-
Medical journals
- Career
Effect of Extended-Release Metformin on Cognitive Functions in Older Frail Women with Diabetes and Hypertension
14. 3. 2024
Women have a higher risk of geriatric frailty regardless of age and menopausal status. This risk further increases with the presence of diabetes and hypertension, which also elevate the risk of cognitive dysfunction. According to available data, metformin may reduce the risk of developing frailty in postmenopausal women. A recently published Italian study, LEOPARDESS, aimed to evaluate the effect of extended-release metformin on the cognitive functions of this population of women.
Extended-Release Metformin in Older Patients
Metformin is an oral antidiabetic drug that remains the cornerstone of type 2 diabetes (T2D) treatment in both younger and older patients. Recent studies have suggested its beneficial effect in postmenopausal women and in reducing the risk of developing frailty in old age (frailty). The extended-release (XR) form of metformin exhibits fewer gastrointestinal side effects than conventional (immediate-release) metformin, which can be particularly significant in older patients. Some studies have also found a difference in the development of cognitive functions when using extended-release versus immediate-release metformin. Italian authors evaluated the impact of metformin XR on cognitive functions in older frail patients with T2D and hypertension in a study published in April 2023.
Methodology and Study Course
Women over 65 years old with T2D and hypertension who met the criteria for frailty were included in the study. Frailty was defined as an unintentional body weight loss of ≥ 4.5 kg in the last year, handgrip strength in the lowest quintile for age and BMI, exhaustion reported by the patient herself, walking speed in the lowest quintile for age and height, and a low level of physical activity, also at the level of the lowest quintile. Included women also had to have a Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) score of < 26.
The women were treated both with and without metformin XR (500 mg). The control group included older women with T2D, hypertension, and frailty treated with conventional metformin (500 mg) or untreated with metformin, and a group of older men with T2D, hypertension, and frailty treated with metformin XR (500 mg). Thus, the study included 4 therapeutic groups of patients over 65 years old with T2D, hypertension, and frailty: 40 women with metformin XR, 38 women without metformin, 36 women with conventional metformin, and 31 men with metformin XR.
The follow-up lasted 6 months. The assessed parameter was cognitive functions measured by MoCa score.
Study Findings
After 6 months of treatment, a significant difference in MoCa cognitive function scores was found in women treated with metformin XR compared to the study entry (p = 0.007), with women not taking metformin (p = 0.041), with men with metformin XR (p = 0.016), and with women with conventional metformin (p = 0.048). The MoCa scores at study entry and after 6 months are shown in the graph below.
Fig. MoCa Cognitive Function Scores in Therapeutic Groups at Study Entry and After 6 Months
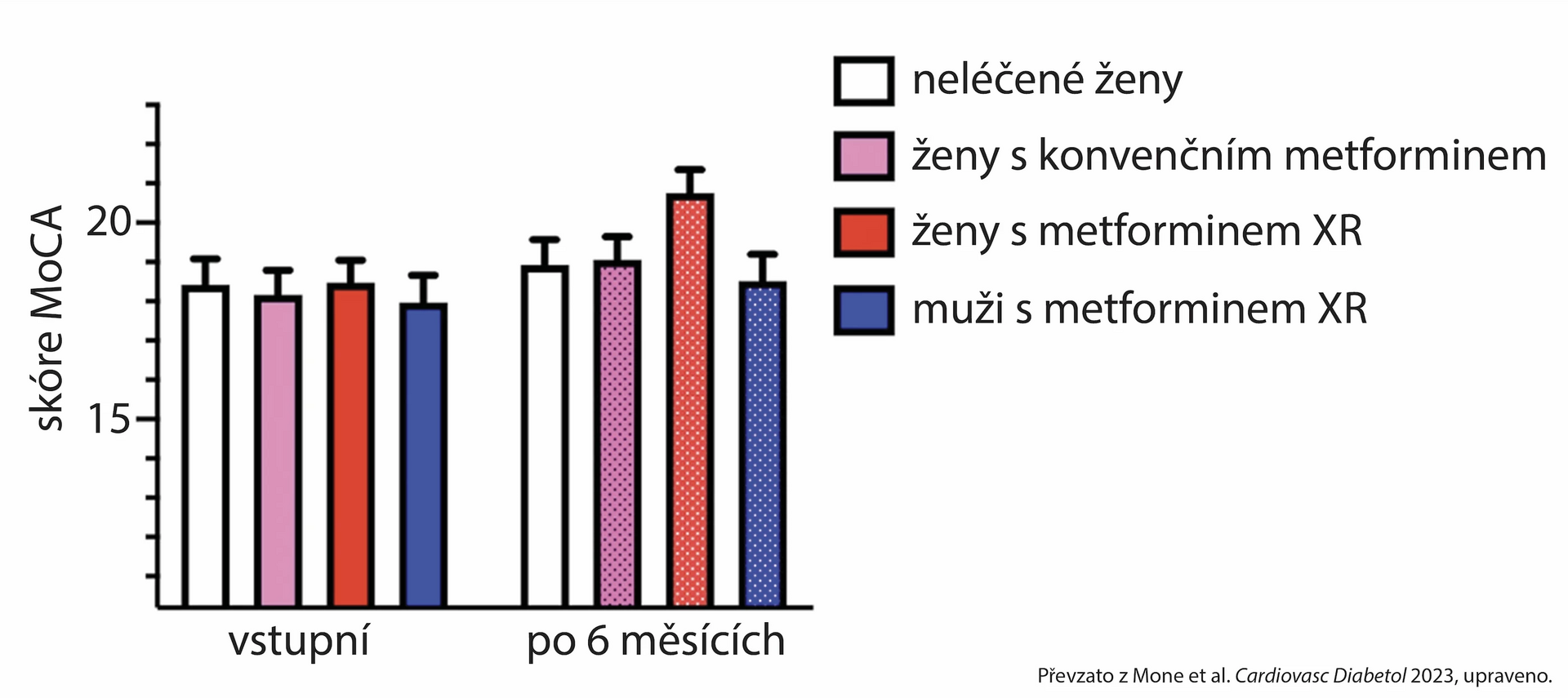
The benefit of metformin XR in terms of cognitive functions in older frail women with T2D and hypertension was also confirmed in a multivariable analysis after accounting for potentially confounding parameters, such as age, BMI, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, heart rate, blood glucose, and serum creatinine levels. In this analysis, only age, BMI, and the use of metformin XR correlated with MoCa scores.
Conclusion
According to the study authors, this study was the first to demonstrate the beneficial effect of metformin XR on cognitive functions in older frail women with T2D and hypertension.
(zza)
Source: Mone P., Martinelli G., Lucariello A. et al. Extended-release metformin improves cognitive impairment in frail older women with hypertension and diabetes: preliminary results from the LEOPARDESS Study. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2023 Apr 21; 22 (1): 94, doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01817-4.
Did you like this article? Would you like to comment on it? Write to us. We are interested in your opinion. We will not publish it, but we will gladly answer you.
Labels
Internal medicine Cardiology General practitioner for adults
Login#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Forgotten passwordEnter the email address that you registered with. We will send you instructions on how to set a new password.
- Career


