question remains: Why do malaria parasites go to the DLN? This question gains additional significance when one considers that the LN is dispensable for parasite development but imperative for host immune responses. As there is no evidence for sporozoite chemotaxis to lymphatic vessels, parasite entry into the lymphatic vessels in the skin appears to be an accidental but migration-dependent process. Importantly, this phenomenon is not unique to rodent malaria models but was also observed in early human studies [73]. Together, these results underscore the importance of live, motile sporozoites in the induction of CD8+ T cell responses and thus, have implications for whole parasite vaccine efforts.
Materials and Methods
Mice
All animal procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Johns Hopkins University (Protocol number: MO13H123) following the NIH guidelines for animal housing and care or performed according to protocols approved by the NIAID and NIH Animal Care and Use Committee. A detailed list of mouse strains can be found in the S1 Methods section.
Parasites and immunizations
P. berghei CS5M parasites [7] and P. berghei ANKA parasites expressing GFP under the HSP70 promoter (P. berghei-ConF) have been described previously [51]. P. berghei CS5MΔN parasites were created by transfection of P. berghei ANKA with a linearized pR-CSRepΔN5M plasmid. The pR-CSRepΔN5M plasmid was generated by ligating an EagI-PacI digestion product of the pCSRep5M plasmid into the pR-CSRepΔN plasmid containing the N-terminal deletion of the CSP locus and a drug selection cassette [36]. Mutant parasites were selected by pyrimethamine and cloned by limiting dilution. Sporozoites were dissected by hand from Anopheles stephensi salivary glands, radiation-attenuated in a cesium radiator at 20,000 rad., and injected ID with a nanofil syringe equipped with a 33 gauge needle (World Precision Instruments, Sarasota, FL). Alternatively, mice were injected by the bites of 20–30 irradiated day 21 P. berghei CS5M-infected mosquitoes. P. berghei CS5M-GFP parasites were generated by crossing P. berghei CS5M parasites with P. berghei ConF parasites, followed by selection as described previously [74].
Quantification of parasite RNA in DLN
At the indicated time points, LNs were harvested in TRIzol Reagent (Life Technologies) and parasite RNA was extracted according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Parasite burden was measured by RT-PCR using primers that recognize P. berghei specific sequences within the 18S rRNA and SYBR Green (Applied Biosystems) as outlined previously [75]. Parasite burdens were normalized with GAPDH expression.
Lymphocyte isolation
Single cell suspensions were prepared by grinding the spleen and DLNs between the rough sides of 2 microscope slides and by filtering with nylon mesh. Liver homogenates were passed over a 35% percoll gradient and filtered through nylon mesh. Lymphocytes were resuspended in DMEM supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS), 50 mM sodium bicarbonate, 2mM glutamine, 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin, 25 mM HEPES.
Adoptive CD8+ T cell transfer
OT-1 T cells or polyclonal control CD8+ T cells were sorted with a MACS CD8-negative selection kit (Miltenyi). Prior to cell transfer, the quality of purification was verified by flow cytometry using antibodies against Vα2 and CD8. Cells of approximately 90% purity were stained and transferred 1 day before sporozoite inoculation.
Quantification of CD8+ T cell expansion in vivo
5×103 OT-1 (CD45.1+) cells were transferred IV to recipient (CD45.2+) mice 1 day before needle or mosquito bite inoculation of irradiated sporozoites. In some experiments, expansion of OT-1 cells was measured by flow cytometry on days 8, 10, 14, or 17. In other experiments, 1–2×106 OT-1 cells were labeled with 10 μM CFSE (Invitrogen) or 100 μM CellTracker Blue CMF2HC (Invitrogen) and transferred IV to recipient mice. OT-1 cluster formation and proliferation were evaluated 8–72 hours after sporozoite inoculation.
Confocal microscopy and histo-cytometry
Detailed methods for sample preparation, imaging, and data analysis are available in the S1 Methods section.
Multi-photon intravital imaging
Mice were anesthetized and popliteal LNs were exposed. MP-IVM was performed by a protocol modified from a previous report [76].
Analysis
Flow cytometric data was analyzed with FlowJo software (TreeStar). Raw imaging data were processed and analyzed with Imaris software (Bitplane). Differences between two groups were compared using a Student’s t test (two-tailed) for normal distributions or Mann-Whitney test for non-normal distributions. One-way analysis of variance with Tukey post-test was used to compare differences between more than two groups. (ns = not significant, * = P < 0.05, ** = P < 0.01, *** = P < 0.001)
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. Nussenzweig RS, Vanderberg J, Most H, Orton C (1967) Protective immunity produced by the injection of x-irradiated sporozoites of Plasmodium berghei. Nature 216 : 160–162. 6057225
2. Romero P, Maryanski JL, Corradin G, Nussenzweig RS, Nussenzweig V, et al. (1989) Cloned cytotoxic T cells recognize an epitope in the circumsporozoite protein and protect against malaria. Nature 341 : 323–326. 2477703
3. Weiss WR, Berzofsky JA, Houghten RA, Sedegah M, Hollindale M, et al. (1992) A T cell clone directed at the circumsporozoite protein which protects mice against both Plasmodium yoelii and Plasmodium berghei. J Immunol 149 : 2103–2109. 1517574
4. Chakravarty S, Cockburn IA, Kuk S, Overstreet MG, Sacci JB, et al. (2007) CD8+ T lymphocytes protective against malaria liver stages are primed in skin-draining lymph nodes. Nat Med 13 : 1035–1041. 17704784
5. Cockburn IA, Amino R, Kelemen RK, Kuo SC, Tse S-W, et al. (2013) In vivo imaging of CD8+ T cell-mediated elimination of malaria liver stages. PNAS 110 : 9090–9095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1303858110 23674673
6. Obeid M, Franetich JF, Lorthiois A, Gego A, Grüner AC, et al. (2013) Skin-draining lymph node priming is sufficient to induce sterile immunity against pre-erythrocytic malaria. EMBO Mol Med 5 : 250–263. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201201677 23255300
7. Cockburn IA, Tse SW, Radtke AJ, Srinivasan P, Chen YC, et al. (2011) Dendritic cells and hepatocytes use distinct pathways to process protective antigen from Plasmodium in vivo. PLoS Pathog 7: e1001318. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001318 21445239
8. Lau LS, Fernandez-Ruiz D, Mollard V, Sturm A, Neller MA, et al. (2014) CD8+ T cells from a novel T cell receptor transgenic mouse induce liver-stage immunity that can be boosted by blood-stage infection in rodent malaria. PLoS Pathog 10: e1004135. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004135 24854165
9. Jobe O, Donofrio G, Sun G, Liepinsh D, Schwenk R, et al. (2009) Immunization with radiation-attenuated Plasmodium berghei sporozoites induces liver cCD8alpha+ DC that activate CD8+ T cells against liver-stage malaria. PLoS One 4: e5075. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005075 19347042
10. Jung S, Unutmaz D, Wong P, Sano G, De los Santos K, et al. (2002) In vivo depletion of CD11c+ dendritic cells abrogates priming of CD8+ T cells by exogenous cell-associated antigens. Immunity 17 : 211–220. 12196292
11. Plebanski M, Hannan CM, Behboudi S, Flanagan KL, Apostolopoulos V, et al. (2005) Direct processing and presentation of antigen from malaria sporozoites by professional antigen-presenting cells in the induction of CD8 T-cell responses. Immunol Cell Biol 83 : 307–312. 15877610
12. Heath WR, Carbone FR (2009) Dendritic cell subsets in primary and secondary T cell responses at body surfaces. Nat Immunol 10 : 1237–1244. doi: 10.1038/ni.1822 19915624
13. Igyarto BZ, Haley K, Ortner D, Bobr A, Gerami-Nejad M, et al. (2011) Skin-resident murine dendritic cell subsets promote distinct and opposing antigen-specific T helper cell responses. Immunity 35 : 260–272. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.06.005 21782478
14. Gerner MY, Kastenmuller W, Ifrim I, Kabat J, Germain RN (2012) Histo-cytometry: a method for highly multiplex quantitative tissue imaging analysis applied to dendritic cell subset microanatomy in lymph nodes. Immunity 37 : 364–376. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.07.011 22863836
15. Kissenpfennig A, Henri S, Dubois B, Laplace-Builhe C, Perrin P, et al. (2005) Dynamics and function of Langerhans cells in vivo: dermal dendritic cells colonize lymph node areas distinct from slower migrating Langerhans cells. Immunity 22 : 643–654. 15894281
16. Seder RA, Chang LJ, Enama ME, Zephir KL, Sarwar UN, et al. (2013) Protection against malaria by intravenous immunization with a nonreplicating sporozoite vaccine. Science 341 : 1359–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.1241800 23929949
17. Chtanova T, Han SJ, Schaeffer M, van Dooren GG, Herzmark P, et al. (2009) Dynamics of T cell, antigen-presenting cell, and pathogen interactions during recall responses in the lymph node. Immunity 31 : 342–355. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.06.023 19699173
18. John B, Harris TH, Tait ED, Wilson EH, Gregg B, et al. (2009) Dynamic Imaging of CD8(+) T cells and dendritic cells during infection with Toxoplasma gondii. PLoS Pathog 5: e1000505. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000505 19578440
19. Iezzi G, Frohlich A, Ernst B, Ampenberger F, Saeland S, et al. (2006) Lymph node resident rather than skin-derived dendritic cells initiate specific T cell responses after Leishmania major infection. J Immunol 177 : 1250–1256. 16818784
20. Ritter U, Meissner A, Scheidig C, Korner H (2004) CD8 alpha - and Langerin-negative dendritic cells, but not Langerhans cells, act as principal antigen-presenting cells in leishmaniasis. Eur J Immunol 34 : 1542–1550. 15162423
21. Allan RS, Waithman J, Bedoui S, Jones CM, Villadangos JA, et al. (2006) Migratory dendritic cells transfer antigen to a lymph node-resident dendritic cell population for efficient CTL priming. Immunity 25 : 153–162. 16860764
22. Belz GT, Smith CM, Kleinert L, Reading P, Brooks A, et al. (2004) Distinct migrating and nonmigrating dendritic cell populations are involved in MHC class I-restricted antigen presentation after lung infection with virus. PNAS 101 : 8670–8675. 15163797
23. Hickman HD, Takeda K, Skon CN, Murray FR, Hensley SE, et al. (2008) Direct priming of antiviral CD8+ T cells in the peripheral interfollicular region of lymph nodes. Nat Immunol 9 : 155–165. doi: 10.1038/ni1557 18193049
24. Kastenmuller W, Brandes M, Wang Z, Herz J, Egen JG, et al. (2013) Peripheral prepositioning and local CXCL9 chemokine-mediated guidance orchestrate rapid memory CD8+ T cell responses in the lymph node. Immunity 38 : 502–513. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.11.012 23352234
25. Norbury CC, Malide D, Gibbs JS, Bennink JR, Yewdell JW (2002) Visualizing priming of virus-specific CD8+ T cells by infected dendritic cells in vivo. Nat Immunol 3 : 265–271. 11828323
26. Sinnis P, Zavala F (2012) The skin: where malaria infection and the host immune response begin. Semin Immunopathol 34 : 787–792. doi: 10.1007/s00281-012-0345-5 23053392
27. Gueirard P, Tavares J, Thiberge S, Bernex F, Ishino T, et al. (2010) Development of the malaria parasite in the skin of the mammalian host. PNAS 107 : 18640–18645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1009346107 20921402
28. Voza T, Miller JL, Kappe SH, Sinnis P (2012) Extrahepatic exoerythrocytic forms of rodent malaria parasites at the site of inoculation: clearance after immunization, susceptibility to primaquine, and contribution to blood-stage infection. Infect Immun 80 : 2158–2164. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00246-12 22431651
29. Bursch LS, Wang L, Igyarto B, Kissenpfennig A, Malissen B, et al. (2007) Identification of a novel population of Langerin+ dendritic cells. J Exp Med 204 : 3147–3156. 18086865
30. Ginhoux F, Collin MP, Bogunovic M, Abel M, Leboeuf M, et al. (2007) Blood-derived dermal langerin+ dendritic cells survey the skin in the steady state. J Exp Med 204 : 3133–3146. 18086862
31. Poulin LF, Henri S, de Bovis B, Devilard E, Kissenpfennig A, et al. (2007) The dermis contains langerin+ dendritic cells that develop and function independently of epidermal Langerhans cells. J Exp Med 204 : 3119–3131. 18086861
32. Flacher V, Douillard P, Ait-Yahia S, Stoitzner P, Clair-Moninot V, et al. (2008) Expression of langerin/CD207 reveals dendritic cell heterogeneity between inbred mouse strains. Immunology 123 : 339–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02785.x 18217955
33. Hollingdale MR, Zavala F, Nussenzweig RS, Nussenzweig V (1982) Antibodies to the protective antigen of Plasmodium berghei sporozoites prevent entry into cultured cells. J Immunol 128 : 1929–1930. 7037957
34. Stewart MJ, Nawrot RJ, Schulman S, Vanderberg JP (1986) Plasmodium berghei sporozoite invasion is blocked in vitro by sporozoite-immobilizing antibodies. Infect Immun 51 : 859–864. 3512436
35. Vanderberg JP, Frevert U (2004) Intravital microscopy demonstrating antibody-mediated immobilisation of Plasmodium berghei sporozoites injected into skin by mosquitoes. Int J Parasitol 34 : 991–996. 15313126
36. Coppi A, Natarajan R, Pradel G, Bennett BL, James ER, et al. (2011) The malaria circumsporozoite protein has two functional domains, each with distinct roles as sporozoites journey from mosquito to mammalian host. J Exp Med 208 : 341–356. doi: 10.1084/jem.20101488 21262960
37. Stewart MJ, Vanderberg JP (1992) Electron microscopic analysis of circumsporozoite protein trail formation by gliding malaria sporozoites. J Protozool 39 : 663–671. 1453354
38. Lindquist RL, Shakhar G, Dudziak D, Wardemann H, Eisenreich T, et al. (2004) Visualizing dendritic cell networks in vivo. Nat Immunol 5 : 1243–1250. 15543150
39. Amino R, Thiberge S, Martin B, Celli S, Shorte S, et al. (2006) Quantitative imaging of Plasmodium transmission from mosquito to mammal. Nat Med 12 : 220–224. 16429144
40. Ingulli E, Mondino A, Khoruts A, Jenkins MK (1997) In vivo detection of dendritic cell antigen presentation to CD4(+) T cells. J Exp Med 185 : 2133–2141. 9182685
41. Mempel TR, Henrickson SE, Von Andrian UH (2004) T-cell priming by dendritic cells in lymph nodes occurs in three distinct phases. Nature 427 : 154–159. 14712275
42. Stoll S, Delon J, Brotz TM, Germain RN (2002) Dynamic imaging of T cell-dendritic cell interactions in lymph nodes. Science 296 : 1873–1876. 12052961
43. Katakai T, Hara T, Lee JH, Gonda H, Sugai M, et al. (2004) A novel reticular stromal structure in lymph node cortex: an immuno-platform for interactions among dendritic cells, T cells and B cells. Int Immunol 16 : 1133–1142. 15237106
44. Germain RN, Jenkins MK (2004) In vivo antigen presentation. Curr Opin Immunol 16 : 120–125. 14734120
45. Edelson BT, Kc W, Juang R, Kohyama M, Benoit LA, et al. (2010) PeripheralCD103+ dendritic cells form a unified subset developmentally related to CD8alpha+ conventional dendritic cells. J Exp Med 207 : 823–836. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091627 20351058
46. Hildner K, Edelson BT, Purtha WE, Diamond M, Matsushita H, et al. (2008) Batf3 deficiency reveals a critical role for CD8alpha+ dendritic cells in cytotoxic T cell immunity. Science 322 : 1097–1100. doi: 10.1126/science.1164206 19008445
47. Tussiwand R, Lee WL, Murphy TL, Mashayekhi M, Kc W, et al. (2012) Compensatory dendritic cell development mediated by BATF-IRF interactions. Nature 490 : 502–507. doi: 10.1038/nature11531 22992524
48. Yamauchi LM, Coppi A, Snounou G, Sinnis P (2007) Plasmodium sporozoites trickle out of the injection site. Cell Microbiol 9 : 1215–1222. 17223931
49. Hafalla JC, Rai U, Morrot A, Bernal-Rubio D, Zavala F, et al. (2006) Priming of CD8+ T cell responses following immunization with heat-killed Plasmodium sporozoites. Eur J Immunol 36 : 1179–1186. 16598821
50. Sano G, Hafalla JC, Morrot A, Abe R, Lafaille JJ, et al. (2001) Swift development of protective effector functions in naive CD8(+) T cells against malaria liver stages. J Exp Med 194 : 173–180. 11457892
51. Amino R, Giovannini D, Thiberge S, Gueirard P, Boisson B, et al. (2008) Host cell traversal is important for progression of the malaria parasite through the dermis to the liver. Cell Host Microbe 3 : 88–96. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2007.12.007 18312843
52. Coppi A, Tewari R, Bishop JR, Bennett BL, Lawrence R, et al. (2007) Heparan sulfate proteoglycans provide a signal to Plasmodium sporozoites to stop migrating and productively invade host cells. Cell Host Microbe 2 : 316–327. 18005753
53. Mota MM, Pradel G, Vanderberg JP, Hafalla JC, Frevert U, et al. (2001) Migration of Plasmodium sporozoites through cells before infection. Science 291 : 141–144. 11141568
54. Vanderberg JP, Chew S, Stewart MJ (1990) Plasmodium sporozoite interactions with macrophages in vitro: a videomicroscopic analysis. J Protozool 37 : 528–536. 2086782
55. Itano AA, McSorley SJ, Reinhardt RL, Ehst BD, Ingulli E, et al. (2003) Distinct dendritic cell populations sequentially present antigen to CD4 T cells and stimulate different aspects of cell-mediated immunity. Immunity 19 : 47–57. 12871638
56. Bachy V, Hervouet C, Becker PD, Chorro L, Carlin LM, et al. (2013) Langerin negative dendritic cells promote potent CD8+ T-cell priming by skin delivery of live adenovirus vaccine microneedle arrays. PNAS 110 : 3041–3046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1214449110 23386724
57. Kastenmuller K, Wille-Reece U, Lindsay RW, Trager LR, Darrah PA, et al. (2011) Protective T cell immunity in mice following protein-TLR7/8 agonist-conjugate immunization requires aggregation, type I IFN, and multiple DC subsets. J Clin Invest 121 : 1782–1796. doi: 10.1172/JCI45416 21540549
58. Mac-Daniel L, Buckwalter MR, Berthet M, Virk Y, Yui K, et al. (2014) Local immune response to injection of Plasmodium sporozoites into the skin. J Immunol 193 : 1246–1257. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302669 24981449
59. Backer R, Schwandt T, Greuter M, Oosting M, Jungerkes F, et al. (2010) Effective collaboration between marginal metallophilic macrophages and CD8+ dendritic cells in the generation of cytotoxic T cells. PNAS 107 : 216–221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909541107 20018690
60. Kastenmuller W, Torabi-Parizi P, Subramanian N, Lammermann T, Germain RN (2012) A spatially-organized multicellular innate immune response in lymph nodes limits systemic pathogen spread. Cell 150 : 1235–1248. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.07.021 22980983
61. Lundie RJ, de Koning-Ward TF, Davey GM, Nie CQ, Hansen DS, et al. (2008) Blood-stage Plasmodium infection induces CD8+ T lymphocytes to parasite-expressed antigens, largely regulated by CD8alpha+ dendritic cells. PNAS 105 : 14509–14514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0806727105 18799734
62. Piva L, Tetlak P, Claser C, Karjalainen K, Renia L, et al. (2012) Cutting edge: Clec9A+ dendritic cells mediate the development of experimental cerebral malaria. J Immunol 189 : 1128–1132. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201171 22732587
63. Arun Kumar K, Sano G-i, Boscardin S, Nussenzweig RS, Nussenzweig MC, et al. (2006) The circumsporozoite protein is an immunodominant protective antigen in irradiated sporozoites. Nature 444 : 937–940. 17151604
64. Butler NS, Schmidt NW, Vaughan AM, Aly AS, Kappe SH, et al. (2011) Superior antimalarial immunity after vaccination with late liver stage-arresting genetically attenuated parasites. Cell Host Microbe 9 : 451–462. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2011.05.008 21669394
65. Murphy SC, Kas A, Stone BC, Bevan MJ (2013) A T-cell response to a liver-stage Plasmodium antigen is not boosted by repeated sporozoite immunizations. PNAS 110 : 6055–6060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1303834110 23530242
66. Bachem A, Guttler S, Hartung E, Ebstein F, Schaefer M, et al. (2010) Superior antigen cross-presentation and XCR1 expression define human CD11c+CD141+ cells as homologues of mouse CD8+ dendritic cells. J Exp Med 207 : 1273–1281. doi: 10.1084/jem.20100348 20479115
67. Crozat K, Guiton R, Contreras V, Feuillet V, Dutertre CA, et al. (2010) The XC chemokine receptor 1 is a conserved selective marker of mammalian cells homologous to mouse CD8alpha+ dendritic cells. J Exp Med 207 : 1283–1292. doi: 10.1084/jem.20100223 20479118
68. Jongbloed SL, Kassianos AJ, McDonald KJ, Clark GJ, Ju X, et al. (2010) Human CD141+ (BDCA-3)+ dendritic cells (DCs) represent a unique myeloid DC subset that cross-presents necrotic cell antigens. J Exp Med 207 : 1247–1260. doi: 10.1084/jem.20092140 20479116
69. Voza T, Kebaier C, Vanderberg JP (2010) Intradermal immunization of mice with radiation-attenuated sporozoites of Plasmodium yoelii induces effective protective immunity. Malar J 9 : 362. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-9-362 21159170
70. Epstein JE, Tewari K, Lyke KE, Sim BKL, Billingsley PF, et al. (2011) Live attenuated malaria vaccine designed to protect through hepatic CD8+ T cell immunity. Science 334 : 475–480. doi: 10.1126/science.1211548 21903775
71. Edwards AD, Diebold SS, Slack EM, Tomizawa H, Hemmi H, et al. (2003) Toll-like receptor expression in murine DC subsets: lack of TLR7 expression by CD8 alpha+ DC correlates with unresponsiveness to imidazoquinolines. Eur J Immunol 33 : 827–833. 12672047
72. Luber CA, Cox J, Lauterbach H, Fancke B, Selbach M, et al. (2010) Quantitative proteomics reveals subset-specific viral recognition in dendritic cells. Immunity 32 : 279–289. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.01.013 20171123
73. Boyd MF, Kitchen SF (1939) The demonstration of sporozoites in human tissues. Am J Trop Med Hyg s1–19, 27–31.
74. Cockburn IA, Tse SW, Zavala F (2014) CD8+ T cells eliminate liver-stage Plasmodium berghei parasites without detectable bystander effect. Infect Immun 82 : 1460–1464. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01500-13 24421043
75. Bruna-Romero O, Hafalla JC, Gonzalez-Aseguinolaza G, Sano G, Tsuji M, et al. (2001) Detection of malaria liver-stages in mice infected through the bite of a single Anopheles mosquito using a highly sensitive real-time PCR. Int J Parasitol 31 : 1499–1502. 11595237
76. Bajenoff M, Egen JG, Koo LY, Laugier JP, Brau F, et al. (2006) Stromal cell networks regulate lymphocyte entry, migration, and territoriality in lymph nodes. Immunity 25 : 989–1001. 17112751
Štítky
Hygiena a epidemiologie Infekční lékařství Laboratoř
Článek 2014 Reviewer Thank YouČlánek Characterization of Metabolically Quiescent Parasites in Murine Lesions Using Heavy Water LabelingČlánek High Heritability Is Compatible with the Broad Distribution of Set Point Viral Load in HIV Carriers
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Pathogens
Nejčtenější tento týden
2015 Číslo 2- Stillova choroba: vzácné a závažné systémové onemocnění
- Perorální antivirotika jako vysoce efektivní nástroj prevence hospitalizací kvůli COVID-19 − otázky a odpovědi pro praxi
- Diagnostika virových hepatitid v kostce – zorientujte se (nejen) v sérologii
- Jak souvisí postcovidový syndrom s poškozením mozku?
- Parazitičtí červi v terapii Crohnovy choroby a dalších zánětlivých autoimunitních onemocnění
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- 2014 Reviewer Thank You
- A Case for Two-Component Signaling Systems As Antifungal Drug Targets
- Prions—Not Your Immunologist’s Pathogen
- Telomeric ORFS in : Does Mediator Tail Wag the Yeast?
- Livestock-Associated : The United States Experience
- The Neurotrophic Receptor Ntrk2 Directs Lymphoid Tissue Neovascularization during Infection
- The Intracellular Bacterium Uses Parasitoid Wasps as Phoretic Vectors for Efficient Horizontal Transmission
- CD200 Receptor Restriction of Myeloid Cell Responses Antagonizes Antiviral Immunity and Facilitates Cytomegalovirus Persistence within Mucosal Tissue
- Phage-mediated Dispersal of Biofilm and Distribution of Bacterial Virulence Genes Is Induced by Quorum Sensing
- CXCL9 Contributes to Antimicrobial Protection of the Gut during Infection Independent of Chemokine-Receptor Signaling
- Mitigation of Prion Infectivity and Conversion Capacity by a Simulated Natural Process—Repeated Cycles of Drying and Wetting
- Approaches Reveal a Key Role for DCs in CD4+ T Cell Activation and Parasite Clearance during the Acute Phase of Experimental Blood-Stage Malaria
- Revealing the Sequence and Resulting Cellular Morphology of Receptor-Ligand Interactions during Invasion of Erythrocytes
- Crystal Structures of the Carboxyl cGMP Binding Domain of the cGMP-dependent Protein Kinase Reveal a Novel Capping Triad Crucial for Merozoite Egress
- Non-redundant and Redundant Roles of Cytomegalovirus gH/gL Complexes in Host Organ Entry and Intra-tissue Spread
- Characterization of Metabolically Quiescent Parasites in Murine Lesions Using Heavy Water Labeling
- A Working Model of How Noroviruses Infect the Intestine
- CD44 Plays a Functional Role in -induced Epithelial Cell Proliferation
- Novel Inhibitors of Cholesterol Degradation in Reveal How the Bacterium’s Metabolism Is Constrained by the Intracellular Environment
- G-Quadruplexes in Pathogens: A Common Route to Virulence Control?
- A Rho GDP Dissociation Inhibitor Produced by Apoptotic T-Cells Inhibits Growth of
- Manipulating Adenovirus Hexon Hypervariable Loops Dictates Immune Neutralisation and Coagulation Factor X-dependent Cell Interaction and
- The RhoGAP SPIN6 Associates with SPL11 and OsRac1 and Negatively Regulates Programmed Cell Death and Innate Immunity in Rice
- Lymph-Node Resident CD8α Dendritic Cells Capture Antigens from Migratory Malaria Sporozoites and Induce CD8 T Cell Responses
- Coordinated Function of Cellular DEAD-Box Helicases in Suppression of Viral RNA Recombination and Maintenance of Viral Genome Integrity
- IL-33-Mediated Protection against Experimental Cerebral Malaria Is Linked to Induction of Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells, M2 Macrophages and Regulatory T Cells
- Evasion of Autophagy and Intracellular Killing by Human Myeloid Dendritic Cells Involves DC-SIGN-TLR2 Crosstalk
- CD8 T Cell Response Maturation Defined by Anentropic Specificity and Repertoire Depth Correlates with SIVΔnef-induced Protection
- Diverse Heterologous Primary Infections Radically Alter Immunodominance Hierarchies and Clinical Outcomes Following H7N9 Influenza Challenge in Mice
- Human Adenovirus 52 Uses Sialic Acid-containing Glycoproteins and the Coxsackie and Adenovirus Receptor for Binding to Target Cells
- Super-Resolution Imaging of ESCRT-Proteins at HIV-1 Assembly Sites
- Disruption of an Membrane Protein Causes a Magnesium-dependent Cell Division Defect and Failure to Persist in Mice
- Recognition of Hyphae by Human Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Is Mediated by Dectin-2 and Results in Formation of Extracellular Traps
- Essential Domains of Invasins Utilized to Infect Mammalian Host Cells
- High Heritability Is Compatible with the Broad Distribution of Set Point Viral Load in HIV Carriers
- Yeast Prions: Proteins Templating Conformation and an Anti-prion System
- A Novel Mechanism of Bacterial Toxin Transfer within Host Blood Cell-Derived Microvesicles
- A Wild Strain Has Enhanced Epithelial Immunity to a Natural Microsporidian Parasite
- Control of Murine Cytomegalovirus Infection by γδ T Cells
- Dimorphism in Fungal Pathogens of Mammals, Plants, and Insects
- Recognition and Activation Domains Contribute to Allele-Specific Responses of an Arabidopsis NLR Receptor to an Oomycete Effector Protein
- Direct Binding of Retromer to Human Papillomavirus Type 16 Minor Capsid Protein L2 Mediates Endosome Exit during Viral Infection
- Characterization of the Mycobacterial Acyl-CoA Carboxylase Holo Complexes Reveals Their Functional Expansion into Amino Acid Catabolism
- Prion Infections and Anti-PrP Antibodies Trigger Converging Neurotoxic Pathways
- Evolution of Genome Size and Complexity in the
- Antibiotic Modulation of Capsular Exopolysaccharide and Virulence in
- IFNγ Signaling Endows DCs with the Capacity to Control Type I Inflammation during Parasitic Infection through Promoting T-bet+ Regulatory T Cells
- Identification of Effective Subdominant Anti-HIV-1 CD8+ T Cells Within Entire Post-infection and Post-vaccination Immune Responses
- Viral and Cellular Proteins Containing FGDF Motifs Bind G3BP to Block Stress Granule Formation
- ATPaseTb2, a Unique Membrane-bound FoF1-ATPase Component, Is Essential in Bloodstream and Dyskinetoplastic Trypanosomes
- Cytoplasmic Actin Is an Extracellular Insect Immune Factor which Is Secreted upon Immune Challenge and Mediates Phagocytosis and Direct Killing of Bacteria, and Is a Antagonist
- A Specific A/T Polymorphism in Western Tyrosine Phosphorylation B-Motifs Regulates CagA Epithelial Cell Interactions
- Within-host Competition Does Not Select for Virulence in Malaria Parasites; Studies with
- A Membrane-bound eIF2 Alpha Kinase Located in Endosomes Is Regulated by Heme and Controls Differentiation and ROS Levels in
- Cytosolic Access of : Critical Impact of Phagosomal Acidification Control and Demonstration of Occurrence
- Role of Pentraxin 3 in Shaping Arthritogenic Alphaviral Disease: From Enhanced Viral Replication to Immunomodulation
- Rational Development of an Attenuated Recombinant Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3 Vaccine Using Prokaryotic Mutagenesis and In Vivo Bioluminescent Imaging
- HITS-CLIP Analysis Uncovers a Link between the Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus ORF57 Protein and Host Pre-mRNA Metabolism
- Molecular and Functional Analyses of a Maize Autoactive NB-LRR Protein Identify Precise Structural Requirements for Activity
- PLOS Pathogens
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Control of Murine Cytomegalovirus Infection by γδ T Cells
- ATPaseTb2, a Unique Membrane-bound FoF1-ATPase Component, Is Essential in Bloodstream and Dyskinetoplastic Trypanosomes
- Rational Development of an Attenuated Recombinant Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3 Vaccine Using Prokaryotic Mutagenesis and In Vivo Bioluminescent Imaging
- Telomeric ORFS in : Does Mediator Tail Wag the Yeast?
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Vladimír Palička, CSc., Dr.h.c., doc. MUDr. Václav Vyskočil, Ph.D., MUDr. Petr Kasalický, CSc., MUDr. Jan Rosa, Ing. Pavel Havlík, Ing. Jan Adam, Hana Hejnová, DiS., Jana Křenková
Autoři: MUDr. Irena Krčmová, CSc.
Autoři: MDDr. Eleonóra Ivančová, PhD., MHA
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Eva Kubala Havrdová, DrSc.
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



